/1 How does ChatGPT work?
Disclaimer: since OpenAI hasn't provided all the details, some parts of the diagram may be inaccurate. @sama, we would love to hear your feedback.
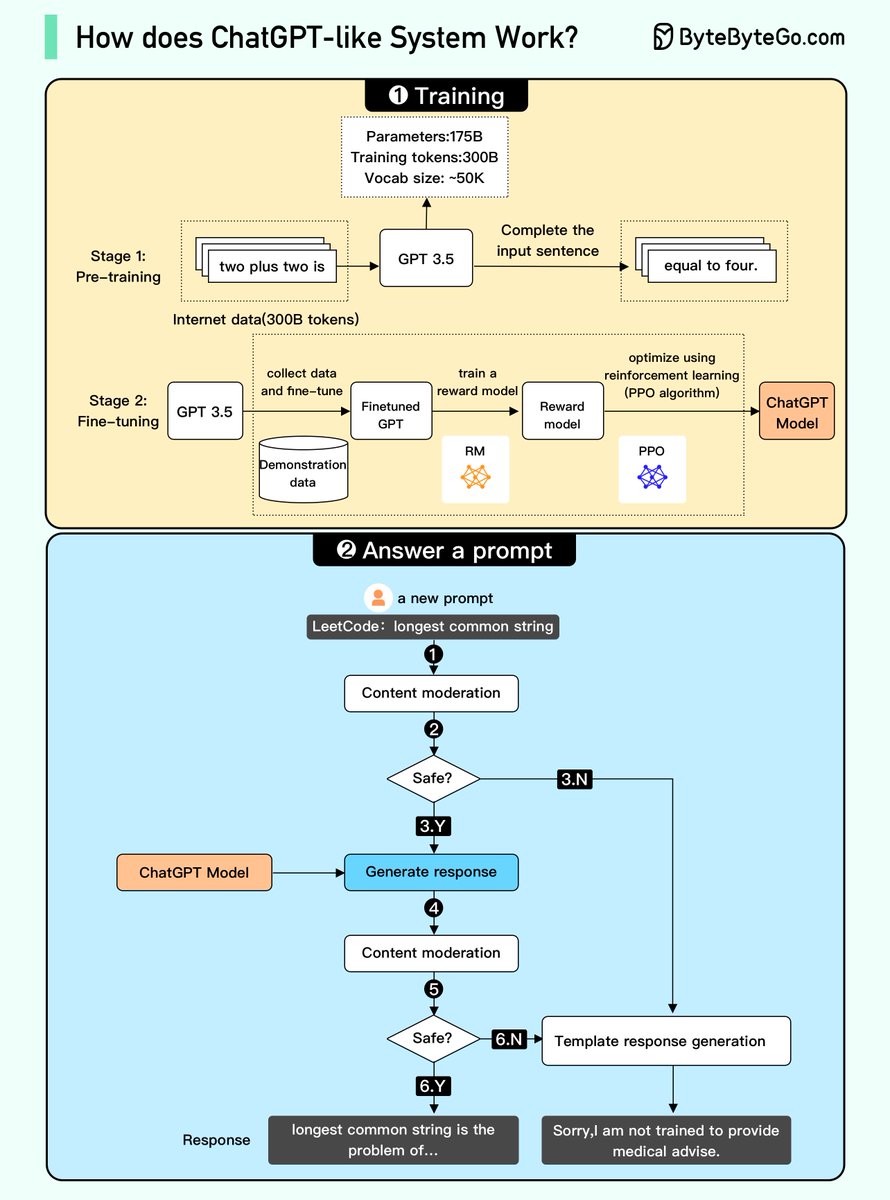
We attempted to explain how it works in the diagram below. The process can be broken down into two parts.
Disclaimer: since OpenAI hasn't provided all the details, some parts of the diagram may be inaccurate. @sama, we would love to hear your feedback.
We attempted to explain how it works in the diagram below. The process can be broken down into two parts.

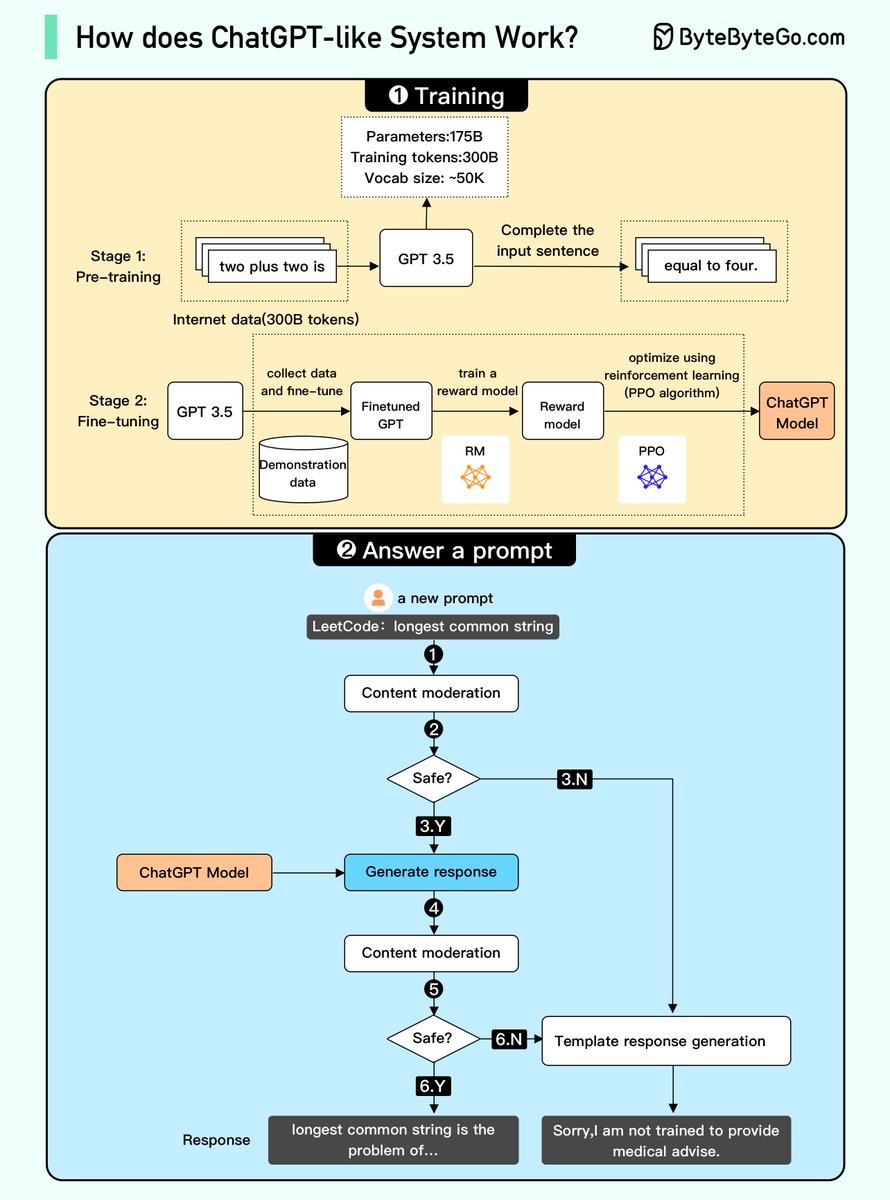
/2 1. Training. To train a ChatGPT model, there are two stages:
- Pre-training: In this stage, we train a GPT model (decoder-only transformer) on a large chunk of internet data.
- Pre-training: In this stage, we train a GPT model (decoder-only transformer) on a large chunk of internet data.

/3 The objective is to train a model that can predict future words given a sentence in a way that is grammatically correct and semantically meaningful.
After the pre-training stage, the model can complete given sentences, but it is not capable of responding to questions.
After the pre-training stage, the model can complete given sentences, but it is not capable of responding to questions.

/4 - Fine-tuning: This stage is a 3-step process that turns the pre-trained model into a question-answering ChatGPT model: 
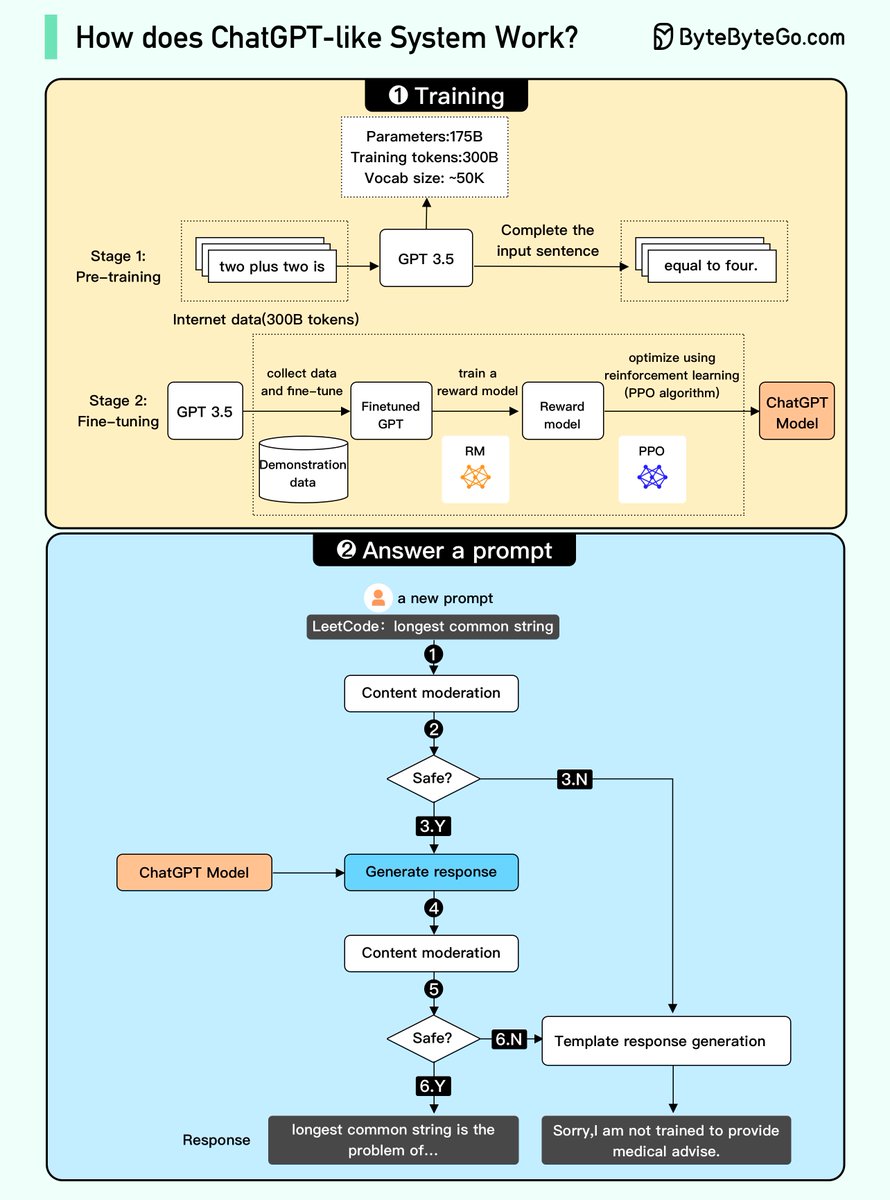
/5 1). Collect training data that comprise (questions and answers), and fine-tune the pre-trained model on this data. The model takes a question as input and learns to generate an answer similar to the training data. 
/6
2). Collect more data that comprise (question, several answers) and train a reward model to rank these answers from most relevant to least relevant.
3). Use reinforcement learning (PPO optimization) to fine-tune the model, so the model's answers are more accurate.
2). Collect more data that comprise (question, several answers) and train a reward model to rank these answers from most relevant to least relevant.
3). Use reinforcement learning (PPO optimization) to fine-tune the model, so the model's answers are more accurate.
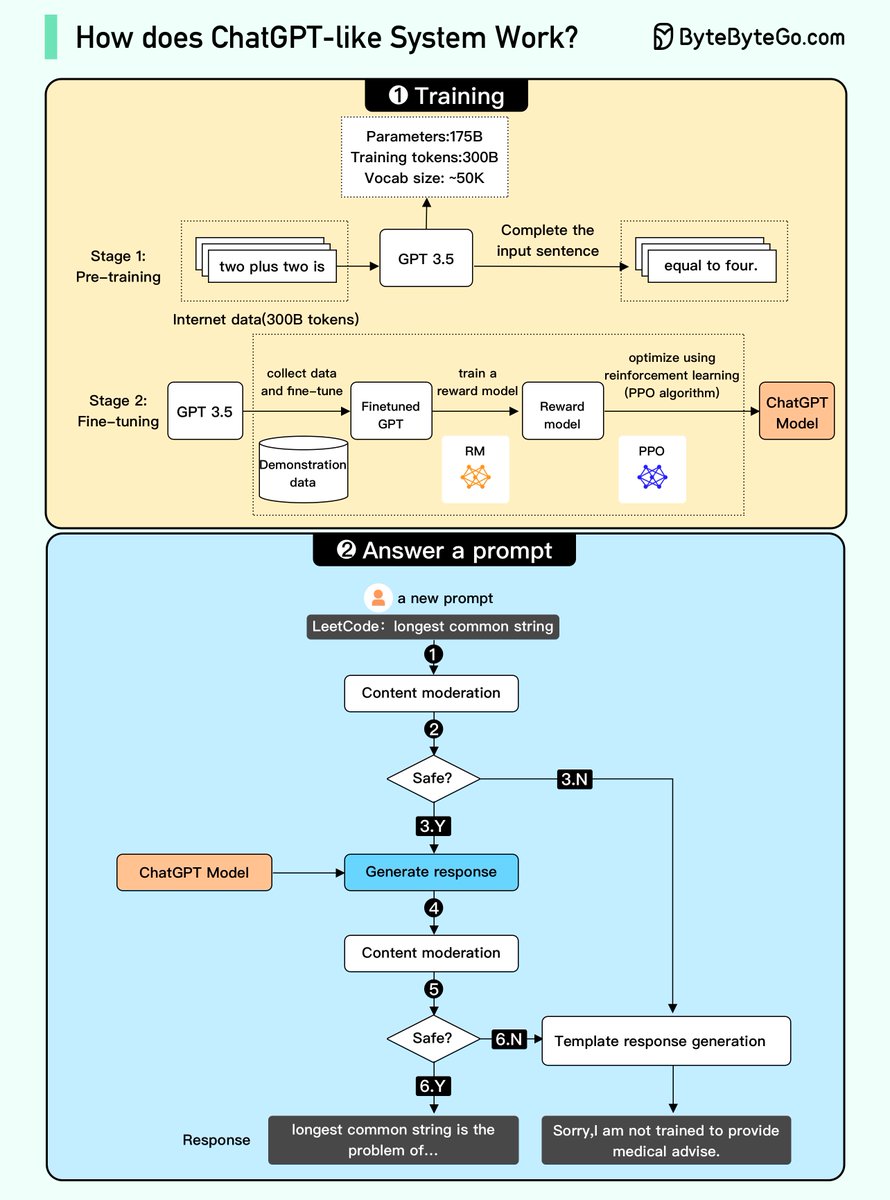
/7 2. Answer a prompt
🔹Step 1: The user enters the full question.
🔹Step 2: The question is sent to a content moderation component. This component ensures that the question does not violate safety guidelines and filters inappropriate questions.
🔹Step 1: The user enters the full question.
🔹Step 2: The question is sent to a content moderation component. This component ensures that the question does not violate safety guidelines and filters inappropriate questions.
/8 🔹Steps 3-4: If the input passes content moderation, it is sent to the chatGPT model. If the input doesn’t pass content moderation, it goes straight to template response generation.
/9 🔹Step 5-6: Once the model generates the response, it is sent to a content moderation component again. This ensures the generated response is safe, harmless, unbiased, etc. 
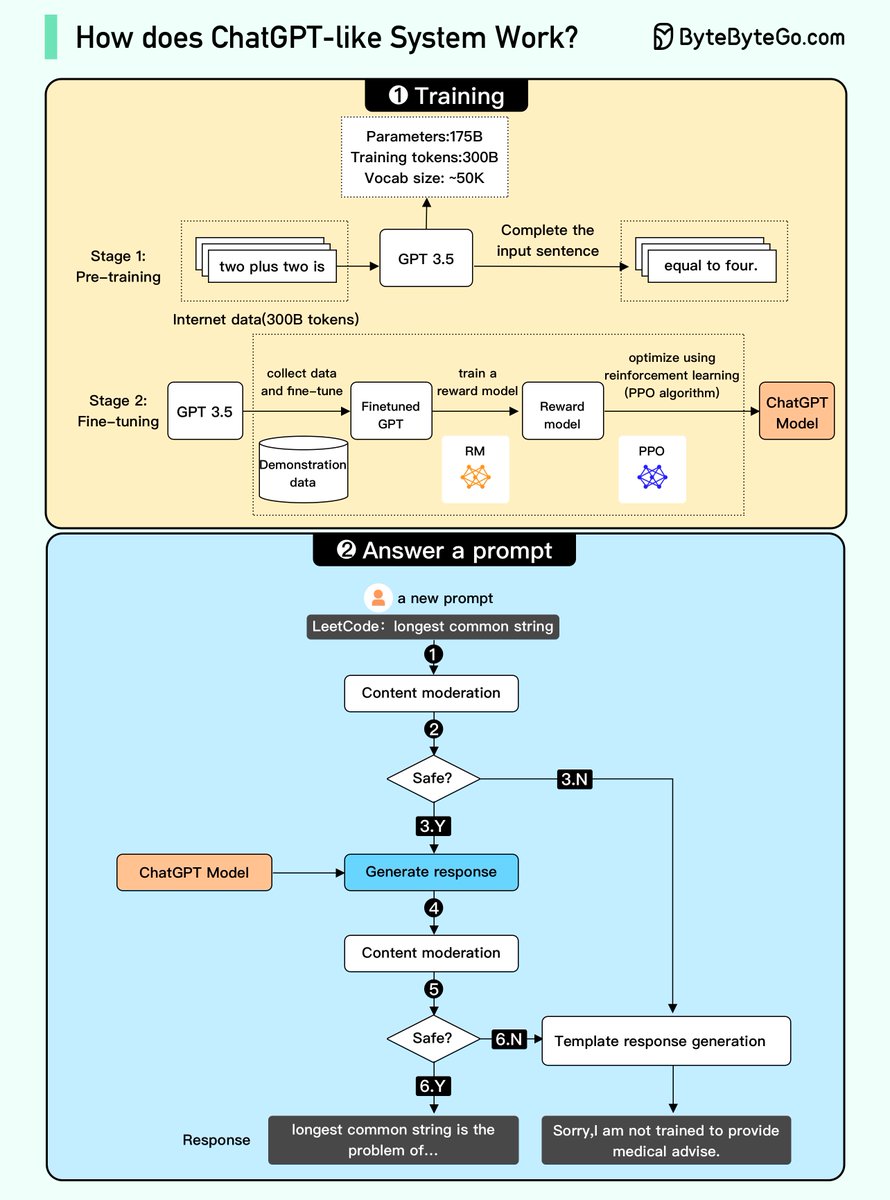
/10 🔹Step 7: If the input passes content moderation, it is shown to the user. If the input doesn’t pass content moderation, it goes to template response generation and shows a template answer to the user. 
/11 Subscribe to our weekly free newsletter to learn something new every week: bit.ly/3FEGliw 
/12 I hope you've found this thread helpful.
Follow me @alexxubyte for more.
Like/Retweet the first tweet below if you can:
Follow me @alexxubyte for more.
Like/Retweet the first tweet below if you can:
https://twitter.com/alexxubyte/status/1620463186460971008
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh