When writing Bash scripts, you will frequently need to stop the execution of a script when a certain condition is met or perform some actions based on a command's exit code.
In this thread I will go over the built-in bash exit command as well as the exit statuses of the commands that have been executed.
Exit Status
When a shell command exits, whether successfully without any errors or unsuccessfully with errors, it returns an exit code.
An exit code of zero indicates that the command was completed properly without any errors, while a non-zero indicates that an error occurred.
When a shell command exits, whether successfully without any errors or unsuccessfully with errors, it returns an exit code.
An exit code of zero indicates that the command was completed properly without any errors, while a non-zero indicates that an error occurred.
The $? is a special shell variable that stores the exit status of the most recently run command:
$ echo $?
$ echo $?
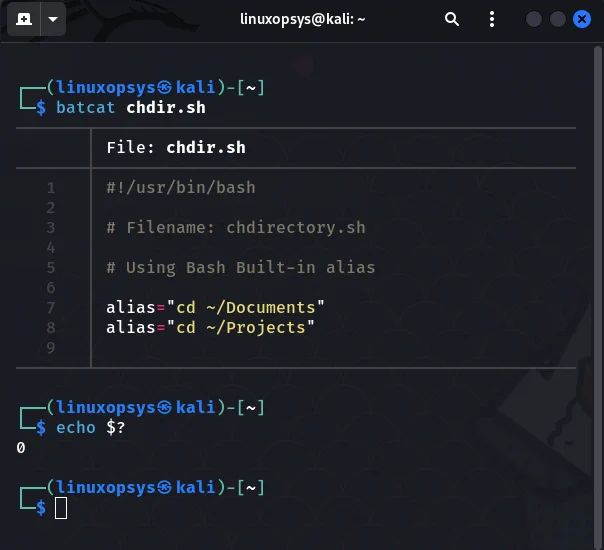
Because the batcat command was completed successfully and without error, the exit code is zero, as expected.
If you attempt to run batcat command on a not-existing file, the exit code will be non-zero as shown below:
$ batcat nullfile
If you attempt to run batcat command on a not-existing file, the exit code will be non-zero as shown below:
$ batcat nullfile
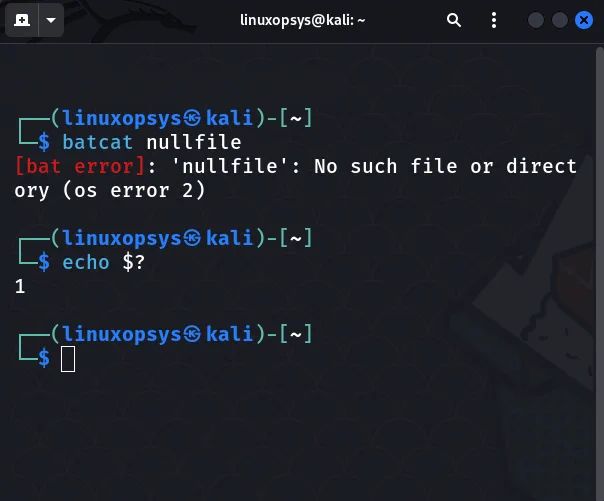
The command's status code can be used for debugging and to determine why it failed. The man pages for each command include information about the exit codes.
When chaining commands using pipes, the exist status code is that of the last command in the chain.
$ ls -lah | head -n 3
When chaining commands using pipes, the exist status code is that of the last command in the chain.
$ ls -lah | head -n 3
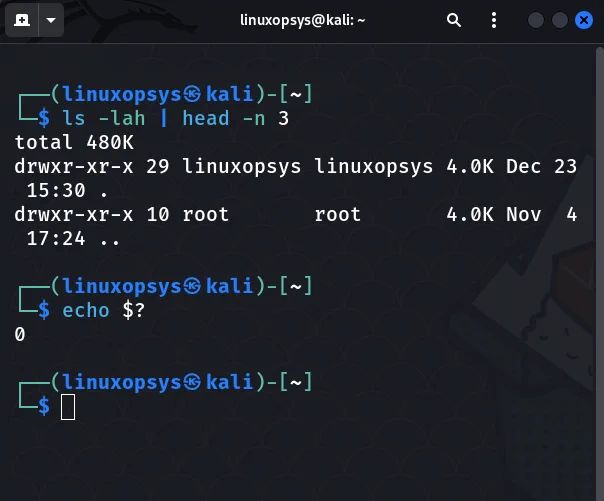
In the preceding example, echo $? prints the exit code of the head command and its zero. To prove this, execute the ls command on a non-existent directory.
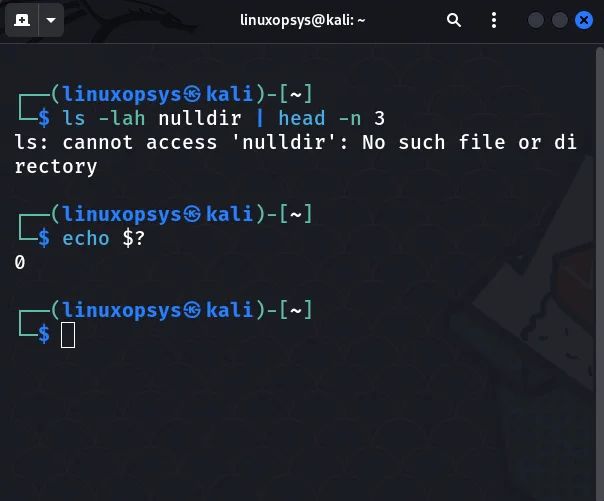
Here you can see the ls command fails but we still get the status code of zero.
$ ls -lah nulldir | head -n e
Here you can see the ls command fails but we still get the status code of zero.
$ ls -lah nulldir | head -n e
The bash exist command:
Now that you know what command exist status codes are, let's look at how to set them using the exit command.
Now that you know what command exist status codes are, let's look at how to set them using the exit command.
The exit command is used to exit the current shell. It takes a number as a parameter and exits the shell with the status of the number you passed as a parameter value.
If no parameters were supplied, it would return the status of the most recently executed command.
If no parameters were supplied, it would return the status of the most recently executed command.
Here is the syntax for the exit command:
$ exit N
When the exit command is used in shell scripts, the value passed to it as an argument is returned to the shell as an exit code.
Here is an example script of using the exit command in shell scripts:


$ exit N
When the exit command is used in shell scripts, the value passed to it as an argument is returned to the shell as an exit code.
Here is an example script of using the exit command in shell scripts:
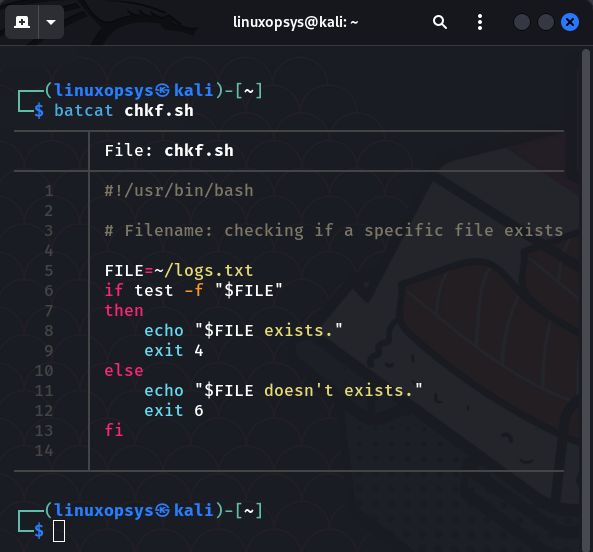

Always remember that if a script ends with exit without specifying a parameter, the script exit code is the last command executed in the script.
This is the same as just exit $? or leaving the script without exit at all.
This is the same as just exit $? or leaving the script without exit at all.

This information should be sufficient to help you understand command exist status codes and the exit command.
That's all! Thank you for getting this far. I hope you find this thread useful.
That's all! Thank you for getting this far. I hope you find this thread useful.
If you did find this thread valuable:
1. Toss us a follow for more daily threads on Linux, sysadmin, and DevOps → @linuxopsys
2. Like and RT the first tweet so other Linux folks can find it too.
1. Toss us a follow for more daily threads on Linux, sysadmin, and DevOps → @linuxopsys
2. Like and RT the first tweet so other Linux folks can find it too.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh














