The Baptist War: The Christmas Rebellion.
On this day in 1831, Over 60,000 enslaved Jamaicans, led by one man, Baptist preacher, Samuel Sharpe, went on to carry out one of the largest Slave Rebellions in West Indian history.
A THREAD



On this day in 1831, Over 60,000 enslaved Jamaicans, led by one man, Baptist preacher, Samuel Sharpe, went on to carry out one of the largest Slave Rebellions in West Indian history.
A THREAD



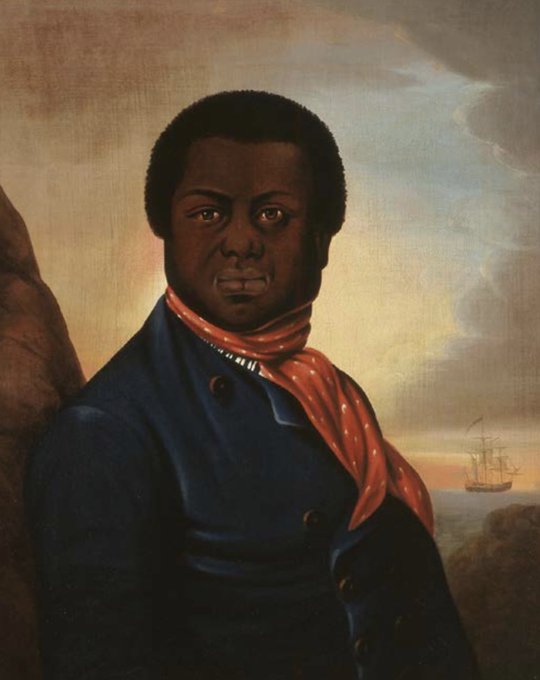
So who was the Baptist preacher, Samuel Sharpe?
He was a baptist deacon and the leader of the native Baptists in Montego Bay. Also he was an avid follower of the growing abolitionist movement in London.
He was a baptist deacon and the leader of the native Baptists in Montego Bay. Also he was an avid follower of the growing abolitionist movement in London.

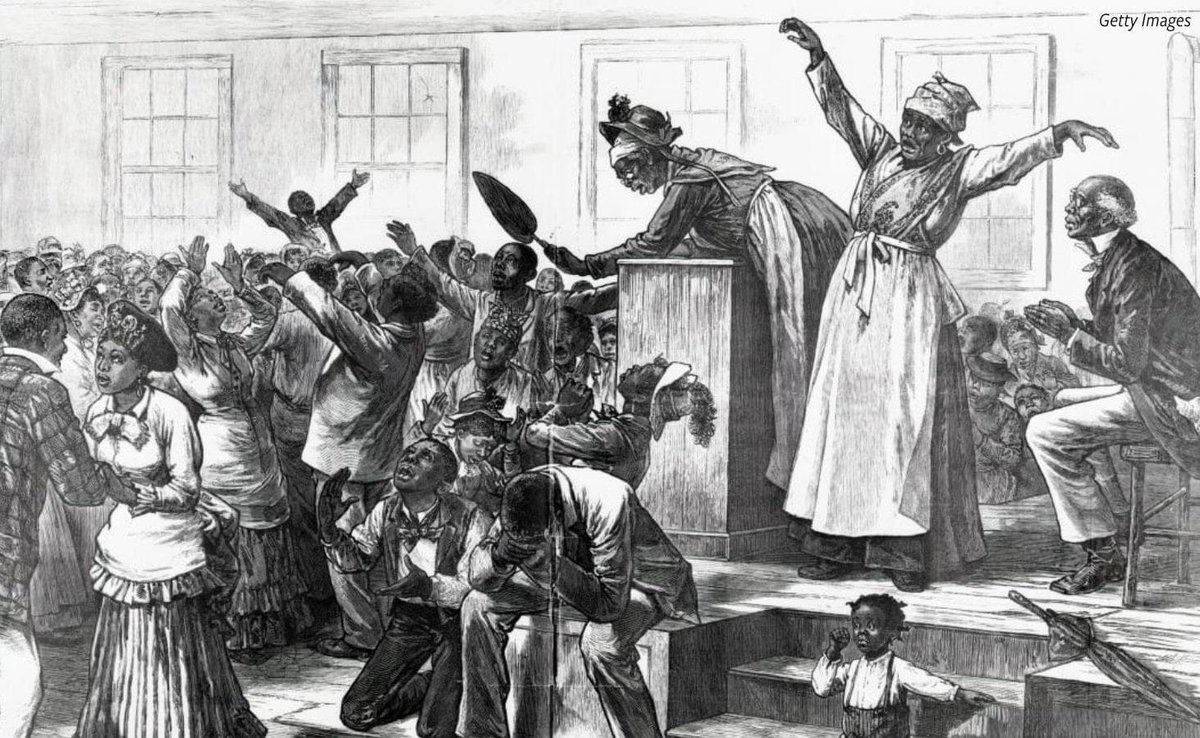
He led a plan for a peaceful general strike to start on Christmas Day in 1831, with the enslaved jamaicans demanding: —more freedom and
—a working wage
and refusing to work unless their demands were met by the state owners and managers.
—a working wage
and refusing to work unless their demands were met by the state owners and managers.
During the 19th century, Jamaica was essentially used as one large plantation by the British.
Almost all residents were enslaved and they outnumbered the whites. Racial tensions were at an all time high.
Almost all residents were enslaved and they outnumbered the whites. Racial tensions were at an all time high.
How did the Rebellion begin?
Sharpe’s call for a general strike had spread throughout Jamaica and news of the plan reached some of the planters.
Thus British troops were sent to St. James & warships were anchored in Montego Bay and the Black River.
Sharpe’s call for a general strike had spread throughout Jamaica and news of the plan reached some of the planters.
Thus British troops were sent to St. James & warships were anchored in Montego Bay and the Black River.
By 27 December 1831, Kensington Estate in the hills above Montego Bay was set on fire, signalling that the slave rebellion had begun. 

A peaceful strike was now impossible, and it quickly became the largest slave rebellion in the West Indies, with as many as 60k of Jamaica's 300k enslaved people arming themselves and seizing property across the island.
The Christmas Rebellion lasted until 4 January 1832. The Jamaicans easily overwhelmed by British forces and the Jamaican government. 

Aftermath:
over 300 enslaved men and women executed as a result of the subsequent trials.
Samuel Sharpe was captured and hanged on May 23 1832 in Montego Bay on a square now called Sam Sharpe Square.


over 300 enslaved men and women executed as a result of the subsequent trials.
Samuel Sharpe was captured and hanged on May 23 1832 in Montego Bay on a square now called Sam Sharpe Square.


He was posthumously named a National Hero of Jamaica in 1975 and his image can be found on the $50 Jamaican banknote. 

🖋️if you love our content, please consider supporting our page on (follow the ko-fi page too for weekly posts roundup) AfricanArchives.Support


• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh