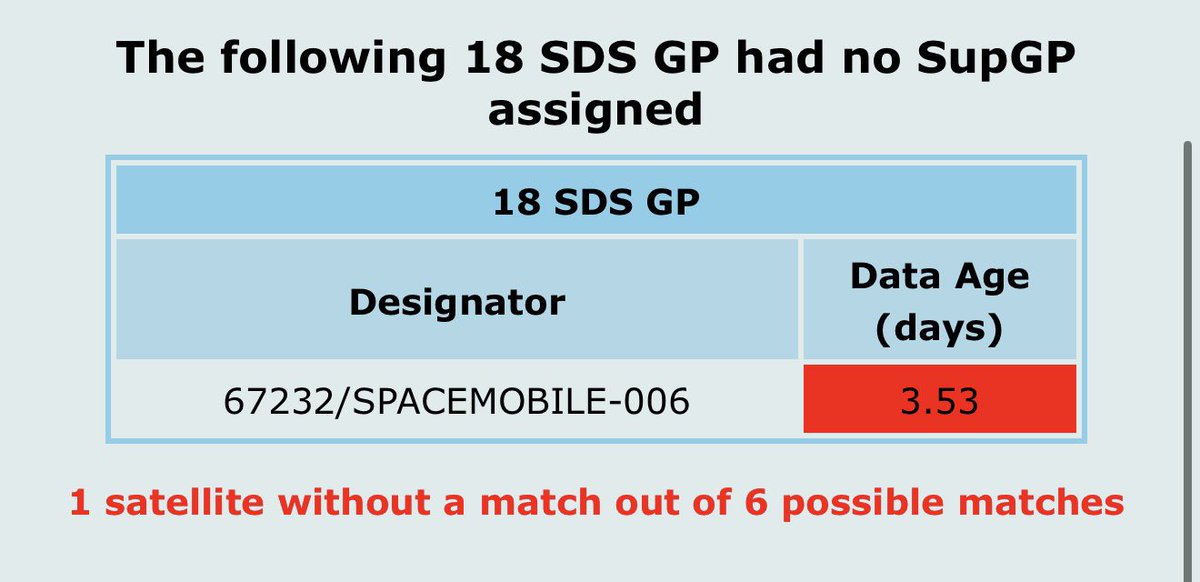
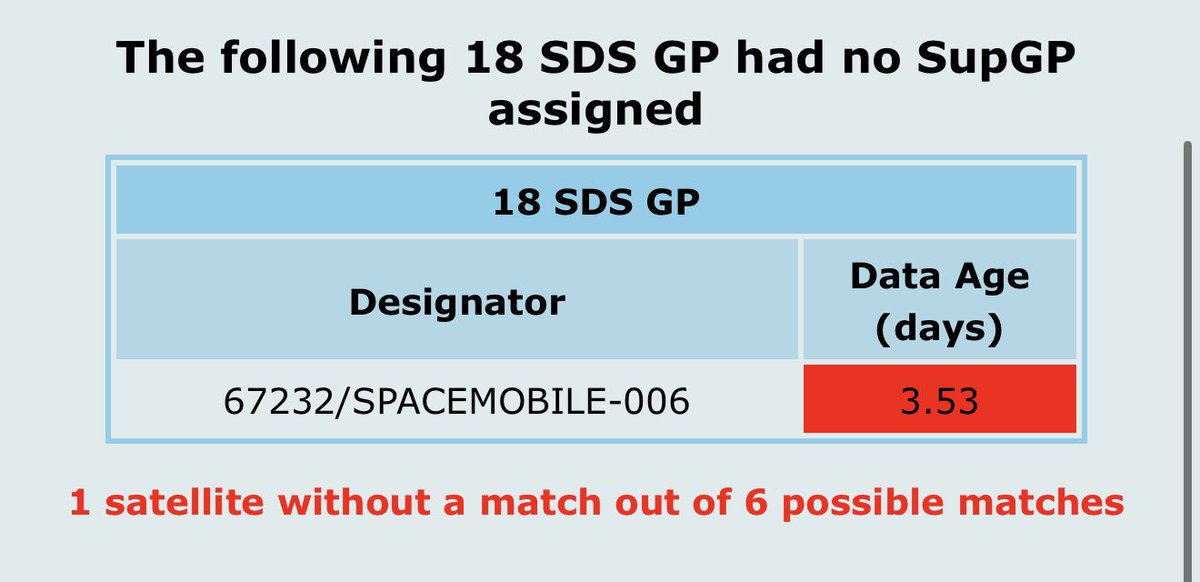
$ASTS satellite #BlueWalker3 in orbit testing is ongoing.
It is the cutting edge of 5g Non-Terrestrial-Network NTN, Direct-To-Handset, DTH, technology.
It has a lot of interesting design choices.
Selected, in tech, standard and regulatory terms as it was purpose built.
1/n
It is the cutting edge of 5g Non-Terrestrial-Network NTN, Direct-To-Handset, DTH, technology.
It has a lot of interesting design choices.
Selected, in tech, standard and regulatory terms as it was purpose built.
1/n

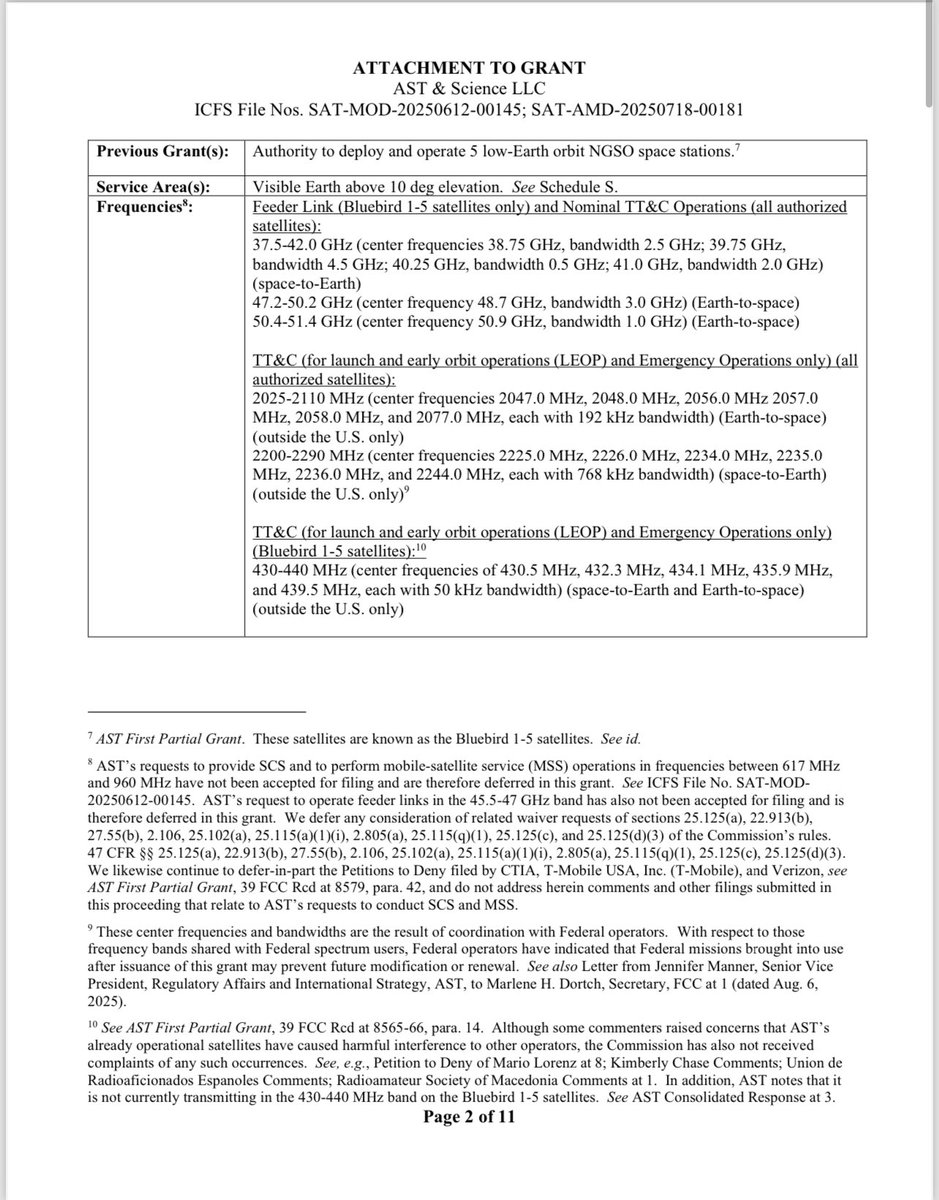
Previous schematic of the transparent satellite AST uses is one of two NTN DTH architectures supported by the global 3GPP 5g standard.
The alternative AST opted out of has parts, or all, of the base-station placed onboard the satellite, whereas ASTs is on earth.
2/n
The alternative AST opted out of has parts, or all, of the base-station placed onboard the satellite, whereas ASTs is on earth.
2/n

Starlink DTH is an add-on functionality to an existing architecture built for another purpose. It uses the other architecture.
This has several implications.
For handoff and multi connectivity.
But importantly ..
3/n

This has several implications.
For handoff and multi connectivity.
But importantly ..
3/n


Having the eNodeB or base-station on the ground like AST does allows access to it and it allows use of COTS cutting edge hardware like Nokia single-RAN Airscale.
AST has been working with Nokia Bell Labs for two years to integrate assuring best possible technology.
4/n

AST has been working with Nokia Bell Labs for two years to integrate assuring best possible technology.
4/n


Satellite communications payload is another choice where AST stands out. It is typical GEO (high altitude) satellite specs, but placed in LEO (low altitude).
A bit like putting an ocean-liner in a pond it might seem.
5/n
A bit like putting an ocean-liner in a pond it might seem.
5/n

That allows for more narrow beams using less power, yet creating high sihnal strengths.
The win is three fold. Good mapping/resolution. High spectrum reuse and high modulation.
Resulting in good coverage and high throughput.
6/n



The win is three fold. Good mapping/resolution. High spectrum reuse and high modulation.
Resulting in good coverage and high throughput.
6/n



Low Earth Orbit has these benefits. Low RTT latency is one. Essential to work with 5g.
But also problems. Latency is still higher than terrestrial towers. Doppler shift needs to be handled and Farraday rotation of the polarization.
These have tweaks that can be tuned.
7/n

But also problems. Latency is still higher than terrestrial towers. Doppler shift needs to be handled and Farraday rotation of the polarization.
These have tweaks that can be tuned.
7/n


But tuning takes time.
I will quote @steve_larrison here.
”Testing is a process, not an event.”
Initial results < final results.
But there is more to architecture.
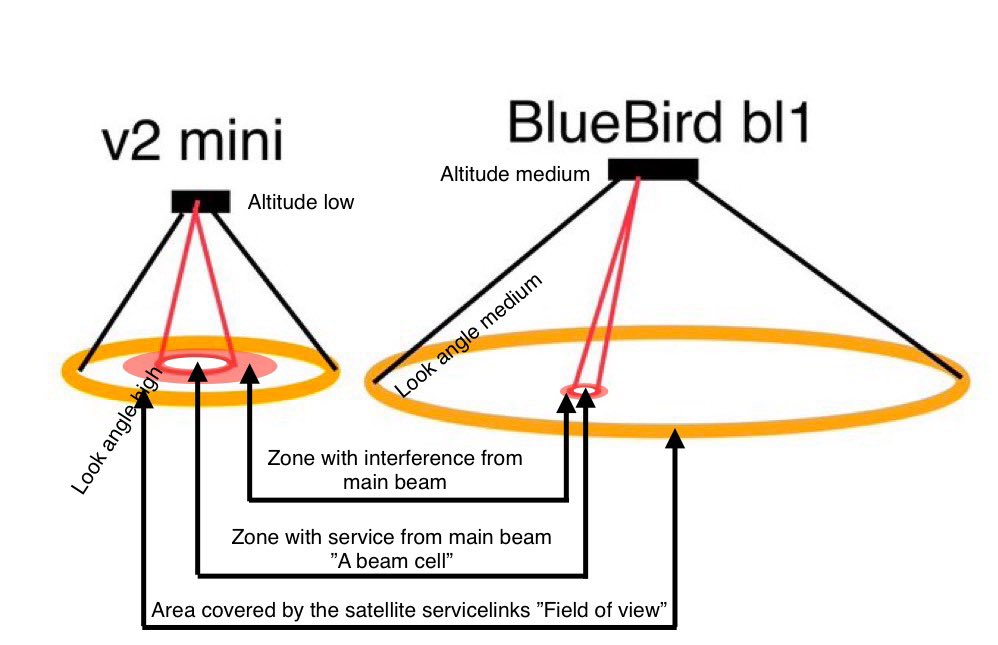
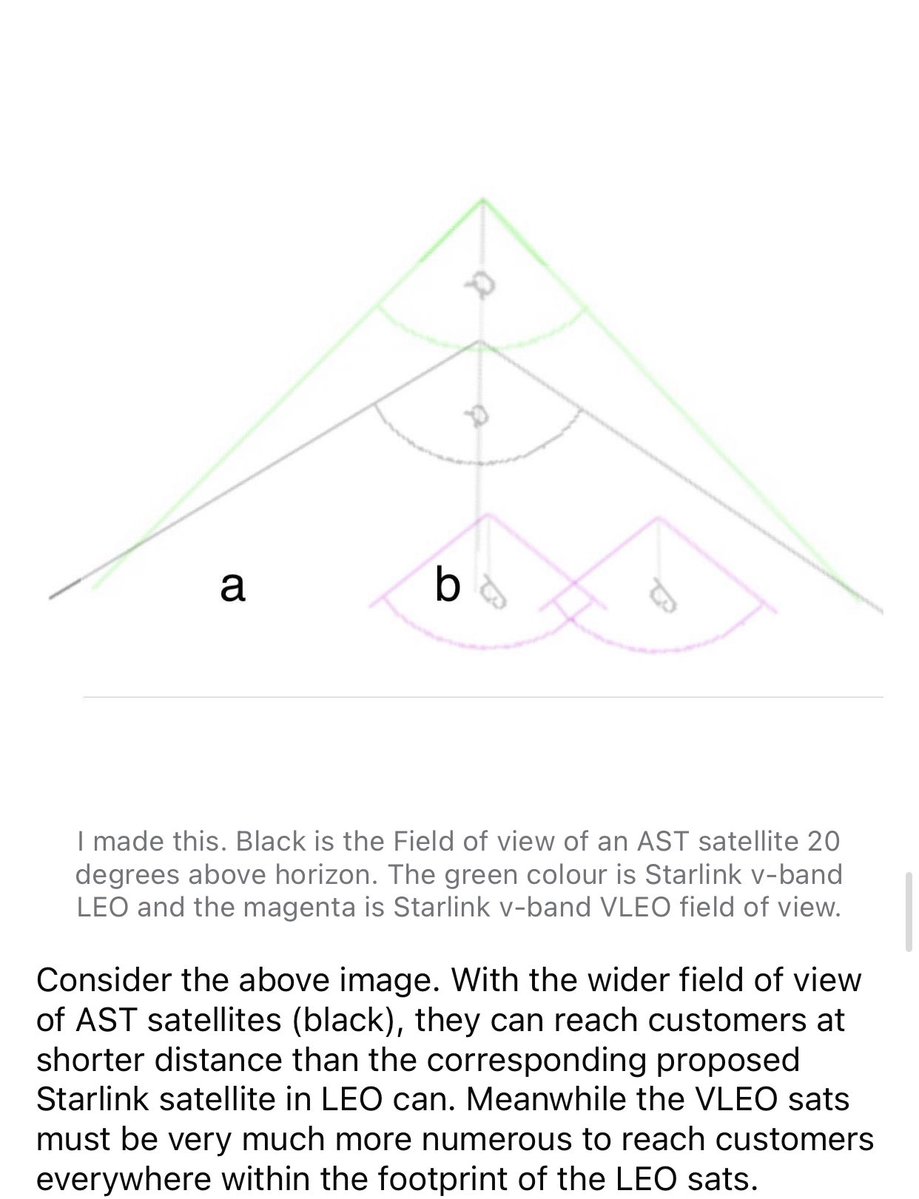
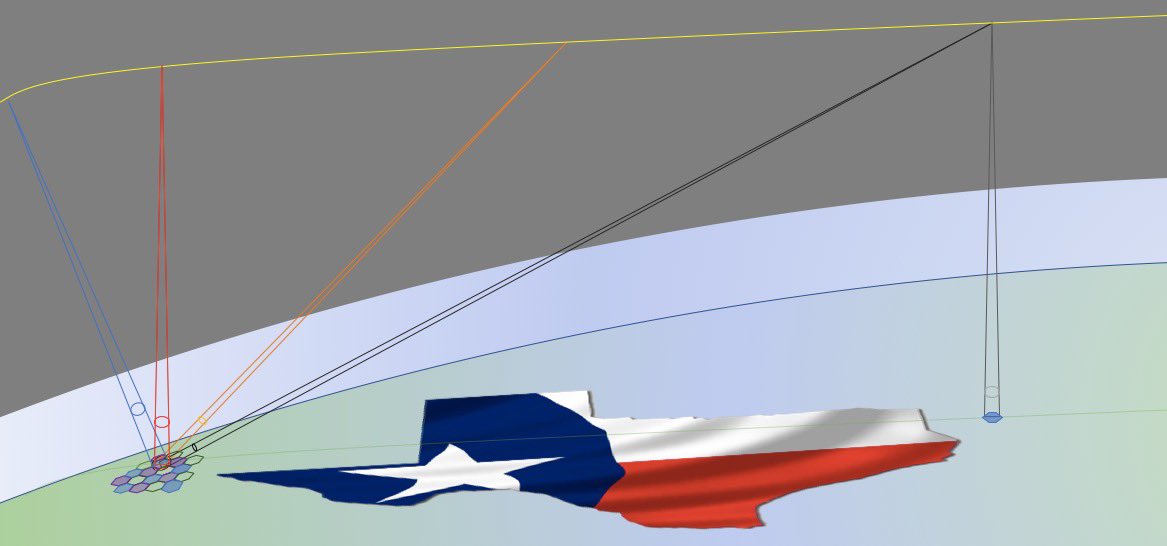
AST BlueBird servicelinks are 20 degrees above horizon.
8/n
I will quote @steve_larrison here.
”Testing is a process, not an event.”
Initial results < final results.
But there is more to architecture.
AST BlueBird servicelinks are 20 degrees above horizon.
8/n

That is another extreme design choice made possible by the huge 20 meter square array. As you need all of it to make a so narrow and strong beam.
The BlueWalker3 test satellite will generate such smsll cells 30-35 degrees above horizon as its phased array is smaller.
9/n
The BlueWalker3 test satellite will generate such smsll cells 30-35 degrees above horizon as its phased array is smaller.
9/n

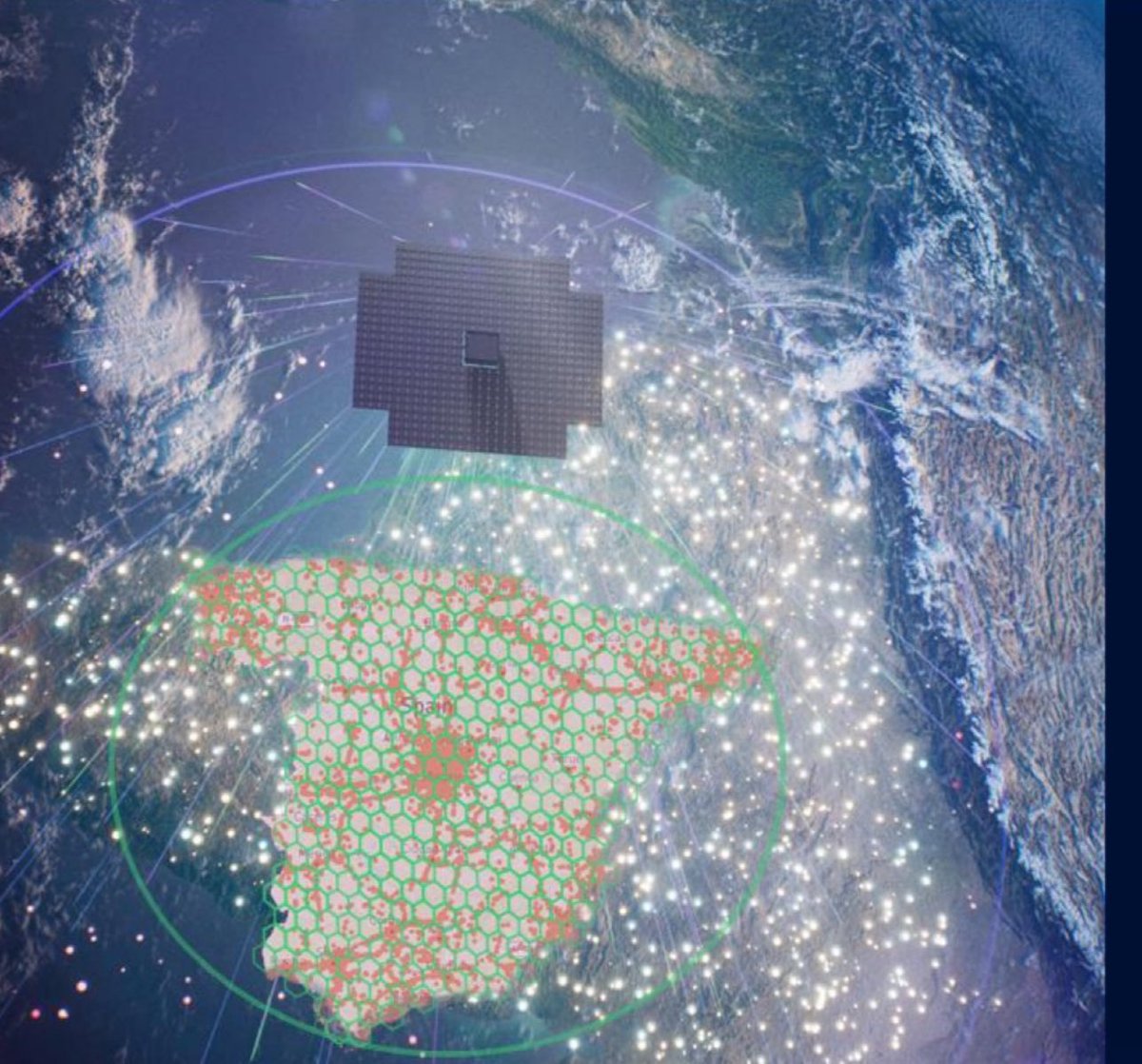
$AST uses fixed cell sites and steerable beams. Beams that are made more narrow and elliptical near the edge of the satellite firld of view in order to cast circular beamcells of uniform size onto the surface of the earth. It does not use moving cells.
10/n

10/n


The backhaul, or feeder link, field of view is even wider. It works down to 10 degrees above horizon as its antenna is a steerable 70 cm dish connecting to huge steerable dishes at the gateways.
11/n
11/n

There is much more, to tell, about the design choices made.
One is that the satellite is FPGA, or software defined. It means they can patch and tweak a lot during in orbit tests.
I will just summarize, for now, that the choices made are very wise as you scrutinize them.
12/12
One is that the satellite is FPGA, or software defined. It means they can patch and tweak a lot during in orbit tests.
I will just summarize, for now, that the choices made are very wise as you scrutinize them.
12/12
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh