Linux Interview Guide!
A thread with 20+ interview questions for mid-to-advanced level Linux administrators🐧👇
A thread with 20+ interview questions for mid-to-advanced level Linux administrators🐧👇

1/20 Q: What is the purpose of the 'ulimit' command in Linux?
A: 'ulimit' is used to set or display user-level resource limits. It can control processes' resource consumption, like memory or file descriptors. #LinuxAdmin #InterviewQuestions
A: 'ulimit' is used to set or display user-level resource limits. It can control processes' resource consumption, like memory or file descriptors. #LinuxAdmin #InterviewQuestions
2/20 Q: Explain the difference between 'hard' and 'soft' limits in ulimit.
A: Hard limits are the maximum values a user can set, while soft limits can be set and changed by the user within the hard limit boundaries. #Linux #SysAdmin
A: Hard limits are the maximum values a user can set, while soft limits can be set and changed by the user within the hard limit boundaries. #Linux #SysAdmin
3/20 Q: Explain the purpose of the 'chroot' command in Linux.
A: 'chroot' changes the apparent root directory for a process. It's often used for creating isolated environments or for system recovery purposes. #LinuxAdmin #Security
A: 'chroot' changes the apparent root directory for a process. It's often used for creating isolated environments or for system recovery purposes. #LinuxAdmin #Security
4/20 Q: How can you check which process is using a specific port in Linux?
A: The 'netstat' or 'ss' command can display a list of network connections, including the processes associated with specific ports. #LinuxNetworking #SysAdmin
A: The 'netstat' or 'ss' command can display a list of network connections, including the processes associated with specific ports. #LinuxNetworking #SysAdmin
5/20 Q: What is SELinux, and how does it enhance Linux security?
A: SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) is a security framework that enforces mandatory access controls, adding an extra layer of security by limiting access to resources. #Security #Linux
A: SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) is a security framework that enforces mandatory access controls, adding an extra layer of security by limiting access to resources. #Security #Linux
6/20 Q: Explain the purpose of 'strace' and 'ltrace' commands in Linux.
A: 'strace' traces system calls made by a process, while 'ltrace' traces library calls. They are helpful for debugging and profiling. #Debugging #LinuxTools
A: 'strace' traces system calls made by a process, while 'ltrace' traces library calls. They are helpful for debugging and profiling. #Debugging #LinuxTools
7/20 Q: How do you find and kill a process by its name in Linux?
A: You can use 'pgrep' to find the process ID (PID) by name and 'kill' or 'killall' to terminate it. Be cautious when killing processes. #LinuxCommands #SysAdmin
A: You can use 'pgrep' to find the process ID (PID) by name and 'kill' or 'killall' to terminate it. Be cautious when killing processes. #LinuxCommands #SysAdmin
8/20 Q: What is 'systemd' in Linux, and how does it differ from 'init'?
A: 'systemd' is a modern init system and service manager, replacing traditional 'init'. It provides better control and management of services and dependencies. #Systemd #Linux
A: 'systemd' is a modern init system and service manager, replacing traditional 'init'. It provides better control and management of services and dependencies. #Systemd #Linux
9/20 Q: What is 'swappiness' in Linux, and how can you adjust it?
A: 'Swappiness' is a kernel parameter that controls the tendency to use swap space. You can adjust it with 'sysctl' or by modifying '/etc/sysctl.conf'. Lower values reduce swapping. #LinuxMemory #SysAdmin
A: 'Swappiness' is a kernel parameter that controls the tendency to use swap space. You can adjust it with 'sysctl' or by modifying '/etc/sysctl.conf'. Lower values reduce swapping. #LinuxMemory #SysAdmin
10/20 Q: Explain the concept of 'OOM Killer' in Linux.
A: The Out-of-Memory (OOM) Killer is a kernel feature that terminates processes when the system runs out of memory to prevent a complete system freeze. It prioritizes processes based on criteria. #LinuxOOM #SysAdmin
A: The Out-of-Memory (OOM) Killer is a kernel feature that terminates processes when the system runs out of memory to prevent a complete system freeze. It prioritizes processes based on criteria. #LinuxOOM #SysAdmin
11/20 Q: What is a 'cgroup' in Linux, & how does it help in process mgmt?
A: Control groups (cgroups) are a kernel feature that manages & limits system resource usage for processes. They help allocate CPU, memory, & other resources to groups of processes. #LinuxCgroups
A: Control groups (cgroups) are a kernel feature that manages & limits system resource usage for processes. They help allocate CPU, memory, & other resources to groups of processes. #LinuxCgroups
12/20 Q: What is a 'kernel panic' in Linux, and how do you troubleshoot it?
A: A kernel panic is a critical error that causes the kernel to halt. To troubleshoot, review the panic message, check system logs, and analyze hardware or driver issues. #KernelPanic #Troubleshooting
A: A kernel panic is a critical error that causes the kernel to halt. To troubleshoot, review the panic message, check system logs, and analyze hardware or driver issues. #KernelPanic #Troubleshooting
13/20 Q: Explain the 'dmesg' command in Linux and its role in kernel troubleshooting.
A: 'dmesg' displays kernel messages, including boot-time diagnostics and hardware-related information. It's helpful for identifying hardware issues and driver problems. #LinuxKernel #SysAdmin
A: 'dmesg' displays kernel messages, including boot-time diagnostics and hardware-related information. It's helpful for identifying hardware issues and driver problems. #LinuxKernel #SysAdmin
14/20 Q: How can u update the Linux kernel, and what precautions should u take?
A: Kernel updates can be done using package managers like 'yum' or 'apt'. Before updating, ensure backups, & understand potential compatibility issues with existing drivers & modules. #KernelUpdate
A: Kernel updates can be done using package managers like 'yum' or 'apt'. Before updating, ensure backups, & understand potential compatibility issues with existing drivers & modules. #KernelUpdate
15/20 Q: Explain 'strace' & 'gdb' in the context of kernel troubleshooting.
A: 'strace' traces system calls, while 'gdb' is a debugger for user-space processes. In kernel troubleshooting, tools like 'ftrace' & 'kgdb' are used for kernel-level debugging. #KernelDebugging
A: 'strace' traces system calls, while 'gdb' is a debugger for user-space processes. In kernel troubleshooting, tools like 'ftrace' & 'kgdb' are used for kernel-level debugging. #KernelDebugging
16/20 Q: Search for all occurrences of the word "error" in a set of log files located in the /var/log directory & its subdirs.
A: You can use the following grep cmd:
grep -r "error" /var/log. This will recursively search for "error" in all files within /var/log and its subdirs.
A: You can use the following grep cmd:
grep -r "error" /var/log. This will recursively search for "error" in all files within /var/log and its subdirs.
17/20 Q: U hv a CSV file named data.csv with columns: Name, Age, & City. Print only the names of people who r older than 30 yrs?
A: U can use this awk cmd:
awk -F, '$2 > 30 {print $1}' data.csv
It sets the field separator as a comma & prints the names of people with an age > 30
A: U can use this awk cmd:
awk -F, '$2 > 30 {print $1}' data.csv
It sets the field separator as a comma & prints the names of people with an age > 30
18/20 Q: Explain how to use 'find' to locate & delete files older than a certain date.
A: To find & delete files older than a specific date, use 'find' with '-mtime' & '-exec' options.
For eg: 'find /path/to/search -type f -mtime +7 -exec rm {} ;'
#LinuxTips #FileManagement
A: To find & delete files older than a specific date, use 'find' with '-mtime' & '-exec' options.
For eg: 'find /path/to/search -type f -mtime +7 -exec rm {} ;'
#LinuxTips #FileManagement
19/20 Q: What is 'kdump' in Linux, and how does it aid in kernel debugging?
A: 'kdump' is a mechanism that captures kernel crash dumps when a system experiences a kernel panic. It helps in post-mortem analysis to diagnose and fix kernel issues. #Kdump #KernelDebugging
A: 'kdump' is a mechanism that captures kernel crash dumps when a system experiences a kernel panic. It helps in post-mortem analysis to diagnose and fix kernel issues. #Kdump #KernelDebugging
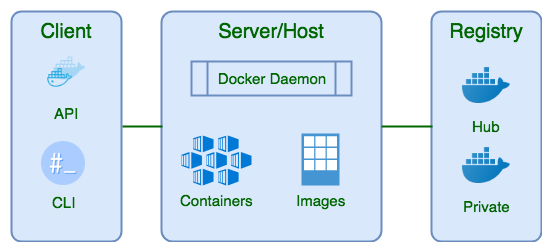
20/20 Q: What are Linux namespaces?
A: Linux namespaces provide resource/processes isolation, making them appear isolated. dey r crucial for containers like Docker.
In Docker, namespaces include PID for process isolation, nw for nw separation, & mount for filesystem isolation.
A: Linux namespaces provide resource/processes isolation, making them appear isolated. dey r crucial for containers like Docker.
In Docker, namespaces include PID for process isolation, nw for nw separation, & mount for filesystem isolation.
1/5 Q: Explain the 'journalctl' command in Linux, & how can it be used to view system logs effectively?
A: 'journalctl' queries & displays systemd journal logs, providing detailed system info & log filtering capabilities. Useful for troubleshooting & monitoring. #LinuxLogs
A: 'journalctl' queries & displays systemd journal logs, providing detailed system info & log filtering capabilities. Useful for troubleshooting & monitoring. #LinuxLogs
2/5 Q: How can u schedule recurring tasks in Linux using 'cron'? Share an eg of a cron job that runs every day at midnight.
A: 'cron' is a powerful job scheduler. To run a task daily at midnight, add this line to the crontab:
0 0 * * * /path/to/cmd.
It runs at 00:00 every day.
A: 'cron' is a powerful job scheduler. To run a task daily at midnight, add this line to the crontab:
0 0 * * * /path/to/cmd.
It runs at 00:00 every day.
3/5 Q: Explain the 'nohup' cmd. How can it be used to run processes dat persist even after logging out of a remote session?
A: It stands for 'no hang up' & is used to run processes in the background, immune to hang-ups (session termination).
Use it like this: 'nohup command &'
A: It stands for 'no hang up' & is used to run processes in the background, immune to hang-ups (session termination).
Use it like this: 'nohup command &'
4/5 Q: What is the role of the 'initrd' (initial ramdisk) in the boot process? Why is it essential, & how is it created?
A: 'initrd' is a temp file system used during the early boot process to load essential drivers & modules. It's created with tools like 'mkinitrd' or 'dracut.'
A: 'initrd' is a temp file system used during the early boot process to load essential drivers & modules. It's created with tools like 'mkinitrd' or 'dracut.'
5/5 Q: What is 'kexec', & how does it differ from a traditional reboot? When to use 'kexec' for booting?
A: 'kexec' allows for a faster, kernel-only reboot w/o going through the entire BIOS & bootloader process. It's useful for debugging or when u need a quick kernel switch.
A: 'kexec' allows for a faster, kernel-only reboot w/o going through the entire BIOS & bootloader process. It's useful for debugging or when u need a quick kernel switch.
Repost the thread if you find it useful. Thanks!
https://twitter.com/devops_tech/status/1709570588623466821?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter