🚨PAPER🚨
A recent study funded by @DegreesNGO, executed by @peteirvine & others aims "to assess the impact of #SAG on Sea Surface Temperature (SST) in the Gulf of Guinea & its causes using GLENS simulations performed under high anthropogenic emission scenario (RCP8.5)."
🧵
1/8
A recent study funded by @DegreesNGO, executed by @peteirvine & others aims "to assess the impact of #SAG on Sea Surface Temperature (SST) in the Gulf of Guinea & its causes using GLENS simulations performed under high anthropogenic emission scenario (RCP8.5)."
🧵
1/8

"Study focus on two dynamically different regions:
🔸Sassandra Upwelling in Côte d’Ivoire (SUC, located east of Cape Palmas)
🔸Takoradi Upwelling in Ghana (TUG, located east of Cape Three Points)"
2/8
🔸Sassandra Upwelling in Côte d’Ivoire (SUC, located east of Cape Palmas)
🔸Takoradi Upwelling in Ghana (TUG, located east of Cape Three Points)"
2/8

Results show that "in the SUC region, under climate change, there is an increase in SST (referred to as the current climate) all year long (by 1.52 °C on average) mainly due to an < in net heat flux (lead by the > in longwave radiation) & also in weak vertical mixing."
3/8

3/8


"Under SAG, SST decreases all the seasonal cycle with its maximum in Dec (−0.4 °C) due to a reduction in the net heat flux (caused by a diminution of #SolarRadiation) & an increase in vertical advection (due to an increase in vertical temp. gradient & vertical velocity)."
4/8

4/8


"In the TUG region, under climate change, SST warming is a little more intense than in the SUC region and SST changes are driven by an increase in the net heat flux and strong stratification."
5/8



5/8
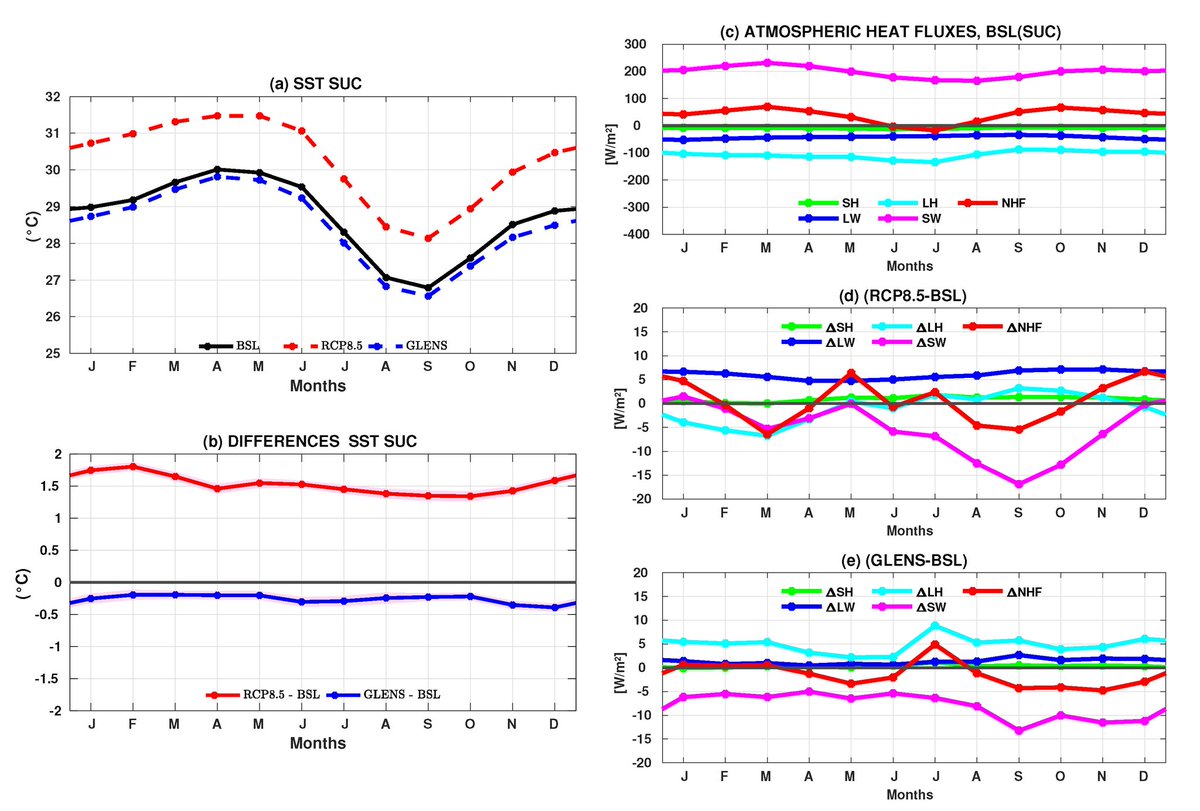



"The cooling of the SST in TUG is similar to the SUC region, but contrary to this region, the cooling
under SAG is not only explained by a decrease in the net heat flux but also by the remote forcing of
wind changes at the western equatorial Atlantic."
6/8
under SAG is not only explained by a decrease in the net heat flux but also by the remote forcing of
wind changes at the western equatorial Atlantic."
6/8

Read open access paper on "Impact of Stratospheric Geoengineering on Sea Surface
Temperature in the Northern Gulf of Guinea" ⬇️
mdpi.com/2225-1154/11/4…
#StratosphericAerosolGeoengineering
#SAG
7/8
Temperature in the Northern Gulf of Guinea" ⬇️
mdpi.com/2225-1154/11/4…
#StratosphericAerosolGeoengineering
#SAG
7/8
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh