Who's that guy on the £20 note?
A painter called Joseph Mallord William Turner.
Does he deserve to be there? Well, he's probably the greatest English artist of all time...
A painter called Joseph Mallord William Turner.
Does he deserve to be there? Well, he's probably the greatest English artist of all time...

Joseph Mallord William Turner was born in London in 1775, the son of a barber.
He made paintings from an early age, and his father sold them in his shop. This prodigously talented boy was destined for greatness, and at just 14 he joined the Royal Academy of Arts...
He made paintings from an early age, and his father sold them in his shop. This prodigously talented boy was destined for greatness, and at just 14 he joined the Royal Academy of Arts...

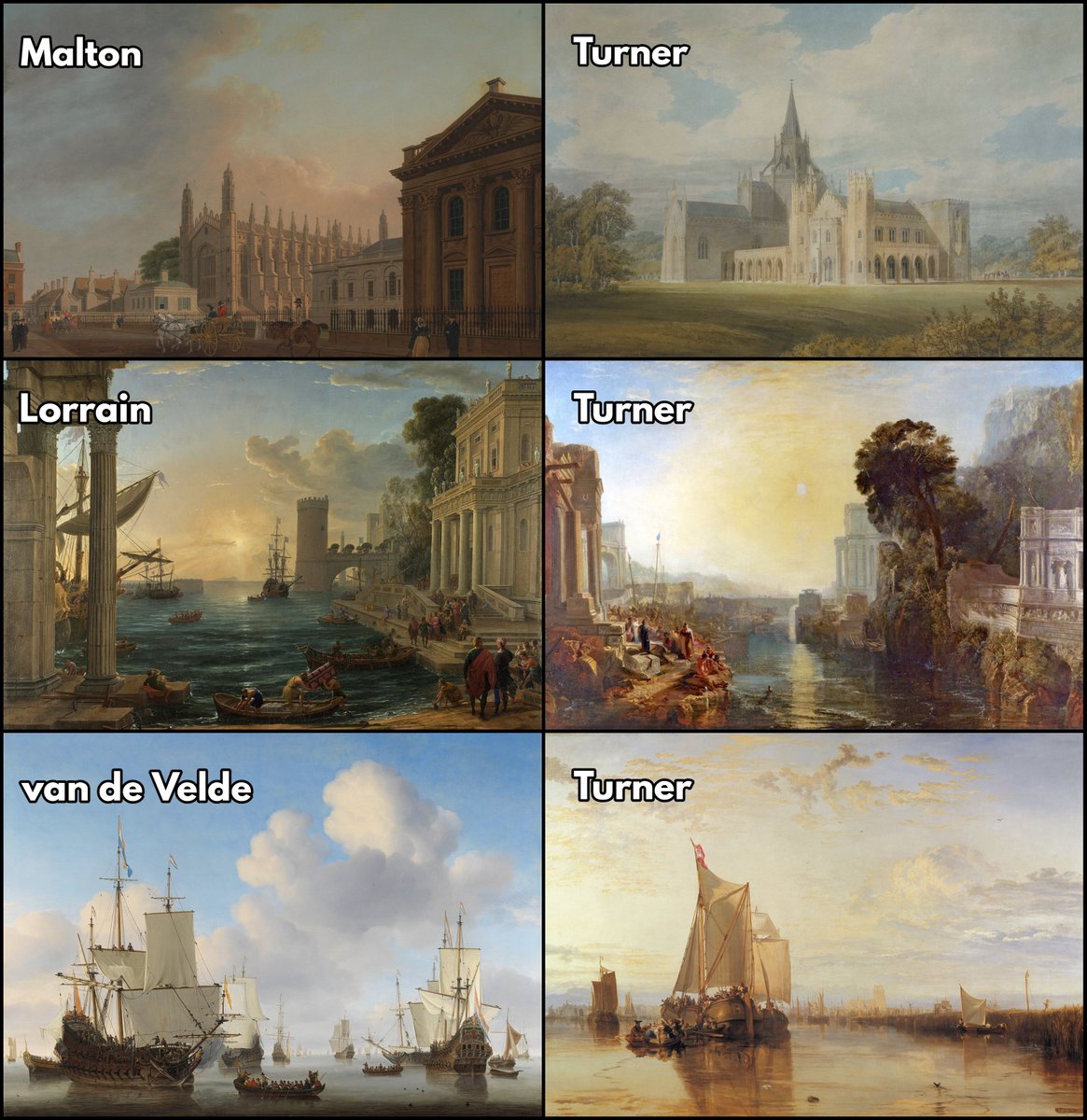
Turner's early influences are clear.
The topographical art of English painters like Thomas Malton; the idyllic landscapes of the 17th century painter Claude Lorrain; the detailed seascapes and ships of the Dutch painter Willem van de Velde.
The topographical art of English painters like Thomas Malton; the idyllic landscapes of the 17th century painter Claude Lorrain; the detailed seascapes and ships of the Dutch painter Willem van de Velde.

Turner's reputation grew during the 1790s. He was a prolific artist and his paintings were always being exhibited in London; the critics liked him, and so did the public.
By the early 1800s he was flooded with commissions, financially secure, and hugely popular.
By the early 1800s he was flooded with commissions, financially secure, and hugely popular.

But during the 1810s he transformed from simply being the greatest landscape artist of the age into something more.
How? There were clues. Take Buttermere, from 1798. Turner was developing a unique style wholly of his own: intense, colourful, luminous, bursting with atmosphere.
How? There were clues. Take Buttermere, from 1798. Turner was developing a unique style wholly of his own: intense, colourful, luminous, bursting with atmosphere.

In Lorrain the landscape was externally beautiful; in van de Velde it was precise; in Malton it was realistic.
But for Turner the landscape became something else entirely: a place of pure colour, mood, atmosphere, drama, and feeling.
Outlines melted; colour came pouring in.
But for Turner the landscape became something else entirely: a place of pure colour, mood, atmosphere, drama, and feeling.
Outlines melted; colour came pouring in.

Turner started painting like nobody in Western Europe had ever done before. Whereas colour in the past had been secondary, Turner made it absolutely dominant.
Even the *way* he mixed his paints and put them on canvas was totally unheard of.
Even the *way* he mixed his paints and put them on canvas was totally unheard of.

Turner travelled often, all around the British Isles and throughout Europe. He still produced relatively "normal" landscapes or cityscapes, which were always popular.
But that didn't stop him from exploring his increasingly unusual style - these are both paintings of Venice.

But that didn't stop him from exploring his increasingly unusual style - these are both paintings of Venice.


As the years wore on Turner leaned even further into this new form of landscape art, and by the 1840s he had entered a phase of total artistic liberation.
In his own words, Turner painted for the imagination rather than for the eye. That was, he said, the "greater truth".
In his own words, Turner painted for the imagination rather than for the eye. That was, he said, the "greater truth".

Turner had come of age during the peak of Romanticism in Britain, which was fundamentally a reaction against the Industrial Revolution and the Enlightenment.
The human spirit, emotion, the beauty of the natural world - all were being destroyed, the Romantics felt.
The human spirit, emotion, the beauty of the natural world - all were being destroyed, the Romantics felt.
Turner's landscapes are not scientific: they attempt neither to understand nor rationalise nature.
And this is at Romanticism's core: a belief in the mystery, power, beauty, drama, and sublimity of nature. But Turner's nature is not merely incomprehensible, it is all-powerful.
And this is at Romanticism's core: a belief in the mystery, power, beauty, drama, and sublimity of nature. But Turner's nature is not merely incomprehensible, it is all-powerful.

Just compare Turner's version of Hannibal Crossing the Alps with Jacques-Louis David's Napoleon Crossing the Alps.
One is Romantic, with human figures dwarfed by vast, magnificent, and unconquerable nature; the other is Neoclassical, with humanity triumphant and centre-stage.

One is Romantic, with human figures dwarfed by vast, magnificent, and unconquerable nature; the other is Neoclassical, with humanity triumphant and centre-stage.


Even when he depicts cityscapes they are shrouded in fog, mist, and fire. The sharp geometry of human construction melts away into water, cloud, smoke, and reflection.
No wonder he painted the fire at the Palace of Westminster in 1834 - here was a moment of supreme drama.
No wonder he painted the fire at the Palace of Westminster in 1834 - here was a moment of supreme drama.

And his most famous painting, included on the £20 note, rather captures this Romantic spirit: The Fighting Temeraire.
It portrays a ship that had taken part in the Battle of Trafalgar being towed away for scrap against a setting sun.
It portrays a ship that had taken part in the Battle of Trafalgar being towed away for scrap against a setting sun.

But Turner, at his boldest, defies categorisation.
Perhaps he perfected Romanticism, but there was simply nobody else who had ever painted like Turner in his later years (with the possible exception of William Blake, another great Romantic, in his own way).
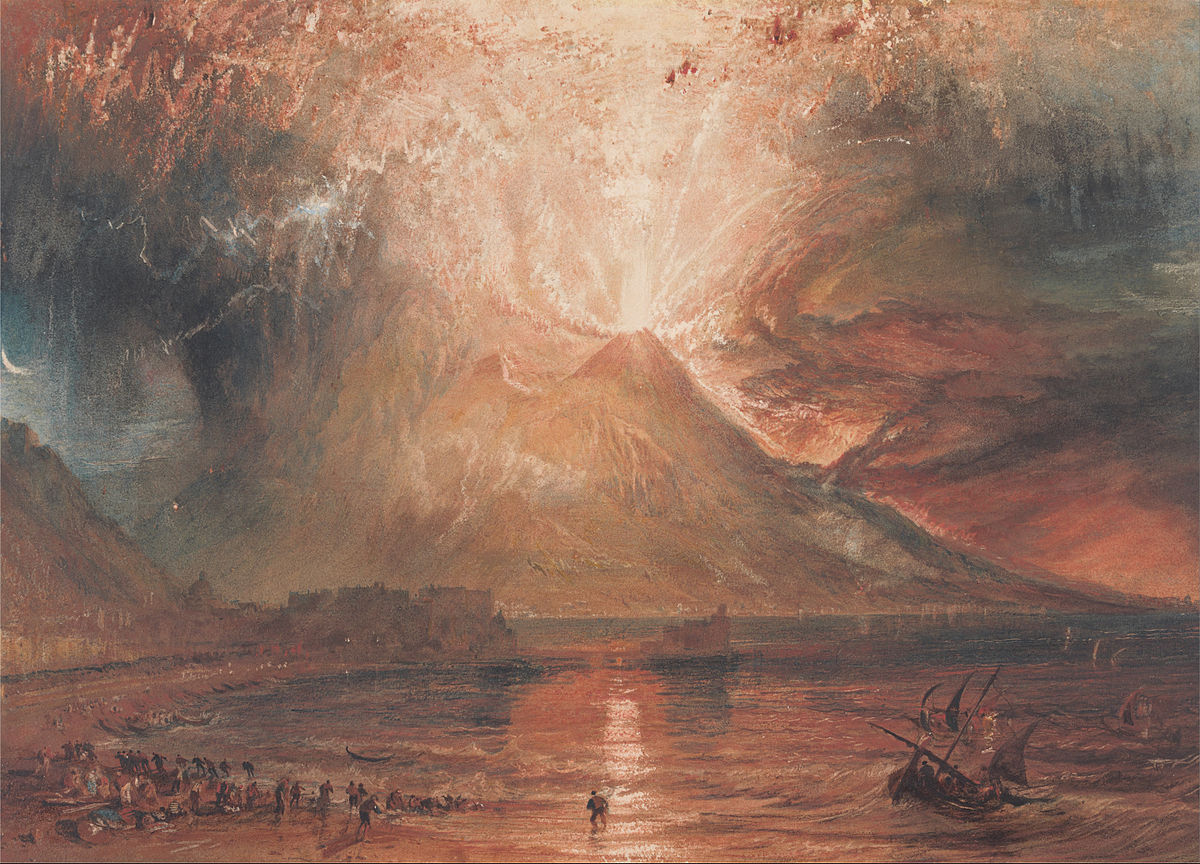
What is this?!
Perhaps he perfected Romanticism, but there was simply nobody else who had ever painted like Turner in his later years (with the possible exception of William Blake, another great Romantic, in his own way).
What is this?!
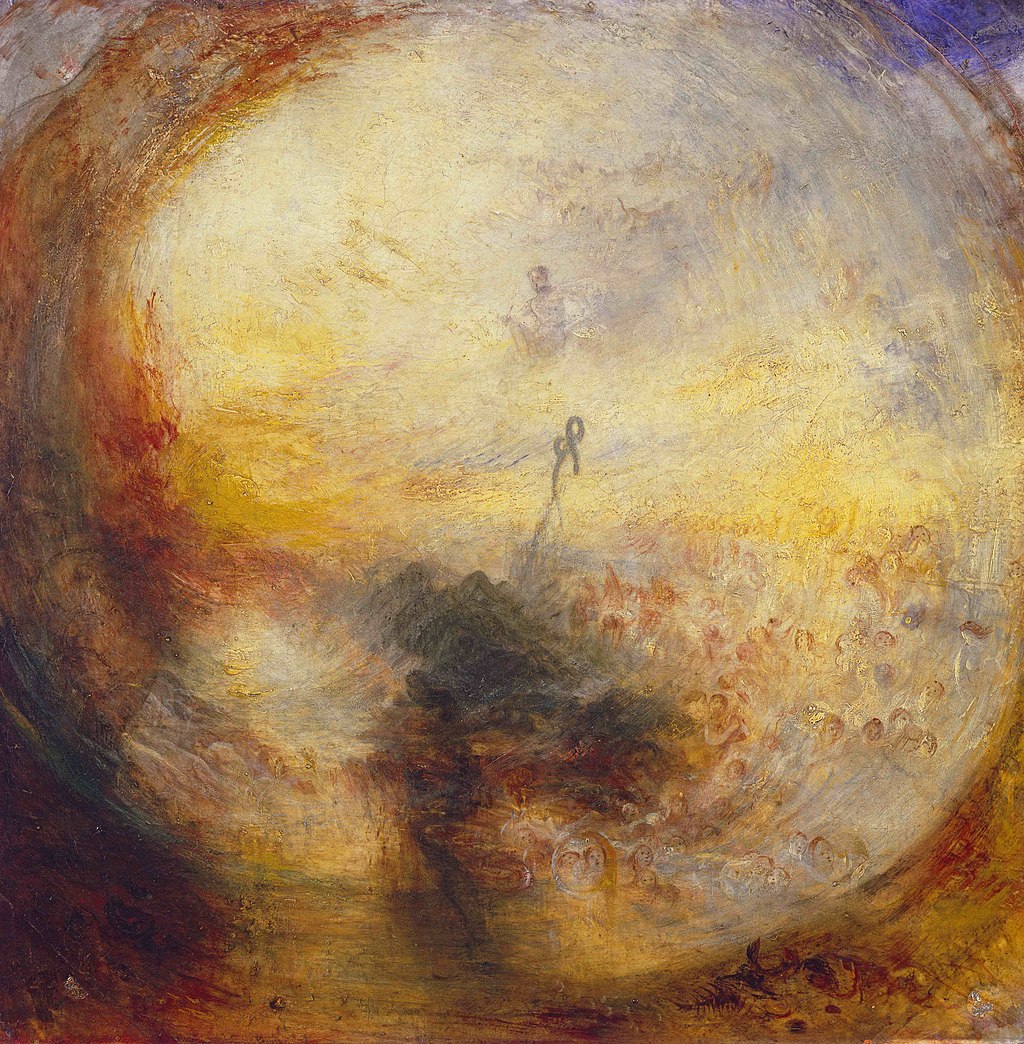
It's tempting to call Turner a Proto-Impressionist. His embrace of colour predated and influenced them, after all.
But Turner was interested by scenes of great scale and drama; the Impressionists weren't. And even at their wildest they never quite painted anything like this:
But Turner was interested by scenes of great scale and drama; the Impressionists weren't. And even at their wildest they never quite painted anything like this:

Turner verged on the abstract. In many of his late paintings it's difficult to make anything out.
And for these reasons his late works weren't universally popular; contemporary critics wrote about "the inconceivable jumble of colours" in paintings like Sunrise with Sea Monsters.
And for these reasons his late works weren't universally popular; contemporary critics wrote about "the inconceivable jumble of colours" in paintings like Sunrise with Sea Monsters.

One critic even accused Turner of painting with "cream, chocolate, egg yolk and currant jelly" - they thought he was tearing up any and all artistic traditions.
Such criticisms aren't so different from those levelled at Impressionism, Cubism, Abstract Art, and so on.
Such criticisms aren't so different from those levelled at Impressionism, Cubism, Abstract Art, and so on.

But of all these radicals, Turner was the very first. And, unlike them, he didn't have artistic companions: this was the artistic movement of one man.
To his critics the once-great Turner had simply lost his mind; some believed it was all a result of failing vision.
To his critics the once-great Turner had simply lost his mind; some believed it was all a result of failing vision.

Turner, even when he had become one of the most popular and successful artists in Britain, remained a complicated and unusual man.
He was kind but ill-tempered, ambitious but secretive, talented but eccentric. And, by the end of his life, a total recluse.
He was kind but ill-tempered, ambitious but secretive, talented but eccentric. And, by the end of his life, a total recluse.
Turner was a prolific artist: he produced hundreds of paintings and thousands of drawings and sketches. Few painters reward exploration of their work like him.
When he died he left all his paintings to the National Gallery and his entire fortune to create a charity for artists.
When he died he left all his paintings to the National Gallery and his entire fortune to create a charity for artists.
No story of Turner is complete without mentioning John Ruskin, probably the most influential cultural critic in 19th century England.
Ruskin became Turner's staunchest defender and it is partially thanks to him that Turner's reputation has endured.
Ruskin became Turner's staunchest defender and it is partially thanks to him that Turner's reputation has endured.

And yet Turner once said of Ruskin:
"He knows a great deal more about my pictures than I do; he puts things into my head, and points out meanings in them that I never intended."
No matter how many words we use, Turner's art is almost beyond critique and understanding.

"He knows a great deal more about my pictures than I do; he puts things into my head, and points out meanings in them that I never intended."
No matter how many words we use, Turner's art is almost beyond critique and understanding.
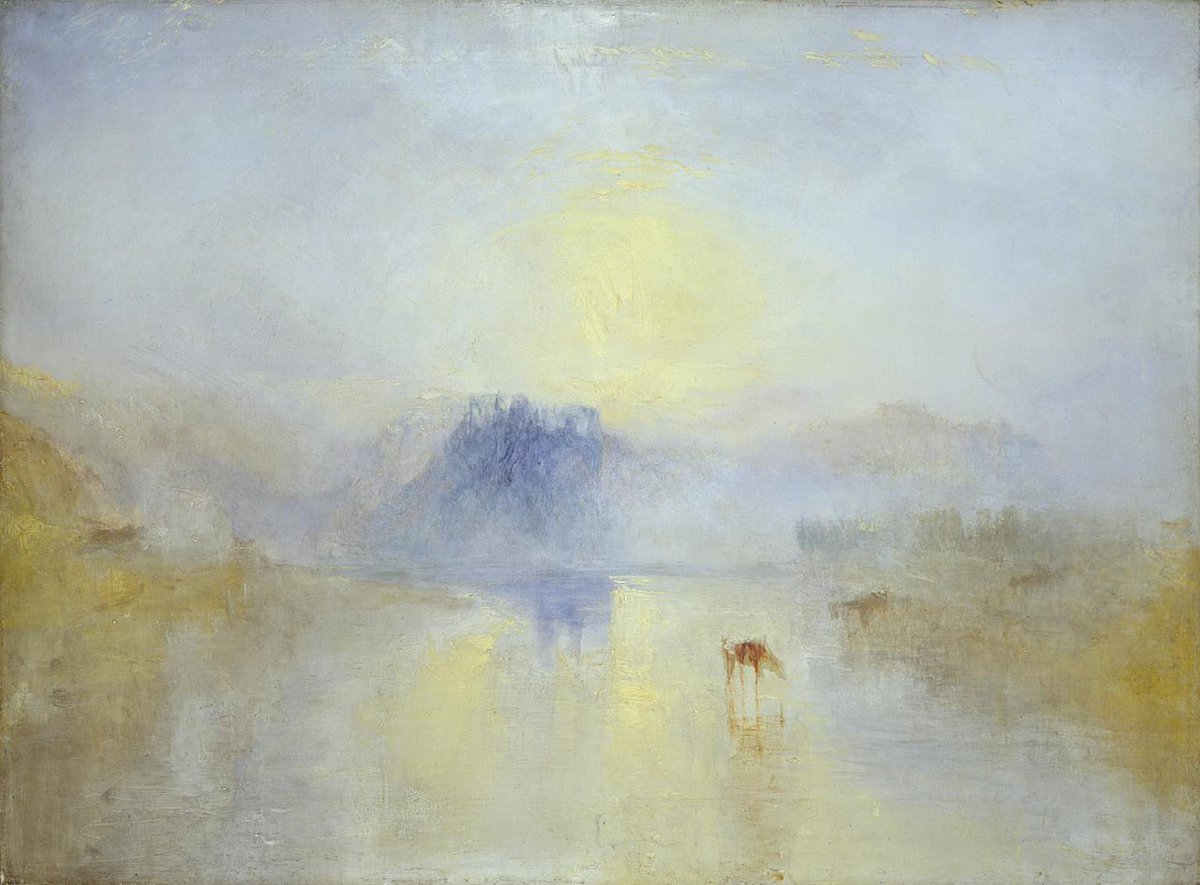


And so that's JMW Turner, the man on the £20 note. One who, by all accounts, probably deserves to be there.
His last words, so legend says, were: "the Sun is God." And that, if anything, captures the spirit of the enigmatic, uncategorisable man & artist that was Turner.
His last words, so legend says, were: "the Sun is God." And that, if anything, captures the spirit of the enigmatic, uncategorisable man & artist that was Turner.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





















