Great question. Let's open the original video. Notice how @albats formulated her question:
"I was told but I could not find this later in the Internet that you had called the Gastarbeiters cockroaches somewhere. Yes or no?"
Her description is (intentionally?) inaccurate
"I was told but I could not find this later in the Internet that you had called the Gastarbeiters cockroaches somewhere. Yes or no?"
Her description is (intentionally?) inaccurate
https://twitter.com/alovlie/status/1611064731191676942
@albats First, @navalny did not technically "call" anyone cockroaches. When making an argument about "too big cockroaches" he illustrated it with a photo of Chechen rebels. This can and will be understood as a reference to generalised Muslims, but (technically) not to "Gastarbeiters" 

Second, @albats framed it as an occasional verbal remark, almost accidental "called somewhere". But there was nothing accidental about it. Verbal narrative, visuals, a TV tune, everything was intentionally dehumanising 

@albats not only framed the cockroaches as an occasional remark, she also (intentionally?) left @navalny an easy way out, by describing the video slightly inaccurately. Navalny did not technically say anything about Gastarbeiters in *this* video
@navalny could say "no, I never called Gastarbeiters cockroaches" and still be *technically* right. Why? Because of the way @albats formulated her question. She (intentionally?) left Navalny a way out. He could've denied an inaccurate accusation and technically be right. Did he?
Best thing @navalny could've done would be to narrow down to an inaccurate Gastarbeiters = cockroaches description by @albats and just deny it. She left him a loophole to save his face. He didn't use it. He attacked his critic comparing him with Putin's propagandists instead 

Best thing @navalny could've down is to stick to original incorrect description and deny it. That would not technically make him a liar. Instead he starts passionately denying ever using this metaphor at all. He chooses to lie 

@albats seems to be taken aback:
"Or may be someone [saw] something like this. So you are sure that in no video clip, nowhere..."
Notice she is narrowing down her original question, talking about a "video clip", which @navalny had produced very few by then
I think she saw it
"Or may be someone [saw] something like this. So you are sure that in no video clip, nowhere..."
Notice she is narrowing down her original question, talking about a "video clip", which @navalny had produced very few by then
I think she saw it

@albats @navalny @navalny respond with another ad hominem attack against a critic who pointed out to a verifiable fact. @albats left him a loophole to deny it, while saving his face - the inaccurate description. But Navalny resorts to lies and ad hominem slander 

Why is this video is even important? Well, because it illustrates a typical reaction of @navalny and his followers to *any* sort of criticism. And pointing out to their past words & actions counts as criticism:
1. Ad hominem attack against a critic
2. Make up some lie about him
1. Ad hominem attack against a critic
2. Make up some lie about him
Honestly, I cannot comprehend why @navalny @leonidvolkov etc. propagate so many *factual* lies. Navalny's Chief of Staff could attack me with some opinion statement ("He's a liar!"). Smarter people do. But he makes a verifiable statement - that I'm paid by Tatarstan President 
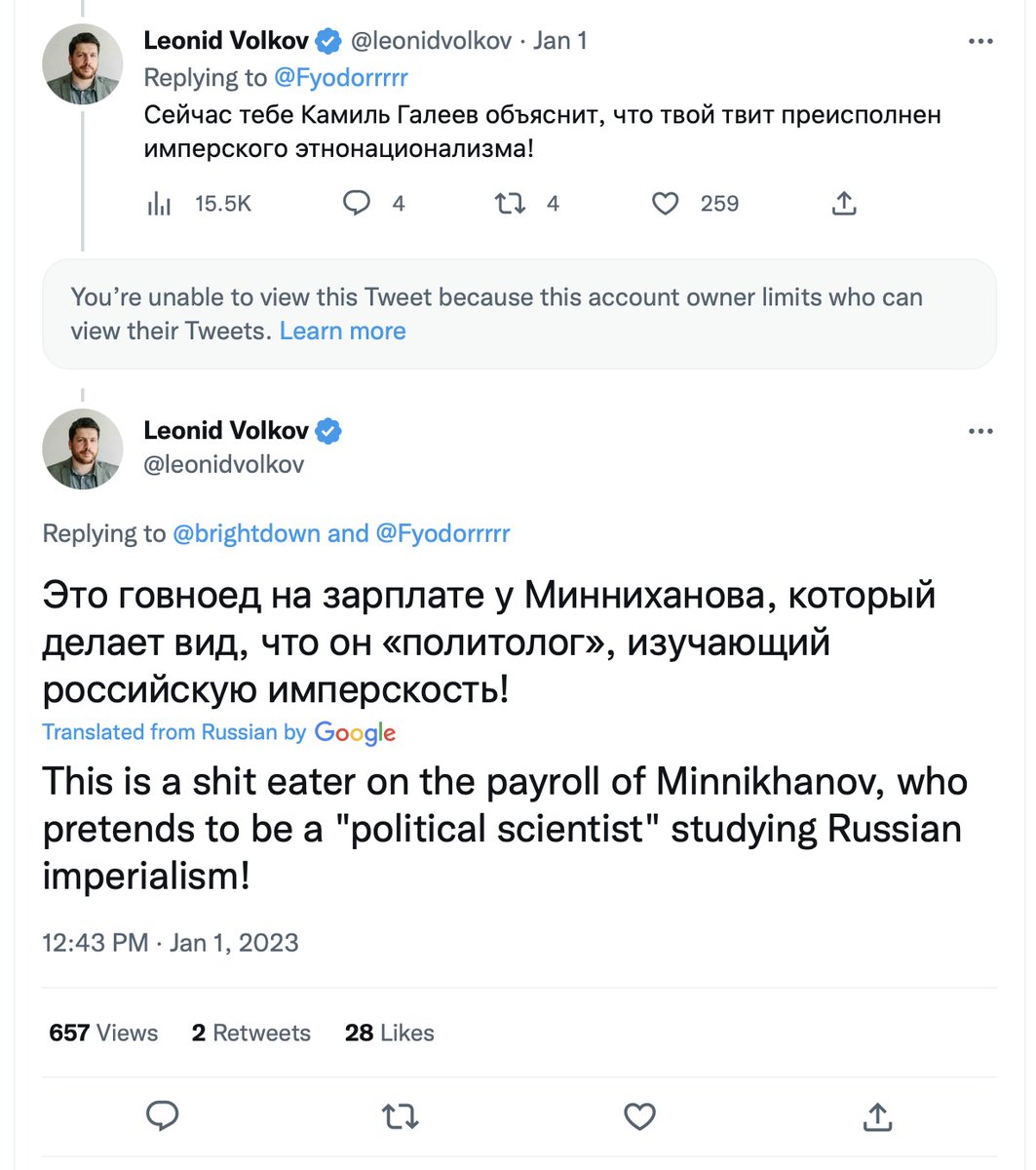
Let me be clear: I see nothing wrong with working for Tatarstan. I just cannot comprehend why @leonidvolkov is randomly making up verifiable factual statements requiring the burden of proof?
My answer: Because these fellows have never been called out
My answer: Because these fellows have never been called out

That is almost amusing. I understand these "oppositionaries" strategy: when facing criticism, always respond with ad hominem against the critic. I'm ok with that. But why are you making *factual* verifiably false statements, I can't get this?
That's just childish
That's just childish

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





