🚨NEW PAPER🚨
"The potential climate impact of #SolarGeoengineering is examined in a recent study using climate model simulations by artificially reducing the incoming solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere."
#ClimateEngineering
#SolarShading
Results discussed in a🧵
1/9

"The potential climate impact of #SolarGeoengineering is examined in a recent study using climate model simulations by artificially reducing the incoming solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere."
#ClimateEngineering
#SolarShading
Results discussed in a🧵
1/9


"Climate scenario simulations reveal that a doubling of atmospheric CO2 induces a surface temperature rise which is amplified over the poles primarily during the respective winter. The warming also causes intensification & poleward shift of the global precipitation pattern."
2/9

2/9


"In the model, a 2.1% globally uniform #SolarReduction can largely compensate the global mean warming caused by a doubling of CO2."
3/9

3/9
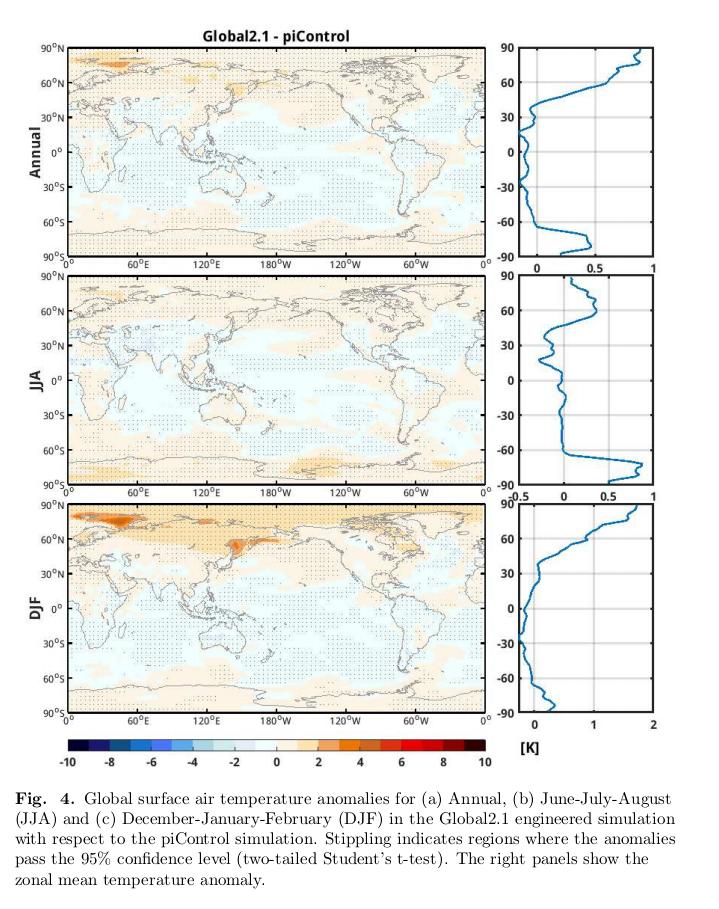

This study finds that "#SolarShading is efficient to restore the temp at the region where the background sunshine is strong, regionally at low-latitudes, seasonally during summer. A 3.6% solar reduction in the tropics can largely reduce the tropical #GlobalWarming as well."
4/9
4/9

"However, it reduces the precipitation at the central tropics, while increase the precipitation over the monsoon region."
5/9
5/9

"Comparatively, a 14% #SolarReduction over the #poles can effectively prevent the polar summer temp increase & sea-ice retreat. However, caused by the increased temp gradient, polar #SolarShading increases the storm activity at high latitudes, especially during summer."
6/9


6/9



The simulations of this study show that "#SolarShading could be an effective way to stabilize the #polar cryosphere. Nevertheless, it has a strong impact on the hydrological cycle & provides a heterogenous regional climate signal."
7/9
7/9
Read the open-access study (Preprint) entitled: The effect of global and regional solar shading onclimate: A simulation study" here ⬇️
researchsquare.com/article/rs-285…
#SolarGeoengineering
#SolarShading
#ClimateEngineering
8/9
researchsquare.com/article/rs-285…
#SolarGeoengineering
#SolarShading
#ClimateEngineering
8/9

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh