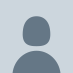
What's the most likely diagnosis?
53 year-old with mild shortness of breath
Hiatal hernia
Pneumothorax
Pneumonia
Pulmonary infarct
Left lower lobe atelectasis
53 year-old with mild shortness of breath
Hiatal hernia
Pneumothorax
Pneumonia
Pulmonary infarct
Left lower lobe atelectasis

Left Lower Lobe Atelectasis
All types of atelectasis involve loss of volume in some or all of a lung with resultant increased density of the involved lung
👉 here is that caused by bronchial obstru, usually a tumor (i.e. a bronchogenic carcinoma), a foreign body or mucus plug
All types of atelectasis involve loss of volume in some or all of a lung with resultant increased density of the involved lung
👉 here is that caused by bronchial obstru, usually a tumor (i.e. a bronchogenic carcinoma), a foreign body or mucus plug
Left lower lobe collapse
👉has distinctive features, and can be readily identified on frontal chest radiographs, provided attention is paid to the normal cardiomediastinal contours
👉has distinctive features, and can be readily identified on frontal chest radiographs, provided attention is paid to the normal cardiomediastinal contours

However, the shadow cast by the heart does make it more difficult to see than the right lower lobe collapse.
Some of the findings of right lower lobe collapse can be grouped together as they are almost identical on both sides.
Some of the findings of right lower lobe collapse can be grouped together as they are almost identical on both sides.

Differential diagnosis
The characteristic shape associated with volume loss usually does not allow for any significant differential diagnosis.
As always one should consider:
left lower lobe consolidation (of the medial basal segment)
pulmonary or posterior mediastinal mass
The characteristic shape associated with volume loss usually does not allow for any significant differential diagnosis.
As always one should consider:
left lower lobe consolidation (of the medial basal segment)
pulmonary or posterior mediastinal mass

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh