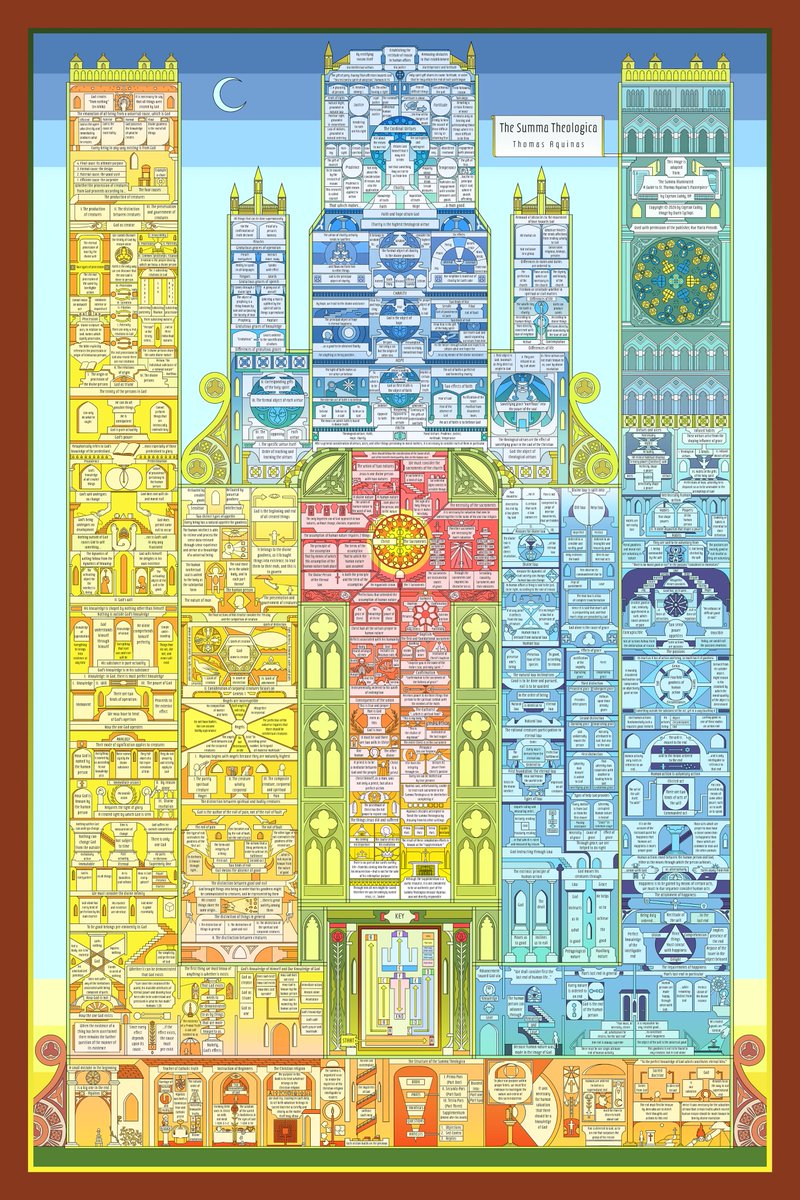
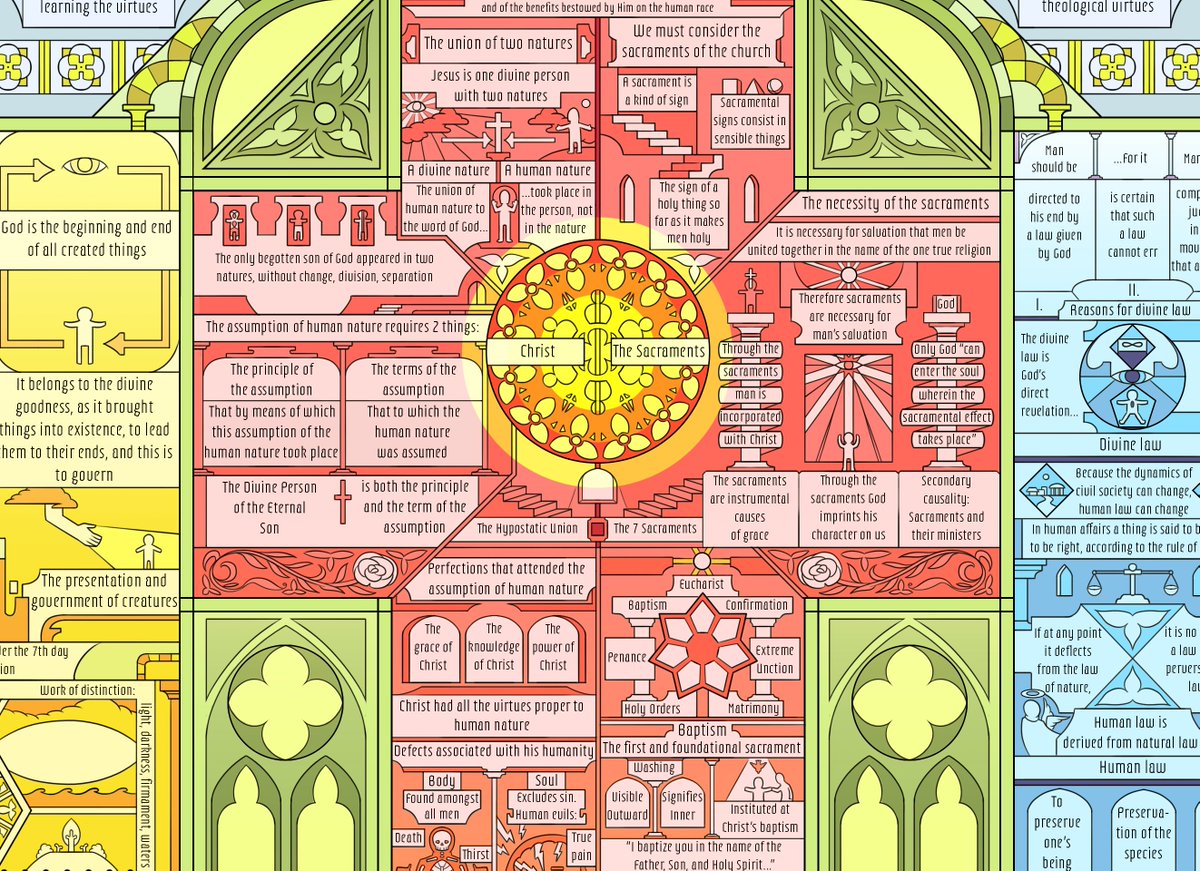
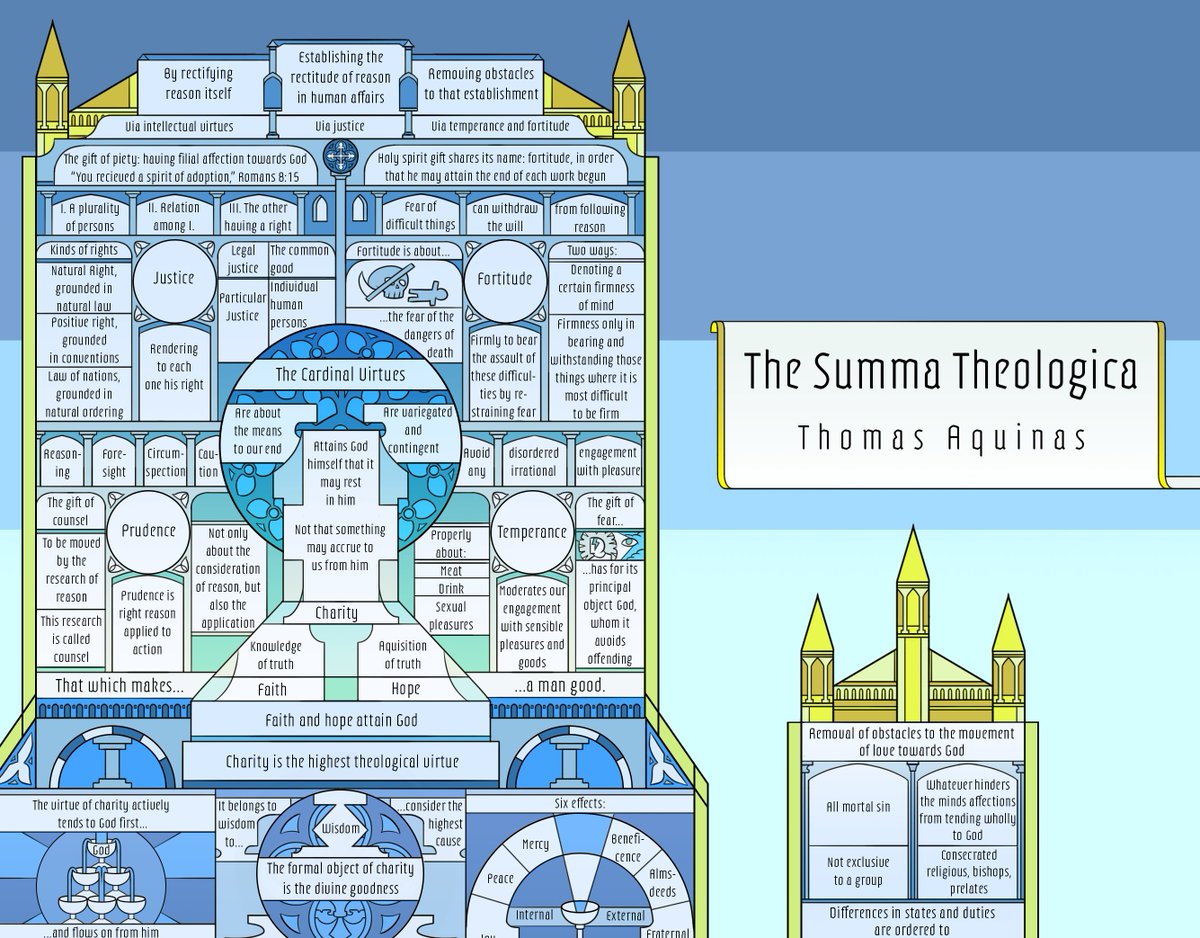
sometimes it feels like there are like 100 people on earth that know the material reality of why the salem witch trials happened
so many myths. was not based on the testimony of children. many people confessed themselves to being witches. i have their letters in books upstairs
so many myths. was not based on the testimony of children. many people confessed themselves to being witches. i have their letters in books upstairs
https://twitter.com/tonyclimate/status/1700523012834082917
people write entire books about the salem witch trials without explaining why someone would point blank tell people they were a witch traveling to black sabbaths and hanging with demons
men confessed to being werewolves. they literally were like “i am actually a werewolf”.
men confessed to being werewolves. they literally were like “i am actually a werewolf”.
reflection: many cultures have some form of what we call shamanism wherein people use psychoactive plants to interact with spirits and do what they call magic, and such things
question: what was this in western culture?
the answer when i return from reading a book to a tiny man
question: what was this in western culture?
the answer when i return from reading a book to a tiny man
https://twitter.com/mogtheurbanite/status/1700672647980351813
alright sorry to keep the crew waiting. it was requested that i read this text. fitting, as it also takes place in new england.
anyway […]
anyway […]

to keep it brief, consider that the conventional narrative of the salem witch trials fits very well into modern narratives: religion bad, people in the past are stupid, large groups of people are often prone to total hysteria - its very easy to accept and fits in perfectly.
to answer the above question, a missing piece of most people’s understanding of western cultural archetypes, in my opinion, is that western culture has an indigenous form of shamanism. its embodied in the witch. the witch is basically the shaman of europe, if you think about it.
if “witch” were a gender neutral term, this would be more obvious. but its not, so, in my opinion, this is rarely fully realized. theres a lot we could go into there but lets keep it moving
many parts of that archetype such as potions, charms, etc., have a real historical aspect
many parts of that archetype such as potions, charms, etc., have a real historical aspect
that real historical aspect, and this whole tale, dovetails with what psychoactive substances were available to people in europe, and later, colonial america.
last piece of hard info is between two classes of drugs: psychedelics and deliriants / dissociatives.
last piece of hard info is between two classes of drugs: psychedelics and deliriants / dissociatives.
not looking up which D term im thinking of, sorry. those days are behind me.
the relevant distinction here is that on psychedelics you almost always know youre on drugs.
on deliriants, you do not. thats a big difference for ethnographic study purposes. example:
the relevant distinction here is that on psychedelics you almost always know youre on drugs.
on deliriants, you do not. thats a big difference for ethnographic study purposes. example:
someone takes mushrooms. they see their blanket patterns moving. 99% of the time, they are aware that this is a hallucination.
on a deliriant, if you are in your closet hallucinating that you are at 7/11, you actually think you are at 7/11.
okay. so, whats the point.
on a deliriant, if you are in your closet hallucinating that you are at 7/11, you actually think you are at 7/11.
okay. so, whats the point.
the point is that deliriants, what i would call solanaceous plants like… datura, henbane, belladonna… etc., were available to there people (western culture) (wypipo) (and beyond but, we’re not talking about that)
so, thats the missing piece. people were using those plants
but
so, thats the missing piece. people were using those plants
but
it goes beyond that, because apparently (how you explain that apparently is going to depend on your metaphysics), the experience isnt random. it has certain patterns and archetypes, such as: flying, shadow people, going to dark “events”, basically all the “witch stuff”.
so, people were making ointments out of these plants and using them and hallucinating that they were doing witch stuff (flying around, meeting demons, etc). however, the crucial distinction is that they were not aware that this was a drug experience. they didnt know that.
from their point of view, they’d put the ointment on in a barn, then fly out of the barn, and go on a journey.
in “real life” they would just pass out on the floor of the barn.
thats why they told people they were witches doing that stuff. they actually thought that they were.
in “real life” they would just pass out on the floor of the barn.
thats why they told people they were witches doing that stuff. they actually thought that they were.
this is documented in a book called ‘hallucinogens and shamanism’ by michael harner, which is mostly about ayahuasca, but has one chapter on… this (in the middle).
lets look at some primary sources
lets look at some primary sources

lady alice kyteler in 1324 also describes an ointment. we’ll get to some more solid examples, but you can see its at least very old
in case you cant understand, this is saying she sat on a staff - like you see witches sitting on a broom. they sat on objects like that:
in case you cant understand, this is saying she sat on a staff - like you see witches sitting on a broom. they sat on objects like that:

sitting on a staff (or broom, or rod) with your feet off the ground confers a feeling of levity and weightlessness, which facilitates the (drug) experience (ie you feel like youre flying or riding something).
theres also another non PG-13 reason. ointment, absorbed quickly… k.
theres also another non PG-13 reason. ointment, absorbed quickly… k.
alright lets just cut to the chase. theres a lot of examples of the staff or them sitting in baskets or things like that.
this guy in the 1690s just lays it out.
lets note that this is a firsthand account that does not fit any conventional understanding of this phenomenon:
this guy in the 1690s just lays it out.
lets note that this is a firsthand account that does not fit any conventional understanding of this phenomenon:
this woman tells the priest she is a witch and travels at night. she isnt tortured or falsely accused and sets out to prove it to the priest, who watches her attempt to do it:




if you only read one read this one.
in 1545, the physician to pope julius the third describes the ointment and its effects after a couple was arrested for witchcraft
(very notable ending)
in 1545, the physician to pope julius the third describes the ointment and its effects after a couple was arrested for witchcraft
(very notable ending)

okay this is already kind of long so i will extremely briefly explicate the material reality of lycanthropy, which is the proper term for werewolfism.
for a variety of reasons, you can speculate, the effects can be different for men and women and tend to cluster on either end.
for a variety of reasons, you can speculate, the effects can be different for men and women and tend to cluster on either end.
although men had the “witch experience” (flying, black sabbath), more often men had the experience of transforming into animals like wolves
aside from humor thats part of why i selected a few with sex above. kind of makes sense men would have a more violent type of hallucination
aside from humor thats part of why i selected a few with sex above. kind of makes sense men would have a more violent type of hallucination
1634
what is not explicated here is “the girdle”. as women would do things to heighten the sensation of flying, men would wear animal pelts in places where their limbs touched their torso (or places like that) so theyd feel the fur while moving and facilitate the hallucination:
what is not explicated here is “the girdle”. as women would do things to heighten the sensation of flying, men would wear animal pelts in places where their limbs touched their torso (or places like that) so theyd feel the fur while moving and facilitate the hallucination:

as promised above here is an example (1602) of a man imprisoned who professes to actually have the ability to become a wolf but says he cant do it without the ointment: 

last note, in 1521 a guy in france confessed to the church (like in a court) that he actually killed and ate people while he was a wolf (oops) 

as you never know who is reading what you write online, i will say two things. a) obviously i would say it is very logical to assume that there is some metaphysical or spiritual aspect at play here, whether they are “pure hallucinations”, or not, or some middle ground.
b) i suppose its relevant, i have personally seen and handled ointments that are like these or that are recreations of these.
the plants described here are actually super dangerous - like, if you cut yourself while on them, you wont know you cut yourself. its at “that level” so, there is no safe way to use them in any way. they kill people. just thought id mention that.
the plants described here are actually super dangerous - like, if you cut yourself while on them, you wont know you cut yourself. its at “that level” so, there is no safe way to use them in any way. they kill people. just thought id mention that.
threads like this often leave my usual orbit (thanks), so if we have not met, i often deal with atypical american / christian religion topics. here is: my dog and calvinism, or another new england file (thread below)
im also releasing a book late november / early december
📕


im also releasing a book late november / early december
📕
https://twitter.com/owenbroadcast/status/1673370236622454784


im going to tether one more new england esoterica thread here. this ones way shorter:
being God in massachusetts:
being God in massachusetts:
https://twitter.com/owenbroadcast/status/1699421618815082658
@DanielSWise someone robs a bank. if you explain why they did that, its interpreted as you defending them. people have careers - and people that dedicate their lives to studying things like witchcraft or psychedelics academically are already predisposed to being sympathetic to those things.
@DanielSWise theres nothing wrong with that in and of itself, i guess, but flip it onto yourself. discard all the accounts i posted as pure fabrications. why the consistent specific details combined with specific plants that actually induce these types of hallucinations?
@DanielSWise because people actually were using the plants in that way. thats the only explanation.
so then youd have to say that the existence of all that played no role in the historical situation. also implausible. thats all im asserting: theres a material reality people are ignorant of.
so then youd have to say that the existence of all that played no role in the historical situation. also implausible. thats all im asserting: theres a material reality people are ignorant of.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh