Physicists and chalkboards!
20 iconic photographs of theoretical physicists in front of their chalkboards.
A Thread 👇 twitter.com/i/web/status/1…
20 iconic photographs of theoretical physicists in front of their chalkboards.
A Thread 👇 twitter.com/i/web/status/1…

1.
Seldon Glashow
Sheldon Glashow received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1979 along with Abdus Salam and Steven Weinberg for their complementary efforts in formulating the electroweak theory, which explains the unity of electromagnetism and the weak force.
Seldon Glashow
Sheldon Glashow received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1979 along with Abdus Salam and Steven Weinberg for their complementary efforts in formulating the electroweak theory, which explains the unity of electromagnetism and the weak force.

2.
Paul Dirac
One of the pioneers of modern quantum theory and 1933 Nobel Prize Winner (with Erwin Schrödinger), Paul Dirac is considered to be one of the greatest physicists of the 20th century. His equation pre
Paul Dirac
One of the pioneers of modern quantum theory and 1933 Nobel Prize Winner (with Erwin Schrödinger), Paul Dirac is considered to be one of the greatest physicists of the 20th century. His equation pre

3.
Richard Feynman
Considered to be one of the greatest explainers of all time, Feynman shared the 1965 Nobel Prize in Physics along with Sin-Itiro Tomonaga and Julian Schwinger for their works in Quantum electrodynamics.
Richard Feynman
Considered to be one of the greatest explainers of all time, Feynman shared the 1965 Nobel Prize in Physics along with Sin-Itiro Tomonaga and Julian Schwinger for their works in Quantum electrodynamics.

4.
Murray Gell-Mann
Gell-Mann (1929 - 2019), one of the founding fathers of elementary particle physics, won the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physics for this contributions to the development of the theory of quarks.
Murray Gell-Mann
Gell-Mann (1929 - 2019), one of the founding fathers of elementary particle physics, won the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physics for this contributions to the development of the theory of quarks.

5.
John Bardeen
He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Brattain for the invention of the transistor; and again in 1972 with Leon N Cooper and John Robert Schrieffer for conventional superconductivity.
John Bardeen
He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Brattain for the invention of the transistor; and again in 1972 with Leon N Cooper and John Robert Schrieffer for conventional superconductivity.
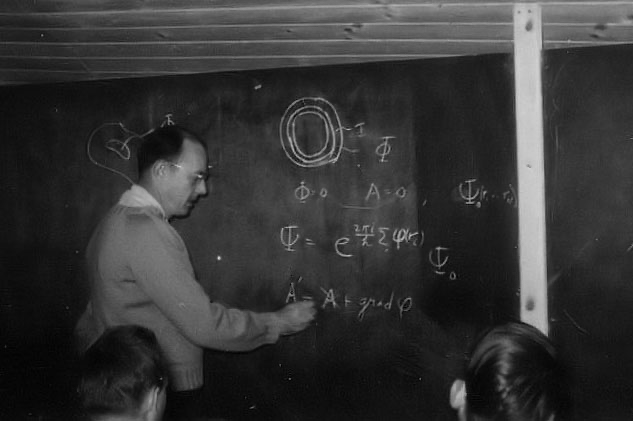
6.
John Bell
John Bell investigated quantum theory in the greatest depth and established what the theory can tell us about the fundamental nature of the physical world.
John Bell
John Bell investigated quantum theory in the greatest depth and established what the theory can tell us about the fundamental nature of the physical world.

7.
Lise Meitner
Lise Meitner, pioneering female physicist and unsung hero of the 20th century. Co-discovered nuclear fission, yet overlooked for the Nobel. A testament to resilience and the power of the human mind.
Lise Meitner
Lise Meitner, pioneering female physicist and unsung hero of the 20th century. Co-discovered nuclear fission, yet overlooked for the Nobel. A testament to resilience and the power of the human mind.

8.
Kip Thorne
2017 Nobel laureate Kip Thorne is a theoretical physicist, known for his contributions in gravitational physics and astrophysics. He was the Feynman Professor of Theoretical Physics at the CalTech until 2009.
Kip Thorne
2017 Nobel laureate Kip Thorne is a theoretical physicist, known for his contributions in gravitational physics and astrophysics. He was the Feynman Professor of Theoretical Physics at the CalTech until 2009.

9.
Albert Einstein
Cited as one of the most influential scientists of the 20th century, A. Einstein (1879 - 1955) developed the theories of general and special relativity, and the photoelectric phenomena (that won him the 1921 Nobel Prize).
Albert Einstein
Cited as one of the most influential scientists of the 20th century, A. Einstein (1879 - 1955) developed the theories of general and special relativity, and the photoelectric phenomena (that won him the 1921 Nobel Prize).
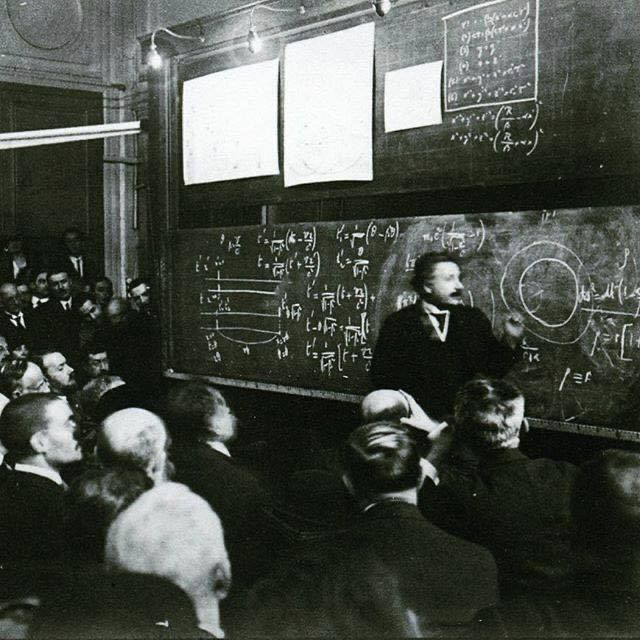

10.
Marie Skłodowska-Curie
A Pioneer in radioactivity research, discovered two elements - Polonium (Z=84) and Radium (Z=88). First woman to win a Nobel, and only person awarded in two different scientific fields (Physics 1903, Chemistry 1911). A legacy of innovation.
Marie Skłodowska-Curie
A Pioneer in radioactivity research, discovered two elements - Polonium (Z=84) and Radium (Z=88). First woman to win a Nobel, and only person awarded in two different scientific fields (Physics 1903, Chemistry 1911). A legacy of innovation.

11.
John Wheeler
Wheeler worked with Niels Bohr in explaining the basic principles behind nuclear fission. He is best known for coining the terms "black hole", "quantum foam", "neutron moderator", "wormhole" and "it from bit", and for hypothesizing the "one-electron universe".
John Wheeler
Wheeler worked with Niels Bohr in explaining the basic principles behind nuclear fission. He is best known for coining the terms "black hole", "quantum foam", "neutron moderator", "wormhole" and "it from bit", and for hypothesizing the "one-electron universe".
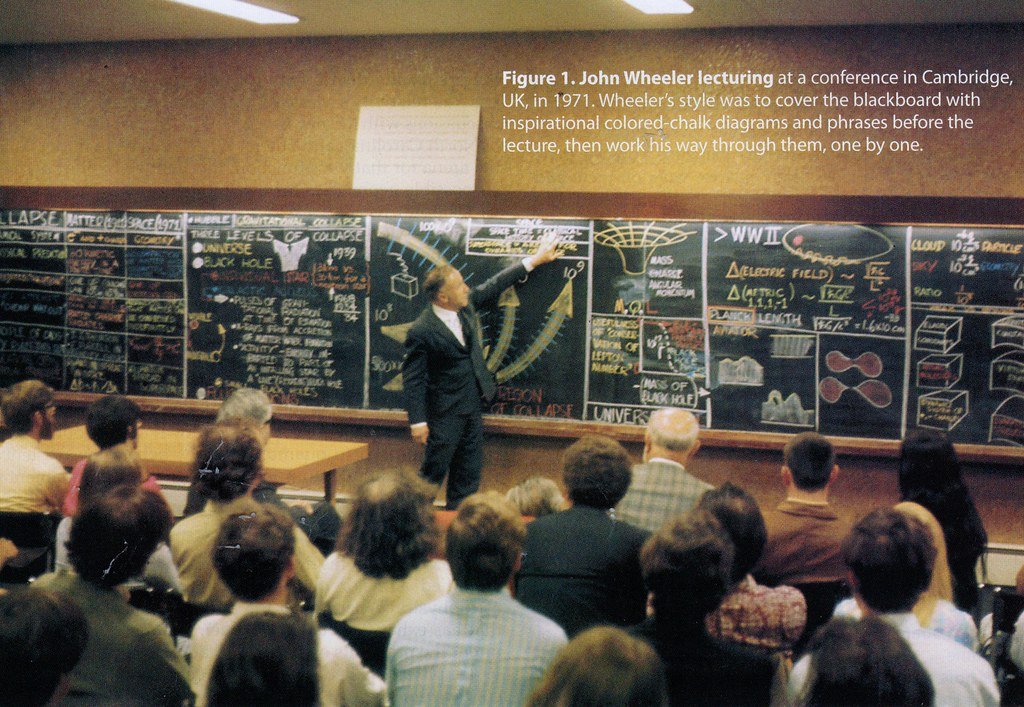

12.
Niels Bohr
One of the pioneers of modern Quantum theory and the atomic structure, Niels Bohr won the 1922 Nobel prize in physics .Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research.
Niels Bohr
One of the pioneers of modern Quantum theory and the atomic structure, Niels Bohr won the 1922 Nobel prize in physics .Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research.

13.
Werner Heisenberg
Heisenberg is best known for his uncertainty principle and theory of quantum mechanics, which he published at the age of twenty-three in 1925. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1932 for his subsequent research and application of this principle.
Werner Heisenberg
Heisenberg is best known for his uncertainty principle and theory of quantum mechanics, which he published at the age of twenty-three in 1925. He was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1932 for his subsequent research and application of this principle.

14.
Abdus Salam
Abdus Salam was the first Pakistani and the first from an Islamic country to receive a Nobel Prize in science and the second from an Islamic country to receive any Nobel Prize.
Abdus Salam
Abdus Salam was the first Pakistani and the first from an Islamic country to receive a Nobel Prize in science and the second from an Islamic country to receive any Nobel Prize.

15.
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Pauli, theoretical physicist and recipient of the 1945 Nobel Prize for Physics for his discovery in 1925 of the "Pauli exclusion principle", which states that in an atom no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously.
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Pauli, theoretical physicist and recipient of the 1945 Nobel Prize for Physics for his discovery in 1925 of the "Pauli exclusion principle", which states that in an atom no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously.

16.
Stephen Hawking
Stephen Hawking was a scientist known for his work with black holes and relativity, and the author of popular science books like 'A Brief History of Time.'
Stephen Hawking
Stephen Hawking was a scientist known for his work with black holes and relativity, and the author of popular science books like 'A Brief History of Time.'

17.
Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Schrödinger, theoretical physicist who contributed to the wave theory of matter and to other fundamentals of quantum mechanics. He shared the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics with British physicist P.A.M. Dirac.
Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Schrödinger, theoretical physicist who contributed to the wave theory of matter and to other fundamentals of quantum mechanics. He shared the 1933 Nobel Prize for Physics with British physicist P.A.M. Dirac.

18.
Steven Weinberg
Steven Weinberg (1933 - 2021) played a significant role in formulating and establishing theoretical physics’ two standard models - the standard model of fundamental interactions and the standard model of cosmology.
Steven Weinberg
Steven Weinberg (1933 - 2021) played a significant role in formulating and establishing theoretical physics’ two standard models - the standard model of fundamental interactions and the standard model of cosmology.

19.
C.V. Raman
He was the first Asian to receive a Nobel prize in science, following the discovery of a light scattering effect called "Rama effect" that has since become a key characterization tool in materials science.
C.V. Raman
He was the first Asian to receive a Nobel prize in science, following the discovery of a light scattering effect called "Rama effect" that has since become a key characterization tool in materials science.

20.
J. Robert Oppenheimer
J. Robert Oppenheimer is often called the "father of the atomic bomb" for leading the Manhattan Project, the program that developed the first nuclear weapon during World War II.
J. Robert Oppenheimer
J. Robert Oppenheimer is often called the "father of the atomic bomb" for leading the Manhattan Project, the program that developed the first nuclear weapon during World War II.

Download the interactive Cosmic Quartet Printable Physics Posters 👇
• Black Hole Brilliance
• Wormhole Wanderlust
• Quantum Connection and
• Dark Matter Mystery
physicshistory.gumroad.com/l/sciposters
• Black Hole Brilliance
• Wormhole Wanderlust
• Quantum Connection and
• Dark Matter Mystery
physicshistory.gumroad.com/l/sciposters

We hope you enjoyed this journey through the charismatic beauty of chalkboards and the titans of theoretical and experimental physics.
You can check out our other threads on Physics 👇
You can check out our other threads on Physics 👇
https://twitter.com/physinhistory/status/1651584611544186881?s=46&t=vMsjMEZP_cYdwWGGJlOKyw
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter
















