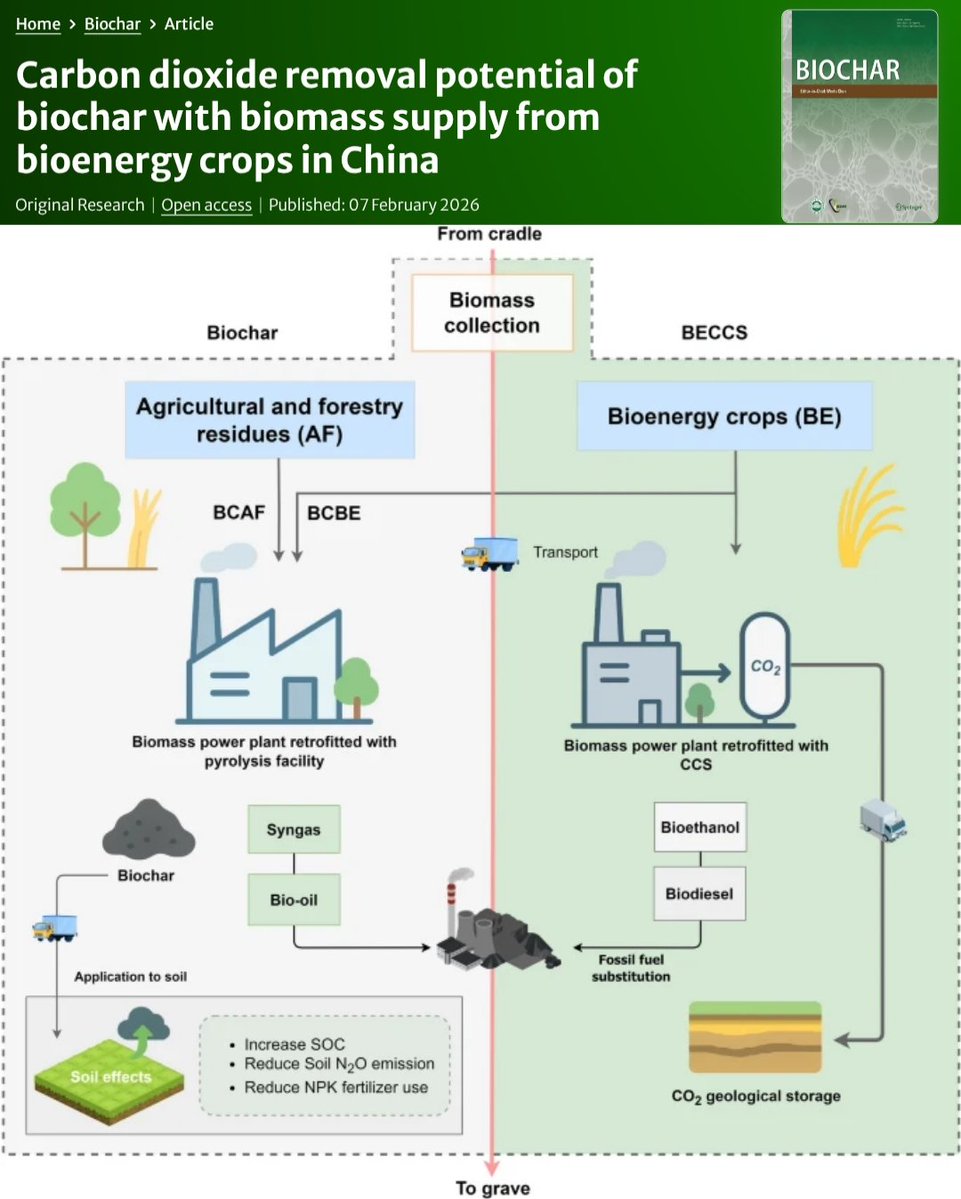
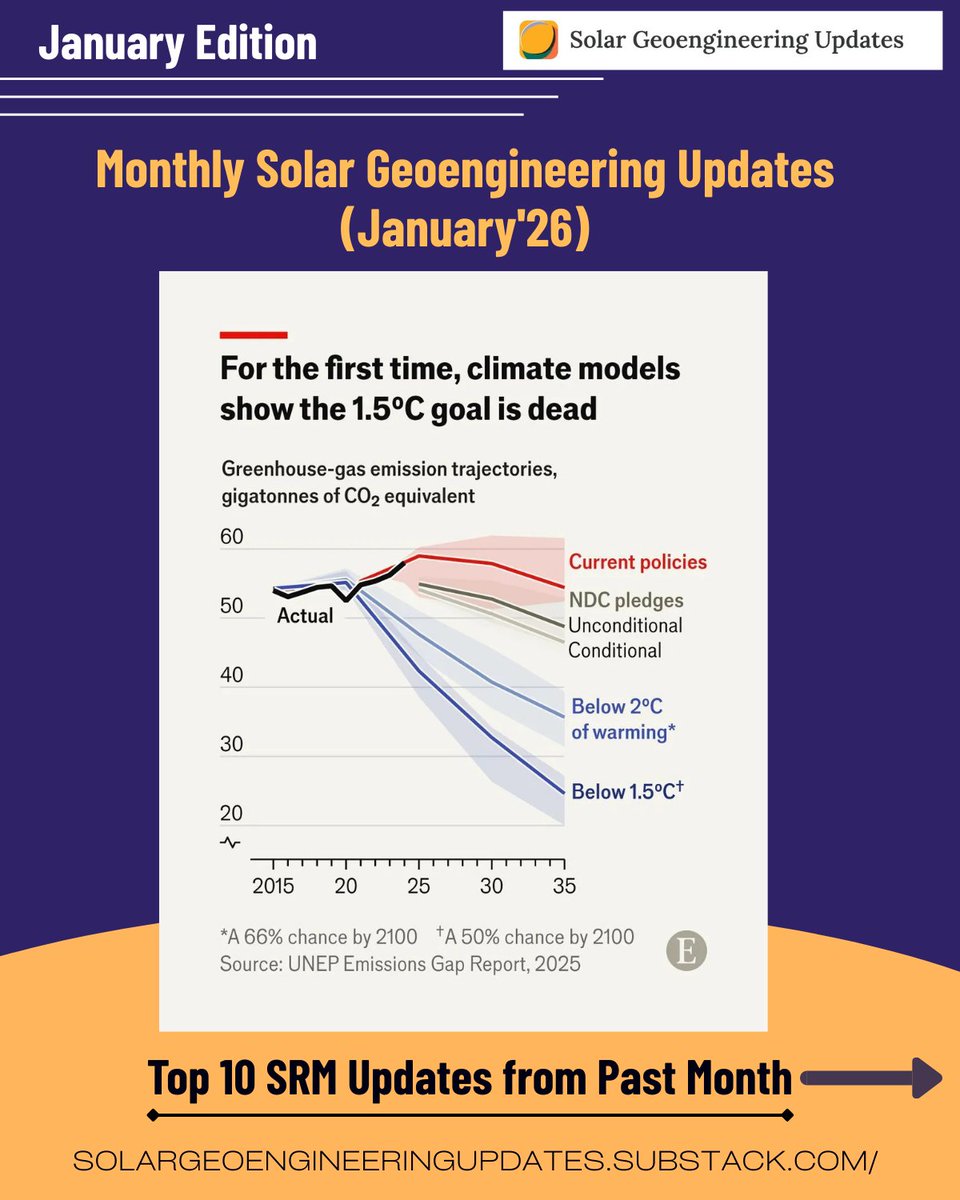
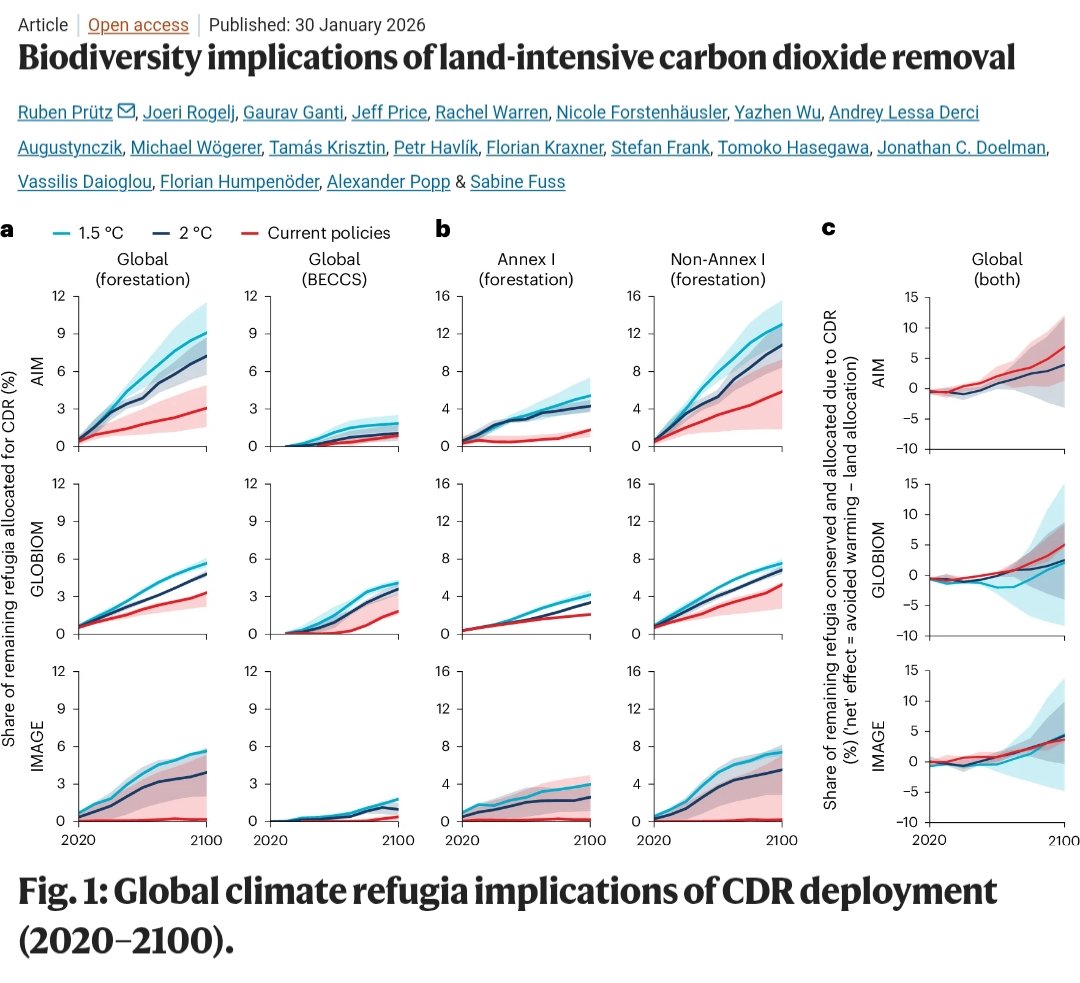
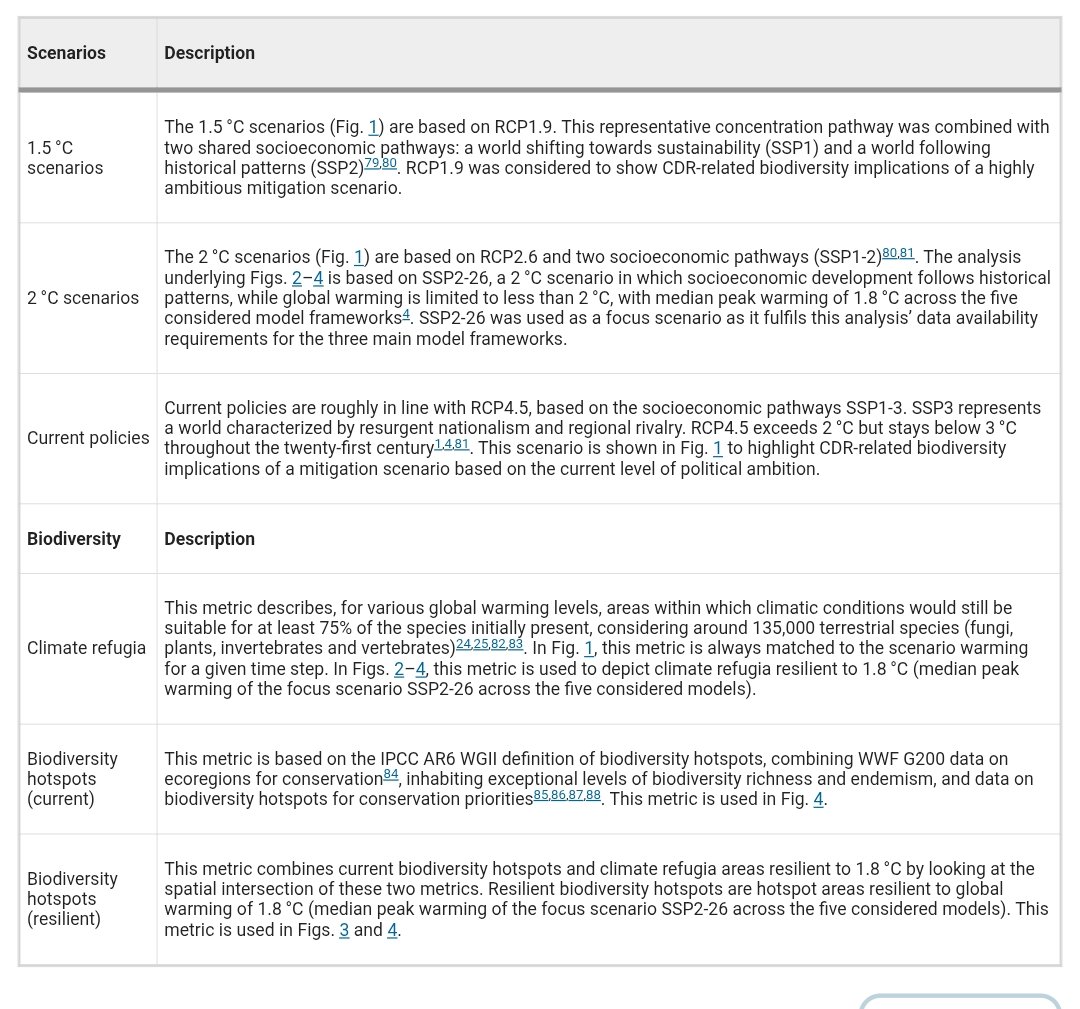
🚨UPCOMING EVENTS🚨
Sixteenth @IAMConsortium Annual Meeting
📅 November 14th-16th, 2023
📍Venice, Italy 🇮🇹- Hybrid format
📢 The IAMC solicits abstracts for oral & poster presentations on various research topics including #CarbonDioxideRemoval & #NatureBasedSolution.
🧵 1/5
Sixteenth @IAMConsortium Annual Meeting
📅 November 14th-16th, 2023
📍Venice, Italy 🇮🇹- Hybrid format
📢 The IAMC solicits abstracts for oral & poster presentations on various research topics including #CarbonDioxideRemoval & #NatureBasedSolution.
🧵 1/5

For more information, visit ⬇️
a1d0g2.emailsp.com/f/rnl.aspx/?fd…
#CarbonDioxideRemoval
#NatureBasedSolutions
5/5
a1d0g2.emailsp.com/f/rnl.aspx/?fd…
#CarbonDioxideRemoval
#NatureBasedSolutions
5/5

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh