SOLID principle is one of the most important design principles in OOP languages like Java, Python, C#, etc.
Sadly, most of the programmers find it super difficult to understand.
Here's the simplest guide to understand SOLID principles:
Sadly, most of the programmers find it super difficult to understand.
Here's the simplest guide to understand SOLID principles:
1. Full form
S = Single Responsibility Principle
O = Open/Closed Principle
L = Liskov Substitution Principle
I = Interface Segregation Principle
D = Dependency Inversion Principle
(we will use Java to understand them)
S = Single Responsibility Principle
O = Open/Closed Principle
L = Liskov Substitution Principle
I = Interface Segregation Principle
D = Dependency Inversion Principle
(we will use Java to understand them)
2. Single Responsibility
A class should always have one responsibility and there should be only a single reason to change it.
A class should always have one responsibility and there should be only a single reason to change it.
2.1. Bad Implementation
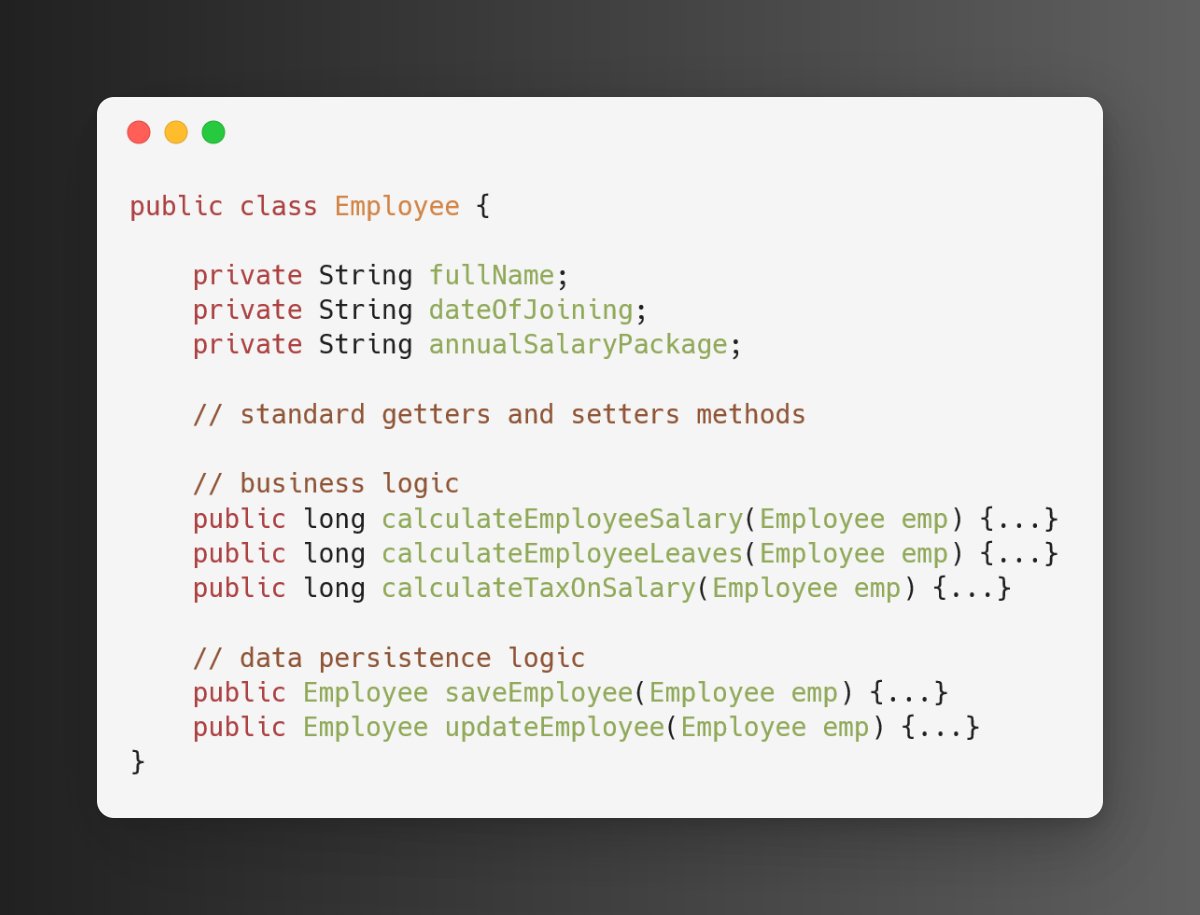
Below Employee class contains personal details, business logic to perform a few calculations, and DB logic to save/update.
Our class is tightly coupled, hard to maintain, multiple reasons to modify this class.
Below Employee class contains personal details, business logic to perform a few calculations, and DB logic to save/update.
Our class is tightly coupled, hard to maintain, multiple reasons to modify this class.
2.2. Good Implementation:
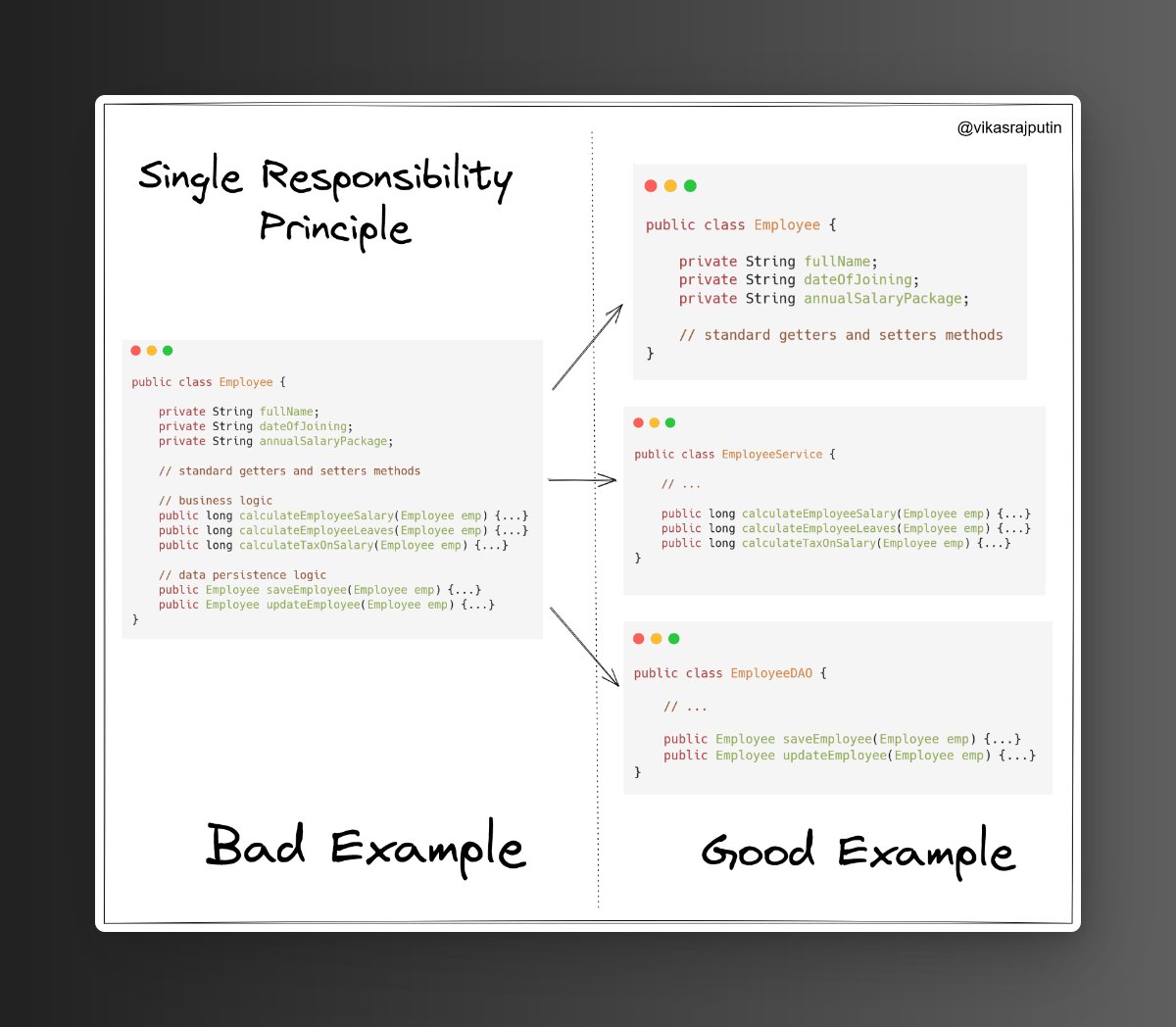
We can split a single Employee class into multiple classes as per their specific responsibility.
It made our class loosely coupled, easy to maintain, and only single reason to modify.
We can split a single Employee class into multiple classes as per their specific responsibility.
It made our class loosely coupled, easy to maintain, and only single reason to modify.
3. Open Close
Class should be Open for Extension but Closed for Modification.
Class should be Open for Extension but Closed for Modification.
3.1. Bad Implementation
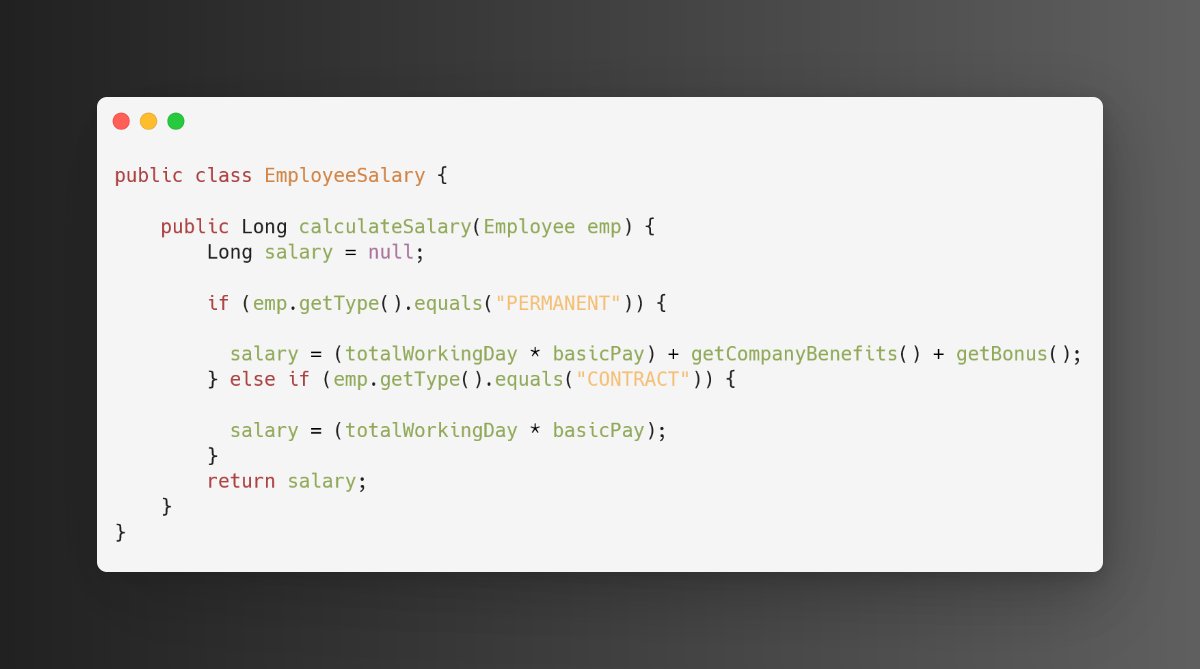
Below EmployeeSalary class calculates salary based on employee type: Permanent and Contractual.
Issue: In the future, if a new type(Part-time Employee) comes then the code needs to be modified to calculate the salary based on employee type.
Below EmployeeSalary class calculates salary based on employee type: Permanent and Contractual.
Issue: In the future, if a new type(Part-time Employee) comes then the code needs to be modified to calculate the salary based on employee type.
3.2. Good Implementation:
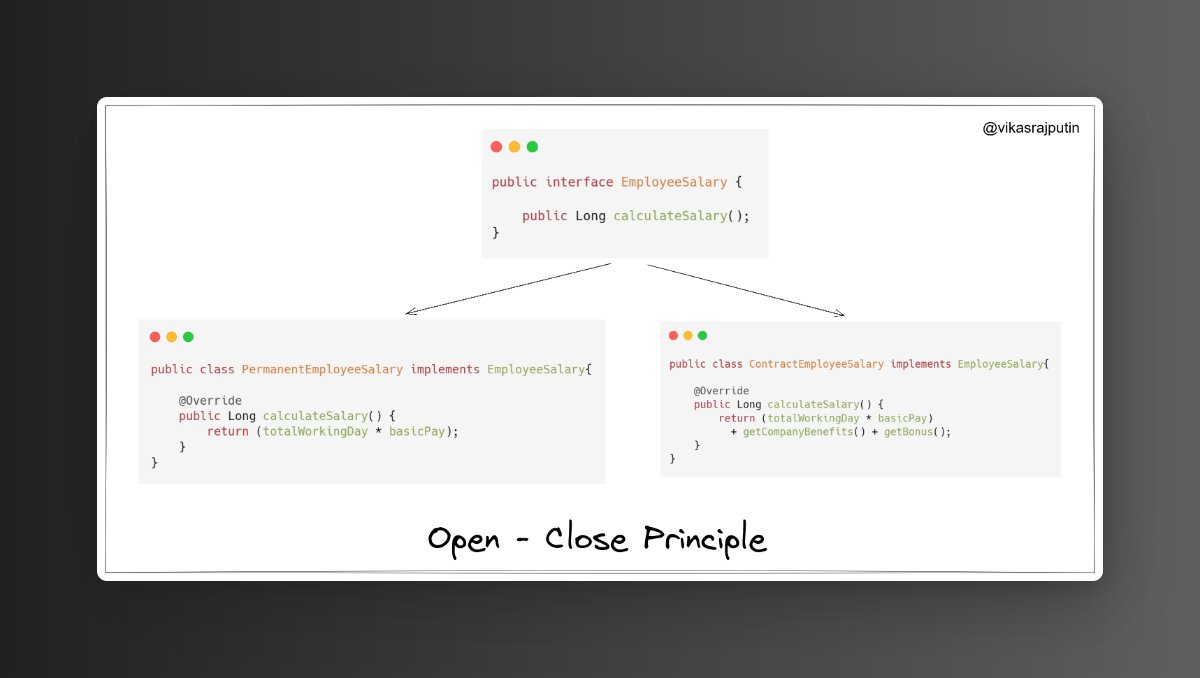
We can introduce a new interface EmployeeSalary and create two child classes for Permanent and Contractual Employees.
By doing this, when a new type comes then a new child class needs to be created and our core logic will also not change from this.
We can introduce a new interface EmployeeSalary and create two child classes for Permanent and Contractual Employees.
By doing this, when a new type comes then a new child class needs to be created and our core logic will also not change from this.
4. Liskov Substitution
Child Classes should be replaceable with Parent Classes without breaking the behavior of our code.
Child Classes should be replaceable with Parent Classes without breaking the behavior of our code.
4.1. Bad Implementation
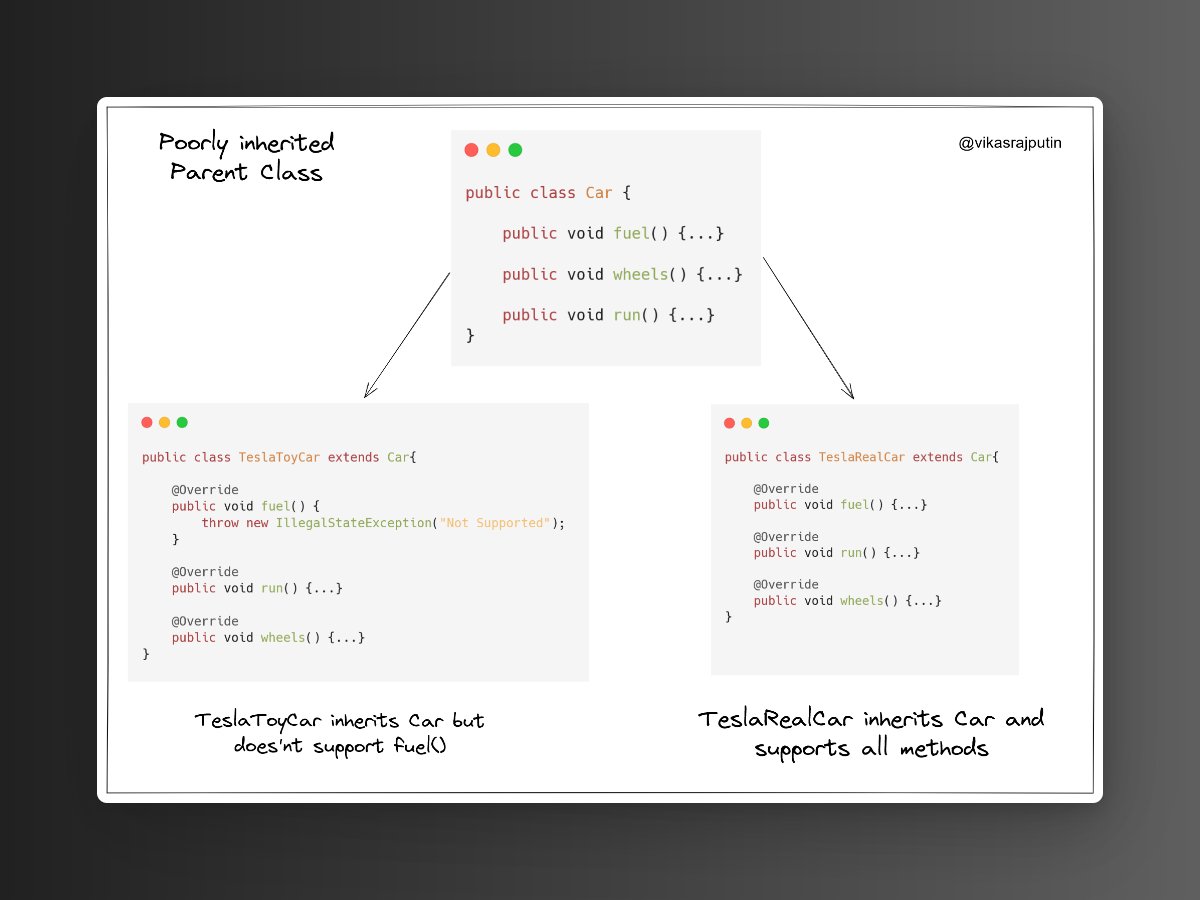
Below, TeslaToyCar extends Car but does not support fuel() method as its toy. That's why it's violating the LS principle.
In our code where ever we've used Car, we can't substitute it directly with TeslaToyCar because fuel() will throw Exception.
Below, TeslaToyCar extends Car but does not support fuel() method as its toy. That's why it's violating the LS principle.
In our code where ever we've used Car, we can't substitute it directly with TeslaToyCar because fuel() will throw Exception.
4.2. Good Implementation
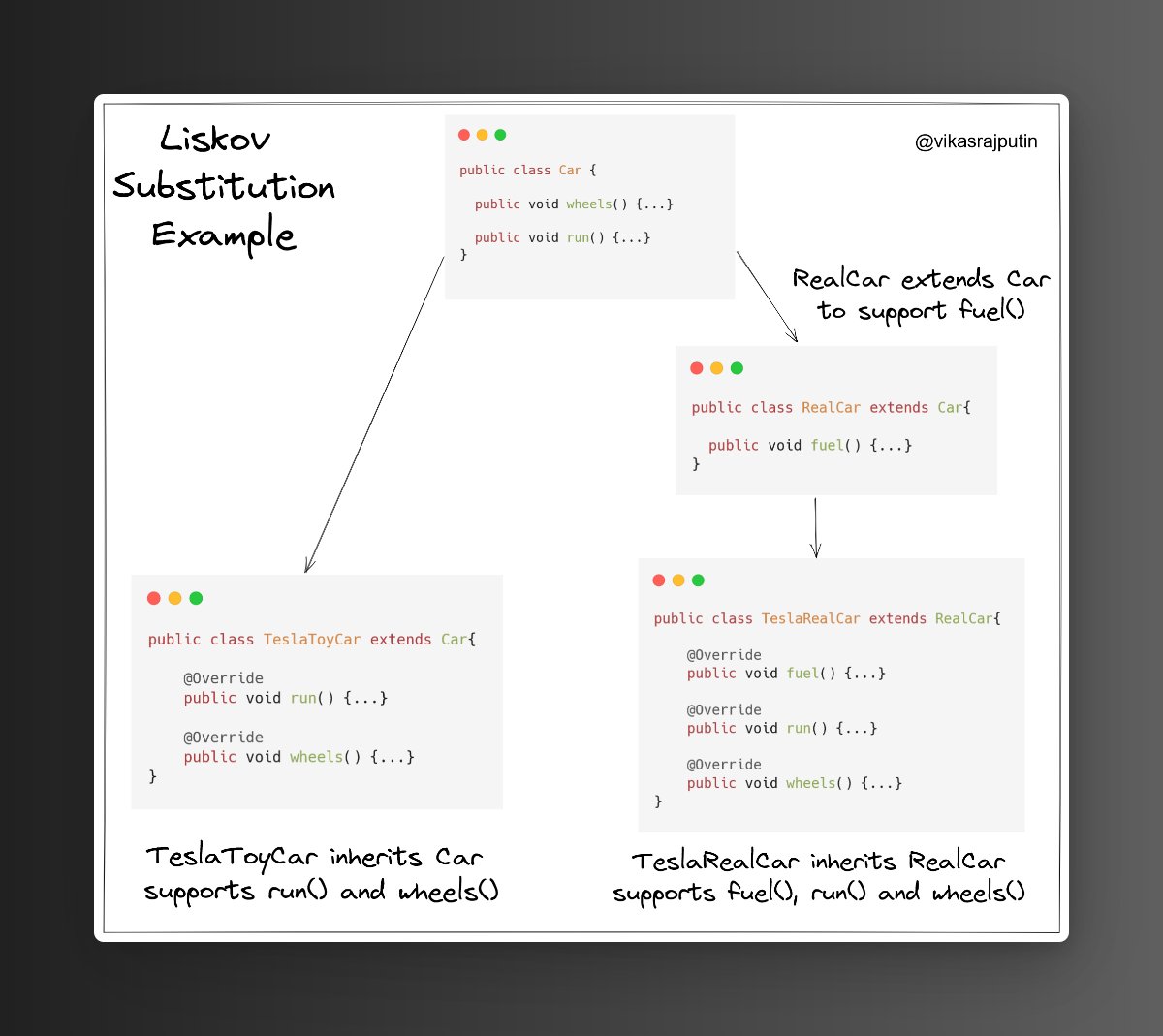
Creating new subclass RealCar from parent Car class, so that RealCar can support fuel() and Car can support generic functions support by any type of car.
As shown below, TeslaToyCar and TeslaRealCar can be substituted with their respective Parent class.
Creating new subclass RealCar from parent Car class, so that RealCar can support fuel() and Car can support generic functions support by any type of car.
As shown below, TeslaToyCar and TeslaRealCar can be substituted with their respective Parent class.
5. Interface Segregation:
Interface should only have methods that are applicable to all child classes.
If an interface contains a method applicable to some child classes then we need to force the rest to provide dummy implementation.
Move such methods to a new interface.
Interface should only have methods that are applicable to all child classes.
If an interface contains a method applicable to some child classes then we need to force the rest to provide dummy implementation.
Move such methods to a new interface.
5.1. Bad Implementation:
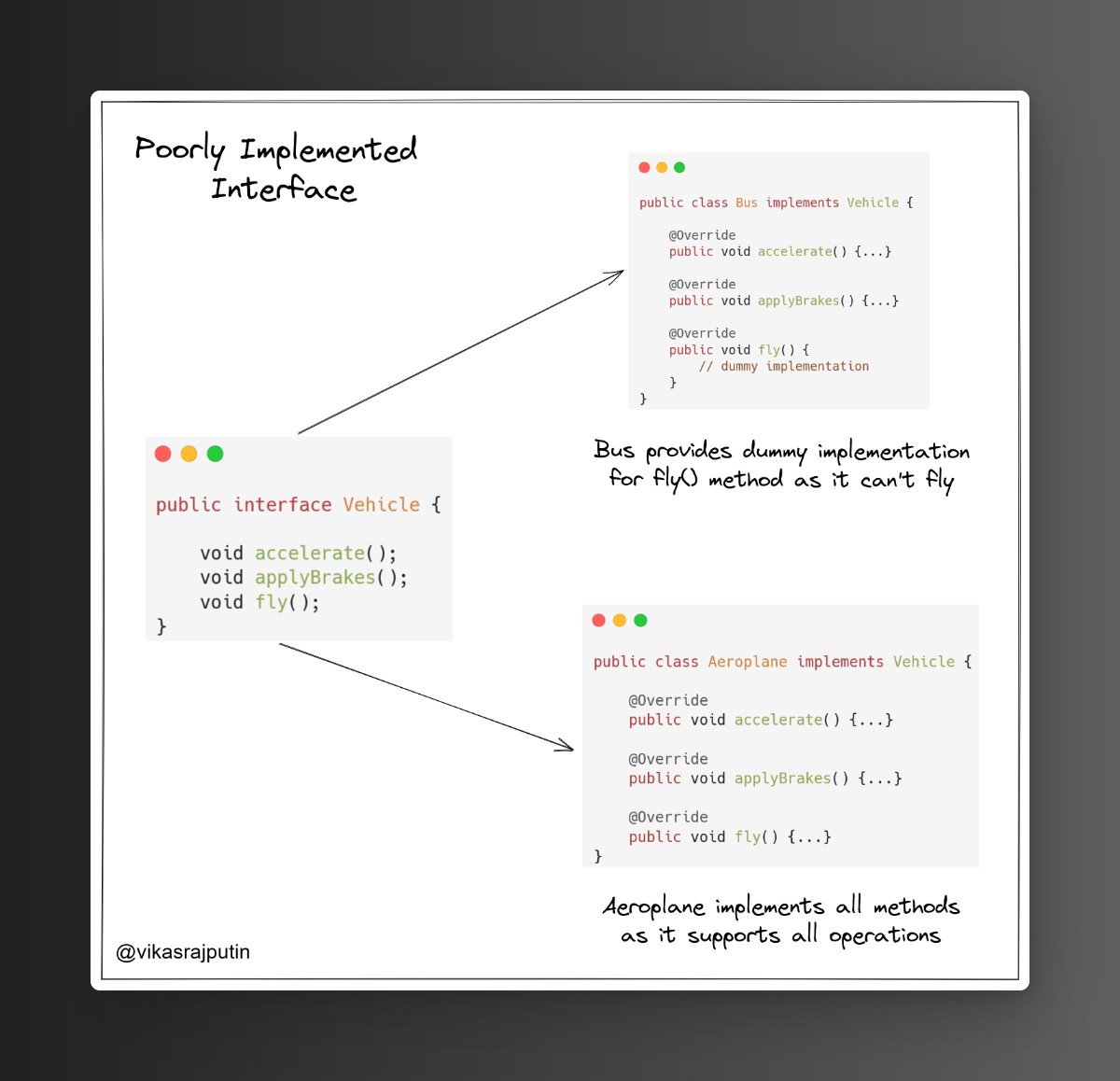
Vehicle interface contains the fly() method which is not supported by all vehicles i.e. Bus, Car, etc. Hence they've to forcefully provide a dummy implementation.
It violates the Interface Segregation principle as shown below:
Vehicle interface contains the fly() method which is not supported by all vehicles i.e. Bus, Car, etc. Hence they've to forcefully provide a dummy implementation.
It violates the Interface Segregation principle as shown below:
5.2. Good Implementation:
Pulling out fly() method into new Flyable interface solves the issue.
Now, Vehicle interface contains methods supported by all Vehicles.
And, Aeroplane implements both Vehicle and Flyable interface as it can fly too.
Pulling out fly() method into new Flyable interface solves the issue.
Now, Vehicle interface contains methods supported by all Vehicles.
And, Aeroplane implements both Vehicle and Flyable interface as it can fly too.

6. Dependency Inversion
Class should depend on abstractions (interface and abstract class) instead of concrete implementations.
It makes our classes de-coupled with each other.
If implementation changes then the class referring to it via abstraction won't change.
Class should depend on abstractions (interface and abstract class) instead of concrete implementations.
It makes our classes de-coupled with each other.
If implementation changes then the class referring to it via abstraction won't change.
6.1. Bad Implementation
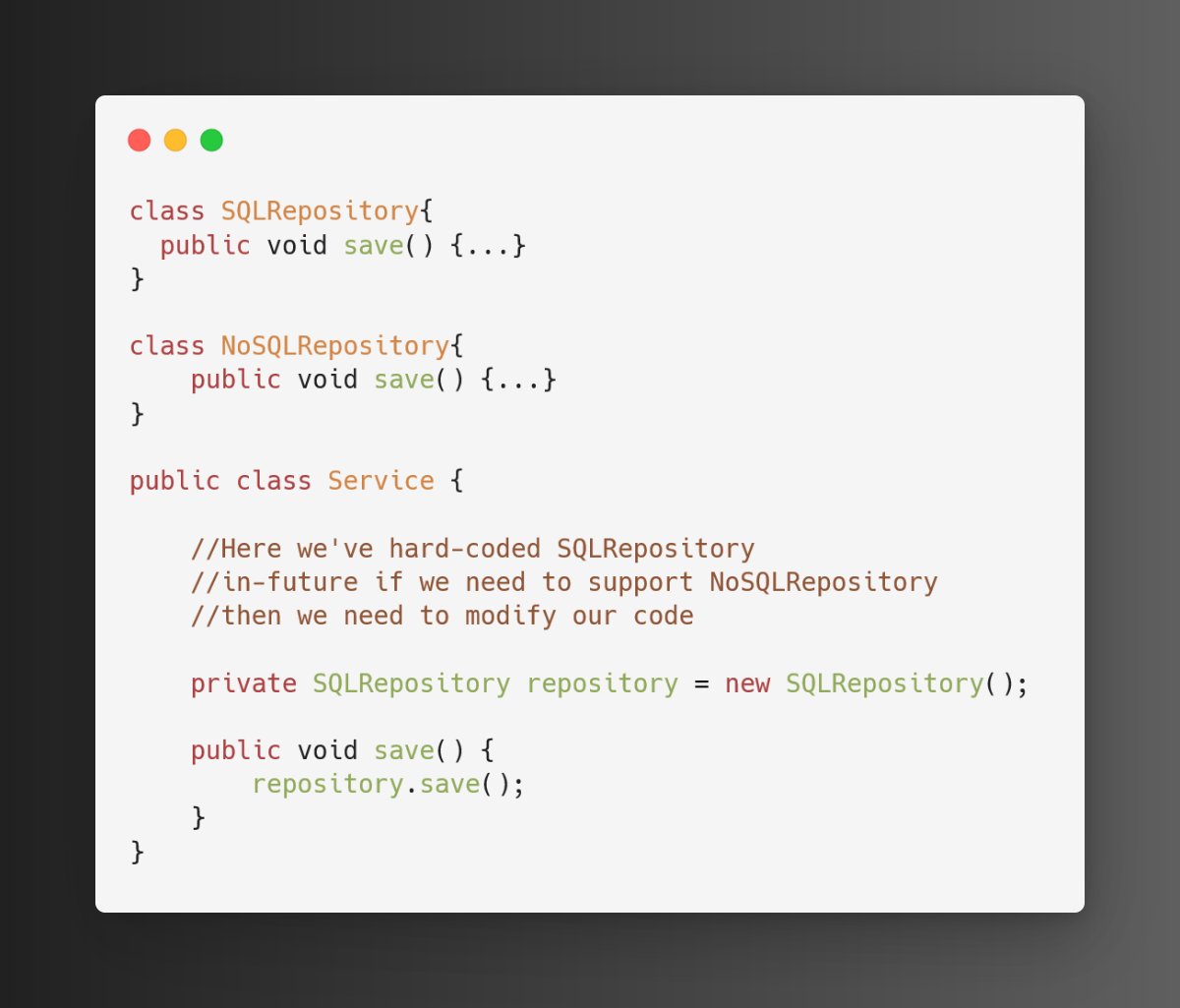
We've got a Service class, in which we've directly referenced concrete class(SQLRepository).
Issue: Our class is now tightly coupled with SQLRepository, in future if we need to start supporting NoSQLRepository then we need to change Service class.
We've got a Service class, in which we've directly referenced concrete class(SQLRepository).
Issue: Our class is now tightly coupled with SQLRepository, in future if we need to start supporting NoSQLRepository then we need to change Service class.
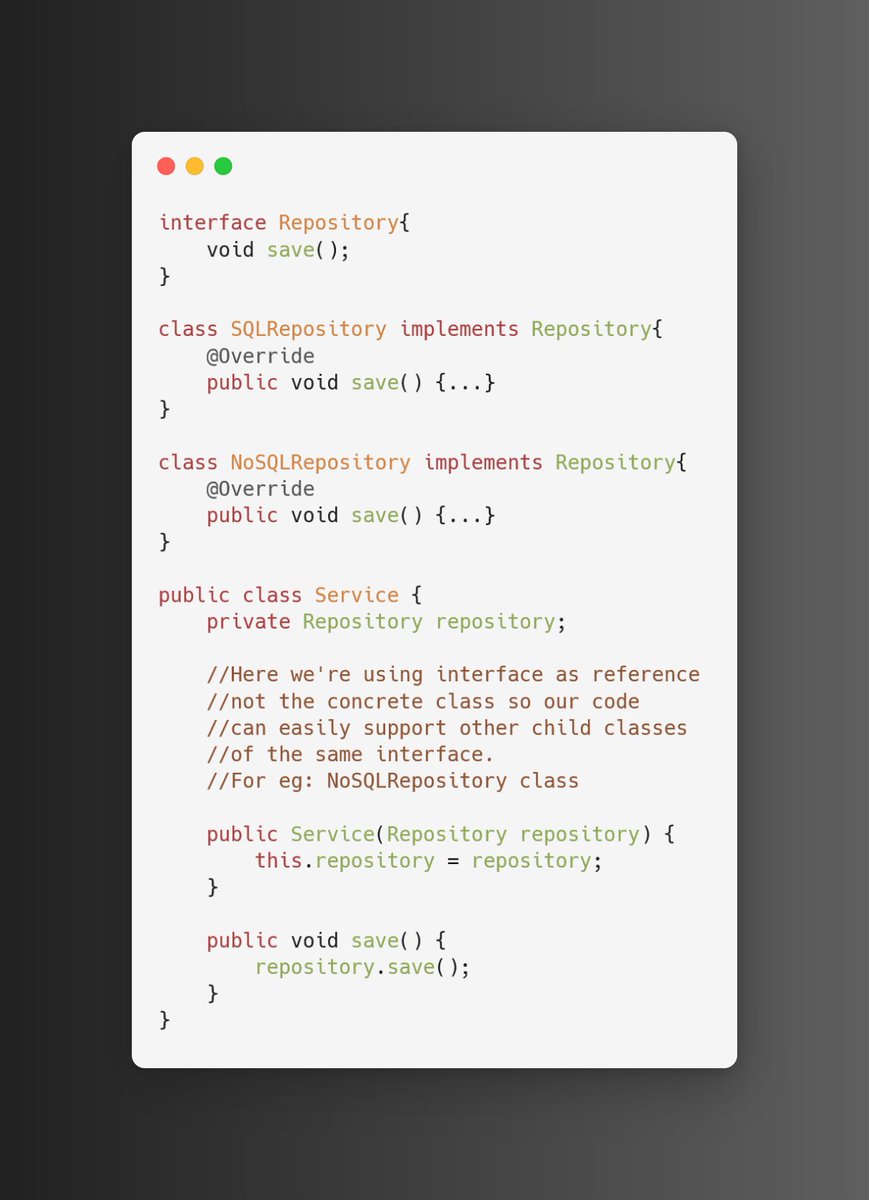
6.2. Good Implementation
Create a parent interface Repository and SQL and NoSQL Repository implements it.
Service class refers to Repository interface, in future if we need to support NoSQL then simply need to pass its instance in constructor without changing Service class.
Create a parent interface Repository and SQL and NoSQL Repository implements it.
Service class refers to Repository interface, in future if we need to support NoSQL then simply need to pass its instance in constructor without changing Service class.
Thanks for reading!
This Saturday, I'm sharing my life story to @thehumansoftech and will be sharing my entire journey as a Backend Engineer do join in.
Details below:
This Saturday, I'm sharing my life story to @thehumansoftech and will be sharing my entire journey as a Backend Engineer do join in.
Details below:
https://x.com/thehumansoftech/status/1715011863946080510?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






