1/ 🛠️ 🛠️ #Avalanche Cortina 8 is out: 🛠️ 🛠️
This is the last release in a series of database migrations. It is optional but recommended.
🔍 Release Focus: P-Chain Pruning/Indexing + Primary Network Partial Sync + Subnet Validator Diff Regression Fix https://t.co/bUw5r0urpCgithub.com/ava-labs/avala…


This is the last release in a series of database migrations. It is optional but recommended.
🔍 Release Focus: P-Chain Pruning/Indexing + Primary Network Partial Sync + Subnet Validator Diff Regression Fix https://t.co/bUw5r0urpCgithub.com/ava-labs/avala…

2/ ✅ Compatibility Check: VM Interface (v27) ✅
Cortina 8 does NOT modify the VM interface. If you are running a Custom VM on v1.10.5-v1.10.7, it will work with v1.10.8.
Cortina 8 does NOT modify the VM interface. If you are running a Custom VM on v1.10.5-v1.10.7, it will work with v1.10.8.
3/ 🚧 ATTENTION OPERATORS 🚧
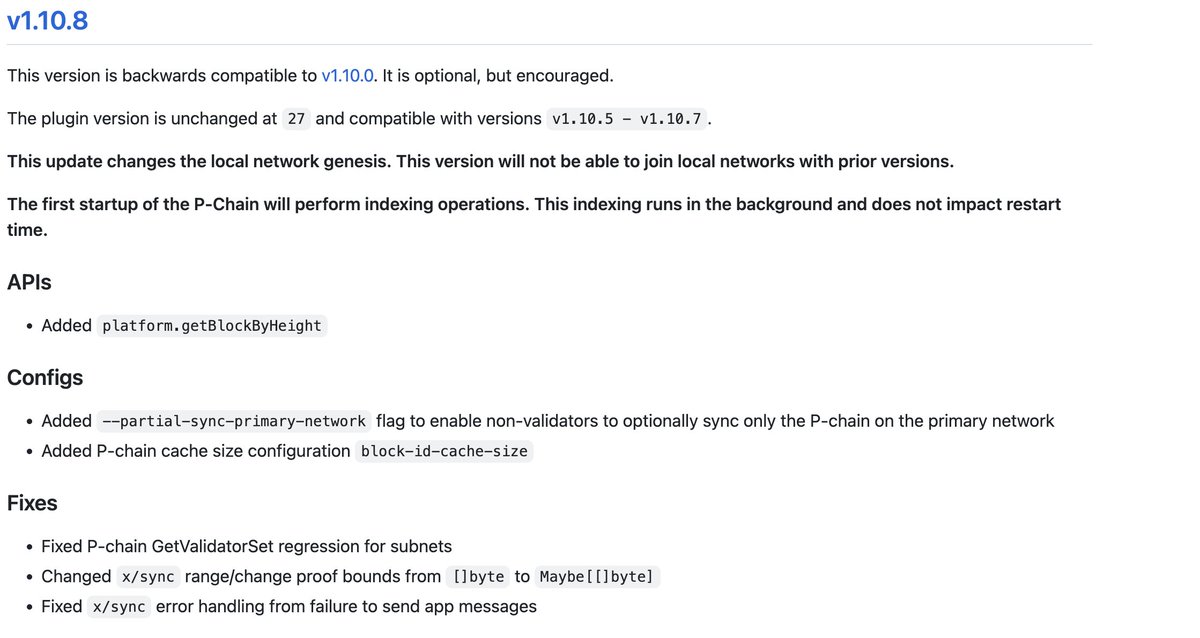
AvalancheGo@v1.10.8 prunes unused P-Chain block data when starting up for the first time (in the background).
You will see elevated disk/CPU/memory usage for the first ~10 hours after upgrading. **This is expected.**
AvalancheGo@v1.10.8 prunes unused P-Chain block data when starting up for the first time (in the background).
You will see elevated disk/CPU/memory usage for the first ~10 hours after upgrading. **This is expected.**
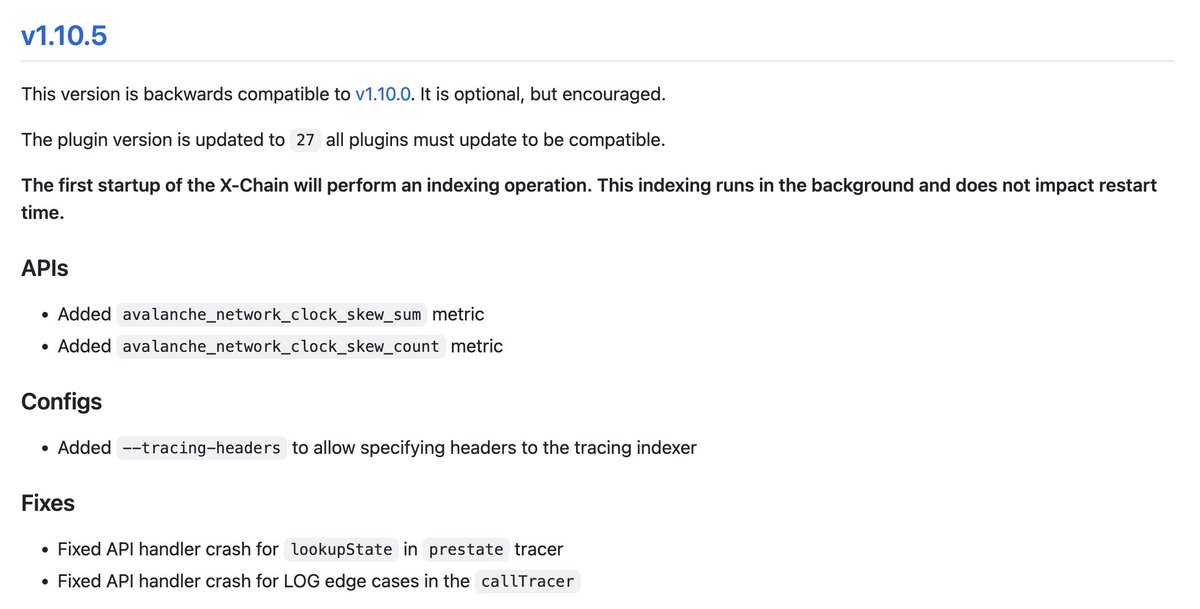
4/ P-Chain Height Pruning/Indexing
Cortina 8 deletes rejected blocks from disk (we stopped writing them a few releases ago) and reformats the disk format of accepted blocks to be more minimal. Additionally, this release indexes blockIDs by height.
github.com/ava-labs/avala…
Cortina 8 deletes rejected blocks from disk (we stopped writing them a few releases ago) and reformats the disk format of accepted blocks to be more minimal. Additionally, this release indexes blockIDs by height.
github.com/ava-labs/avala…
5/ P-Chain Height Pruning/Indexing (continued)
With this release, all chains on the Primary Network are now height indexed. This unblocks the rollout of concurrent block fetching during bootstrapping (which should dramatically reduce the time it takes to sync a new node).
With this release, all chains on the Primary Network are now height indexed. This unblocks the rollout of concurrent block fetching during bootstrapping (which should dramatically reduce the time it takes to sync a new node).
6/ Primary Network Partial Sync
One of the most common feature requests we've heard is to reduce the overhead of running an #Avalanche Subnet.
Cortina 8 introduces a new sync mode that allows **Subnet API** nodes to ONLY INDEX THE P-CHAIN (no X/C).
github.com/ava-labs/avala…
One of the most common feature requests we've heard is to reduce the overhead of running an #Avalanche Subnet.
Cortina 8 introduces a new sync mode that allows **Subnet API** nodes to ONLY INDEX THE P-CHAIN (no X/C).
github.com/ava-labs/avala…
7/ Primary Network Partial Sync (continued)
The mode can reduce Primary Network overhead (CPU/Disk) by 80%+ for node operators that only support Subnet APIs without disabling the ability to verify AWM messages.
The mode can reduce Primary Network overhead (CPU/Disk) by 80%+ for node operators that only support Subnet APIs without disabling the ability to verify AWM messages.
8/ PNPS (continued pt. 2)
WARNING: This mode makes it impossible to verify the integrity of P-Chain Atomic Imports (which require validating Atomic Exports on X/C).
You will rely on the consensus of the Primary Network alone to determine tx validity in this mode.
WARNING: This mode makes it impossible to verify the integrity of P-Chain Atomic Imports (which require validating Atomic Exports on X/C).
You will rely on the consensus of the Primary Network alone to determine tx validity in this mode.
9/ Subnet Validator Diff Regression Fix
Cortina 7 introduced a regression in validator diff calculation on nodes running Subnets (can cause sputtery block production and temporary instability after a validator unstakes). Cortina 8 fixes this.
github.com/ava-labs/avala…
Cortina 7 introduced a regression in validator diff calculation on nodes running Subnets (can cause sputtery block production and temporary instability after a validator unstakes). Cortina 8 fixes this.
github.com/ava-labs/avala…
10/ Validator Diff Regression
All Subnet operators running v1.10.7 should update to v1.10.8 to avoid any inconvenience due to this regression.
Shoutout to the @dexalot team for helping to debug this issue. 🙏
All Subnet operators running v1.10.7 should update to v1.10.8 to avoid any inconvenience due to this regression.
Shoutout to the @dexalot team for helping to debug this issue. 🙏
11/ As always, if you are looking for a job in crypto, check out my mega thread covering all the roles we are hiring for at @avalabsofficial 👀 👀 👀:
https://twitter.com/_patrickogrady/status/1613608950896947200
12/ You can read the unrolled version of this thread here: typefully.com/_patrickogrady…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter