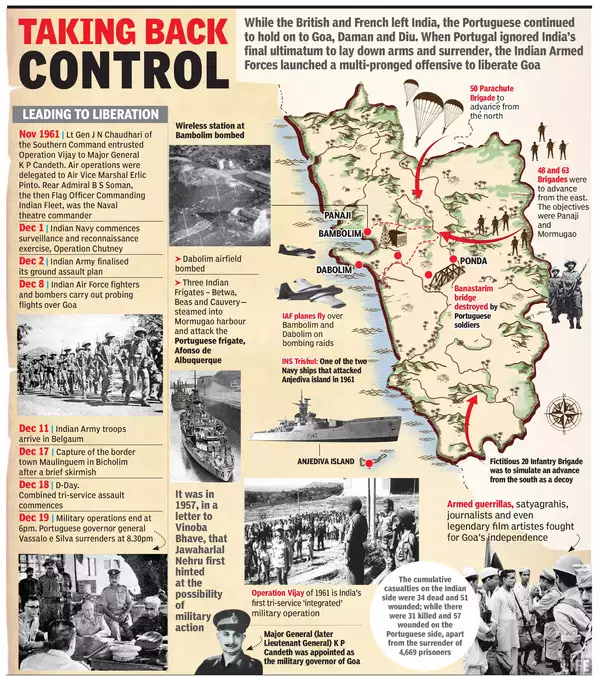
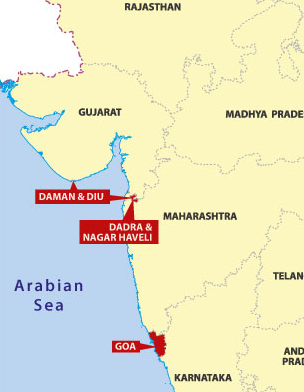
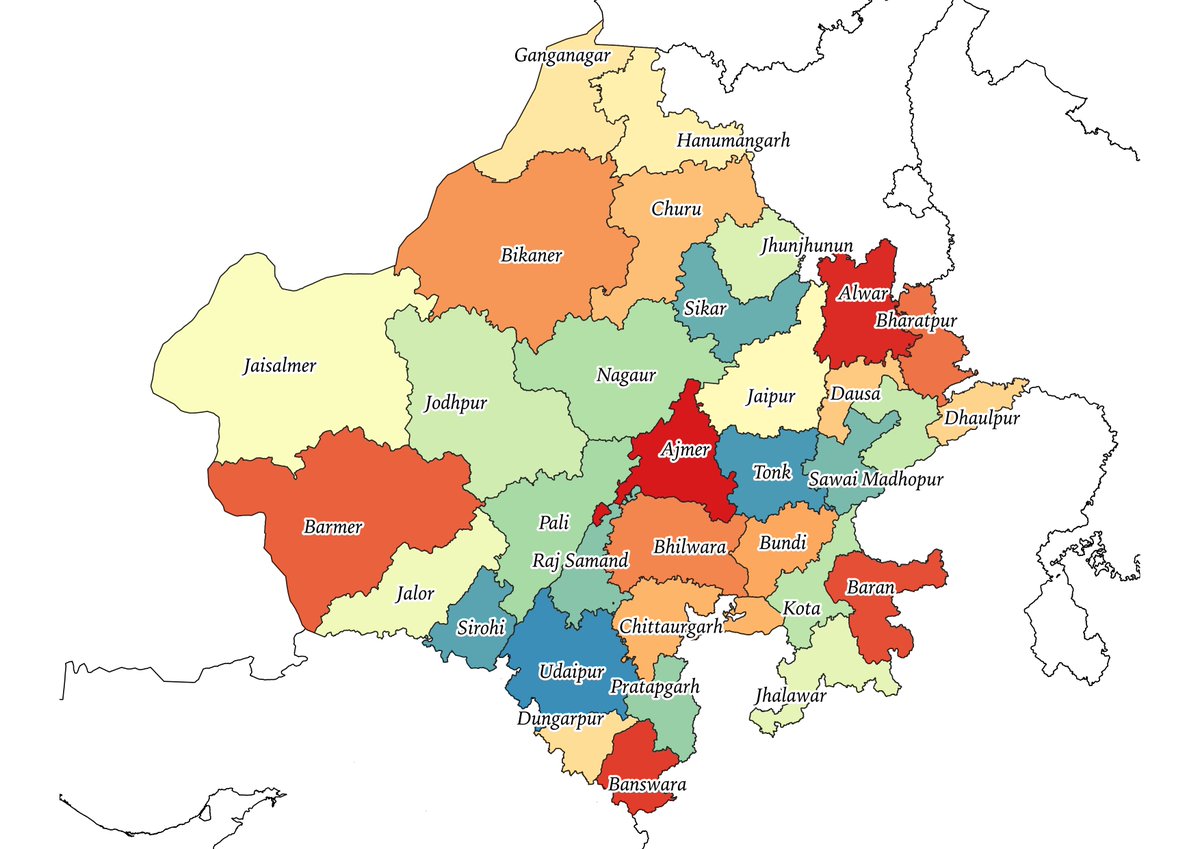
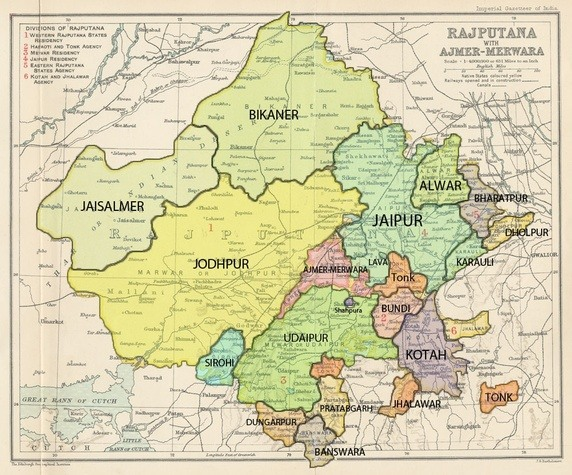
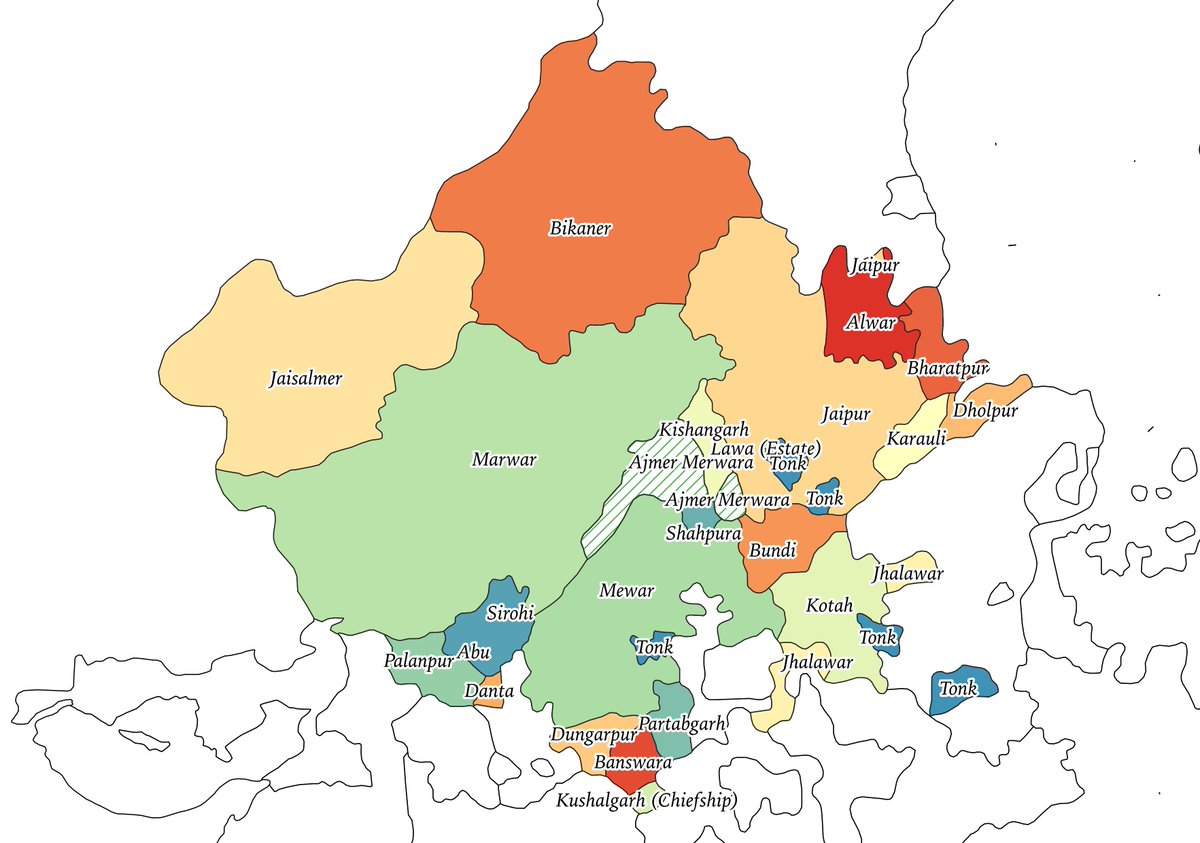
1/n : Today, we bring to you the visual story of the formation of the state of Karnataka, a land for Kannada speakers amalgamated from five different administrative regions of British India.
Mysore State, Hyderabad State, Madras Presidency, Bombay Presidency and Coorg.


Mysore State, Hyderabad State, Madras Presidency, Bombay Presidency and Coorg.
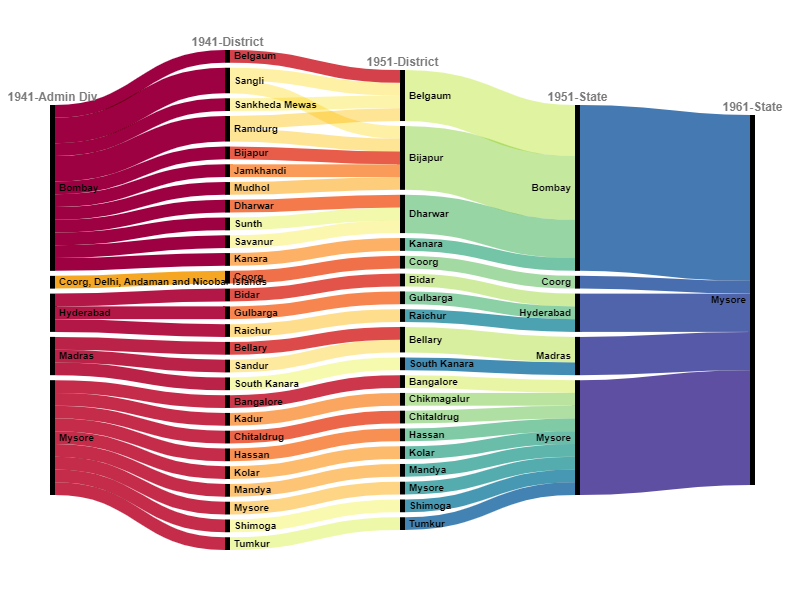
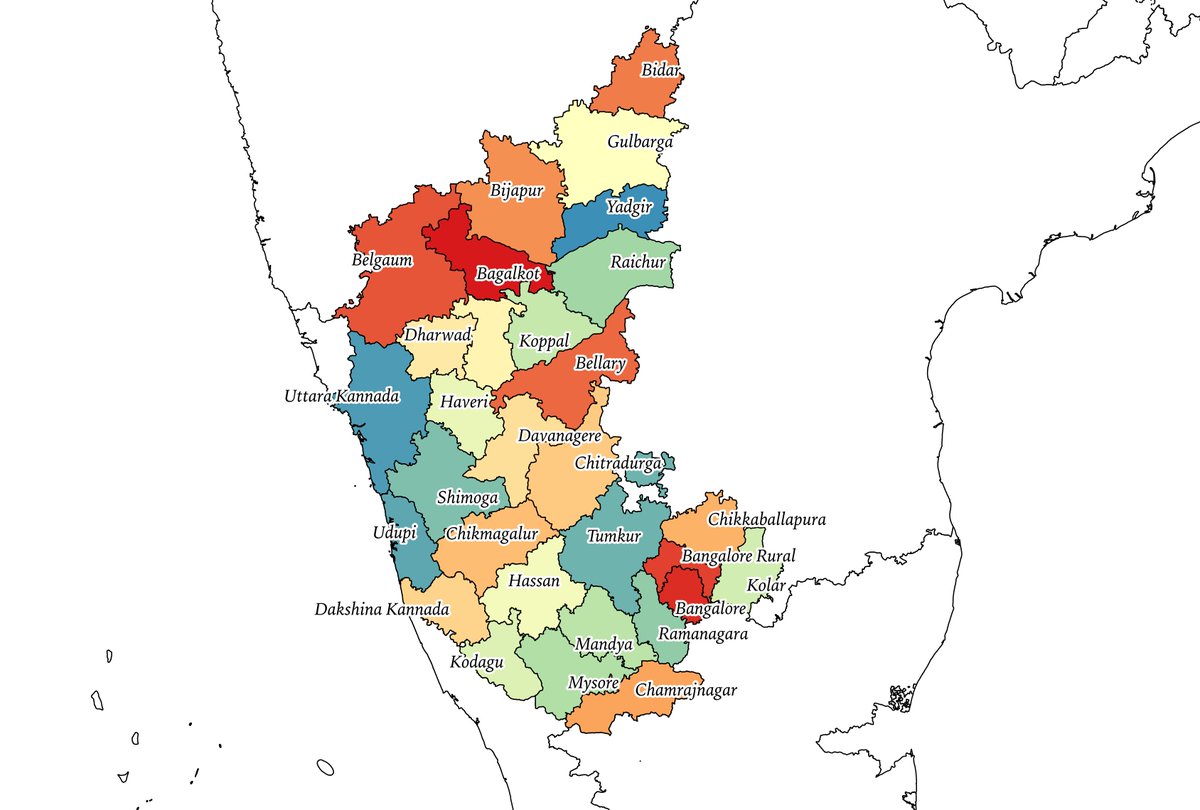
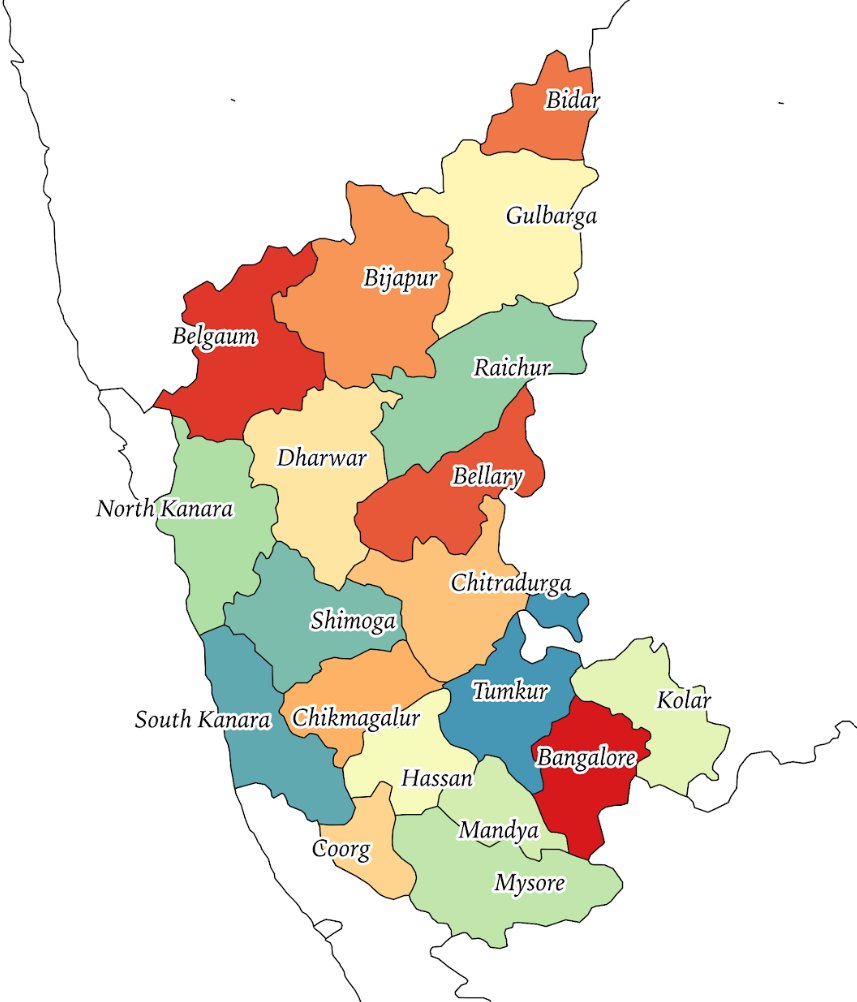
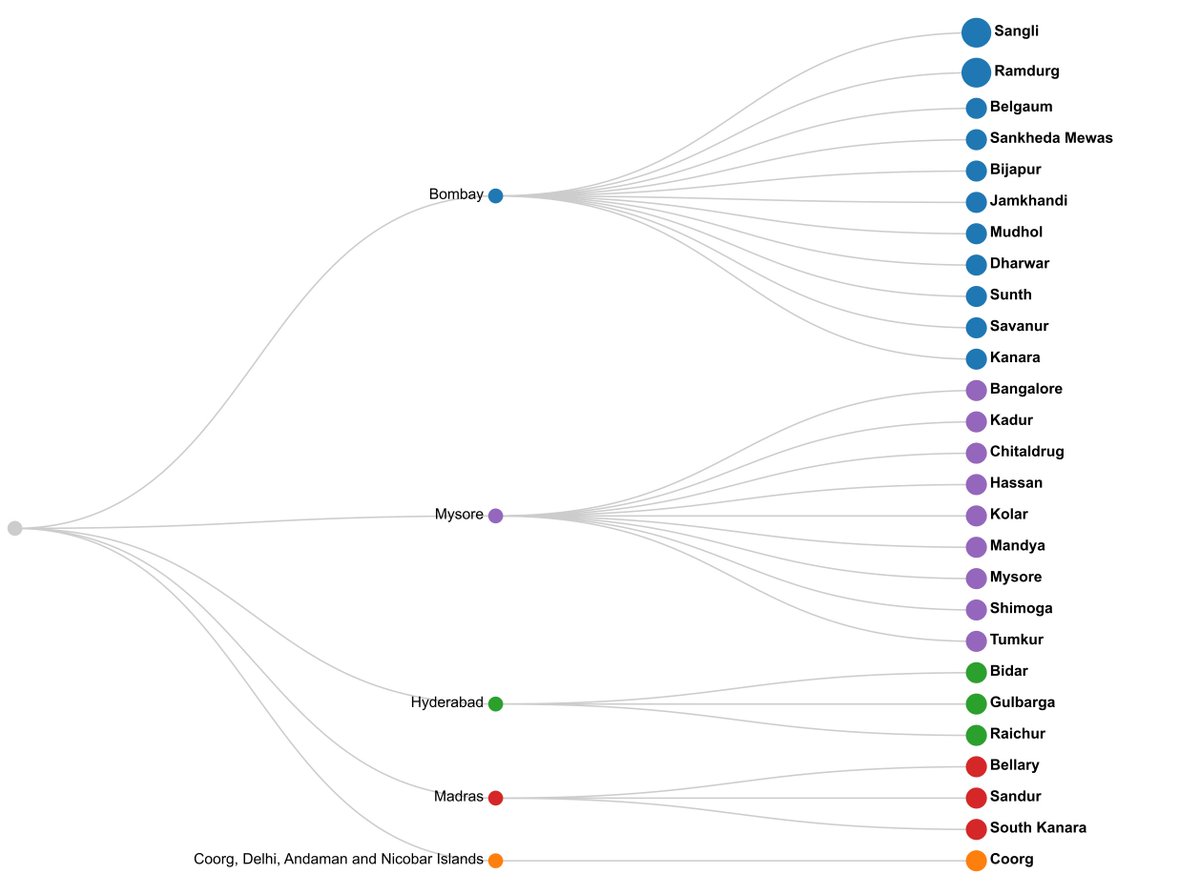
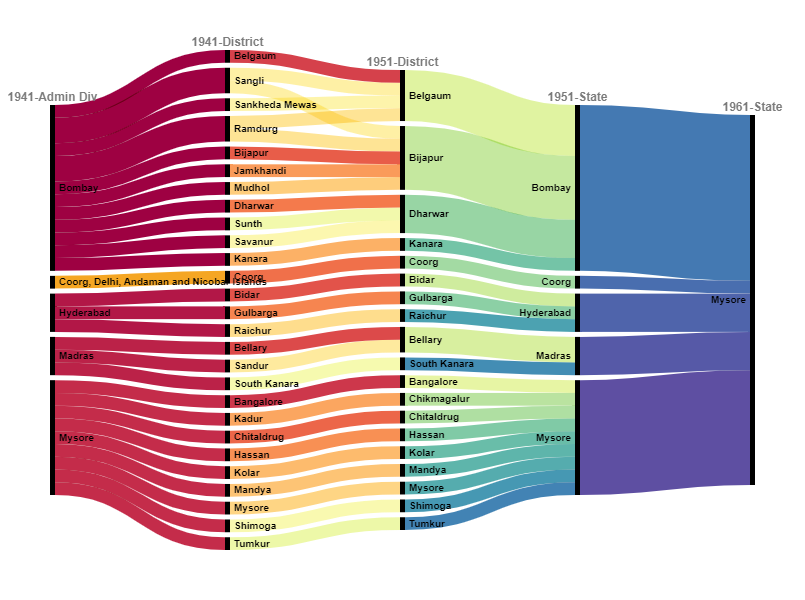
2/n: Kannada speakers were spread along the following districts in different British provinces and princely states. Some princely states like Sangli and Ramdurg had scattered regions in modern-day Karnataka. 
5/n : Mysore's integration into the Indian Union was seamless. In Aug 1947, the Maharajah signed the Instrument of Accession and Standstill Agreement. June 1949 he revised it for broader legislative powers, except in taxes. Mysore joined the Federal Financial Integration in 1950


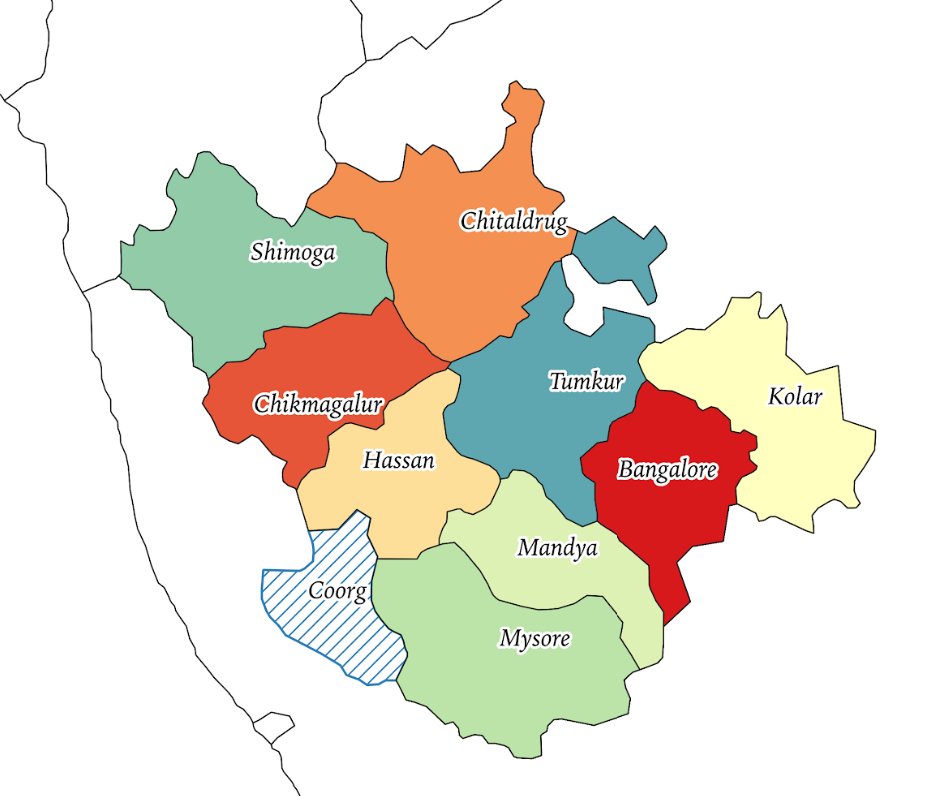

6/n: At the time of South Canara district’s transfer from Madras to Mysore state, a Kollegal taluk of Coimbatore state was also transferred to the state of Mysore on linguistic lines. Post-independence, Coorg was demarcated as Part-C state and centrally administered
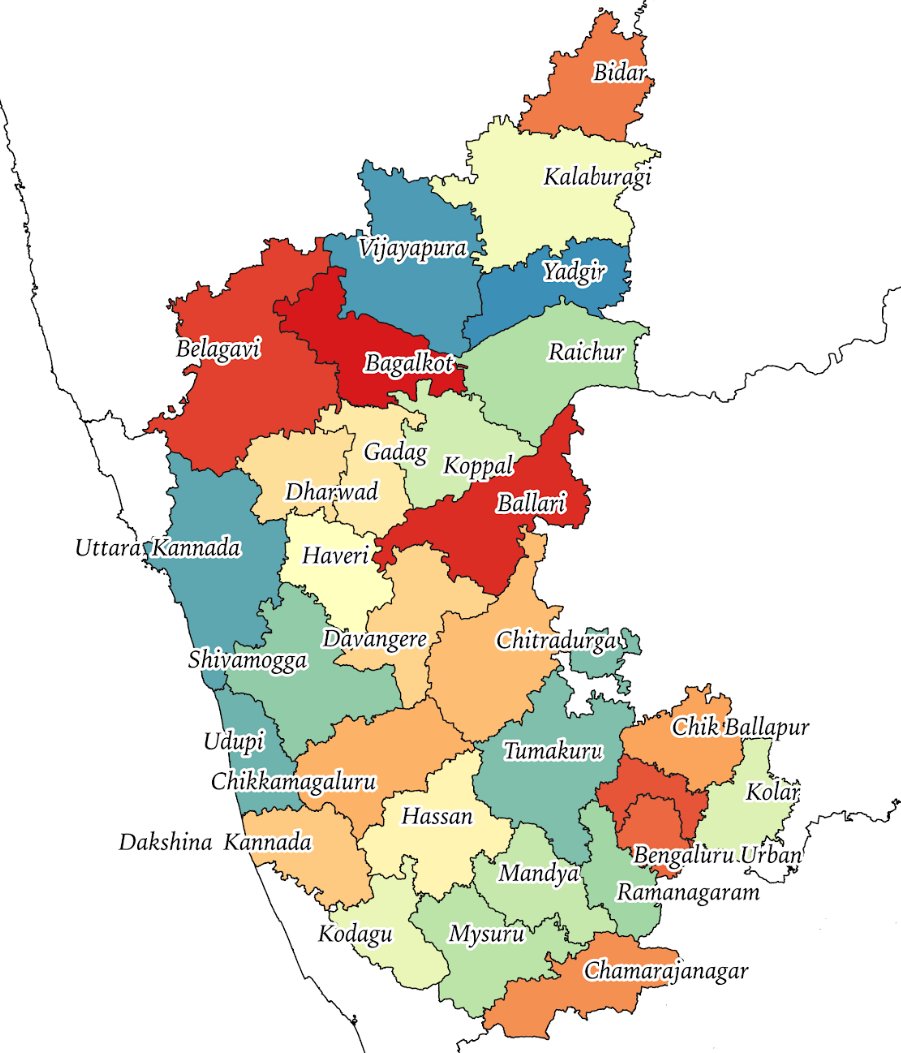
7/n: 1953-1956: SRC and Formation of Mysore State: Kannada-speaking regions of Bombay, Hyderabad, and Madars- integrated with Mysore. Considering Coorg’s greater linguistic and cultural linkages with Karnataka, the state was integrated within Mysore.




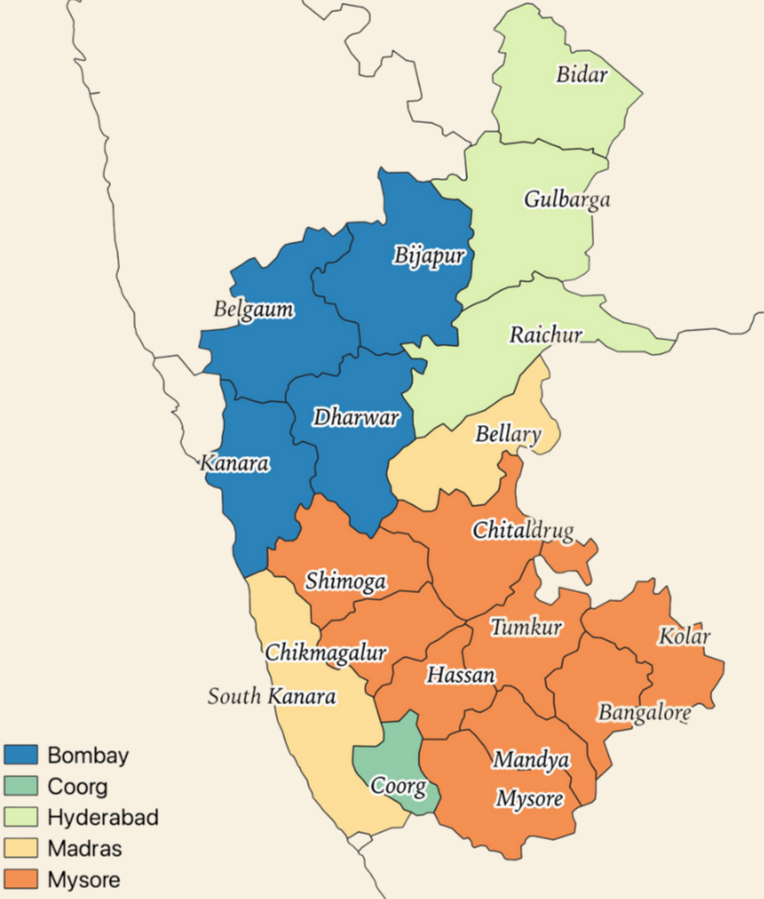
10/n: Sources- White Paper on Indian States (1950); The Story of Integration of India - V P Menon (1956); Administrative Atlas of India (2011). Origin Story of India’s States -Venkataraghavan Subha Srinivasan (2020).
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh