Twitter has enforced very strict rate limiting. Some people cannot even see their own tweets.
Rate limiting is a very important yet often overlooked topic. Let's use this opportunity to take a look at what it is and the most popular algorithms.
A thread.
#RateLimitExceeded
Rate limiting is a very important yet often overlooked topic. Let's use this opportunity to take a look at what it is and the most popular algorithms.
A thread.
#RateLimitExceeded

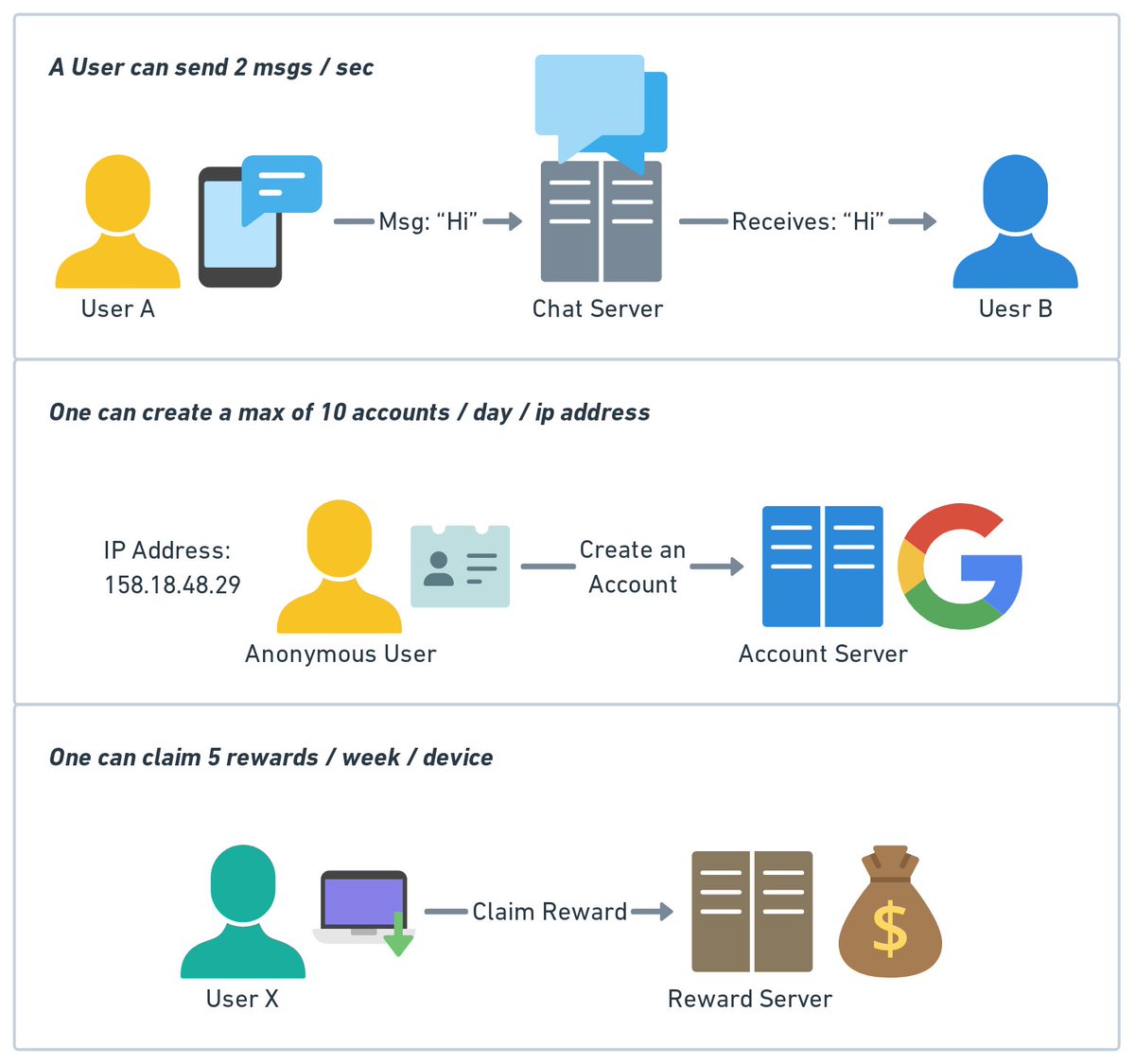
What is rate limiting? Rate limiting controls the rate at which users or services can access a resource. Here are some examples:
- A user can send a message no more than 2 per second
- One can create a maximum of 10 accounts per day from the same IP address
- A user can send a message no more than 2 per second
- One can create a maximum of 10 accounts per day from the same IP address
Fixed Window Counter
The algorithm divides the timeline into fixed-size time windows and assigns a counter for each window. Each request increments the counter by some value. Once the counter reaches the threshold, subsequent requests are blocked until the new time window begins
The algorithm divides the timeline into fixed-size time windows and assigns a counter for each window. Each request increments the counter by some value. Once the counter reaches the threshold, subsequent requests are blocked until the new time window begins

Sliding Window Log
The Sliding Window Log algorithm fixes the issue with the Fixed Window Counter algorithm where it allows more requests to slip through at the edges of a time window.
The Sliding Window Log algorithm fixes the issue with the Fixed Window Counter algorithm where it allows more requests to slip through at the edges of a time window.

Sliding Window Counter
The Sliding Window Counter algorithm is a more efficient variation of the Sliding Window Log algorithm. It is a hybrid that combines the fixed window counter and sliding window log.
The Sliding Window Counter algorithm is a more efficient variation of the Sliding Window Log algorithm. It is a hybrid that combines the fixed window counter and sliding window log.

Token Bucket
The Token Bucket algorithm is widely used for rate limiting. It is simple, well understood and commonly used by large tech companies. Both Amazon and Stripe use this algorithm to throttle their API requests.
The Token Bucket algorithm is widely used for rate limiting. It is simple, well understood and commonly used by large tech companies. Both Amazon and Stripe use this algorithm to throttle their API requests.

Leaky Bucket
The algorithm uses a "bucket" metaphor but processes requests differently. Requests enter the bucket and are processed at a fixed rate, simulating a "leak" in the bucket. If the bucket becomes full, new requests are discarded until there is space available.
The algorithm uses a "bucket" metaphor but processes requests differently. Requests enter the bucket and are processed at a fixed rate, simulating a "leak" in the bucket. If the bucket becomes full, new requests are discarded until there is space available.

Reference: blog.bytebytego.com/p/rate-limitin…
I hope you've found this thread helpful.
Follow me @alexxubyte for more.
Like/Retweet the first tweet below if you can:
Follow me @alexxubyte for more.
Like/Retweet the first tweet below if you can:
https://twitter.com/alexxubyte/status/1675291451394232320
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh