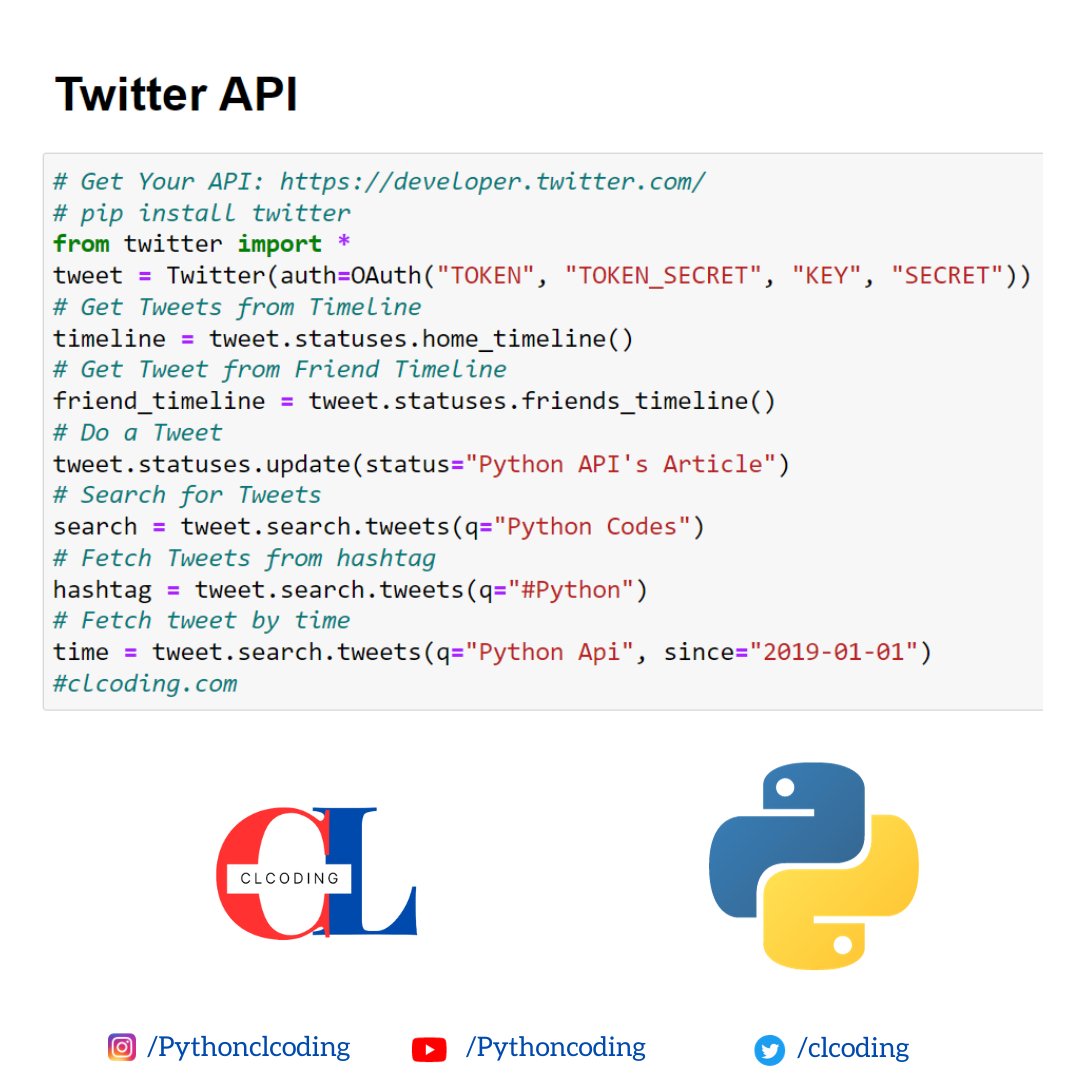
Master in Data Science in 15 hours
🧵:
🧵:
For more understanding - clcoding.com/p/master-in-da…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter