1. This History Thread is about relations of Burma (Myanmar) with Bangladesh & Pakistan. Burma’s western neighbor Bangladesh was part of Pakistan from 1947-1971. In a region of turmoil, Bangladesh/Myanmar river border has been a lifeline for refugees. #WhatsHappeningInMyanmar 







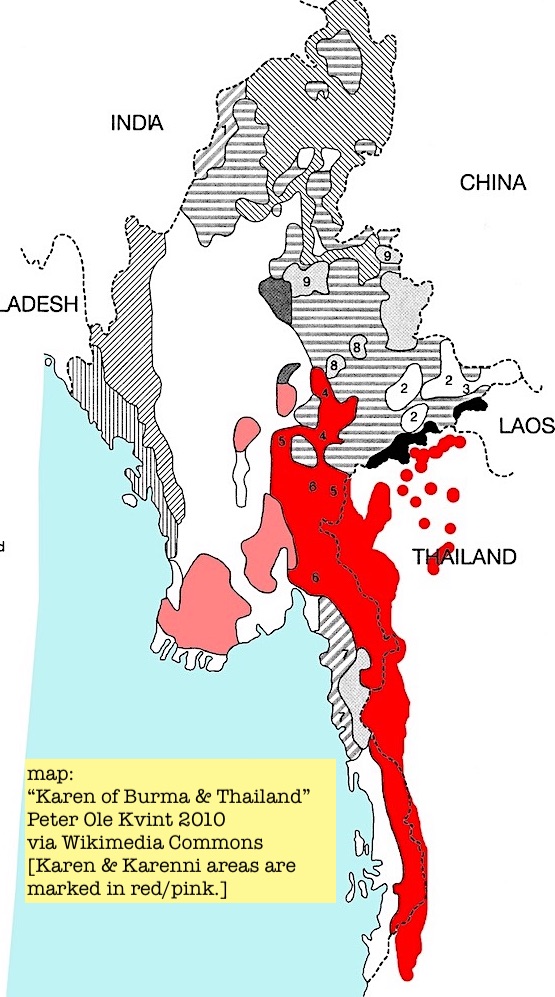
2. Arakan, now Rakhine State of Myanmar (Burma) was inhabited by Mro & Chakma people, later Rakhines & Rohingyas. Coastal & valley trading cities rose in Arakan from 3rd-4th C. By 14th C. Arakan a “vassal state” of Bengal Sultanate which spread out from Ganges–Brahmaputra Delta. 

3. 1406 Burmese (Ava) invaded Arakan’s Lemro cities, whose ruler Min Saw Mon fled to Bengal Sultanate. 1430 Bengal’s Sultan Nasir-ud-din Shah helped Min Saw Mon retake Arakan from Ava. 1512–16 Bengal Sultanate conquered Kingdom of Mrauk U (Arakan.) 

4. 16th C. Arakan navy challenged Mughal Bengal to control Chittagong port. Arakan burned Bengal’s Dhaka city. With Portuguese freebooters Arakan raided Bengal for slaves, sold many to Dutch East India Co. In 1666 Bengal, w. Dutch & Portuguese naval assistance, retook Chittagong. 

5. When Burmese conquered Arakan 1784-5, hundreds of thousands fled Arakan to Bengal (under British control from late 18th C.) Arakan/Bengal border clashes in 1824 sparked 1st Anglo-Burmese War. British defeated Burmese in Arakan, 1826 treaty ceded Arakan to British. 

6. When WW2 Japanese invaders took Arakan, Chittagong (Bengal, India) was staging area of Allies 1st, 2nd & 3rd Arakan campaigns aimed at retaking Burma. Tens of thousands civilians, mainly Rohingyas, fled WW2 Japanese invasion & interethnic violence to British-controlled Bengal. 

7. Independent after WW2, Burma retained all of Arakan, which had a “new” neighbor as India was partitioned with Pakistan created from predominantly Muslim regions, including East Bengal (which became East Pakistan 1955.) Burma & Pakistan diplomatic relations established in 1947. 

8. After centuries of population migrations & borderline drawn by British Colonial govt, related ethnic groups lived on both sides of East Bengal - Burma border, including Rakhine/Marma, Chakma/Daingnet/Thet, Khami/Khumi & Mro, as well as Rohingyas who had fled strife in Arakan. 

9. Some Rohingya leaders lobbied unsuccessfully to have northern Arakan join East Bengal (Pakistan.) Rohingyas were politically marginalized in 1950s Burma & small Mujahid rebellion broke out. Pakistan govt. denied the Mujahid support & arrested their leader in 1954. 

10. In 1971 Bangladesh (East Pakistan) fought a war to gain independence from Pakistan, succeeding after India intervened against Pakistan. Burma backed Pakistan in the conflict but recognized new nation Bangladesh in 1972. Burma dictator Gen. Ne Win visited Bangladesh ‘74. 

11. Gen. Ne Win’s Burma dictatorship oppressed many ethnic groups incl. Rakhines & Rohingyas of Arakan (Rakhine St.) 1977-8 human rights violations of Ne Win regime’s Operation Nagamin caused est. 200,000+ Rohingyas to flee to Bangladesh, which negotiated (& forced) their return. 

12. When Myanmar (Burma) junta increased troops in N. Rakhine St. 1991-92, est. 250,000 Rohingyas fled to Bangladesh camps. Bangladesh used beatings, denial of food to coerce returns. 10,000 Rohingyas entered Bangladesh 1996 fleeing forced labor, troop buildup in N. Rakhine St. 

13. Thousands of Rohingyas who fled Burma regime attacks in 1970s-90s made their way to slums of Karachi, Pakistan where they found work in fishing industry, chronically impoverished. thenational.ae/world/asia/roh…
14. During 1970s-90s some small armed groups from Burma (Myanmar) Rakhine St. including Rohingya factions as well as predominantly Rakhine Communist groups & All Burma Students' Democratic Front used border regions of Bangladesh for safe houses or training camps. 

15. 1980s-90s small armed group Rohingya Solidarity Organization reportedly had some training/support from Pakistan-based “extremist pan-Islamic groups.” Some Rohingyas, mostly from Pakistan refugee population, trained in Pakistan to fight for Taliban in Afghanistan 1990s-2001. 

16. Bangladesh/Myanmar diplomatic crisis occurred in Dec. 1991 when Myanmar SLORC regime forces of "Operation Pyi Thaya" seeking Rohingya Solidarity Organization camps crossed border & attacked a Bangladesh Rifles border security post in Bandarban, inflicting multiple casualties. 

17. When Rohingyas fled violence in 2012 Bangladesh turned away river boats, barred foreign aid groups from camps. But foreign aid was sought when Rohingyas fled genocidal attacks in 2016 (est. 65,000 to Bangladesh) & 2017 (est. 740,000+ to Bangladesh.) indianexpress.com/article/world/…
18. Bangladesh camps for Rohingyas: fenced-in fire hazards lacking education & employment + a “prison island.” Hopelessness & violence lead to dangerous boat escape attempts. Alternatives: livable “refugee cities” model or major 3rd country resettlement. archive.dhakatribune.com/opinion/op-ed/…
19. 2022-23 Bangladesh importing rice from Myanmar in trade facilitated by Myanmar coup regime. China has been promoting meetings between Bangladesh government & Myanmar coup regime to promote Rohingya repatriation despite unsafe conditions for return. irrawaddy.com/news/burma/chi…
20. Bangladesh/Myanmar border has long been smuggling route (rice, drugs etc.) Since 2017 a few thousand refugees stranded in contested border “no man’s land” particularly vulnerable to armed groups ARSA, new RSO, border forces, criminal activities, fire. forsea.co/trouble-in-no-…
21. Myanmar military have violated Bangladesh border & airspace, including during conflict w. Arakan Army. Multiple violations of Bangladesh border/airspace by Myanmar coup airforce & artillery Aug.-Sept. 2022, Bangladesh responded w. diplomatic protests. irrawaddy.com/news/burma/mya…
22. Pakistanis demonstrated against Myanmar military/govt 2017 genocidal attacks on Rohingyas. Pakistan govt. condemned the attacks but didn’t sanction Myanmar or grant rights like National Identity Cards to Pakistan’s resident Rohingya refugee population. hrw.org/news/2017/09/1…
23. Myanmar made deal for Pakistan/China JF-17 planes (malfunctioning) from Pakistan in 2016. After Feb. 2021 Myanmar coup, reported military visits betw. Pakistan & Myanmar coup regime to discuss Pakistan arms sales, w. implications of China involvement. irrawaddy.com/news/burma/mya…
24/24. Thanks @paiselface for question that inspired this thread. My new 3 part essay “A Death in Arakan” is at @MekongReview. My previous Burma History Threads & reports including new Chin State report are at: projectmaje.org 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh