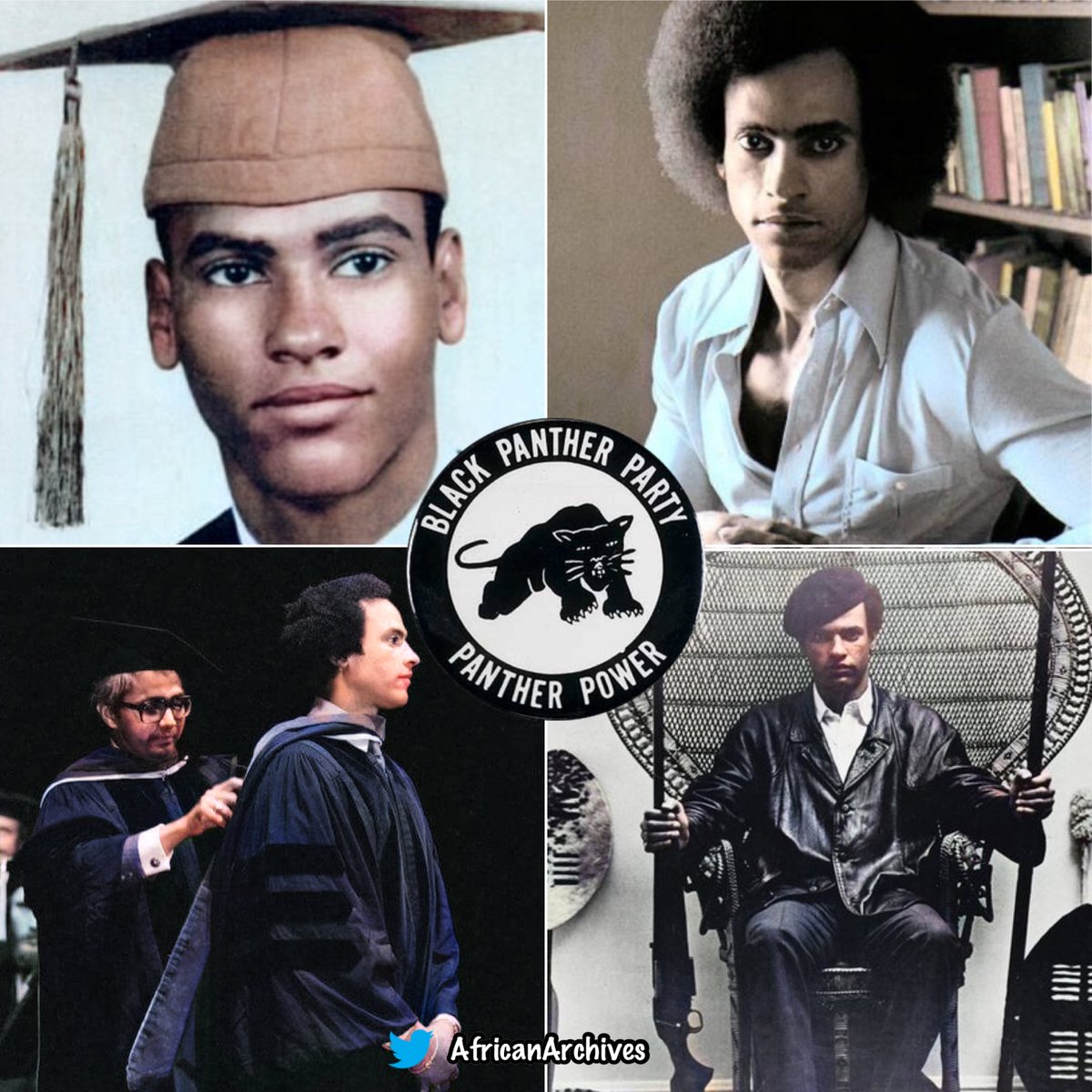
Happy 81st Birthday to the late Huey P. Newton. He was the co-founder & leader of the Black Panther Party for Self Defense.
It was originally founded to fight police racism, they were dedicated to liberating people from white supremacism & much more. #BlackHistoryMonth
A THREAD
It was originally founded to fight police racism, they were dedicated to liberating people from white supremacism & much more. #BlackHistoryMonth
A THREAD

In the wake of the assassination of Malcolm X in 1965, Merritt Junior College students Huey P. Newton and Bobby Seale founded the Black Panther Party for Self-Defense on October 15, 1966, in West Oakland, California. Shortening its name to the Black Panther Party. 



The party sought to set itself apart from black cultural nationalist organizations, such as the Universal Negro Improvement Association & the Nation of Islam, to which it was commonly compared. 

Although the groups shared certain philosophical positions and tactical features, the Black Panther Party & cultural nationalists differed on a number of basic points.
For instance, whereas black cultural nationalists generally regarded all white people as oppressors…
For instance, whereas black cultural nationalists generally regarded all white people as oppressors…
the Black Panther Party distinguished between racist and nonracist whites & allied themselves with progressive members of the latter group.
Also, whereas cultural nationalists generally viewed all black people as oppressed, the BPP believed that black capitalists & elites could and typically did exploit and oppress others, particularly the African American working class.
The party’s original purpose was to patrol black neighbourhoods to protect residents from acts of police brutality.
The Panthers eventually developed into a Marxist revolutionary group that called for the arming of all African Americans…
The Panthers eventually developed into a Marxist revolutionary group that called for the arming of all African Americans…

…the exemption of African Americans from the draft and from all sanctions of so-called white America, the release of all African Americans from jail & the payment reparations for centuries of exploitation by white Americans.
At its peak in the late 1960s, Panther membership exceeded 2,000, and the organization operated chapters in several major American cities. 

The Black Panther Party found itself squarely in the crosshairs of the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and its counterintelligence program, COINTELPRO. In fact, in 1969 FBI director J. Edgar Hoover considered the Black Panther Party the greatest threat to national security.
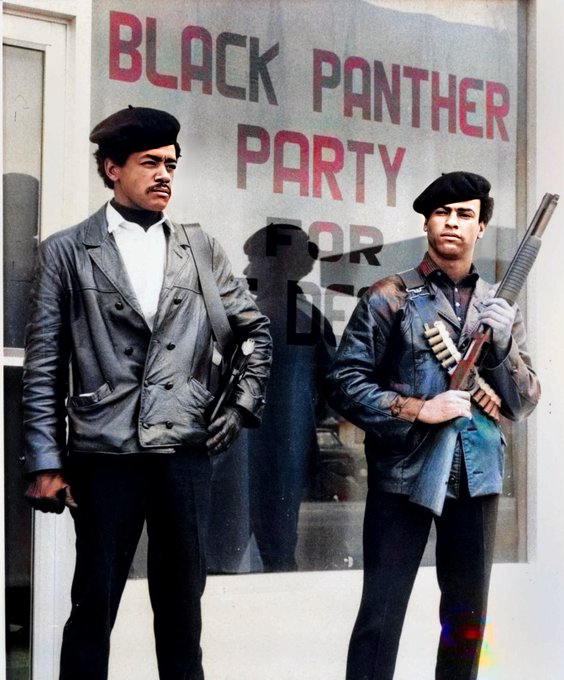
The Black Panther Party came into the national spotlight in May 1967 when a small group of its members, led by its chair, Seale, marched fully armed into the California state legislature in Sacramento. 

Emboldened by the view that African Americans had a constitutional right to bear arms (based on the Second Amendment of the U.S. Constitution), the Black Panther Party marched on the body as a protest against the pending Mulford Act.
The Mulford Act was a 1967 California bill prohibiting the public carrying of loaded firearms, named after Assemblyman Don Mulford.
The bill was signed by California Governor Ronald Reagan.
The bill was signed by California Governor Ronald Reagan.
The Black Panther Party viewed the gun control bill, as a political maneuver to thwart the organization’s effort to combat police brutality in the Oakland community.
In addition to challenging police brutality, the Party launched Survival Programs and provided community help, such as education, tuberculosis testing, legal aid, transportation assistance, ambulance service, and the manufacture and distribution of free shoes to poor people. 

Notwithstanding the social services, the FBI declared the group a communist organization and an enemy of the government.
The measures employed were so extreme that, years later when they were revealed, the director of the FBI publicly apologized for “wrongful uses of power”
The measures employed were so extreme that, years later when they were revealed, the director of the FBI publicly apologized for “wrongful uses of power”
If you love my content, You can support my history page/project here through donations/tips to keep up on: ko-fi.com/africanarchives 

Dr. Huey P. Newton had a PHD in Social Science. His doctoral dissertation was entitled War Against the Panthers: A Study of Repression in America.
You can read it here: ouleft.org/wp-content/upl…
You can read it here: ouleft.org/wp-content/upl…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh