
1/ 😱😱😱 Why is this valve in the ascending aorta⁉️
Join me as we learn about TAVR complications.
Another @Cardionerds thread….
Farley et al: rb.gy/zu3ay3
#CardioTwitter #ACCMedStudent
Join me as we learn about TAVR complications.
Another @Cardionerds thread….
Farley et al: rb.gy/zu3ay3
#CardioTwitter #ACCMedStudent

2/ 🌟We know the TAVR success story has been extraordinary and is continuously evolving
⚠️⚠️BUT... like all procedures, TAVR has its fair share of complications we have to keep in mind
jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.…
⚠️⚠️BUT... like all procedures, TAVR has its fair share of complications we have to keep in mind
jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.…

3/Keep reading to:
▶️Understand the periprocedural TAVR complications
▶️Appreciate the prevalence of TAVR complications
▶️Recognize the late complications of TAVR
▶️Understand the periprocedural TAVR complications
▶️Appreciate the prevalence of TAVR complications
▶️Recognize the late complications of TAVR
4/First, how do you feel about your understanding of the common and less common complications of TAVR?
5/Let’s jump right into the “Big 5” periprocedural complications coined by Eberhard Grube and Jan-Malte Sinning that plague the TAVR procedure:
1️⃣paravalvular leak (PVL)
2️⃣vascular/bleeding
3️⃣stroke
4️⃣AKI
5️⃣conduction disturbances
jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.…
1️⃣paravalvular leak (PVL)
2️⃣vascular/bleeding
3️⃣stroke
4️⃣AKI
5️⃣conduction disturbances
jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.…

6/Let’s make the “Big 5” less intimidating by breaking each down one by one:
1️⃣PVL
Any amount of PVL occurs in about 70% of cases
▶️during deployment, the TAVR valve expands against the calcified native aortic valve
1️⃣PVL
Any amount of PVL occurs in about 70% of cases
▶️during deployment, the TAVR valve expands against the calcified native aortic valve
7/▶️the calcified valve is helpful to anchor the TAVR valve, but can prevent proper sealing of the valve➡️leakage
Original trials had moderate-severe PVL in up to 24%
With newer valves (more pronounced "skirts" to mitigate leak) and more operator experience incidence is <2%
Original trials had moderate-severe PVL in up to 24%
With newer valves (more pronounced "skirts" to mitigate leak) and more operator experience incidence is <2%
8/2️⃣vascular/bleeding
▶️utilizing arteries and veins & manipulating catheters➡️⬆️risk of bleeding 🩸and vascular complications
▶️incidence of🩸has improved over time with recent TVT registry data showing ⬇️ risk from 5.5% in 2012/13 to 2.93% in 2019
jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.…
▶️utilizing arteries and veins & manipulating catheters➡️⬆️risk of bleeding 🩸and vascular complications
▶️incidence of🩸has improved over time with recent TVT registry data showing ⬇️ risk from 5.5% in 2012/13 to 2.93% in 2019
jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.…
9/Cool Tip:
@CCFcards showed that unilateral access (delivery sheath & sheath used for aortic root angiography on ipsilateral femoral artery) is safe &useful for bailout in vascular access complications @tavrkapadia @GrantReed @SergeHarbMD @LarsSvenssonMD
rb.gy/bfmufi
@CCFcards showed that unilateral access (delivery sheath & sheath used for aortic root angiography on ipsilateral femoral artery) is safe &useful for bailout in vascular access complications @tavrkapadia @GrantReed @SergeHarbMD @LarsSvenssonMD
rb.gy/bfmufi
10/3️⃣stroke
▶️Catheters in the heart & aorta ➡️ ⬆️ risk of throwing a clot into the brain
▶️valve deployment causes calcium debris to break off of the native valve➡️brain
▶️30-day stroke risk ranges 2-5%
👉stroke risk has decreased over time rb.gy/y7en5w
▶️Catheters in the heart & aorta ➡️ ⬆️ risk of throwing a clot into the brain
▶️valve deployment causes calcium debris to break off of the native valve➡️brain
▶️30-day stroke risk ranges 2-5%
👉stroke risk has decreased over time rb.gy/y7en5w
11/4️⃣AKI
▶️incidence of AKI (stage I-III) after TAVR is ~20%
🤔 I wonder why kidney injury is so common in TAVR?!
▶️contrast use
▶️periods of extreme hypotension (ex. during valve deployment)
▶️large catheters in the aorta ➡️ cholesterol emboli
▶️incidence of AKI (stage I-III) after TAVR is ~20%
🤔 I wonder why kidney injury is so common in TAVR?!
▶️contrast use
▶️periods of extreme hypotension (ex. during valve deployment)
▶️large catheters in the aorta ➡️ cholesterol emboli
12/5️⃣conduction disturbances
▶️conduction system traverses the membranous septum right under the aortic annulus
▶️valve expansion can lead to compression of the conduction system
▶️can lead to LBBB (4-65%), AF (6.3-7.2%), and high-degree AV block
jacc.org/doi/abs/10.101…
▶️conduction system traverses the membranous septum right under the aortic annulus
▶️valve expansion can lead to compression of the conduction system
▶️can lead to LBBB (4-65%), AF (6.3-7.2%), and high-degree AV block
jacc.org/doi/abs/10.101…

13/mechanical complications:
💥annular rupture(.4-1%)
💥valve embolization(<1%)
💥ventricular perforation(1%)
💥aortic dissection(0.2%)
💥VSD(20 cases from 2002-15)
💥intracardiac shunts(0.5%)
💥coronary obstruction(<1% in native TAVRs, 2.5-3.5% in valve in valve)
💥suicide LV
💥annular rupture(.4-1%)
💥valve embolization(<1%)
💥ventricular perforation(1%)
💥aortic dissection(0.2%)
💥VSD(20 cases from 2002-15)
💥intracardiac shunts(0.5%)
💥coronary obstruction(<1% in native TAVRs, 2.5-3.5% in valve in valve)
💥suicide LV
14/Check out Episode 55 on post-TAVR suicide LV with @doctormontano @DocTravesty @pkothapalliMDand #DrMichaelGrzeskowiak from @DellMedCardio
And this great infographic by @EvelynSongMD and @karanpdesai ⬇️
rb.gy/a3qnad
And this great infographic by @EvelynSongMD and @karanpdesai ⬇️
rb.gy/a3qnad

15/ Ok, so we made it through TAVR with no complications. We're cleared!!🙌
❌❌❌
Long-term complications can be categorized as bioprosthetic valve dysfunction (BVD)
1️⃣Non-structural etiologies
2️⃣Structural etiologies
jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.…
❌❌❌
Long-term complications can be categorized as bioprosthetic valve dysfunction (BVD)
1️⃣Non-structural etiologies
2️⃣Structural etiologies
jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.…
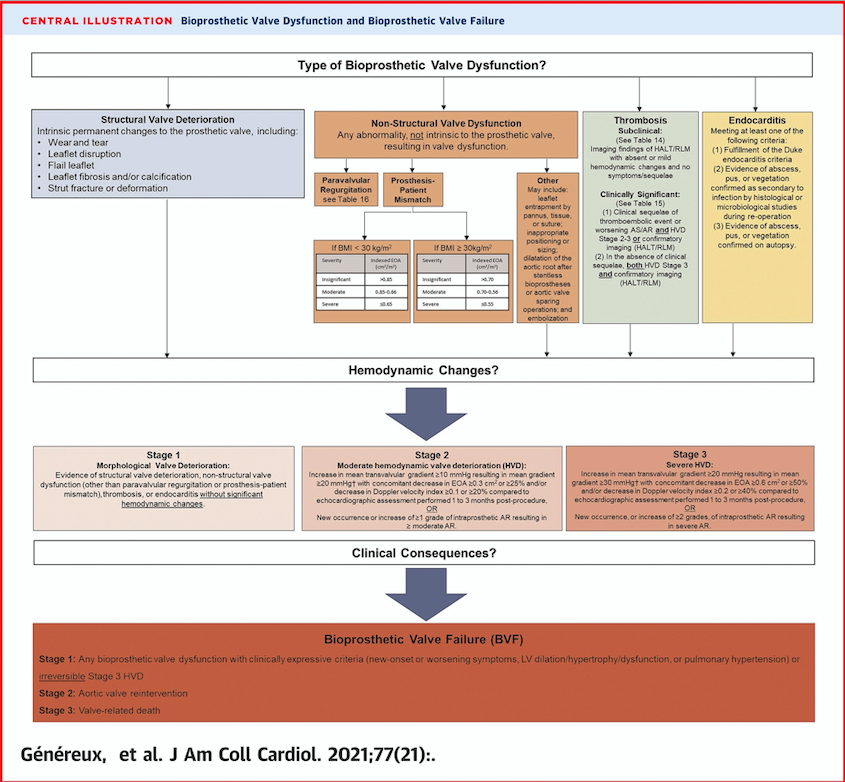
16/Nonstructural 🟰 hemodynamic valve dysfunction not intrinsic to the valve
These include:
▶️PVL (see tweet #6)
▶️patient prosthesis mismatch (PPM): effective orifice area of the valve is too small in relation to the patient's body
These include:
▶️PVL (see tweet #6)
▶️patient prosthesis mismatch (PPM): effective orifice area of the valve is too small in relation to the patient's body
17/Structural causes include:
▶️leaflet wear and tear
▶️disruption
▶️flail leaflet
▶️leaflet fibrosis and/or calcification and thickening
▶️strut or stent fracture
▶️endocarditis (0.3 to 2 per 100 person-years)
▶️thrombosis
▶️leaflet wear and tear
▶️disruption
▶️flail leaflet
▶️leaflet fibrosis and/or calcification and thickening
▶️strut or stent fracture
▶️endocarditis (0.3 to 2 per 100 person-years)
▶️thrombosis
18/Thrombosis is classified as either clinical or subclinical leaflet thrombosis
▶️clinical leaflet thrombosis occurs in 0.5% as ⬆️ gradients & recurrent symptoms
▶️subclinical leaflet thrombosis has been reported in 10-15% of TAVRs and has no symptoms
▶️clinical leaflet thrombosis occurs in 0.5% as ⬆️ gradients & recurrent symptoms
▶️subclinical leaflet thrombosis has been reported in 10-15% of TAVRs and has no symptoms
19/Let's make sure you learned something.
I feel comfortable with my understanding of the complications of TAVR and what to keep in mind for our post-op TAVR pts?
I feel comfortable with my understanding of the complications of TAVR and what to keep in mind for our post-op TAVR pts?
20/A huge thank you to @saahilaj for his invaluable mentorship, @TDonisan & @AmitGoyalMD for reviewing! shoutout to #HouseThomas for the constant support!
21/ Keep an eye out for more 🧵 as we take a deep dive into the epidemiology, preventions, and management of each of these complications!
22/References:
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
uptodate.com/contents/trans…
interventional.theclinics.com/article/S2211-…
jamanetwork.com/journals/jamac…
jscai.org/article/S2772-…
ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/JA…
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35268271/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33213729/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27889349/
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
uptodate.com/contents/trans…
interventional.theclinics.com/article/S2211-…
jamanetwork.com/journals/jamac…
jscai.org/article/S2772-…
ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/JA…
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35268271/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33213729/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27889349/
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh


![Courtesy of @GoldbergJBCTMD [Dr. Joshua Goldberg]](https://pbs.twimg.com/media/Fp_aVGwX0AY9WNZ.jpg)







