20 Linux administration tips and tricks to help you excel in a DevOps career!
A journey from Linux Admin to DevOps Engineer 🛣️
A journey from Linux Admin to DevOps Engineer 🛣️

1/20: 🐧 Master the Command Line:
Get comfortable with the Linux command line - it's your Swiss Army knife for DevOps tasks. Learn basic commands like ls, cd, cp, mv, cat, echo and more.
Get comfortable with the Linux command line - it's your Swiss Army knife for DevOps tasks. Learn basic commands like ls, cd, cp, mv, cat, echo and more.
2/20: 📁 File Permissions:
Understand file permissions (chmod), ownership (chown), and groups. Managing access control is crucial in a DevOps role.
Understand file permissions (chmod), ownership (chown), and groups. Managing access control is crucial in a DevOps role.
3/20: 🚀 SSH Key Pairs:
Generate SSH key pairs for secure server access. Use ssh-agent to manage keys and never store private keys in plaintext.
Generate SSH key pairs for secure server access. Use ssh-agent to manage keys and never store private keys in plaintext.
4/20: 🔒 Firewall Rules:
Learn iptables or use firewalld to control network traffic. Properly configuring firewalls is vital for server security.
Learn iptables or use firewalld to control network traffic. Properly configuring firewalls is vital for server security.
5/20: 🔄 Regular Backups:
Set up automated backups using tools like rsync or tar. Regular backups can save your data in emergencies.
Set up automated backups using tools like rsync or tar. Regular backups can save your data in emergencies.
6/20: 📝 Scripting Skills:
Become proficient in Bash or Python scripting to automate repetitive tasks. This is the heart of DevOps automation.
Become proficient in Bash or Python scripting to automate repetitive tasks. This is the heart of DevOps automation.
7/20: 🧩 Package Management:
Know your package manager (apt, yum, dnf). Keep software up to date and resolve dependencies efficiently.
Know your package manager (apt, yum, dnf). Keep software up to date and resolve dependencies efficiently.
8/20: 🌐 Network Troubleshooting:
Learn how to diagnose network issues with tools like ping, traceroute, and netstat. Mastering networking is key to DevOps.
Learn how to diagnose network issues with tools like ping, traceroute, and netstat. Mastering networking is key to DevOps.
9/20: 💡 Process Management:
Use commands like ps, top, and systemctl to monitor and manage processes. Keep an eye on server performance.
Use commands like ps, top, and systemctl to monitor and manage processes. Keep an eye on server performance.
10/20: 📂 Disk Management:
Master commands like df and du to manage disk space. Use LVM for flexible storage management.
Master commands like df and du to manage disk space. Use LVM for flexible storage management.
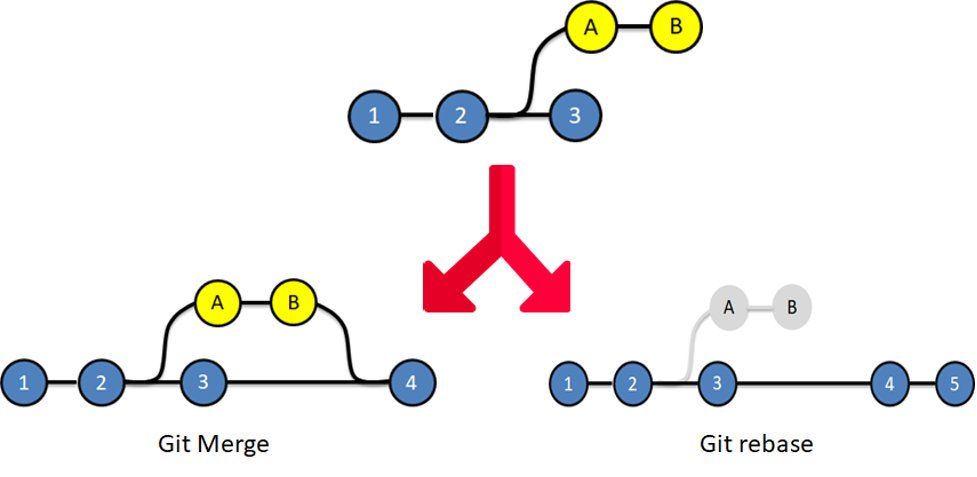
11/20: 🐙 Version Control:
Get comfortable with Git for tracking changes to your code and configurations. Git is essential for collaboration.
Get comfortable with Git for tracking changes to your code and configurations. Git is essential for collaboration.
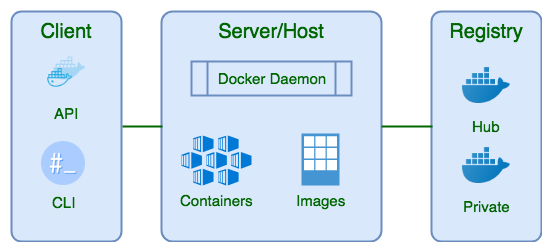
12/20: 🐳 Containerization:
Explore Docker and container orchestration tools like Kubernetes. Containers simplify deployment and scaling.
Explore Docker and container orchestration tools like Kubernetes. Containers simplify deployment and scaling.
13/20: 🛠️ Configuration Management:
Learn tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef to automate server configuration and ensure consistency.
Learn tools like Ansible, Puppet, or Chef to automate server configuration and ensure consistency.
14/20: ☁️ Cloud Services:
Familiarize yourself with cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or GCP. Infrastructure as Code (IAC) is a game-changer.
Familiarize yourself with cloud providers like AWS, Azure, or GCP. Infrastructure as Code (IAC) is a game-changer.
15/20: 🧪 Testing & CI/CD:
Integrate testing into your DevOps pipelines. Use Jenkins, Travis CI, or GitLab CI for continuous integration and delivery.
Integrate testing into your DevOps pipelines. Use Jenkins, Travis CI, or GitLab CI for continuous integration and delivery.
16/20: 📈 Monitoring & Logging:
Implement monitoring with tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or Nagios. Centralized logging (ELK stack) helps troubleshoot issues.
Implement monitoring with tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or Nagios. Centralized logging (ELK stack) helps troubleshoot issues.
17/20: 🚧 Infrastructure as Code (IAC):
Write infrastructure code with Terraform or CloudFormation to automate provisioning and scaling of resources.
Write infrastructure code with Terraform or CloudFormation to automate provisioning and scaling of resources.
18/20: 🔄 Automation & Orchestration:
Use tools like Kubernetes, Docker Swarm, or Apache Mesos for container orchestration. Automation streamlines tasks.
Use tools like Kubernetes, Docker Swarm, or Apache Mesos for container orchestration. Automation streamlines tasks.
19/20: 🏆 Certifications:
Consider certifications like AWS Certified DevOps Engineer, Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA), or Red Hat Certified Engineer (RHCE) to validate your skills.
Consider certifications like AWS Certified DevOps Engineer, Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA), or Red Hat Certified Engineer (RHCE) to validate your skills.
20/20: 🌟 Continuous Learning:
Stay updated with the ever-evolving DevOps landscape. Attend conferences, read blogs, and keep experimenting to excel in your career. #DevOps #LinuxAdmin
Stay updated with the ever-evolving DevOps landscape. Attend conferences, read blogs, and keep experimenting to excel in your career. #DevOps #LinuxAdmin
In addition to the above security is a critical aspect of DevOps and Linux administration. Here are some additional security-focused tips and tricks 👇
1/6: 🔒 Security Basics:
Prioritize security from the start. Understand the principle of least privilege (PoLP) and the importance of the CIA triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability).
Prioritize security from the start. Understand the principle of least privilege (PoLP) and the importance of the CIA triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability).
2/6: 🛡️ Updates & Patching:
Regularly update your Linux systems and software to patch vulnerabilities. Automated patch management tools can help.
Regularly update your Linux systems and software to patch vulnerabilities. Automated patch management tools can help.
3/6: 🧩 Security Hardening:
Harden your Linux servers by disabling unnecessary services, configuring a host-based firewall, and implementing SELinux or AppArmor for mandatory access control.
Harden your Linux servers by disabling unnecessary services, configuring a host-based firewall, and implementing SELinux or AppArmor for mandatory access control.
4/6: 🔑 Key Management:
Use SSH keys with strong passphrases. Disable password-based authentication to reduce the attack surface.
Use SSH keys with strong passphrases. Disable password-based authentication to reduce the attack surface.
5/6: 🚫 Intrusion Detection:
Implement intrusion detection systems (IDS) like Fail2ban or OSSEC to monitor and block suspicious activities.
Implement intrusion detection systems (IDS) like Fail2ban or OSSEC to monitor and block suspicious activities.
6/6: 🕵️♂️ Security Auditing:
Regularly audit your systems with tools like Lynis or OpenSCAP. Conduct penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities.
Regularly audit your systems with tools like Lynis or OpenSCAP. Conduct penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities.
Keep learning, practicing, and adapting to new technologies. DevOps is a dynamic field, and these skills will help you thrive in it! 🚀👨💻 #DevOpsTips #Linux #SysAdmin
Repost the thread if you find it useful. Thanks!
https://twitter.com/devops_tech/status/1709136219643453805?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter