The #vasopressor session has started with 1️⃣“When is radial artery pressure unreliable?”
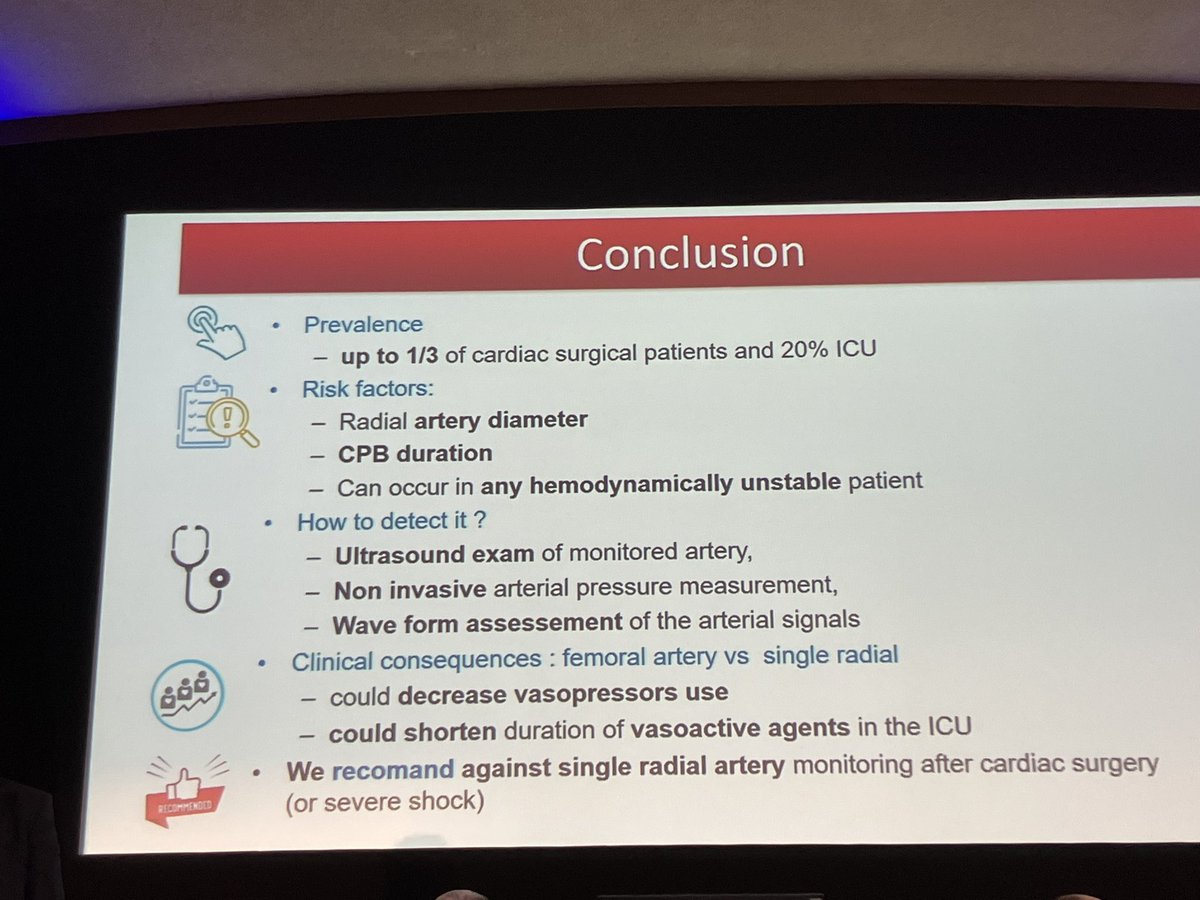
Detection
🔸Invasive vs Non-invasive
🔸Brain monitoring
🔸Mitral valve gradient
🔸Artery stenosis
🔸Waveform
👇Possible mechanisms of radial vs femoral differences
@ISICEM #isicem23

Detection
🔸Invasive vs Non-invasive
🔸Brain monitoring
🔸Mitral valve gradient
🔸Artery stenosis
🔸Waveform
👇Possible mechanisms of radial vs femoral differences
@ISICEM #isicem23
https://twitter.com/YukiKotani5/status/1638256892450336772

2️⃣Peripheral vasopressor use @HalliePrescott
🔸Low rates of complications reported up to 48 h with monitoring protocol
🔸Peripheral administration may avoid central line insertion (& its complications)
🔸Peripheral administration is becoming more common.
@ISICEM #isicem23
🔸Low rates of complications reported up to 48 h with monitoring protocol
🔸Peripheral administration may avoid central line insertion (& its complications)
🔸Peripheral administration is becoming more common.
@ISICEM #isicem23

3️⃣Early #norepinephrine infusion by Prof. JL Teboul.
🔸In 2018, 12% of intensivists used early norepinephrine but experts seemed to like it.
🔸Norepinephrine may increase preload/cardiac contractility
🔸Small RCTs suggest a trend of clinical benefits
@ISICEM #isicem23
🔸In 2018, 12% of intensivists used early norepinephrine but experts seemed to like it.
🔸Norepinephrine may increase preload/cardiac contractility
🔸Small RCTs suggest a trend of clinical benefits
@ISICEM #isicem23

4️⃣How to promote venous constriction
👍Reduces unstressed volume and increases preload
😥Increases venous resistance and capillary leakage
💉Most vasopressors may affect venous veins.
@ISICEM #isicem23

👍Reduces unstressed volume and increases preload
😥Increases venous resistance and capillary leakage
💉Most vasopressors may affect venous veins.
@ISICEM #isicem23


5️⃣When to start vasopressin? @daretha75
🔸IPD meta-analysis found a reduced risk of RRT in septic shock
🔸May not promote inflammatory reactions while norepi does
🔸Studies suggest less complications in patients with early vasopressin
More data are needed!
@ISICEM #isicem23
🔸IPD meta-analysis found a reduced risk of RRT in septic shock
🔸May not promote inflammatory reactions while norepi does
🔸Studies suggest less complications in patients with early vasopressin
More data are needed!
@ISICEM #isicem23

6️⃣New vasopressor agents @KhannaAshishCCM
🔸Angiotensin 2 and renin is a hot topic🔥
Findings from ATHOS-3
Need for point-of-care assay
🔸Centhaquine: a novel alpha 2 agonists
🔸Future: RCTs for early multimodal strategy?
@ISICEM #isicem23


🔸Angiotensin 2 and renin is a hot topic🔥
Findings from ATHOS-3
Need for point-of-care assay
🔸Centhaquine: a novel alpha 2 agonists
🔸Future: RCTs for early multimodal strategy?
@ISICEM #isicem23

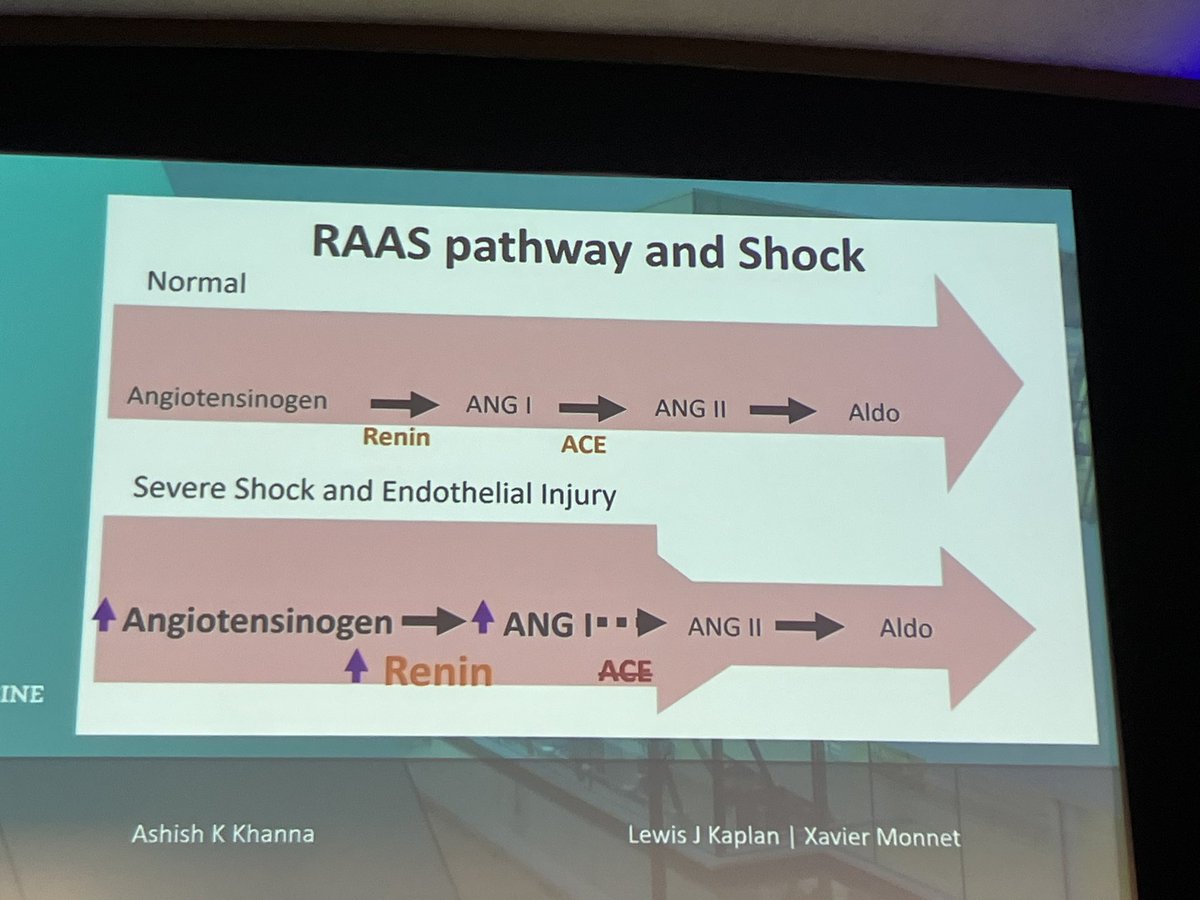

7️⃣Angiotensin 2 @BellomoRinaldo
🔸ATHOS3 suggests a signal toward clinical benefits in selected populations
🔸Animal studies show its immunomodulatory/ opsonizing effects
🔸decreases cardiac inflammation/injury compared with norepi
@ISICEM #isicem23

🔸ATHOS3 suggests a signal toward clinical benefits in selected populations
🔸Animal studies show its immunomodulatory/ opsonizing effects
🔸decreases cardiac inflammation/injury compared with norepi
@ISICEM #isicem23


8️⃣Vasopressor test
🔸Higher MAP target in selected pts (e.g., chronic hypertension)
🔸Andromeda shock trial found difficulties in the vasopressor test (due to e.g., persistent hypotension/adverse effects)
🔸Andromeda shock 2 is ongoing in a larger scale
@ISICEM #isicem23
🔸Higher MAP target in selected pts (e.g., chronic hypertension)
🔸Andromeda shock trial found difficulties in the vasopressor test (due to e.g., persistent hypotension/adverse effects)
🔸Andromeda shock 2 is ongoing in a larger scale
@ISICEM #isicem23

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh