National Divorce
Within the next year Russia will spiral into a deep political crisis. There is a nonzero chance that it may scale up existing separatist tendencies leading to the breakup of the empire. In this thread I will outline a model of how this process could look like🧵
Within the next year Russia will spiral into a deep political crisis. There is a nonzero chance that it may scale up existing separatist tendencies leading to the breakup of the empire. In this thread I will outline a model of how this process could look like🧵

Russia is the last European colonial empire that remains largely intact. It was a relatively small polity whose enormous territorial expansion started for real only in the 16th c. This time frame largely overlaps with the establishment of the first European overseas empires 

Those who doubt colonial nature of Russia point out to how different it was from what is now seen as the epitome of British colonialism - the British empire. Indeed, Russian colonialism was very dissimilar from the Anglo one, but often strikingly similar to the Iberoamerican 

We can understand Russia easier if we see it as an Iberoamerican-type empire that didn't break up yet. Russian Federation holding Siberia is not unlike Spain holding Mexico or Portugal holding Brazil
(You can get Eurasianism better if you see it as the Russian Lusotropicalism)
(You can get Eurasianism better if you see it as the Russian Lusotropicalism)

Parallels with Spain and Portugal can be helpful for modelling a potential breakup of Russia. As the inner structure of these empires are not dissimilar, the mechanism of their breakup may go in a similar way, too - starting from their trigger (a military defeat by a third power)
I would argue that a defeat by Ukraine would have greater effect on Russia than any defeat by France could inflict on Spain/Portugal. Ukraine was never seen within Russia as an independent power, only as a separatist province populated by the inferior (if related) bumpkins 

Russian empire is held not only by force, but also by mythos. Which is:
1. Russia is a superior military power -> You won't beat it off anyway
2. There is no salvation for provinces except within Russia -> Without Russia, you will fall into the Stone Age, figuratively speaking
1. Russia is a superior military power -> You won't beat it off anyway
2. There is no salvation for provinces except within Russia -> Without Russia, you will fall into the Stone Age, figuratively speaking

From the Russian perspective Ukraine is a rebel province. Therefore, the war with Ukraine is a test for the imperial mythos (= seceding province will fall into the Stone Age). If that doesn't happen, well, then we must throw you into the Stone Age to maintain the mythos 

Territorial integrity of Russia is kept by the Imperial Mythos:
1. You can't survive without us
2. We can destroy you at any moment
These two assumptions keep the empire together. Both of them are being tested in Ukraine
(That's why Russia *must* destroy the infrastructure)
1. You can't survive without us
2. We can destroy you at any moment
These two assumptions keep the empire together. Both of them are being tested in Ukraine
(That's why Russia *must* destroy the infrastructure)

At this point belief in the assumption 2 is very much weakened. Ukraine did not only stand its ground (which very few believed in back in Feb), but is currently bringing war into Russia, making strikes on the Russian strategic bombers located very far away from the border 

That makes any potential ceasefire a point bifurcation. It opens two scenarios:
1. Russia regroups, restocks, reattacks and wins -> Assumptions 1,2 are true
2. Russia fails to do so -> Assumptions 1,2 are false
The empire's fate depends on whether it can crash a rebel province
1. Russia regroups, restocks, reattacks and wins -> Assumptions 1,2 are true
2. Russia fails to do so -> Assumptions 1,2 are false
The empire's fate depends on whether it can crash a rebel province
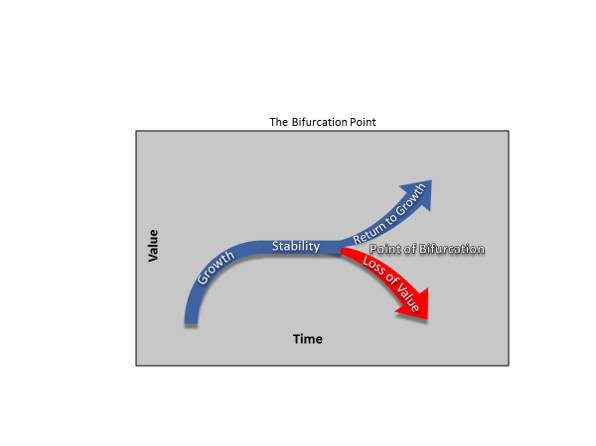
Now let's assume Russia failed to crash Ukraine and could not persuade its population it would be able to do so in the future. That can be enough to shake the faith in both assumptions of the imperial mythos thus triggering the process of disintegration
Now let's discuss a probable scenario of how the National Divorce could look like:
1. Most likely it will not be launched by any sort of oppositionaries/activists but by the already existing regional interest groups whose character may vary enormously from region to region
1. Most likely it will not be launched by any sort of oppositionaries/activists but by the already existing regional interest groups whose character may vary enormously from region to region

2. Most likely the National Divorce will not start in the ethic republics. People think ethnic separatism is likely to destroy Russia, therefore, it is very unlikely to happen. This is too obvious -> precautions are taken. It's more likely to start in unlikely "Russian" regions
3. Most likely the process will start de facto and then formalised legally much later, perhaps very much later. It will likely proceed in the form of local interest groups taking more power, pursuing more regional protectionism, etc. than making some open declarations
4. Where could it all start? Three most likely candidates
- All predominantly "Russian" -> few precautions are taken
- Independently rich -> They effectively pay others' regions bills rather than live on the handouts
- Strong regional elites only partially cleansed by Moscow
- All predominantly "Russian" -> few precautions are taken
- Independently rich -> They effectively pay others' regions bills rather than live on the handouts
- Strong regional elites only partially cleansed by Moscow

5. The process of disintegration is likely to happen in a few iterations. The less regions keep obeying to Moscow and paying taxes to it, the less motivation the other will have cost-benefit wise. Richer regions have more motivation to launch it than the poorer ones
6. Contrary to the popular opinion, the disintegration and the formation of new states is likely to happen on the regional, rather than "ethnic" or "racial" basis. It's highly unlikely that the disintegration goes along the ethnic lines
7. Historically speaking, instruments tend to evolve into the institutions. In particular, administrative borders tend to evolve into the national ones. Much like in the Latin America, the disintegration will go along the administrative, rather than ethnic borders
8. New states will likely look as a collection of N (N≥1) former Russian regions. Former administrative demarkation between provinces will turn into the national borders
Administrative borders becoming the national ones is Lindy
Administrative borders becoming the national ones is Lindy
9. Ethnicity, race and culture is *not* enough for the new states to work out. For them to succeed they must be able to pay their bills. Ergo, the principle of economic clusters will be at least as important for defining their borders as the ethnic or cultural one 

10. The key question is not the Caucasus or even Volga question. It is the question of Siberia. Siberia is the jewel in the Russian crown that pays the bills of the empire. Should it keep control over Siberia, it can easily win back everything else. Should it lose it, it is done 
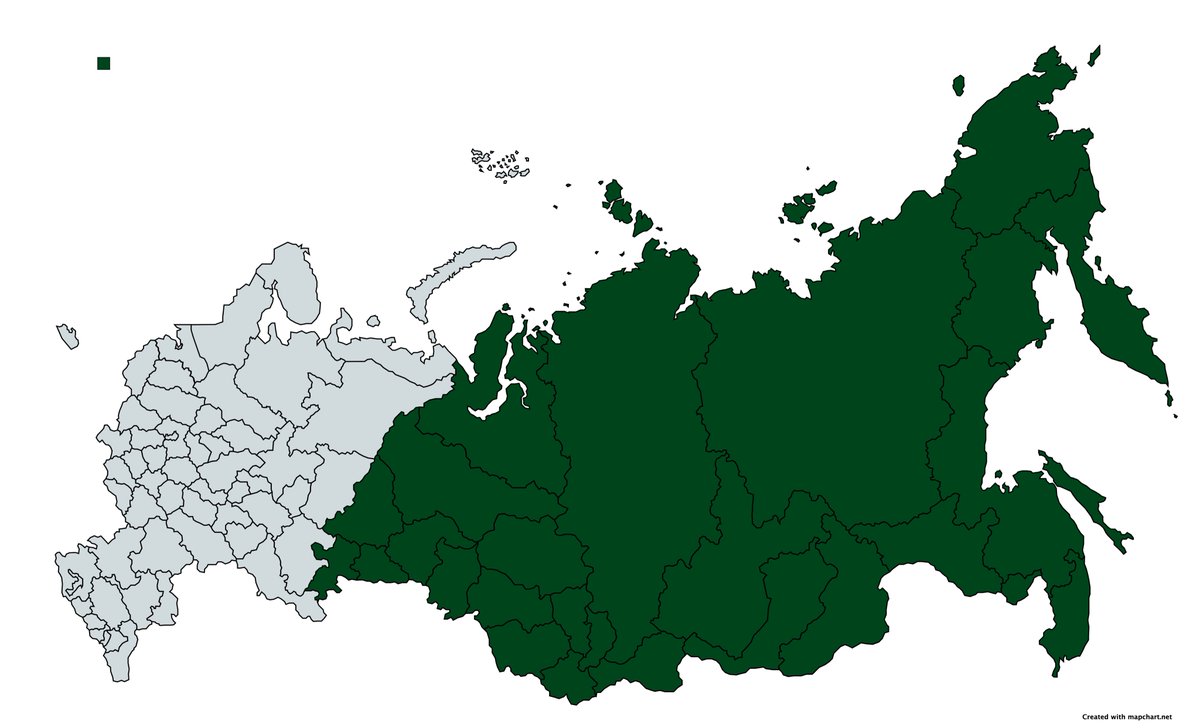
That should be enough to introduce the idea. I will elaborate on details in separate materials. End of 🧵
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





