DOCUMENTS: Through a records request, I have acquired the University of Missouri's rubric for evaluating diversity statements.
As usual, the rubric proves the critics' point: DEI evaluations invite viewpoint discrimination.
As usual, the rubric proves the critics' point: DEI evaluations invite viewpoint discrimination.

As it turns out, Mizzou routinely uses diversity statements in hiring.
According to its Inclusive Excellence Plan, the College of Arts and Science has expanded its use of the statements. The college of agriculture has committed to using them for “all faculty applications.”
According to its Inclusive Excellence Plan, the College of Arts and Science has expanded its use of the statements. The college of agriculture has committed to using them for “all faculty applications.”

Mizzou’s Division of Biological Sciences (why is it always biology?) heavily weighs diversity statements.
Its website advertises its “equal weighting of the research, teaching, and inclusion and equity statements" in the first round of faculty job application reviews.
Its website advertises its “equal weighting of the research, teaching, and inclusion and equity statements" in the first round of faculty job application reviews.

Meanwhile, Mizzou’s training on “Best Practice for Inclusive Excellence in Faculty Hiring” encourages hiring committees to assess job candidates’ contributions to DEI using a pre-established rubric. 





Again, the Mizzou rubric I obtained through a FOIA request perfectly illustrates how diversity statement policies invite viewpoint discrimination. 


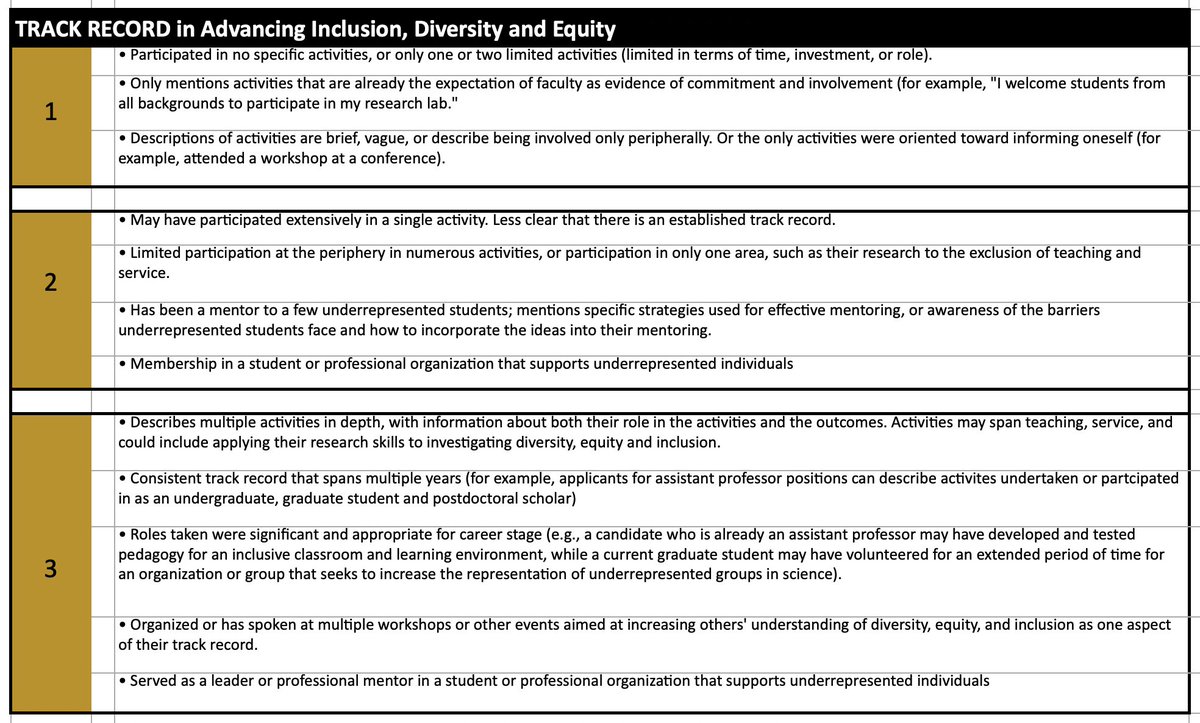
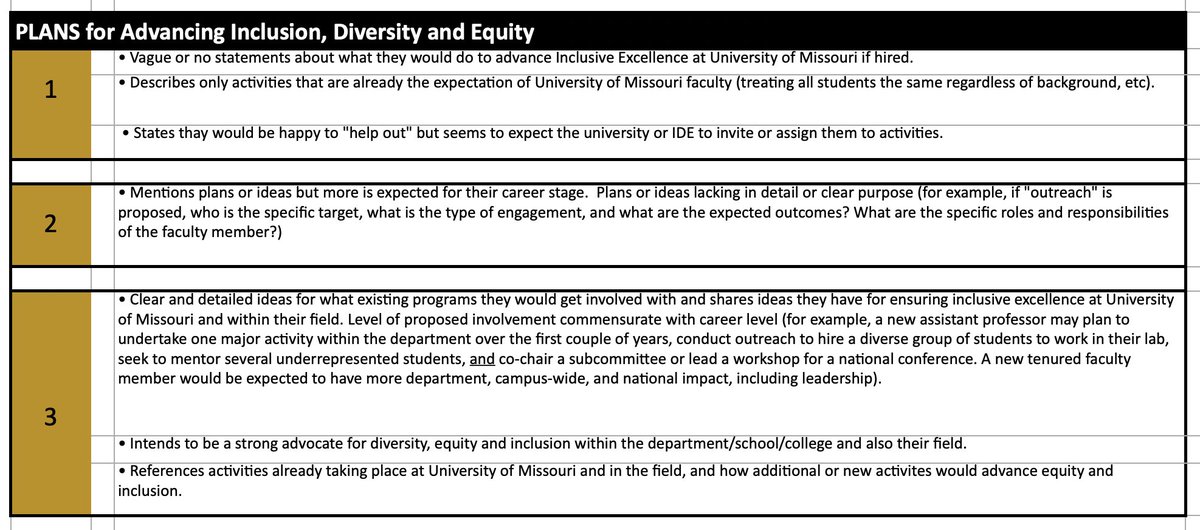
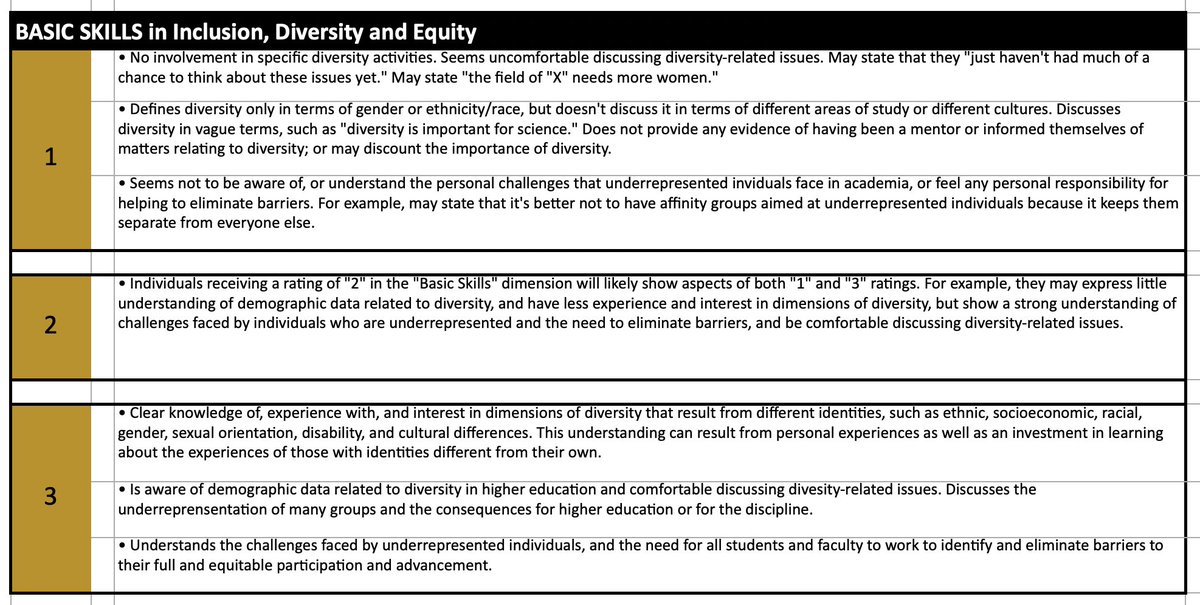
Though innocuous-sounding, the phrase “diversity, equity, and inclusion” doesn't imply a set of neutral values.
In practice, it implies a set of controversial views about race, gender, and social justice. Again and again, this is demonstrated by university DEI initiatives.
In practice, it implies a set of controversial views about race, gender, and social justice. Again and again, this is demonstrated by university DEI initiatives.
By now, it should be obvious that diversity statements will inevitably function as ideological litmus tests—and huge failures of priority.
Unfortunately, they’re alive and well at the University of Missouri.
Unfortunately, they’re alive and well at the University of Missouri.
Read the full story, and take a look at the rubric, at @MindingCampus. Through top-quality research and reporting, we're documenting the ways that DEI has invaded higher education to the detriment of our public and private universities.
mindingthecampus.org/2023/02/23/doc…
mindingthecampus.org/2023/02/23/doc…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




























