𝗔𝗽𝗽𝗲𝗮𝗿𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗳𝗼𝗿 𝗮 𝘀𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺 𝗱𝗲𝘀𝗶𝗴𝗻 𝗶𝗻𝘁𝗲𝗿𝘃𝗶𝗲𝘄 ?
Read this 8 system design non-functional requirements.
Non-Functional requirements defines qualities of a system, how a system is supposed to be.
For example: scalable, highly available, fast etc
Read this 8 system design non-functional requirements.
Non-Functional requirements defines qualities of a system, how a system is supposed to be.
For example: scalable, highly available, fast etc

𝟭. 𝗔𝘃𝗮𝗶𝗹𝗮𝗯𝗶𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘆
Availability = system uptime, the percentage of time system has been up
99% availability = the system was unavailable about 3.65 days a year.
Availability is measured as the success rate of requests.
99% availability = 99/100 = 1 req of 100 fails.
Availability = system uptime, the percentage of time system has been up
99% availability = the system was unavailable about 3.65 days a year.
Availability is measured as the success rate of requests.
99% availability = 99/100 = 1 req of 100 fails.

𝟭.𝗮 𝗙𝗮𝘂𝗹𝘁 𝘁𝗼𝗹𝗲𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗲
If a system is fault tolerant, then it is also highly available.
A fault tolerant system aims 0 downtime.
A fault tolerant system is designed to continue to operate even if one of its connecting components fails.
If a system is fault tolerant, then it is also highly available.
A fault tolerant system aims 0 downtime.
A fault tolerant system is designed to continue to operate even if one of its connecting components fails.
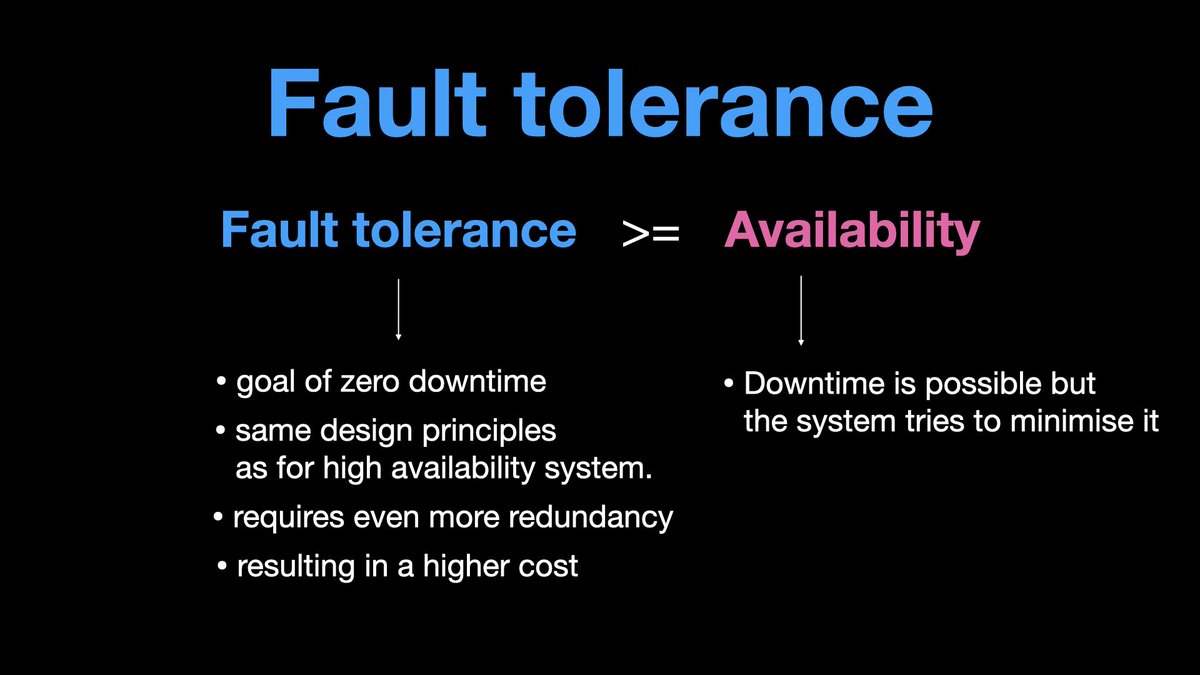
eg. An airplane is a fault tolerant system, even if one engine fails, the other engine resumes immediately, and the system continues to operate.
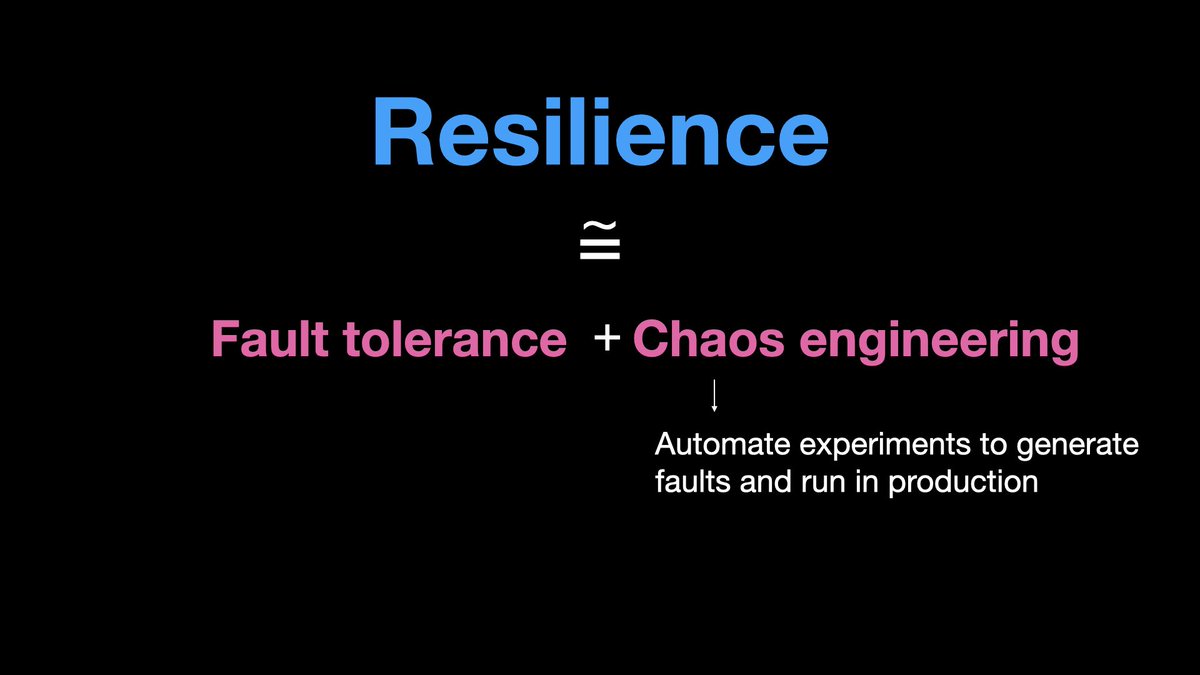
𝟭.𝗯 𝗥𝗲𝘀𝗶𝗹𝗶𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗲
A resilience system is almost the same as a fault tolerant system, one extra thing is,
𝟭.𝗯 𝗥𝗲𝘀𝗶𝗹𝗶𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗲
A resilience system is almost the same as a fault tolerant system, one extra thing is,
a resilient system is designed to be periodically tested for fault tolerance.
A resilient system has a practice of periodically testing the system for faults by deliberately generating faults. Done using caos engineering, game day engineering etc
A resilient system has a practice of periodically testing the system for faults by deliberately generating faults. Done using caos engineering, game day engineering etc
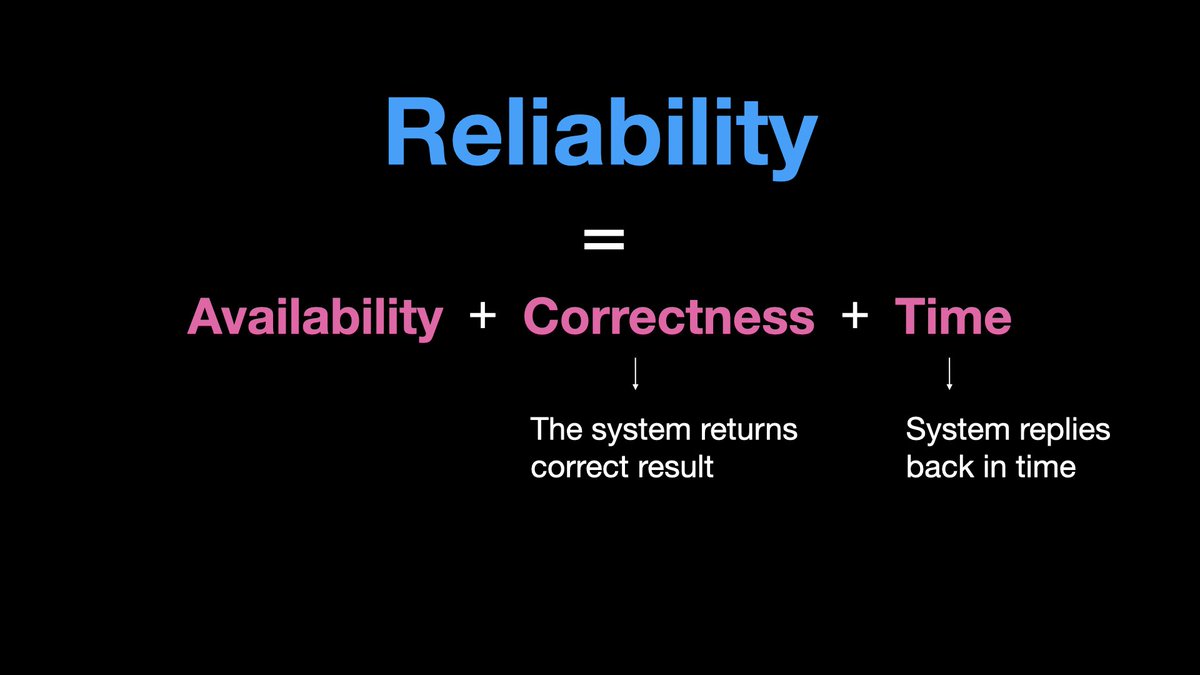
𝟭.𝗰 𝗥𝗲𝗹𝗶𝗮𝗯𝗶𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘆
You may have a highly available system, but it might still suffer with frequent data corruption, and returns incorrect results.
Or the system is too slow and response is no longer useful.
Although we have availability, we don’t have reliability.
You may have a highly available system, but it might still suffer with frequent data corruption, and returns incorrect results.
Or the system is too slow and response is no longer useful.
Although we have availability, we don’t have reliability.
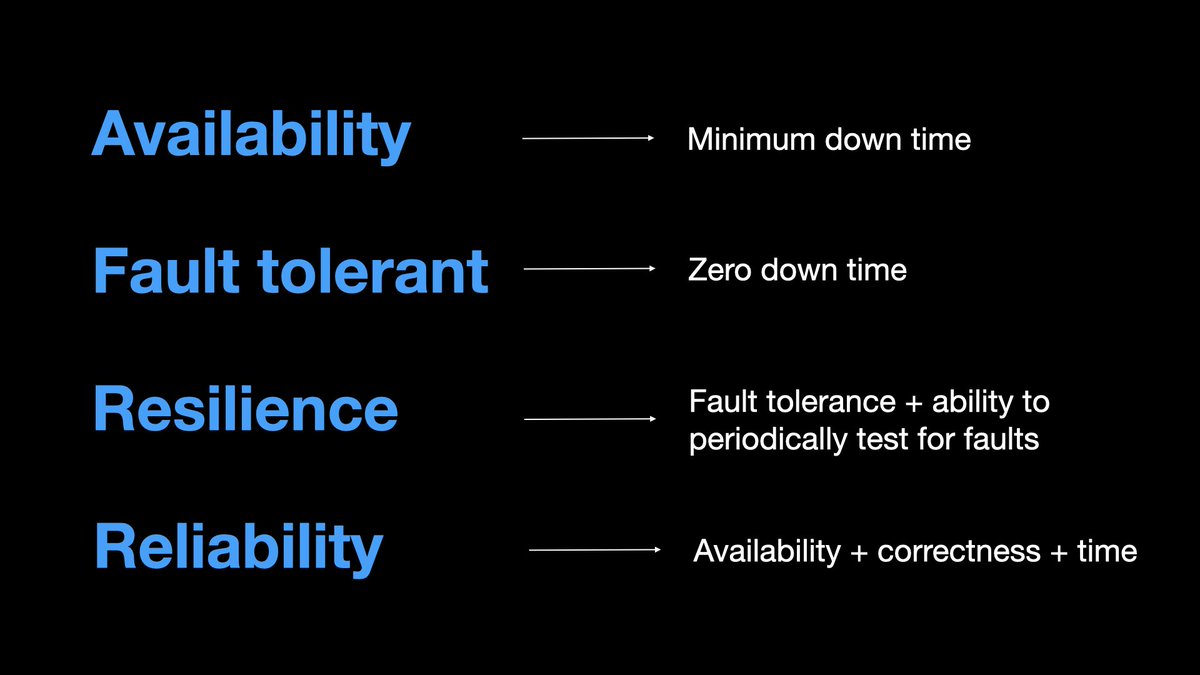
Fault tolerant, resilience, and reliability relate to the same concept, availability.
When your interviewer asks you to design a fault-tolerant or resilient or reliable system, apply the same set of principles and best practices that is used for availability.
When your interviewer asks you to design a fault-tolerant or resilient or reliable system, apply the same set of principles and best practices that is used for availability.
You can scale a system horizontally or vertically.
Ideally, horizontal and vertical scaling can be used in conjunction, eg, scale horizontally, then vertically, then again horizontally.
Ideally, horizontal and vertical scaling can be used in conjunction, eg, scale horizontally, then vertically, then again horizontally.
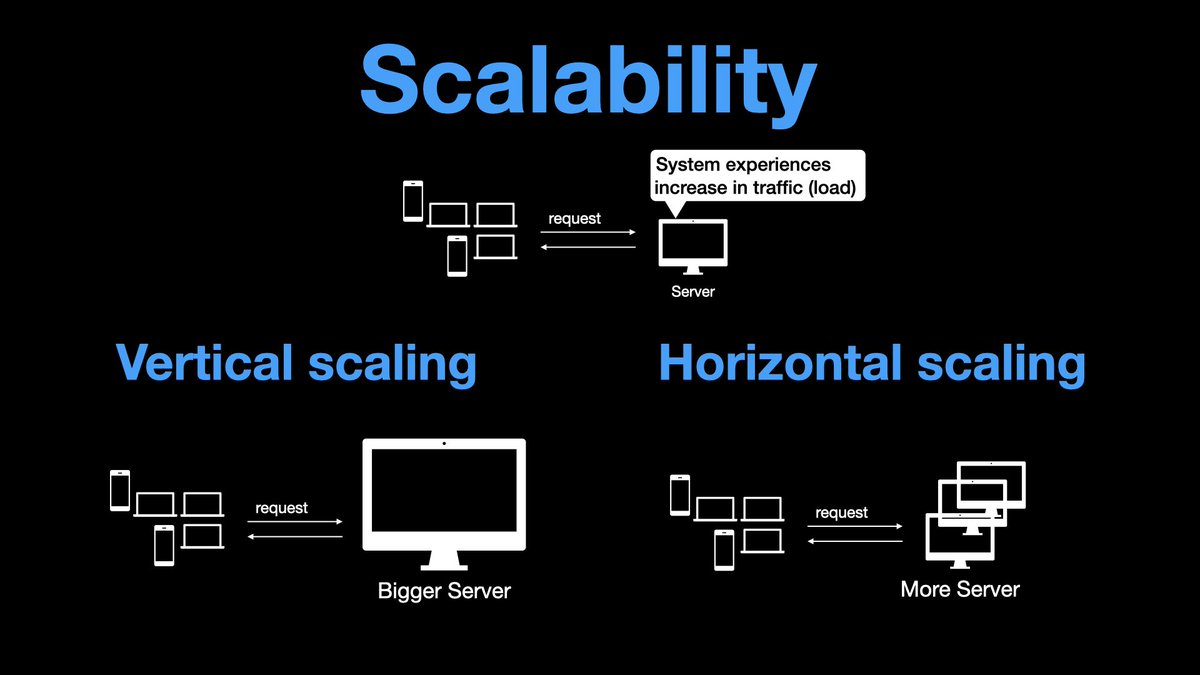
If our system is elastic, we can start with N machines at the start of the day, and keep adding machines throughout the day as the load increases. After the peak load has passed, we gradually decrease the number of machines. 
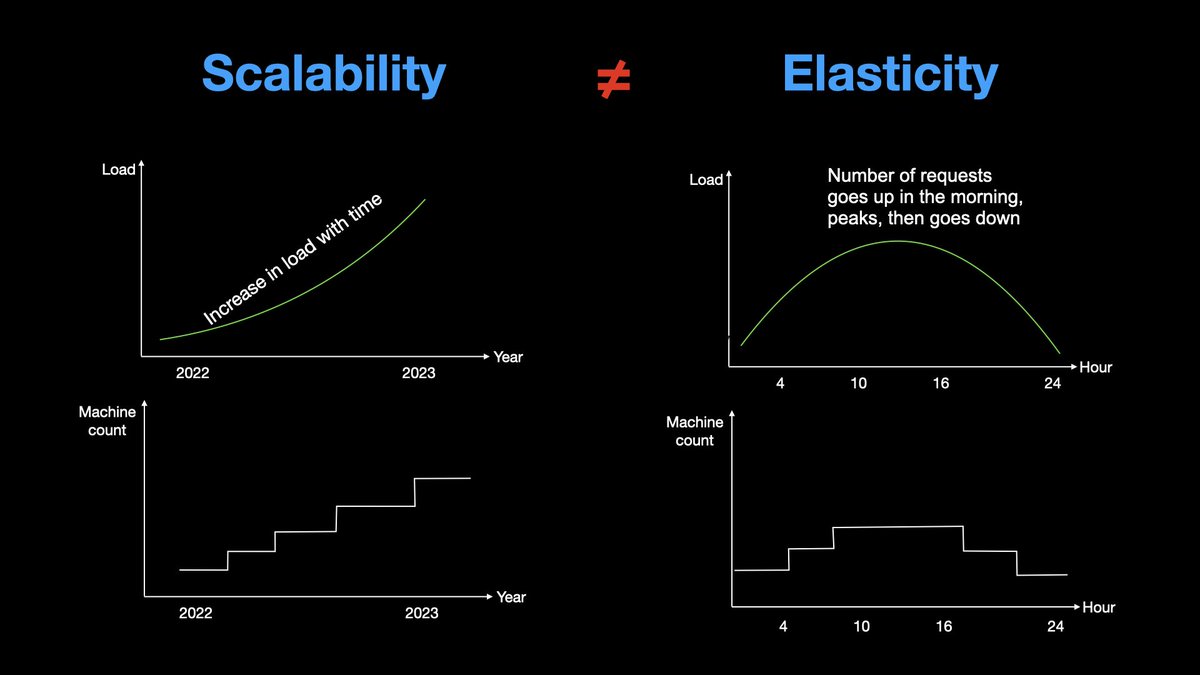
𝟯. 𝗣𝗲𝗿𝗳𝗼𝗿𝗺𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗲
A highly performance system is quick with its request and response processing.
If your interviewer asked you to design a performant system, think in terms of latency and throughput.
A highly performance system is quick with its request and response processing.
If your interviewer asked you to design a performant system, think in terms of latency and throughput.
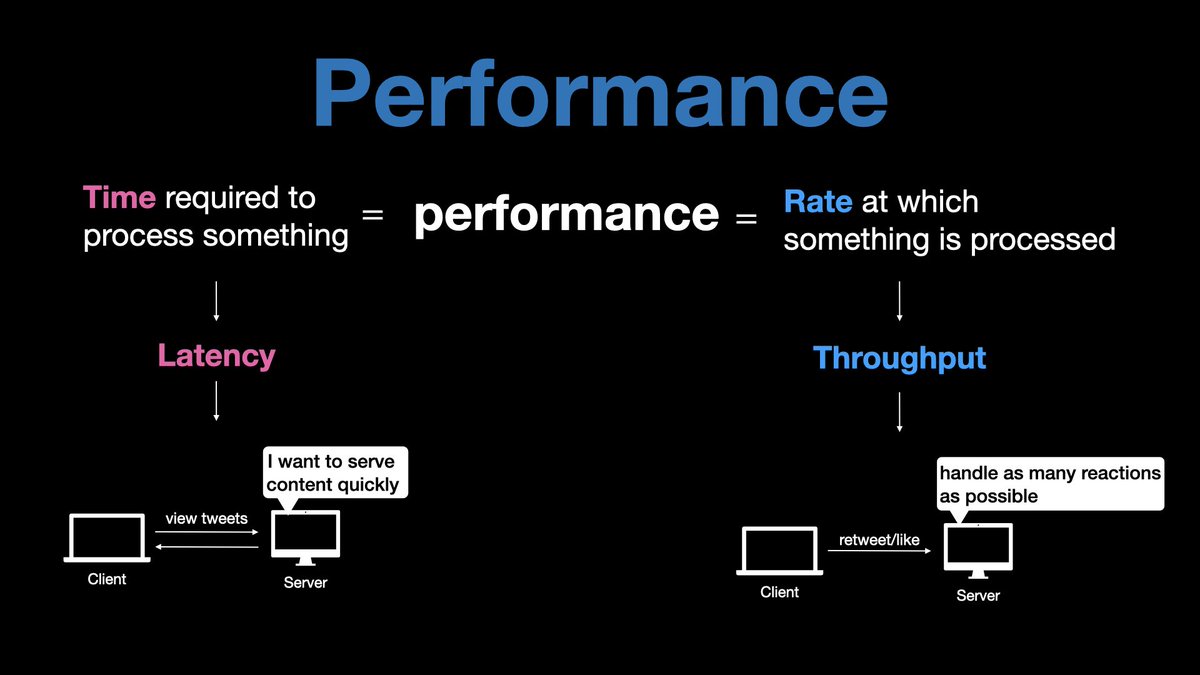
𝟰. 𝗗𝘂𝗿𝗮𝗯𝗶𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘆
In a durable system, once data is successfully submitted, it can not be lost.
You can achieve durability using
- Backup
- Raid
- Replication
In a durable system, once data is successfully submitted, it can not be lost.
You can achieve durability using
- Backup
- Raid
- Replication
𝟱. 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝘀𝗶𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗻𝗰𝘆
Consistency guarantees that your data is consistent across all distributed copies.
In a large distributed system consistency is hard to achieve.
Cap theorem tells that in case of a network partition, you can choose either consistent or availability.
Consistency guarantees that your data is consistent across all distributed copies.
In a large distributed system consistency is hard to achieve.
Cap theorem tells that in case of a network partition, you can choose either consistent or availability.
𝟲. 𝗠𝗮𝗶𝗻𝘁𝗮𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗯𝗶𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘆
Maintainability is the ability of the system to go through repairs/modifications while it is up and running.
Once a fault is detected, it is desirable to be able to apply the necessary improvements asap, without having to shut down the system.
Maintainability is the ability of the system to go through repairs/modifications while it is up and running.
Once a fault is detected, it is desirable to be able to apply the necessary improvements asap, without having to shut down the system.

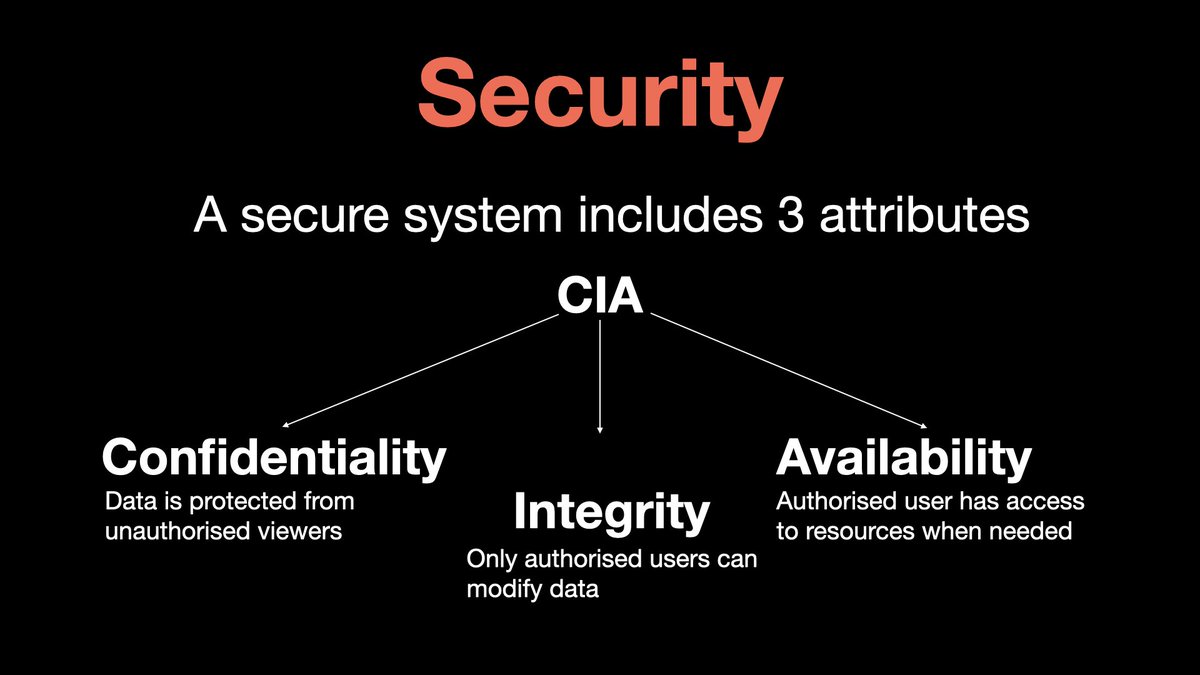
𝟳. 𝗦𝗲𝗰𝘂𝗿𝗶𝘁𝘆
Security assures that all data within the system or its part is protected against any malware attacks/unauthorized access.
Security system include three fundamentals attributes, often referred to as the CIA triad
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- availability
Security assures that all data within the system or its part is protected against any malware attacks/unauthorized access.
Security system include three fundamentals attributes, often referred to as the CIA triad
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- availability
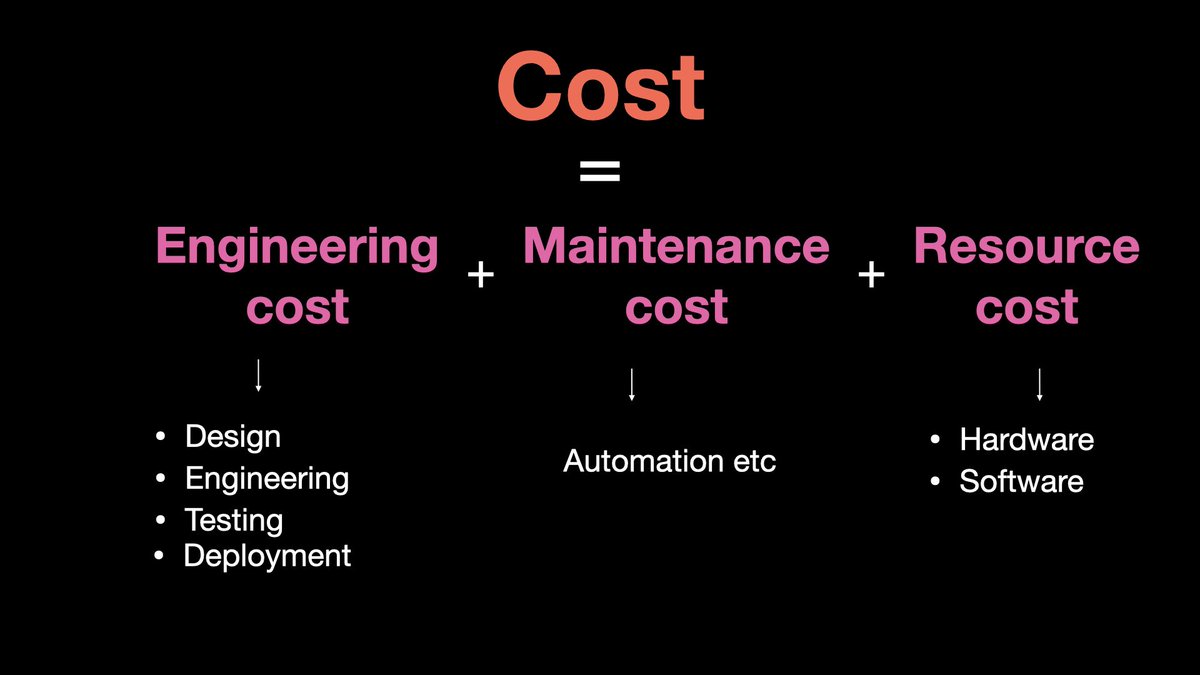
8. Cost
Cost non-functional requirement can be classified into - Development cost
- Maintenance cost
- Resource cost
Cost non-functional requirement can be classified into - Development cost
- Maintenance cost
- Resource cost
Closing this thread now.
These are important system design concepts, and each non-functional requirement deserves a detailed post of its own.
More on that later.
Retweet and follow @happydecoder ❤️
These are important system design concepts, and each non-functional requirement deserves a detailed post of its own.
More on that later.
Retweet and follow @happydecoder ❤️
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter














