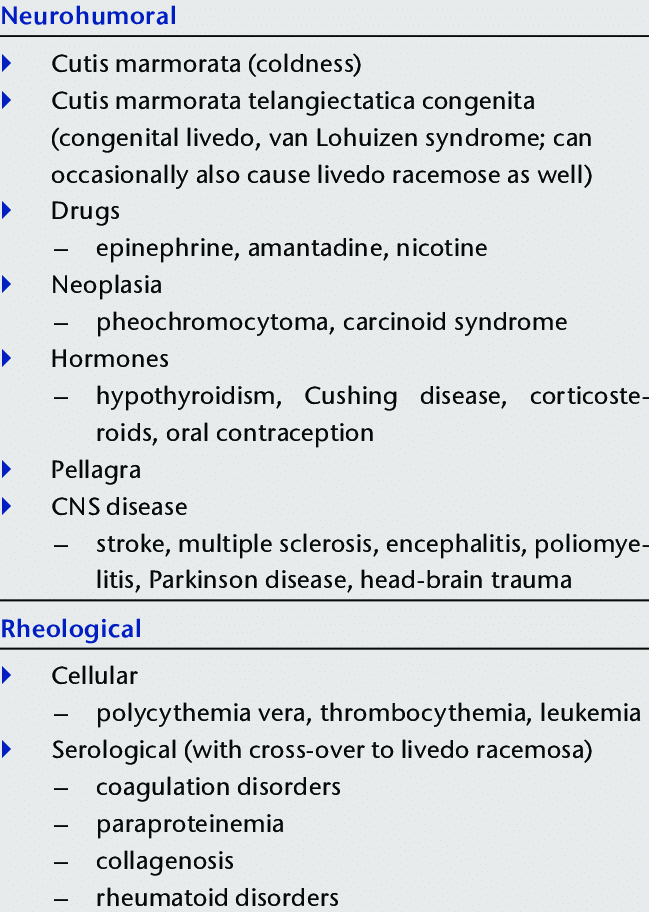
A 63-year-old man
👉developed purplish discoloration of his face after he underwent stenting and balloon dilation of the left CCA
What is the name of this finding?
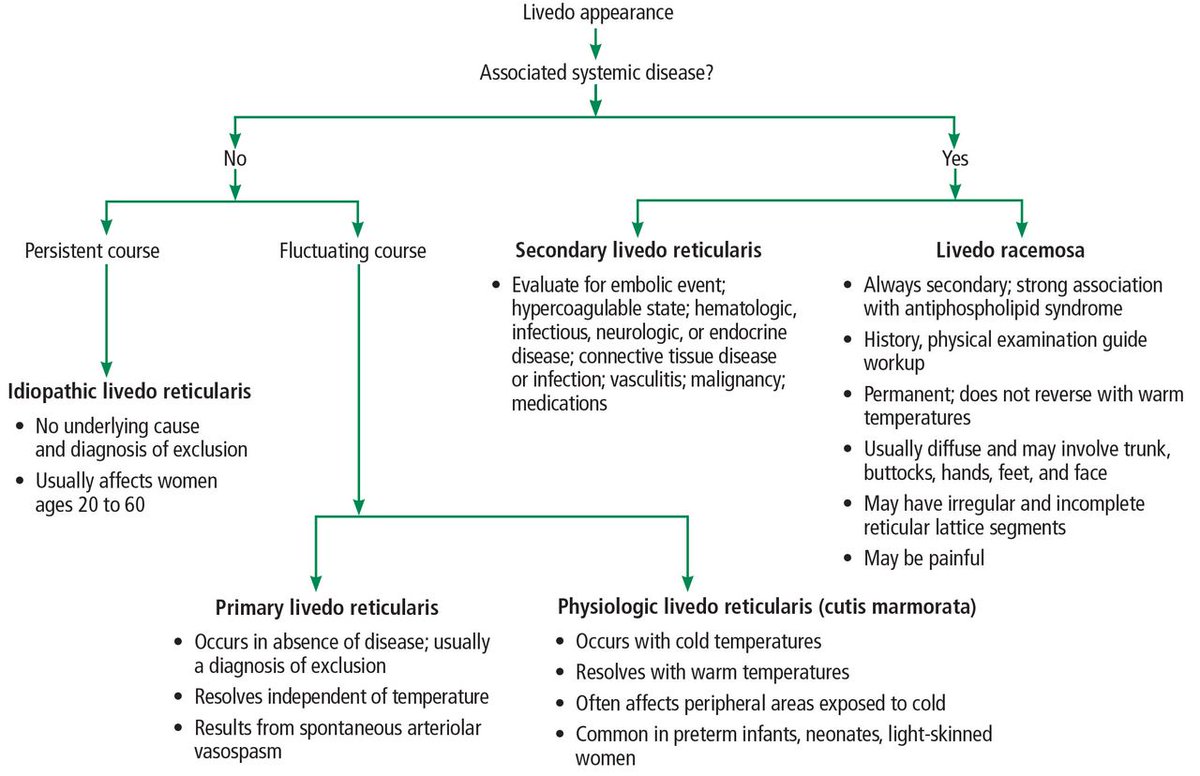
Cutis marmorata
Harlequin syndrome
Livedo racemosa
Livedo reticularis
Telangiectasia
👉developed purplish discoloration of his face after he underwent stenting and balloon dilation of the left CCA
What is the name of this finding?
Cutis marmorata
Harlequin syndrome
Livedo racemosa
Livedo reticularis
Telangiectasia
Shivering, sweating, and confusion developed immediately after artery dilation,
👉along with a left gaze preference, dysarthria, and hemiparesis on the right side of his body
*
Over the next 20 minutes, livedo reticularis developed on the left side of his face
👉along with a left gaze preference, dysarthria, and hemiparesis on the right side of his body
*
Over the next 20 minutes, livedo reticularis developed on the left side of his face
An embolic protection device had been used during the procedure
*
Digital subtraction angiography
👉 patent left internal carotid artery
👉 an occluded distal left facial artery
*
No intracranial hemorrhage was seen on CT of the head
*
Digital subtraction angiography
👉 patent left internal carotid artery
👉 an occluded distal left facial artery
*
No intracranial hemorrhage was seen on CT of the head
👉 transferred to the (ICU),
👉 MRI and angiography of the brain revealed
👉 infarctions in the territory of the lt middle cerebral artery with patent vasculature
*
An acute embolic stroke and cholesterol embolization syndrome of the face were diagnosed
👉 MRI and angiography of the brain revealed
👉 infarctions in the territory of the lt middle cerebral artery with patent vasculature
*
An acute embolic stroke and cholesterol embolization syndrome of the face were diagnosed
An embolic protection device had been used during the procedure
*
Digital subtraction angiography
👉 patent left internal carotid artery
👉 an occluded distal left facial artery
*
No intracranial hemorrhage was seen on CT of the head
*
Digital subtraction angiography
👉 patent left internal carotid artery
👉 an occluded distal left facial artery
*
No intracranial hemorrhage was seen on CT of the head

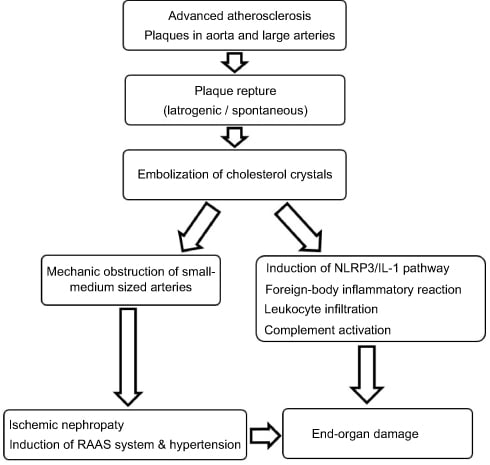
👉cholesterol embolization syndrome, atherosclerotic plaque contents from large-caliber arteries embolize to smaller arteries
👉 lead to vascular occlusion, inflammation, and end-organ damage
👉 lead to vascular occlusion, inflammation, and end-organ damage
Livedo reticularis is one of the most common skin manifestations of the syndrome
♦️
👉 received supportive care in the IC
👉 livedo reticularis resolved 1 week after the event
👉 neurologic deficits persisted at the time of his discharge from the hospital 2 months later.
♦️
👉 received supportive care in the IC
👉 livedo reticularis resolved 1 week after the event
👉 neurologic deficits persisted at the time of his discharge from the hospital 2 months later.
Cholesterol Embolization Syndrome after Carotid-Artery Stenting
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
nejm.org/doi/full/10.10…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh