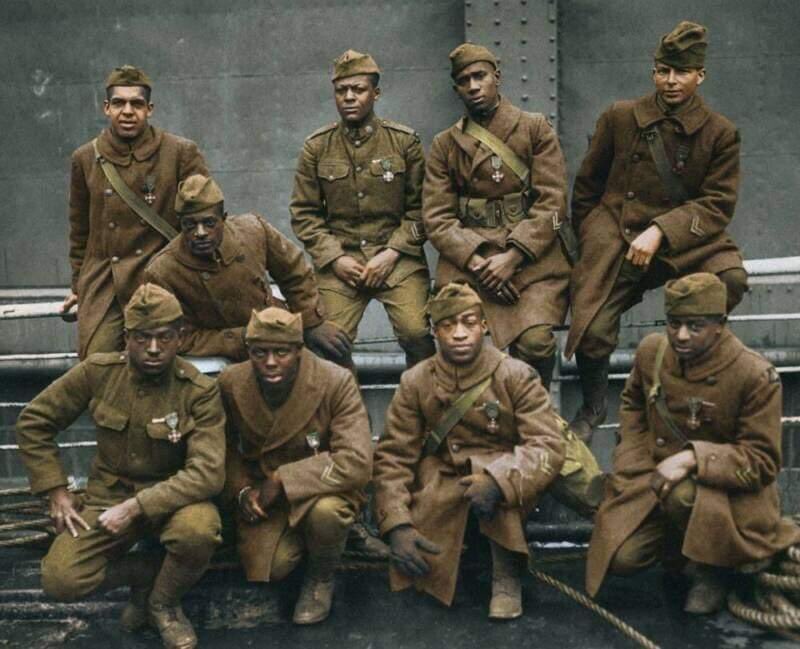
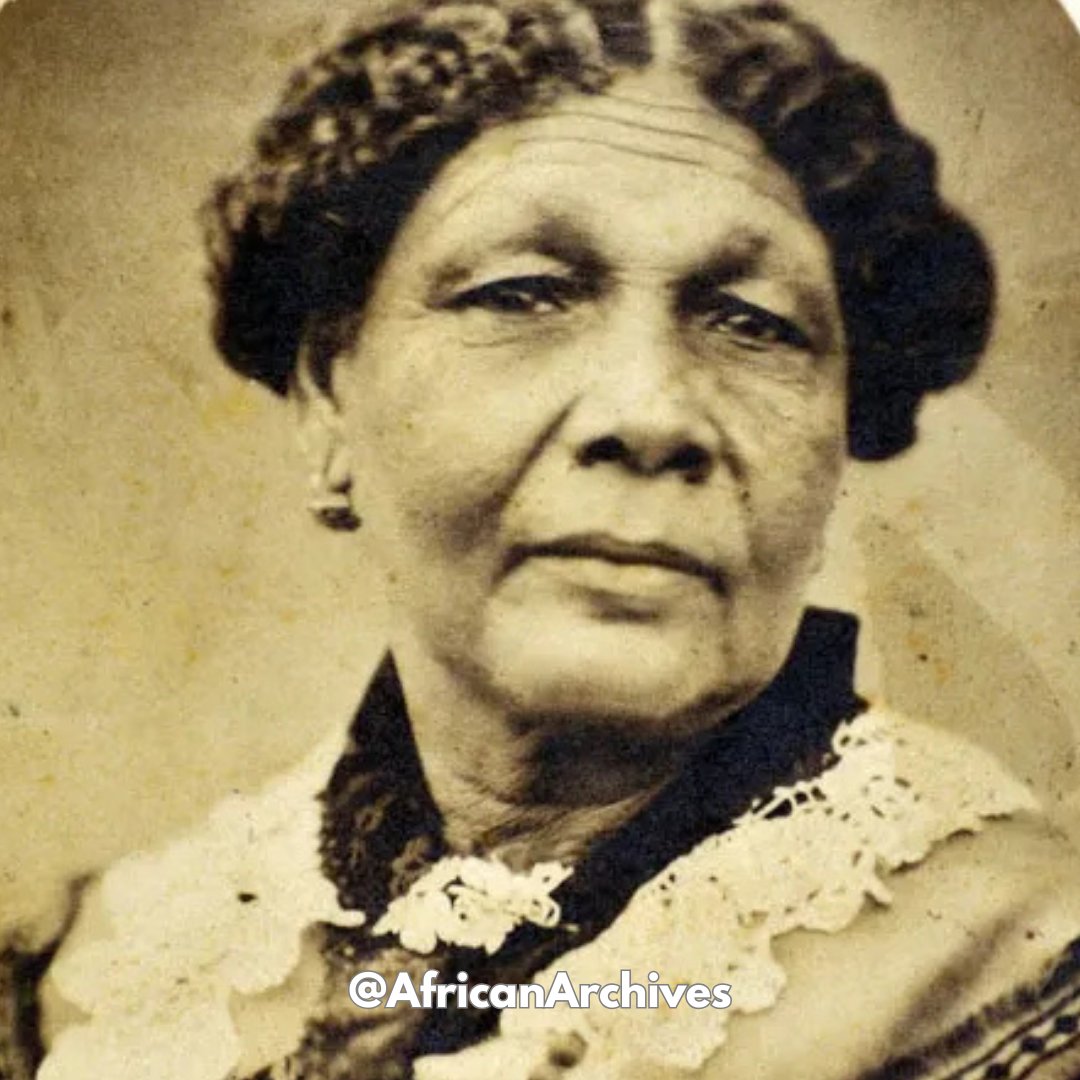
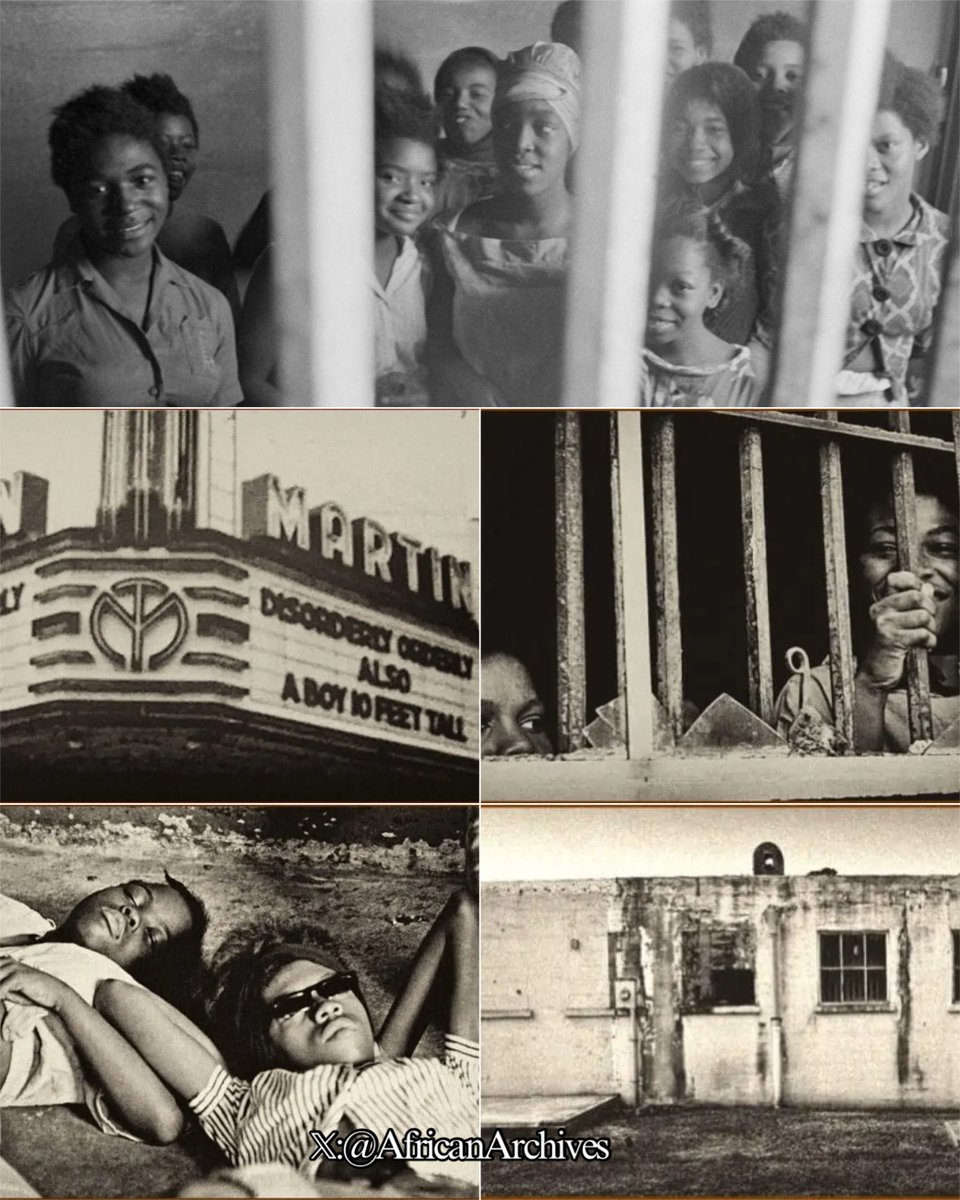
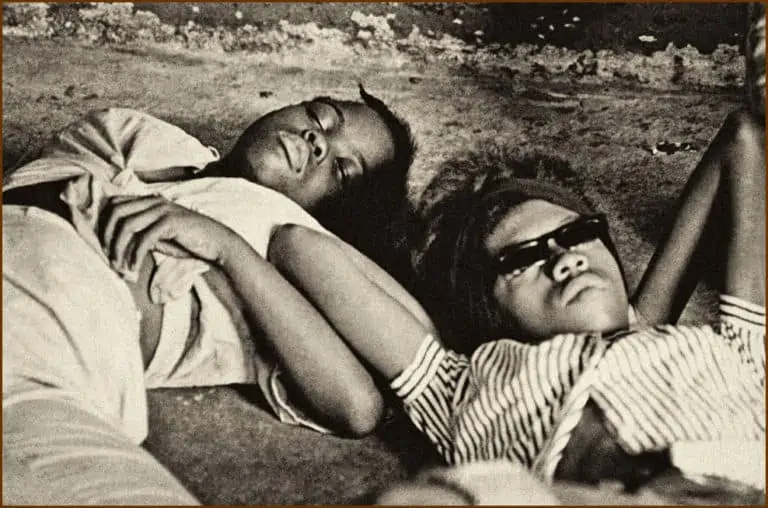
Gaspar Yanga was a liberator and one of Mexico’s heroes, enslaved from West Africa. He fought for the abolition of slavery in Mexico. He was known as “America’s First Liberator” or “El Primer Libertador de las Americas.”
The town of Yanga, Mexico is named after him.
THREAD
The town of Yanga, Mexico is named after him.
THREAD

El Yanga was an African abolitionist and a leader of a slave rebellion in Mexico during the early period of Spanish colonial rule. Mexico was called 'New Spain'. 

Gaspar Yanga, often called Yanga, El Yanga, or Nyanga, was said to be a member of the royal family of Gabon, Africa, before being kidnapped and placed in the Middle Passage to the new world. 

He came to be the head of a group of slaves who were revolting near Vera Cruz, around 1570. Escaping to the highland terrain, he and his people built a small free colony. For more than 30 years it grew, partially surviving by capturing caravans bringing goods to Vera Cruz. 

In 1609, however, the Spanish colonial government sent troops from Pueblo to enslave Yanga and his people again. The Spanish numbered around 550, of which perhaps 100 were Spanish regulars.
Yanga and the Maroons facing them were an irregular force of 100 fighters with some type of firearm, and 400 more with stones, machetes, and bows and arrows. 

These troops were led by Francisco de la Matosa, an Angolan. Yanga, who was quite old at this time, employed his troops' superior knowledge of the area to draw them to the negotiating table.
Yanga’s terms of peace asked for a treaty akin to those that had settled hostilities between Indians and Spaniards: an area of self-rule, in return for tribute, and promises to support the Spanish if they were attacked.
He proposed his district would return any slaves which might flee to it to soothe the worries of the many slave owners in the region. The Spaniards refused the terms, a battle was fought, and the Spaniards advanced into the settlement and burned it. 

Yanga’s people fled into the surrounding highlands, and the Spaniards could not achieve a conclusive victory. Unable to win definitively, they agreed to a conference.
Eventually, Yanga's terms were agreed to, with the additional condition that only Franciscan priests would tend to the people, and that Yanga's family would be granted the right of rule. Finally, in 1630, the town of Yanga was officially established. It remains to this day. 

🖋️if you love our content, please consider supporting our page on (follow the ko-fi page too for weekly posts roundup) AfricanArchives.Support


• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh