JWT is now become the de-facto standard for authenticating Modern APIs.
This guide will make it dead simple for you to understand JWT:
This guide will make it dead simple for you to understand JWT:
1. JWT stands for JSON Web Token
2. It's a token that is used to authenticate and authorize users in an application.
"authenticate" means who they're.
"authorize" means what they can access.
The token itself contains, all the necessary information about the user, like user ID and role, etc, in a JSON.
"authenticate" means who they're.
"authorize" means what they can access.
The token itself contains, all the necessary information about the user, like user ID and role, etc, in a JSON.
3. JWT tokens are typically generated by the server and sent to the client after a successful login.
The client can then use the JWT token (with each request) to authenticate and authorize itself to the server.
Typically the token looks like this:
The client can then use the JWT token (with each request) to authenticate and authorize itself to the server.
Typically the token looks like this:
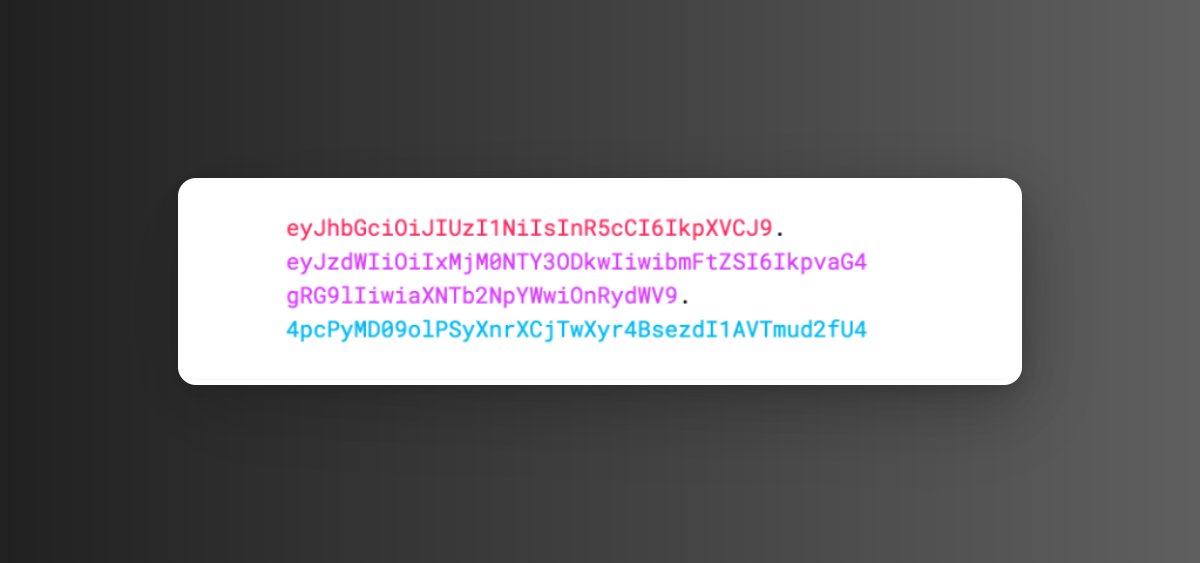
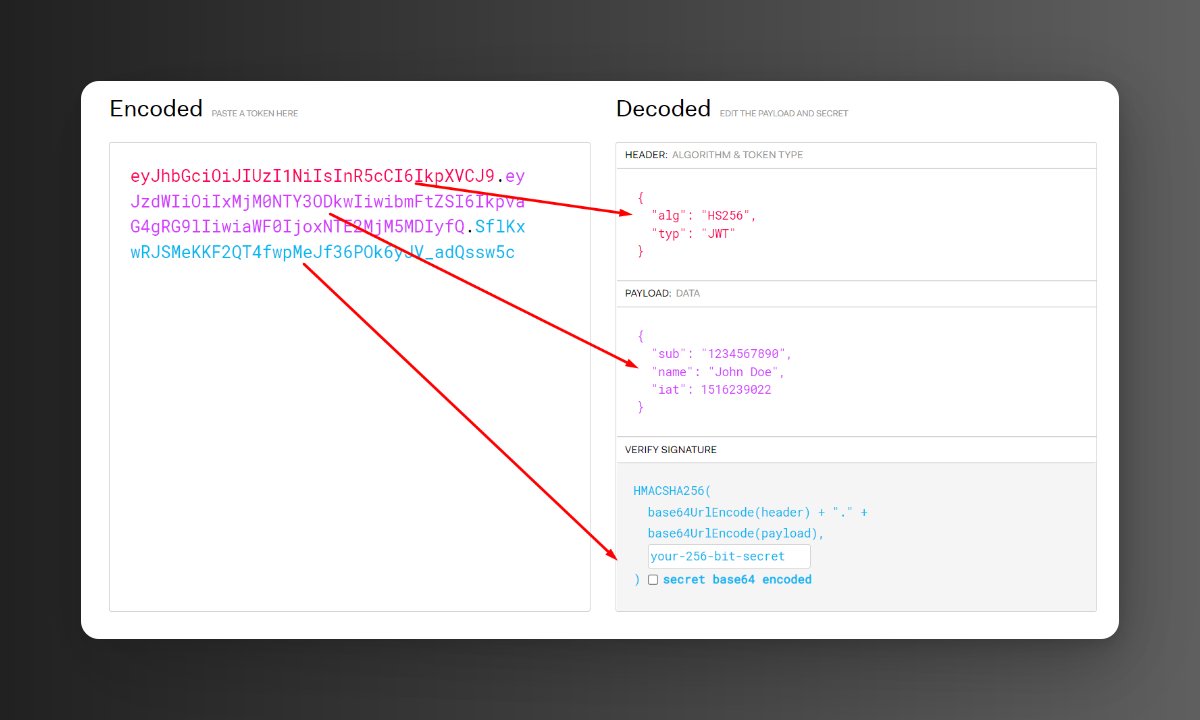
4. JWT has three parts:
a) Header (highlighted in red below)
b) Payload (highlighted in pink below)
c) Signature (highlighted in blue below)
On left you can see the encoded token, on right we can see decoded JSON object with 3 parts.
a) Header (highlighted in red below)
b) Payload (highlighted in pink below)
c) Signature (highlighted in blue below)
On left you can see the encoded token, on right we can see decoded JSON object with 3 parts.
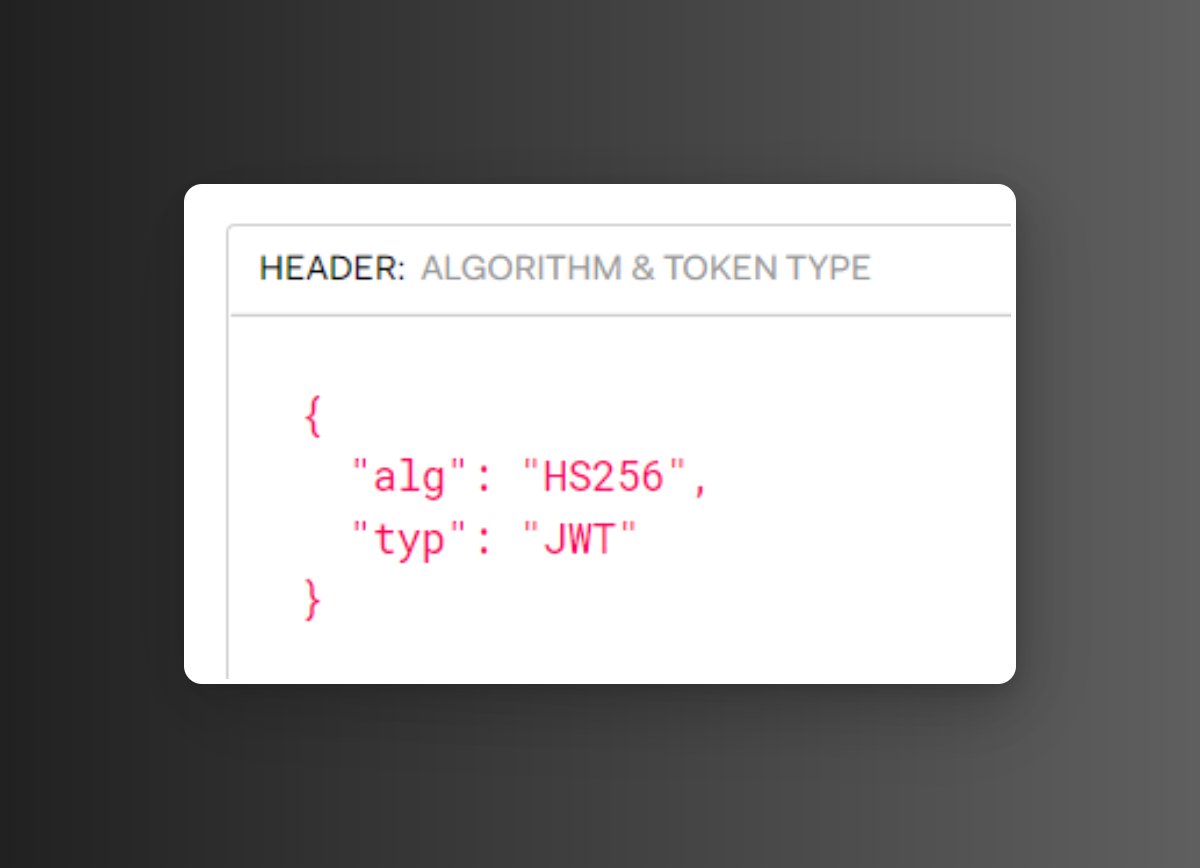
The header typically consists of two parts: the type of the token, which is usually JWT, and the signing algorithm being used, such as HMAC SHA256 or RSA. 
The payload contains the claims, which are statements about an entity (typically, the user) and additional metadata.
Claims are typically represented as key-value pairs and can include information such as the user's ID, name, email, and roles.
Claims are typically represented as key-value pairs and can include information such as the user's ID, name, email, and roles.

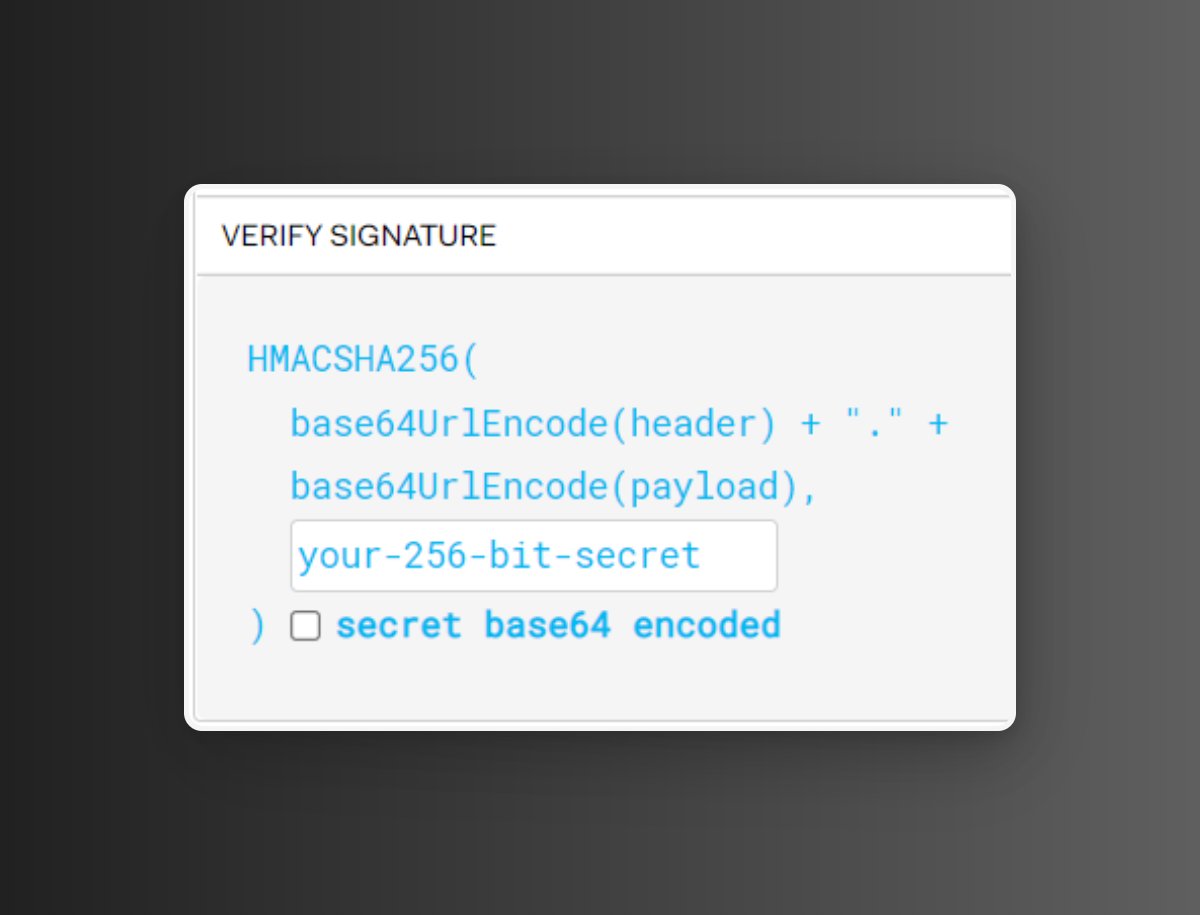
The signature is used to verify that the sender of the JWT is who it says it is and to ensure that the message has not been tampered with. 
That's a quick introduction to JWT!
Follow me @vikasrajputin for more.
If you find this thread helpful then Like/Retweet the first tweet below:
Follow me @vikasrajputin for more.
If you find this thread helpful then Like/Retweet the first tweet below:
https://twitter.com/vikasrajputin/status/1658107716202536960
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






