THE CTIL FILES #1
Many people insist that governments aren't involved in censorship, but they are. And now, a whistleblower has come forward with an explosive new trove of documents, rivaling or exceeding the Twitter Files and Facebook Files in scale and importance.
Many people insist that governments aren't involved in censorship, but they are. And now, a whistleblower has come forward with an explosive new trove of documents, rivaling or exceeding the Twitter Files and Facebook Files in scale and importance.
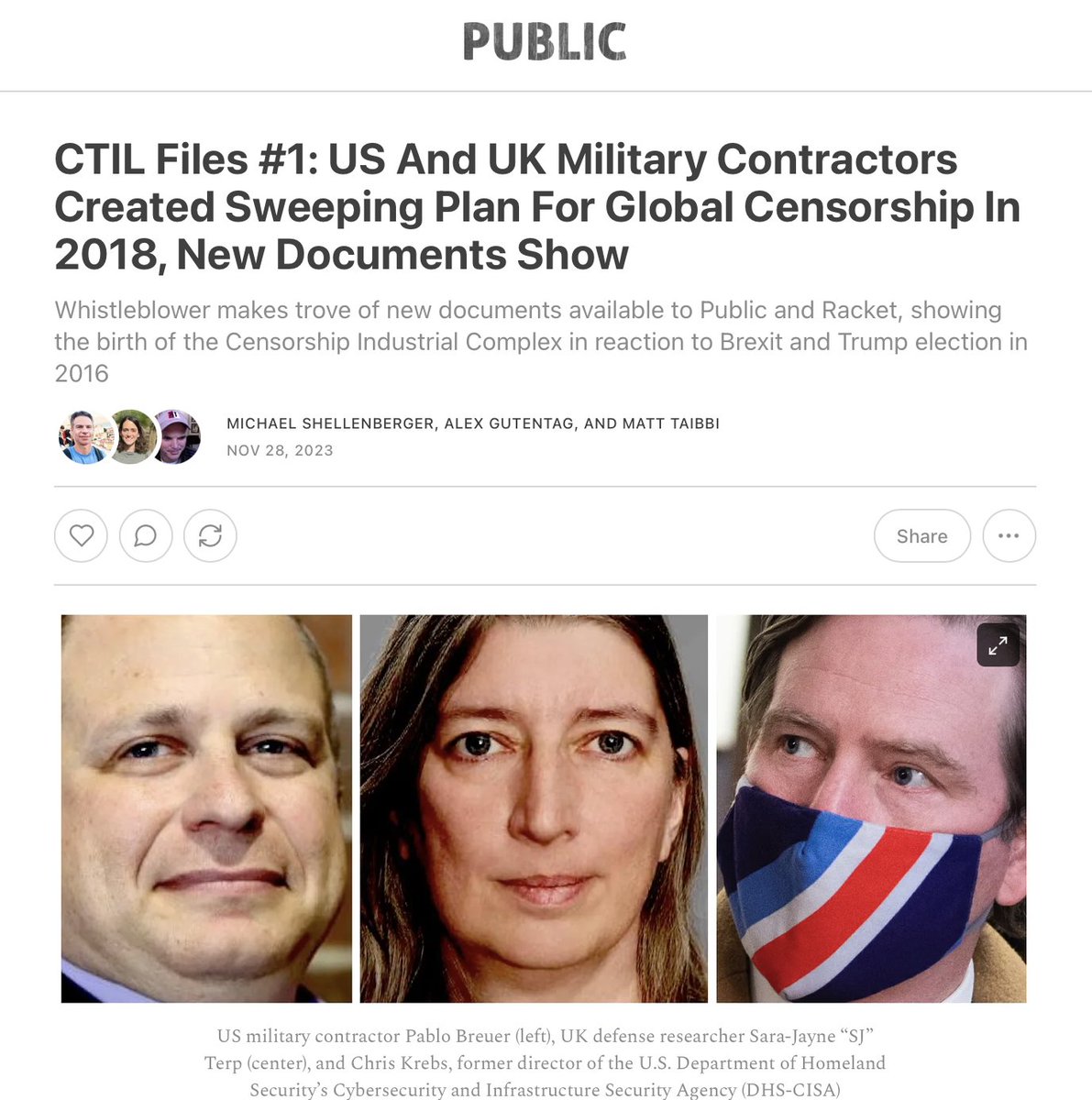
CTIL Files #1: US And UK Military Contractors Created Sweeping Plan For Global Censorship In 2018, New Documents Show
Whistleblower makes trove of new documents available to Public and Racket, showing the birth of the Censorship Industrial Complex in reaction to Brexit and Trump election in 2016
by @shellenberger @galexybrane @mtaibbi
US military contractor Pablo Breuer (left), UK defense researcher Sara-Jayne “SJ” Terp (center), and Chris Krebs, former director of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (DHS-CISA)
A whistleblower has come forward with an explosive new trove of documents, rivaling or exceeding the Twitter Files and Facebook Files in scale and importance. They describe the activities of an “anti-disinformation” group called the Cyber Threat Intelligence League, or CTIL, that officially began as the volunteer project of data scientists and defense and intelligence veterans but whose tactics over time appear to have been absorbed into multiple official projects, including those of the Department of Homeland Security (DHS).
The CTI League documents offer the missing link answers to key questions not addressed in the Twitter Files and Facebook Files. Combined, they offer a comprehensive picture of the birth of the “anti-disinformation” sector, or what we have called the Censorship Industrial Complex.
The whistleblower's documents describe everything from the genesis of modern digital censorship programs to the role of the military and intelligence agencies, partnerships with civil society organizations and commercial media, and the use of sock puppet accounts and other offensive techniques.
"Lock your shit down," explains one document about creating "your spy disguise.”
Another explains that while such activities overseas are "typically" done by "the CIA and NSA and the Department of Defense," censorship efforts "against Americans" have to be done using private partners because the government doesn't have the "legal authority."
The whistleblower alleges that a leader of CTI League, a “former” British intelligence analyst, was “in the room” at the Obama White House in 2017 when she received the instructions to create a counter-disinformation project to stop a "repeat of 2016."
Over the last year, Public, Racket, congressional investigators, and others have documented the rise of the Censorship Industrial Complex, a network of over 100 government agencies and nongovernmental organizations that work together to urge censorship by social media platforms and spread propaganda about disfavored individuals, topics, and whole narratives.
The US Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Information Security Agency (CISA) has been the center of gravity for much of the censorship, with the National Science Foundation financing the development of censorship and disinformation tools and other federal government agencies playing a supportive role.
Emails from CISA’s NGO and social media partners show that CISA created the Election Integrity Partnership (EIP) in 2020, which involved the Stanford Internet Observatory (SIO) and other US government contractors. EIP and its successor, the Virality Project (VP), urged Twitter, Facebook and other platforms to censor social media posts by ordinary citizens and elected officials alike.
Despite the overwhelming evidence of government-sponsored censorship, it had yet to be determined where the idea for such mass censorship came from. In 2018, an SIO official and former CIA fellow, Renee DiResta, generated national headlines before and after testifying to the US Senate about Russian government interference in the 2016 election.
But what happened between 2018 and Spring 2020? The year 2019 has been a black hole in the research of the Censorship Industrial Complex to date. When one of us, Michael, testified to the U.S. House of Representatives about the Censorship Industrial Complex in March of this year, the entire year was missing from his timeline.
An Earlier Start Date for the Censorship Industrial Complex
Now, a large trove of new documents, including strategy documents, training videos, presentations, and internal messages, reveal that, in 2019, US and UK military and intelligence contractors led by a former UK defense researcher, Sara-Jayne “SJ” Terp, developed the sweeping censorship framework. These contractors co-led CTIL, which partnered with CISA in the spring of 2020.
In truth, the building of the Censorship Industrial Complex began even earlier — in 2018.
Internal CTIL Slack messages show Terp, her colleagues, and officials from DHS and Facebook all working closely together in the censorship process.
The CTIL framework and the public-private model are the seeds of what both the US and UK would put into place in 2020 and 2021, including masking censorship within cybersecurity institutions and counter-disinformation agendas; a heavy focus on stopping disfavored narratives, not just wrong facts; and pressuring social media platforms to take down information or take other actions to prevent content from going viral.
In the spring of 2020, CTIL began tracking and reporting disfavored content on social media, such as anti-lockdown narratives like “all jobs are essential,” “we won’t stay home,” and “open America now.” CTIL created a law enforcement channel for reporting content as part of these efforts. The organization also did research on individuals posting anti-lockdown hashtags like #freeCA and kept a spreadsheet with details from their Twitter bios. The group also discussed requesting “takedowns” and reporting website domains to registrars.
CTIL’s approach to “disinformation” went far beyond censorship. The documents show that the group engaged in offensive operations to influence public opinion, discussing ways to promote “counter-messaging,” co-opt hashtags, dilute disfavored messaging, create sock puppet accounts, and infiltrate private invite-only groups.
In one suggested list of survey questions, CTIL proposed asking members or potential members, “Have you worked with influence operations (e.g. disinformation, hate speech, other digital harms etc) previously?” The survey then asked whether these influence operations included “active measures” and “psyops.”
These documents came to us via a highly credible whistleblower. We were able to independently verify their legitimacy through extensive cross-checking of information to publicly available sources. The whistleblower said they were recruited to participate in CTIL through monthly cybersecurity meetings hosted by DHS.
The FBI declined to comment. CISA did not respond to our request for comment. And Terp and the other key CTIL leaders also did not respond to our requests for comment.
But one person involved, Bonnie Smalley, replied over Linked in, saying, “all i can comment on is that i joined cti league which is unaffiliated with any govt orgs because i wanted to combat the inject bleach nonsense online during covid…. i can assure you that we had nothing to do with the govt though.”
Yet the documents suggest that government employees were engaged members of CTIL. One individual who worked for DHS, Justin Frappier, was extremely active in CTIL, participating in regular meetings and leading trainings.
CTIL’s ultimate goal, said the whistleblower, ”was to become part of the federal government. In our weekly meetings, they made it clear that they were building these organizations within the federal government, and if you built the first iteration, we could secure a job for you.”
Terp’s plan, which she shared in presentations to information security and cybersecurity groups in 2019, was to create “Misinfosec communities” that would include government.
Both public records and the whistleblower’s documents suggest that she achieved this. In April 2020, Chris Krebs, then-Director of CISA, announced on Twitter and in multiple articles, that CISA was partnering with CTIL. “It’s really an information exchange,” said Krebs.
The documents also show that Terp and her colleagues, through a group called MisinfoSec Working Group, which included DiResta, created a censorship, influence, and anti-disinformation strategy called Adversarial Misinformation and Influence Tactics and Techniques (AMITT). They wrote AMITT by adapting a cybersecurity framework developed by MITRE, a major defense and intelligence contractor that has an annual budget of $1 to $2 billion in government funding.
Terp later used AMITT to develop the DISARM framework, which the World Health Organization then employed in “countering anti-vaccination campaigns across Europe.”
A key component of Terp’s work through CTIL, MisinfoSec, and AMITT was to insert the concept of “cognitive security” into the fields of cybersecurity and information security.
The sum total of the documents is a clear picture of a highly coordinated and sophisticated effort by the US and UK governments to build a domestic censorship effort and influence operations similar to the ones they have used in foreign countries. At one point, Terp openly referenced her work “in the background” on social media issues related to the Arab Spring. Another time, the whistleblower said, she expressed her own apparent surprise that she would ever use such tactics, developed for foreign nationals, against American citizens.
According to the whistleblower, roughly 12-20 active people involved in CTILworked at the FBI or CISA. “For a while, they had their agency seals — FBI, CISA, whatever — next to your name,” on the Slack messaging service, said the whistleblower. Terp “had a CISA badge that went away at some point,” the whistleblower said.
The ambitions of the 2020 pioneers of the Censorship Industrial Complex went far beyond simply urging Twitter to slap a warning label on Tweets, or to put individuals on blacklists.
The AMITT framework calls for discrediting individuals as a necessary prerequisite of demanding censorship against them. It calls for training influencers to spread messages. And it calls for trying to get banks to cut off financial services to individuals who organize rallies or events.The timeline of CISA’s work with CTIL leading up to its work with EIP and VP strongly suggests that the model for public-private censorship operations may have originated from a framework originally created by military contractors. What’s more, the techniques and materials outlined by CTIL closely resemble materials later created by CISA’s Countering Foreign Intelligence Task Force and Mis-, Dis-, and Maliformation team.
Over the next several days and weeks, we intend to present these documents to Congressional investigators, and will make public all of the documents we can while also protecting the identity of the whistleblower and other individuals who are not senior leaders or public figures.
But for now, we need to take a closer look at what happened in 2018 and 2019, leading up to the creation of CTIL, as well as this group’s key role in the formation and growth of the Censorship Industrial Complex.




Whistleblower makes trove of new documents available to Public and Racket, showing the birth of the Censorship Industrial Complex in reaction to Brexit and Trump election in 2016
by @shellenberger @galexybrane @mtaibbi
US military contractor Pablo Breuer (left), UK defense researcher Sara-Jayne “SJ” Terp (center), and Chris Krebs, former director of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (DHS-CISA)
A whistleblower has come forward with an explosive new trove of documents, rivaling or exceeding the Twitter Files and Facebook Files in scale and importance. They describe the activities of an “anti-disinformation” group called the Cyber Threat Intelligence League, or CTIL, that officially began as the volunteer project of data scientists and defense and intelligence veterans but whose tactics over time appear to have been absorbed into multiple official projects, including those of the Department of Homeland Security (DHS).
The CTI League documents offer the missing link answers to key questions not addressed in the Twitter Files and Facebook Files. Combined, they offer a comprehensive picture of the birth of the “anti-disinformation” sector, or what we have called the Censorship Industrial Complex.
The whistleblower's documents describe everything from the genesis of modern digital censorship programs to the role of the military and intelligence agencies, partnerships with civil society organizations and commercial media, and the use of sock puppet accounts and other offensive techniques.
"Lock your shit down," explains one document about creating "your spy disguise.”
Another explains that while such activities overseas are "typically" done by "the CIA and NSA and the Department of Defense," censorship efforts "against Americans" have to be done using private partners because the government doesn't have the "legal authority."
The whistleblower alleges that a leader of CTI League, a “former” British intelligence analyst, was “in the room” at the Obama White House in 2017 when she received the instructions to create a counter-disinformation project to stop a "repeat of 2016."
Over the last year, Public, Racket, congressional investigators, and others have documented the rise of the Censorship Industrial Complex, a network of over 100 government agencies and nongovernmental organizations that work together to urge censorship by social media platforms and spread propaganda about disfavored individuals, topics, and whole narratives.
The US Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Information Security Agency (CISA) has been the center of gravity for much of the censorship, with the National Science Foundation financing the development of censorship and disinformation tools and other federal government agencies playing a supportive role.
Emails from CISA’s NGO and social media partners show that CISA created the Election Integrity Partnership (EIP) in 2020, which involved the Stanford Internet Observatory (SIO) and other US government contractors. EIP and its successor, the Virality Project (VP), urged Twitter, Facebook and other platforms to censor social media posts by ordinary citizens and elected officials alike.
Despite the overwhelming evidence of government-sponsored censorship, it had yet to be determined where the idea for such mass censorship came from. In 2018, an SIO official and former CIA fellow, Renee DiResta, generated national headlines before and after testifying to the US Senate about Russian government interference in the 2016 election.
But what happened between 2018 and Spring 2020? The year 2019 has been a black hole in the research of the Censorship Industrial Complex to date. When one of us, Michael, testified to the U.S. House of Representatives about the Censorship Industrial Complex in March of this year, the entire year was missing from his timeline.
An Earlier Start Date for the Censorship Industrial Complex
Now, a large trove of new documents, including strategy documents, training videos, presentations, and internal messages, reveal that, in 2019, US and UK military and intelligence contractors led by a former UK defense researcher, Sara-Jayne “SJ” Terp, developed the sweeping censorship framework. These contractors co-led CTIL, which partnered with CISA in the spring of 2020.
In truth, the building of the Censorship Industrial Complex began even earlier — in 2018.
Internal CTIL Slack messages show Terp, her colleagues, and officials from DHS and Facebook all working closely together in the censorship process.
The CTIL framework and the public-private model are the seeds of what both the US and UK would put into place in 2020 and 2021, including masking censorship within cybersecurity institutions and counter-disinformation agendas; a heavy focus on stopping disfavored narratives, not just wrong facts; and pressuring social media platforms to take down information or take other actions to prevent content from going viral.
In the spring of 2020, CTIL began tracking and reporting disfavored content on social media, such as anti-lockdown narratives like “all jobs are essential,” “we won’t stay home,” and “open America now.” CTIL created a law enforcement channel for reporting content as part of these efforts. The organization also did research on individuals posting anti-lockdown hashtags like #freeCA and kept a spreadsheet with details from their Twitter bios. The group also discussed requesting “takedowns” and reporting website domains to registrars.
CTIL’s approach to “disinformation” went far beyond censorship. The documents show that the group engaged in offensive operations to influence public opinion, discussing ways to promote “counter-messaging,” co-opt hashtags, dilute disfavored messaging, create sock puppet accounts, and infiltrate private invite-only groups.
In one suggested list of survey questions, CTIL proposed asking members or potential members, “Have you worked with influence operations (e.g. disinformation, hate speech, other digital harms etc) previously?” The survey then asked whether these influence operations included “active measures” and “psyops.”
These documents came to us via a highly credible whistleblower. We were able to independently verify their legitimacy through extensive cross-checking of information to publicly available sources. The whistleblower said they were recruited to participate in CTIL through monthly cybersecurity meetings hosted by DHS.
The FBI declined to comment. CISA did not respond to our request for comment. And Terp and the other key CTIL leaders also did not respond to our requests for comment.
But one person involved, Bonnie Smalley, replied over Linked in, saying, “all i can comment on is that i joined cti league which is unaffiliated with any govt orgs because i wanted to combat the inject bleach nonsense online during covid…. i can assure you that we had nothing to do with the govt though.”
Yet the documents suggest that government employees were engaged members of CTIL. One individual who worked for DHS, Justin Frappier, was extremely active in CTIL, participating in regular meetings and leading trainings.
CTIL’s ultimate goal, said the whistleblower, ”was to become part of the federal government. In our weekly meetings, they made it clear that they were building these organizations within the federal government, and if you built the first iteration, we could secure a job for you.”
Terp’s plan, which she shared in presentations to information security and cybersecurity groups in 2019, was to create “Misinfosec communities” that would include government.
Both public records and the whistleblower’s documents suggest that she achieved this. In April 2020, Chris Krebs, then-Director of CISA, announced on Twitter and in multiple articles, that CISA was partnering with CTIL. “It’s really an information exchange,” said Krebs.
The documents also show that Terp and her colleagues, through a group called MisinfoSec Working Group, which included DiResta, created a censorship, influence, and anti-disinformation strategy called Adversarial Misinformation and Influence Tactics and Techniques (AMITT). They wrote AMITT by adapting a cybersecurity framework developed by MITRE, a major defense and intelligence contractor that has an annual budget of $1 to $2 billion in government funding.
Terp later used AMITT to develop the DISARM framework, which the World Health Organization then employed in “countering anti-vaccination campaigns across Europe.”
A key component of Terp’s work through CTIL, MisinfoSec, and AMITT was to insert the concept of “cognitive security” into the fields of cybersecurity and information security.
The sum total of the documents is a clear picture of a highly coordinated and sophisticated effort by the US and UK governments to build a domestic censorship effort and influence operations similar to the ones they have used in foreign countries. At one point, Terp openly referenced her work “in the background” on social media issues related to the Arab Spring. Another time, the whistleblower said, she expressed her own apparent surprise that she would ever use such tactics, developed for foreign nationals, against American citizens.
According to the whistleblower, roughly 12-20 active people involved in CTILworked at the FBI or CISA. “For a while, they had their agency seals — FBI, CISA, whatever — next to your name,” on the Slack messaging service, said the whistleblower. Terp “had a CISA badge that went away at some point,” the whistleblower said.
The ambitions of the 2020 pioneers of the Censorship Industrial Complex went far beyond simply urging Twitter to slap a warning label on Tweets, or to put individuals on blacklists.
The AMITT framework calls for discrediting individuals as a necessary prerequisite of demanding censorship against them. It calls for training influencers to spread messages. And it calls for trying to get banks to cut off financial services to individuals who organize rallies or events.The timeline of CISA’s work with CTIL leading up to its work with EIP and VP strongly suggests that the model for public-private censorship operations may have originated from a framework originally created by military contractors. What’s more, the techniques and materials outlined by CTIL closely resemble materials later created by CISA’s Countering Foreign Intelligence Task Force and Mis-, Dis-, and Maliformation team.
Over the next several days and weeks, we intend to present these documents to Congressional investigators, and will make public all of the documents we can while also protecting the identity of the whistleblower and other individuals who are not senior leaders or public figures.
But for now, we need to take a closer look at what happened in 2018 and 2019, leading up to the creation of CTIL, as well as this group’s key role in the formation and growth of the Censorship Industrial Complex.



“Volunteer” and “Former” Government Agents
Bloomberg, Washington Post and others published credulous stories in the spring of 2020 claiming that the CTI League was simply a group of volunteer cybersecurity experts. Its founders were: a “former” Israeli intelligence official, Ohad Zaidenberg; a Microsoft “security manager,” Nate Warfield; and the head of sec ops for DEF CON, a hackers convention, Marc Rogers. The articles claimed that those highly skilled cybercrime professionals had decided to help billion-dollar hospitals, on their own time and without pay, for strictly altruistic motives.
In just one month, from mid-March to mid-April, the supposedly all-volunteer CTIL had grown to “1,400 vetted members in 76 countries spanning 45 different sectors,” had “helped to lawfully take down 2,833 cybercriminal assets on the internet, including 17 designed to impersonate government organizations, the United Nations, and the World Health Organization,” and had “identified more than 2,000 vulnerabilities in healthcare institutions in more than 80 countries.”
At every opportunity the men stressed that they were simply volunteers motivated by altruism. “I knew I had to do something to help,” said Zaidenberg. ”There is a really strong appetite for doing good in the community,” Rogers said during an Aspen Institute webinar.
And yet a clear goal of CTIL’s leaders was to build support for censorship among national security and cybersecurity institutions. Toward that end, they sought to promote the idea of “cognitive security” as a rationale for government involvement in censorship activities. “Cognitive security is the thing you want to have,” said Terp on a 2019 podcast. “You want to protect that cognitive layer. It basically, it’s about pollution. Misinformation, disinformation, is a form of pollution across the Internet.”
Terp and Pablo Breuer, another CTIL leader, like Zaidenberg, had backgrounds in the military and were former military contractors. Both have worked for SOFWERX, “a collaborative project of the U.S. Special Forces Command and Doolittle Institute.” The latter transfers Air Force technology, through the Air Force Resource Lab, to the private sector.
According to Terp’s bio on the website of a consulting firm she created with Breuer, “She’s taught data science at Columbia University, was CTO of the UN’s big data team, designed machine learning algorithms and unmanned vehicle systems at the UK Ministry of Defence.
Breuer is a former US Navy commander. According to his bio, he was “military director of US Special Operations Command Donovan Group and senior military advisor and innovation officer to SOFWERX, the National Security Agency, and U.S. Cyber Command as well as being the Director of C4 at U.S. Naval Forces Central Command.” Breuer is listed as having been in the Navy during the creation of CTIL on his LinkedIn page.
In June, 2018, Terp attended a ten-day military exercise organized by the US Special Operations Command, where she says she first met Breuer and discussed modern disinformation campaigns on social media. Wired summed up the conclusions they drew from their meeting: “Misinformation, they realized, could be treated the same way: as a cybersecurity problem.” And so they created CogSec with David Perlman and another colleague, Thaddeus Grugq, at the lead. In 2019, Terp co-chaired the Misinfosec Working Group within CogSec.
Breuer admitted in a podcast that his aim was to bring military tactics to use on social media platforms in the U.S. “I wear two hats,” he explained. “The military director of the Donovan Group, and one of two innovation officers at Sofwerx, which is a completely unclassified 501c3 nonprofit that's funded by U. S. Special Operations Command.”
Breuer went on to describe how they thought they were getting around the First Amendment. His work with Terp, he explained, was a way to get “nontraditional partners into one room,” including “maybe somebody from one of the social media companies, maybe a few special forces operators, and some folks from Department of Homeland Security… to talk in a non-attribution, open environment in an unclassified way so that we can collaborate better, more freely and really start to change the way that we address some of these issues.”
The Misinfosec report advocated for sweeping government censorship and counter-misinformation. During the first six months of 2019, the authors say, they analyzed “incidents,” developed a reporting system, and shared their censorship vision with “numerous state, treaty and NGOs.”
In every incident mentioned, the victims of misinformation were on the political Left, and they included Barack Obama, John Podesta, Hillary Clinton, and Emmanuel Macron. The report was open about the fact that its motivation for counter-misinformation were the twin political earthquakes of 2016: Brexit and the election of Trump.
“A study of the antecedents to these events lead us to the realization that there’s something off kilter with our information landscape,” wrote Terp and her co-authors. “The usual useful idiots and fifth columnists—now augmented by automated bots, cyborgs and human trolls—are busily engineering public opinion, stoking up outrage, sowing doubt and chipping away at trust in our institutions. And now it’s our brains that are being hacked.”
The Misinfosec report focused on information that “changes beliefs” through “narratives,” and recommended a way to counter misinformation by attacking specific links in a “kill chain” or influence chain from the misinfo “incident” before it becomes a full-blown narrative.
The report laments that governments and corporate media no longer have full control of information. “For a long time, the ability to reach mass audiences belonged to the nation-state (e.g. in the USA via broadcast licensing through ABC, CBS and NBC). Now, however, control of informational instruments has been allowed to devolve to large technology companies who have been blissfully complacent and complicit in facilitating access to the public for information operators at a fraction of what it would have cost them by other means.”
The authors advocated for police, military, and intelligence involvement in censorship, across Five Eyes nations, and even suggested that Interpol should be involved.
The report proposed a plan for AMITT and for security, intelligence, and law enforcement collaboration and argued for immediate implementation. “We do not need, nor can we afford, to wait 27 years for the AMITT (Adversarial Misinformation and Influence Tactics and Techniques) framework to go into use.”
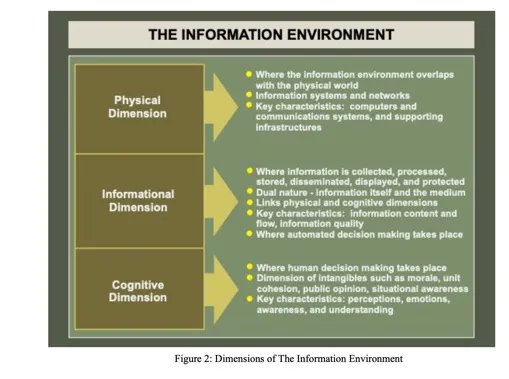
The authors called for placing censorship efforts inside of “cybersecurity” even while acknowledging that “misinformation security” is utterly different from cybersecurity. They wrote that the third pillar of “The information environment” after physical and cybersecurity should be “The Cognitive Dimension.”
The report flagged the need for a kind of pre-bunking to “preemptively inoculate a vulnerable population against messaging.” The report also pointed to the opportunity to use the DHS-funded Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs) as the homes for orchestrating public-private censorship, and argued that these ISACs should be used to promote confidence in government.
It is here that we see the idea for the EIP and VP: “While social media is not identified as a critical sector, and therefore doesn’t qualify for an ISAC, a misinformation ISAC could and should feed indications and warnings into ISACs.”
Terp’s view of “disinformation” was overtly political. “Most misinformation is actually true,” noted Terp in the 2019 podcast, “but set in the wrong context.” Terp is an eloquent explainer of the strategy of using “anti-disinformation” efforts to conduct influence operations. “You're not trying to get people to believe lies most of the time. Most of the time, you're trying to change their belief sets. And in fact, really, uh, deeper than that, you're trying to change, to shift their internal narratives… the set of stories that are your baseline for your culture. So that might be the baseline for your culture as an American.”
In the fall, Terp and others sought to promote their report. The podcast Terp did with Breuer in 2019 was one example of this effort. Together Terp and Breuer described the “public-private” model of censorship laundering that DHS, EIP, and VP would go on to embrace.
Breuer spoke freely, openly stating that the information and narrative control he had in mind was comparable to that implemented by the Chinese government, only made more palatable for Americans. “If you talk to the average Chinese citizen, they absolutely believe that the Great Firewall of China is not there for censorship. They believe that it's there because the Chinese Communist Party wants to protect the citizenry and they absolutely believe that's a good thing. If the US government tried to sell that narrative, we would absolutely lose our minds and say, ‘No, no, this is a violation of our First Amendment rights. So the in-group and out-group messaging have to be often different.”



Bloomberg, Washington Post and others published credulous stories in the spring of 2020 claiming that the CTI League was simply a group of volunteer cybersecurity experts. Its founders were: a “former” Israeli intelligence official, Ohad Zaidenberg; a Microsoft “security manager,” Nate Warfield; and the head of sec ops for DEF CON, a hackers convention, Marc Rogers. The articles claimed that those highly skilled cybercrime professionals had decided to help billion-dollar hospitals, on their own time and without pay, for strictly altruistic motives.
In just one month, from mid-March to mid-April, the supposedly all-volunteer CTIL had grown to “1,400 vetted members in 76 countries spanning 45 different sectors,” had “helped to lawfully take down 2,833 cybercriminal assets on the internet, including 17 designed to impersonate government organizations, the United Nations, and the World Health Organization,” and had “identified more than 2,000 vulnerabilities in healthcare institutions in more than 80 countries.”
At every opportunity the men stressed that they were simply volunteers motivated by altruism. “I knew I had to do something to help,” said Zaidenberg. ”There is a really strong appetite for doing good in the community,” Rogers said during an Aspen Institute webinar.
And yet a clear goal of CTIL’s leaders was to build support for censorship among national security and cybersecurity institutions. Toward that end, they sought to promote the idea of “cognitive security” as a rationale for government involvement in censorship activities. “Cognitive security is the thing you want to have,” said Terp on a 2019 podcast. “You want to protect that cognitive layer. It basically, it’s about pollution. Misinformation, disinformation, is a form of pollution across the Internet.”
Terp and Pablo Breuer, another CTIL leader, like Zaidenberg, had backgrounds in the military and were former military contractors. Both have worked for SOFWERX, “a collaborative project of the U.S. Special Forces Command and Doolittle Institute.” The latter transfers Air Force technology, through the Air Force Resource Lab, to the private sector.
According to Terp’s bio on the website of a consulting firm she created with Breuer, “She’s taught data science at Columbia University, was CTO of the UN’s big data team, designed machine learning algorithms and unmanned vehicle systems at the UK Ministry of Defence.
Breuer is a former US Navy commander. According to his bio, he was “military director of US Special Operations Command Donovan Group and senior military advisor and innovation officer to SOFWERX, the National Security Agency, and U.S. Cyber Command as well as being the Director of C4 at U.S. Naval Forces Central Command.” Breuer is listed as having been in the Navy during the creation of CTIL on his LinkedIn page.
In June, 2018, Terp attended a ten-day military exercise organized by the US Special Operations Command, where she says she first met Breuer and discussed modern disinformation campaigns on social media. Wired summed up the conclusions they drew from their meeting: “Misinformation, they realized, could be treated the same way: as a cybersecurity problem.” And so they created CogSec with David Perlman and another colleague, Thaddeus Grugq, at the lead. In 2019, Terp co-chaired the Misinfosec Working Group within CogSec.
Breuer admitted in a podcast that his aim was to bring military tactics to use on social media platforms in the U.S. “I wear two hats,” he explained. “The military director of the Donovan Group, and one of two innovation officers at Sofwerx, which is a completely unclassified 501c3 nonprofit that's funded by U. S. Special Operations Command.”
Breuer went on to describe how they thought they were getting around the First Amendment. His work with Terp, he explained, was a way to get “nontraditional partners into one room,” including “maybe somebody from one of the social media companies, maybe a few special forces operators, and some folks from Department of Homeland Security… to talk in a non-attribution, open environment in an unclassified way so that we can collaborate better, more freely and really start to change the way that we address some of these issues.”
The Misinfosec report advocated for sweeping government censorship and counter-misinformation. During the first six months of 2019, the authors say, they analyzed “incidents,” developed a reporting system, and shared their censorship vision with “numerous state, treaty and NGOs.”
In every incident mentioned, the victims of misinformation were on the political Left, and they included Barack Obama, John Podesta, Hillary Clinton, and Emmanuel Macron. The report was open about the fact that its motivation for counter-misinformation were the twin political earthquakes of 2016: Brexit and the election of Trump.
“A study of the antecedents to these events lead us to the realization that there’s something off kilter with our information landscape,” wrote Terp and her co-authors. “The usual useful idiots and fifth columnists—now augmented by automated bots, cyborgs and human trolls—are busily engineering public opinion, stoking up outrage, sowing doubt and chipping away at trust in our institutions. And now it’s our brains that are being hacked.”
The Misinfosec report focused on information that “changes beliefs” through “narratives,” and recommended a way to counter misinformation by attacking specific links in a “kill chain” or influence chain from the misinfo “incident” before it becomes a full-blown narrative.
The report laments that governments and corporate media no longer have full control of information. “For a long time, the ability to reach mass audiences belonged to the nation-state (e.g. in the USA via broadcast licensing through ABC, CBS and NBC). Now, however, control of informational instruments has been allowed to devolve to large technology companies who have been blissfully complacent and complicit in facilitating access to the public for information operators at a fraction of what it would have cost them by other means.”
The authors advocated for police, military, and intelligence involvement in censorship, across Five Eyes nations, and even suggested that Interpol should be involved.
The report proposed a plan for AMITT and for security, intelligence, and law enforcement collaboration and argued for immediate implementation. “We do not need, nor can we afford, to wait 27 years for the AMITT (Adversarial Misinformation and Influence Tactics and Techniques) framework to go into use.”
The authors called for placing censorship efforts inside of “cybersecurity” even while acknowledging that “misinformation security” is utterly different from cybersecurity. They wrote that the third pillar of “The information environment” after physical and cybersecurity should be “The Cognitive Dimension.”
The report flagged the need for a kind of pre-bunking to “preemptively inoculate a vulnerable population against messaging.” The report also pointed to the opportunity to use the DHS-funded Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs) as the homes for orchestrating public-private censorship, and argued that these ISACs should be used to promote confidence in government.
It is here that we see the idea for the EIP and VP: “While social media is not identified as a critical sector, and therefore doesn’t qualify for an ISAC, a misinformation ISAC could and should feed indications and warnings into ISACs.”
Terp’s view of “disinformation” was overtly political. “Most misinformation is actually true,” noted Terp in the 2019 podcast, “but set in the wrong context.” Terp is an eloquent explainer of the strategy of using “anti-disinformation” efforts to conduct influence operations. “You're not trying to get people to believe lies most of the time. Most of the time, you're trying to change their belief sets. And in fact, really, uh, deeper than that, you're trying to change, to shift their internal narratives… the set of stories that are your baseline for your culture. So that might be the baseline for your culture as an American.”
In the fall, Terp and others sought to promote their report. The podcast Terp did with Breuer in 2019 was one example of this effort. Together Terp and Breuer described the “public-private” model of censorship laundering that DHS, EIP, and VP would go on to embrace.
Breuer spoke freely, openly stating that the information and narrative control he had in mind was comparable to that implemented by the Chinese government, only made more palatable for Americans. “If you talk to the average Chinese citizen, they absolutely believe that the Great Firewall of China is not there for censorship. They believe that it's there because the Chinese Communist Party wants to protect the citizenry and they absolutely believe that's a good thing. If the US government tried to sell that narrative, we would absolutely lose our minds and say, ‘No, no, this is a violation of our First Amendment rights. So the in-group and out-group messaging have to be often different.”


“Hogwarts School of Misinformation”
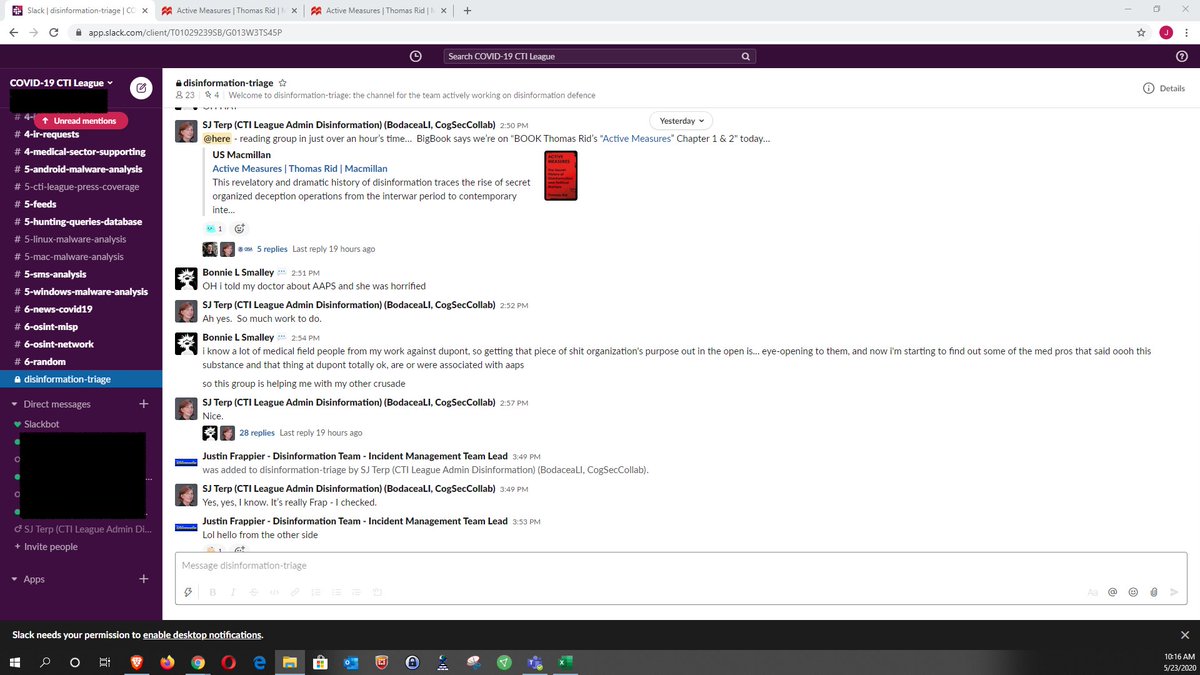
“SJ called us the ‘Hogwarts school for misinformation and disinformation,’” said the whistleblower. “They were superheroes in their own story. And to that effect you could still find comic books on the CISA site.”
CTIL, the whistleblower said, “needed programmers to pull apart information from Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube. For Twitter they created Python code to scrape.”
The CTIL records provided by the whistleblower illustrate exactly how CTIL operated and tracked “incidents,” as well as what it considered to be “disinformation.” About the “we won’t stay home” narrative, CTIL members wrote, “Do we have enough to ask for the groups and/or accounts to be taken down or at a minimum reported and checked?” and “Can we get all troll on their bums if not?”
They tracked posters calling for anti-lockdown protests as disinformation artifacts.
“We should have seen this one coming,” they wrote about the protests. “Bottom line: can we stop the spread, do we have enough evidence to stop superspreaders, and are there other things we can do (are there countermessagers we can ping etc).”
CTIL also worked to brainstorm counter-messaging for things like encouraging people to wear masks and discussed building an amplification network. “Repetition is truth,” said a CTIL member in one training.
CTIL worked with other figures and groups in the Censorship Industrial Complex. Meeting notes indicate that Graphika’s team looked into adopting AMITT and that CTIL wanted to consult DiResta about getting platforms to remove content more quickly.
When asked whether Terp or other CTIL leaders discussed their potential violation of the First Amendment, the whistleblower said, “They did not… The ethos was that if we get away with it, it’s legal, and there were no First Amendment concerns because we have a ‘public-private partnership’ — that’s the word they used to disguise those concerns. ‘Private people can do things public servants can’t do, and public servants can provide the leadership and coordination.’”
Despite their confidence in the legality of their activities, some CTIL members may have taken extreme measures to keep their identities a secret. The group’s handbook recommends using burner phones, creating pseudonymous identities, and generating fake AI faces using the “This person does not exist” website.
In June 2020, the whistleblower says, the secretive group took actions to conceal their activities even more.
One month later, In July 2020, SIO’s Director, Alex Stamos emailed Kate Starbird from the University of Washington’s Center for an Informed Public, writing, “We are working on some election monitoring ideas with CISA and I would love your informal feedback before we go too far down this road . . . . [T]hings that should have been assembled a year ago are coming together quickly this week.”
That summer CISA also created the Countering Foreign Influence Task Force which has measures that reflect CTIL/AMITT methods and includes a “real fake” graphic novel the whistleblower said was first pitched within CTIL.
The “DISARM” framework, which AMITT inspired, has been formally adopted by the European Union and the United States as part of a “common standard for exchanging structured threat information on Foreign Information Manipulation and Interference.”
Until now, the details of CTIL’s activities have received little attention even though the group received publicity in 2020. In September 2020, Wired published an article about CTIL that reads like a company press release. The article, like the Bloomberg and Washington Post stories that spring, accepts unquestioningly that the CTIL was truly a “volunteer” network of “former” intelligence officials from around the world.
But unlike the Bloomberg and Washington Post stories, Wired also describes CTIL’s “anti-misinformation” work. The Wired reporter does not quote any critic of the CTIL activities, but suggests that some might see something wrong with them. “I ask him [CTIL co-founder Marc Rogers] about the notion of viewing misinformation as a cyber threat. “All of these bad actors are trying to do the same thing, Rogers says.”
In other words, the connection between preventing cyber crimes, and “fighting misinformation,” are basically the same because they both involve fighting what the DHS and CTI League alike call “malicious actors,” which is synonymous with “bad guys.”
“Like Terp, Rogers takes a holistic approach to cybersecurity,” the Wired article explains. “First there’s physical security, like stealing data from a computer onto a USB drive. Then there’s what we typically think of as cybersecurity—securing networks and devices from unwanted intrusions. And finally, you have what Rogers and Terp call cognitive security, which essentially is hacking people, using information, or more often, misinformation.”
CTIL appears to have generated publicity about itself in the Spring and Fall of 2020 for the same reason EIP did: to claim later that its work was all out in the open and that anybody who suggested it was secretive was engaging in a conspiracy theory.
“The Election Integrity Partnership has always operated openly and transparently,” EIP claimed in October 2022. “We published multiple public blog posts in the run-up to the 2020 election, hosted daily webinars immediately before and after the election, and published our results in a 290-page final report and multiple peer-reviewed academic journals. Any insinuation that information about our operations or findings were secret up to this point is disproven by the two years of free, public content we have created.”
But as internal messages have revealed, much of what EIP did was secret, as well as partisan, and demanding of censorship by social media platforms, contrary to its claims to the contrary.
EIP and VP, ostensibly, ended, but CTIL is apparently still active today. Several of its members list CTIL as an organization that is still active on their LinkedIn pages.



“SJ called us the ‘Hogwarts school for misinformation and disinformation,’” said the whistleblower. “They were superheroes in their own story. And to that effect you could still find comic books on the CISA site.”
CTIL, the whistleblower said, “needed programmers to pull apart information from Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube. For Twitter they created Python code to scrape.”
The CTIL records provided by the whistleblower illustrate exactly how CTIL operated and tracked “incidents,” as well as what it considered to be “disinformation.” About the “we won’t stay home” narrative, CTIL members wrote, “Do we have enough to ask for the groups and/or accounts to be taken down or at a minimum reported and checked?” and “Can we get all troll on their bums if not?”
They tracked posters calling for anti-lockdown protests as disinformation artifacts.
“We should have seen this one coming,” they wrote about the protests. “Bottom line: can we stop the spread, do we have enough evidence to stop superspreaders, and are there other things we can do (are there countermessagers we can ping etc).”
CTIL also worked to brainstorm counter-messaging for things like encouraging people to wear masks and discussed building an amplification network. “Repetition is truth,” said a CTIL member in one training.
CTIL worked with other figures and groups in the Censorship Industrial Complex. Meeting notes indicate that Graphika’s team looked into adopting AMITT and that CTIL wanted to consult DiResta about getting platforms to remove content more quickly.
When asked whether Terp or other CTIL leaders discussed their potential violation of the First Amendment, the whistleblower said, “They did not… The ethos was that if we get away with it, it’s legal, and there were no First Amendment concerns because we have a ‘public-private partnership’ — that’s the word they used to disguise those concerns. ‘Private people can do things public servants can’t do, and public servants can provide the leadership and coordination.’”
Despite their confidence in the legality of their activities, some CTIL members may have taken extreme measures to keep their identities a secret. The group’s handbook recommends using burner phones, creating pseudonymous identities, and generating fake AI faces using the “This person does not exist” website.
In June 2020, the whistleblower says, the secretive group took actions to conceal their activities even more.
One month later, In July 2020, SIO’s Director, Alex Stamos emailed Kate Starbird from the University of Washington’s Center for an Informed Public, writing, “We are working on some election monitoring ideas with CISA and I would love your informal feedback before we go too far down this road . . . . [T]hings that should have been assembled a year ago are coming together quickly this week.”
That summer CISA also created the Countering Foreign Influence Task Force which has measures that reflect CTIL/AMITT methods and includes a “real fake” graphic novel the whistleblower said was first pitched within CTIL.
The “DISARM” framework, which AMITT inspired, has been formally adopted by the European Union and the United States as part of a “common standard for exchanging structured threat information on Foreign Information Manipulation and Interference.”
Until now, the details of CTIL’s activities have received little attention even though the group received publicity in 2020. In September 2020, Wired published an article about CTIL that reads like a company press release. The article, like the Bloomberg and Washington Post stories that spring, accepts unquestioningly that the CTIL was truly a “volunteer” network of “former” intelligence officials from around the world.
But unlike the Bloomberg and Washington Post stories, Wired also describes CTIL’s “anti-misinformation” work. The Wired reporter does not quote any critic of the CTIL activities, but suggests that some might see something wrong with them. “I ask him [CTIL co-founder Marc Rogers] about the notion of viewing misinformation as a cyber threat. “All of these bad actors are trying to do the same thing, Rogers says.”
In other words, the connection between preventing cyber crimes, and “fighting misinformation,” are basically the same because they both involve fighting what the DHS and CTI League alike call “malicious actors,” which is synonymous with “bad guys.”
“Like Terp, Rogers takes a holistic approach to cybersecurity,” the Wired article explains. “First there’s physical security, like stealing data from a computer onto a USB drive. Then there’s what we typically think of as cybersecurity—securing networks and devices from unwanted intrusions. And finally, you have what Rogers and Terp call cognitive security, which essentially is hacking people, using information, or more often, misinformation.”
CTIL appears to have generated publicity about itself in the Spring and Fall of 2020 for the same reason EIP did: to claim later that its work was all out in the open and that anybody who suggested it was secretive was engaging in a conspiracy theory.
“The Election Integrity Partnership has always operated openly and transparently,” EIP claimed in October 2022. “We published multiple public blog posts in the run-up to the 2020 election, hosted daily webinars immediately before and after the election, and published our results in a 290-page final report and multiple peer-reviewed academic journals. Any insinuation that information about our operations or findings were secret up to this point is disproven by the two years of free, public content we have created.”
But as internal messages have revealed, much of what EIP did was secret, as well as partisan, and demanding of censorship by social media platforms, contrary to its claims to the contrary.
EIP and VP, ostensibly, ended, but CTIL is apparently still active today. Several of its members list CTIL as an organization that is still active on their LinkedIn pages.



I look forward to providing testimony to Congress, this Thursday, about the Censorship Industrial Complex's clear and present threat to the United States of America and other liberal democratic Western democracies, and how we can shut it down.
https://x.com/Weaponization/status/1729184280650404084?s=20
The CTIL Files are a breakthrough because they allow us to see inside of the Censorship Industrial Complex from the perspective of the Deep State.
We now have multiple sight lines: Twitter, Facebook, White House, DHS-CISA.
The CTIL Files are also an indictment of the news media, which participated in CTIL’s disinformation efforts.
Whistleblowers: my DMs on X are open. We will go to prison to protect our sources.
Remember: YOU CANNOT TRUST THE MAINSTREAM NEWS MEDIA. THEY ARE PART OF THE CENSORSHIP AND DISINFORMATION COMPLEX.
The CTIL Files reveal their strategy:
- Denigrate, demonize, and de-humanize their targets
- Demand censorship
- Deny you’ve violated the First Amendment and interfered in elections
We now have multiple sight lines: Twitter, Facebook, White House, DHS-CISA.
The CTIL Files are also an indictment of the news media, which participated in CTIL’s disinformation efforts.
Whistleblowers: my DMs on X are open. We will go to prison to protect our sources.
Remember: YOU CANNOT TRUST THE MAINSTREAM NEWS MEDIA. THEY ARE PART OF THE CENSORSHIP AND DISINFORMATION COMPLEX.
The CTIL Files reveal their strategy:
- Denigrate, demonize, and de-humanize their targets
- Demand censorship
- Deny you’ve violated the First Amendment and interfered in elections
Please subscribe now to help us fight censorship and to watch an exclusive video on the CTIL Files!
https://x.com/shellenberger/status/1729925835266695297?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh