Has there always been a continuous Jewish presence in Israel?
This thread has taken me all week to compile, as the history is so rich, but I will try and address some main points of Jewish presence in Israel from each century.
Let's get started: 🧵🧵🧵
This thread has taken me all week to compile, as the history is so rich, but I will try and address some main points of Jewish presence in Israel from each century.
Let's get started: 🧵🧵🧵

1st - 2nd century:
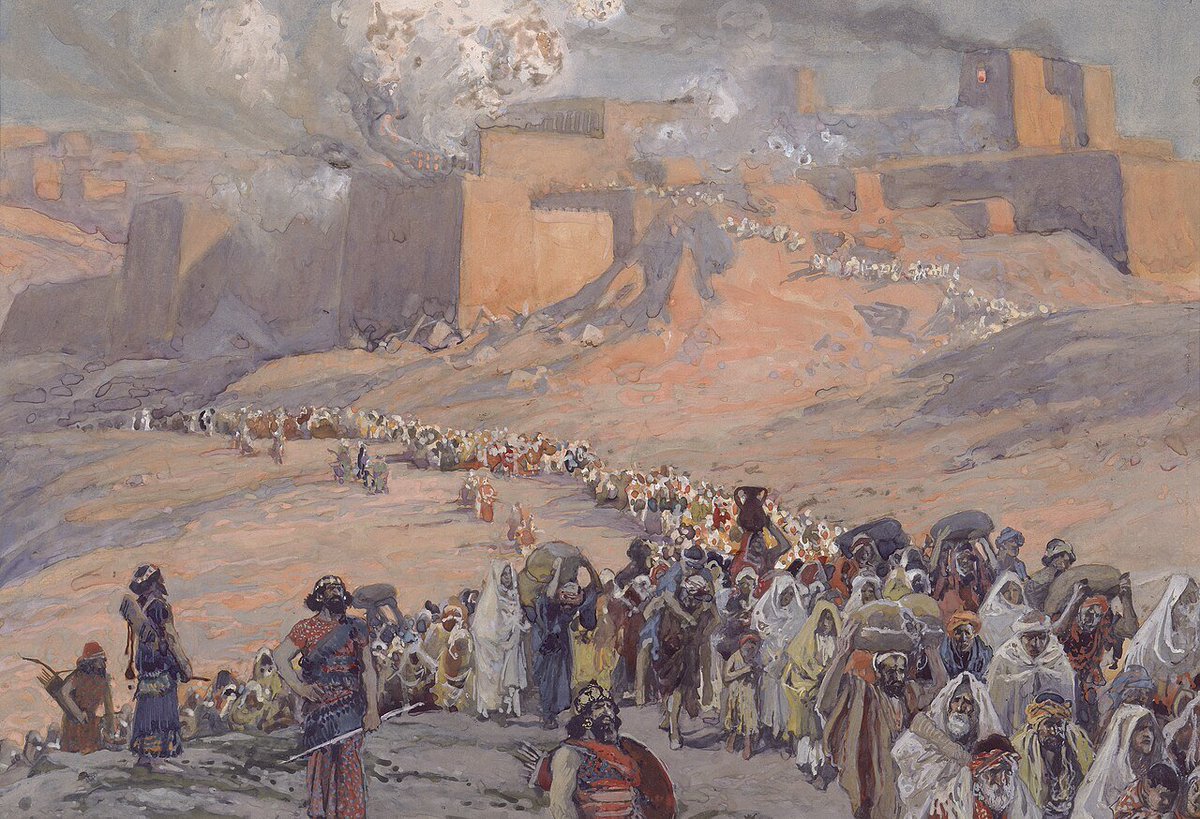
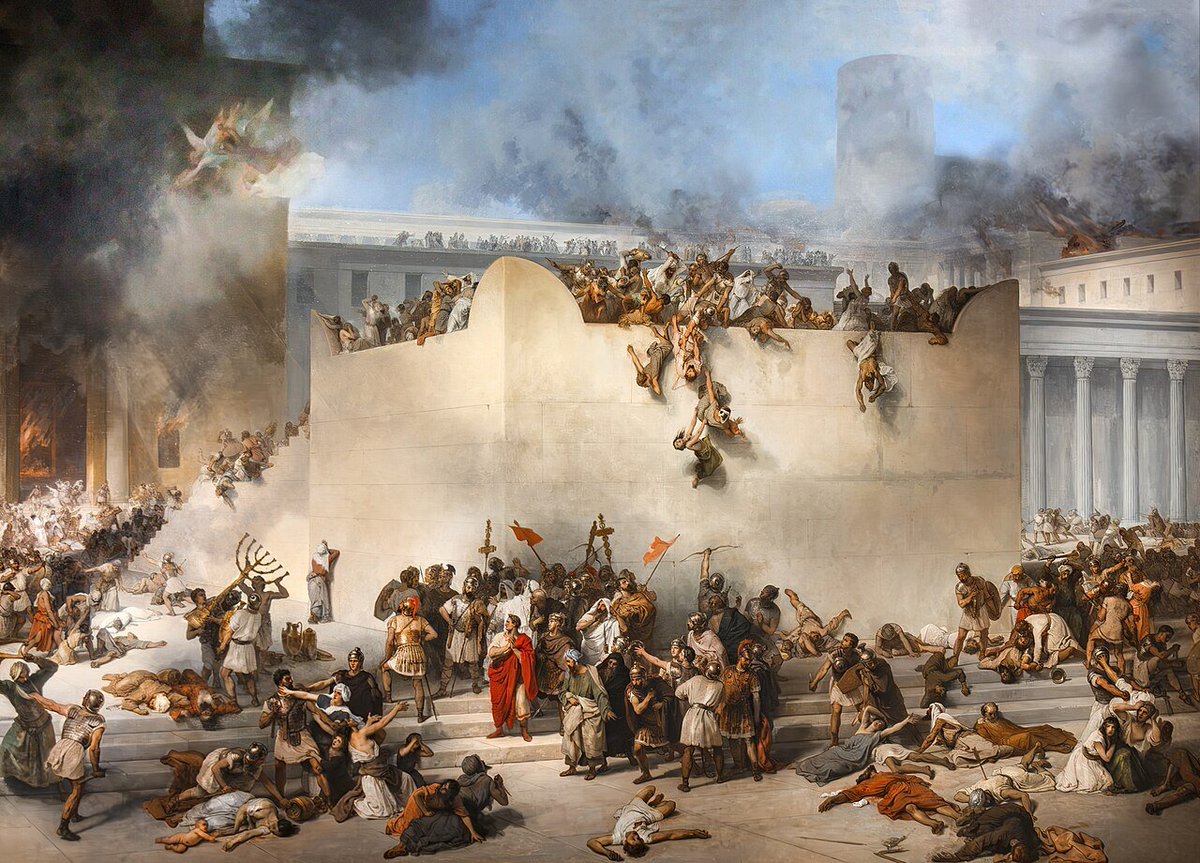
After the destruction of the temple (70 CE) by the Titus and the Romans, many Jews were taken to exile.
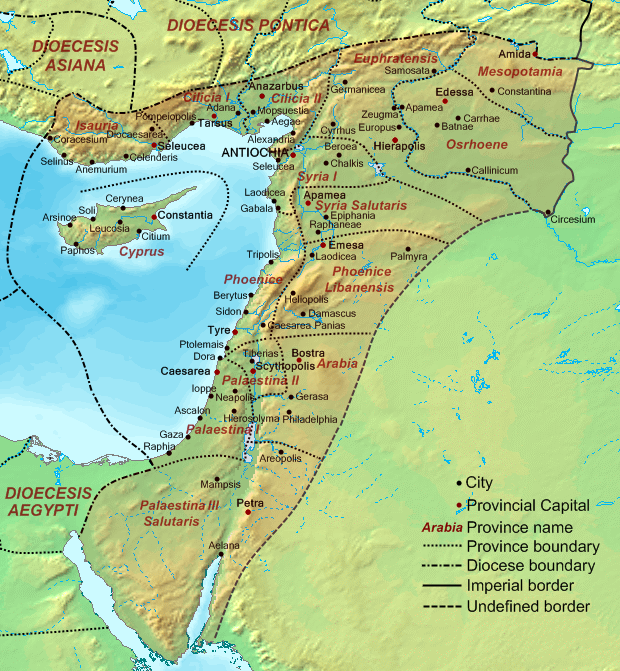
In 131 CE Emperor Hadrian renamed Jerusalem "Aelia Capitolina" and constructed the Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus on the site of the former Jewish temple. Jews were banned from Jerusalem and Roman Judaea was renamed "Syria Palaestina", from which is derived "Palestine" in English and "Filistin" in Arabic.
But did any Jews stay?
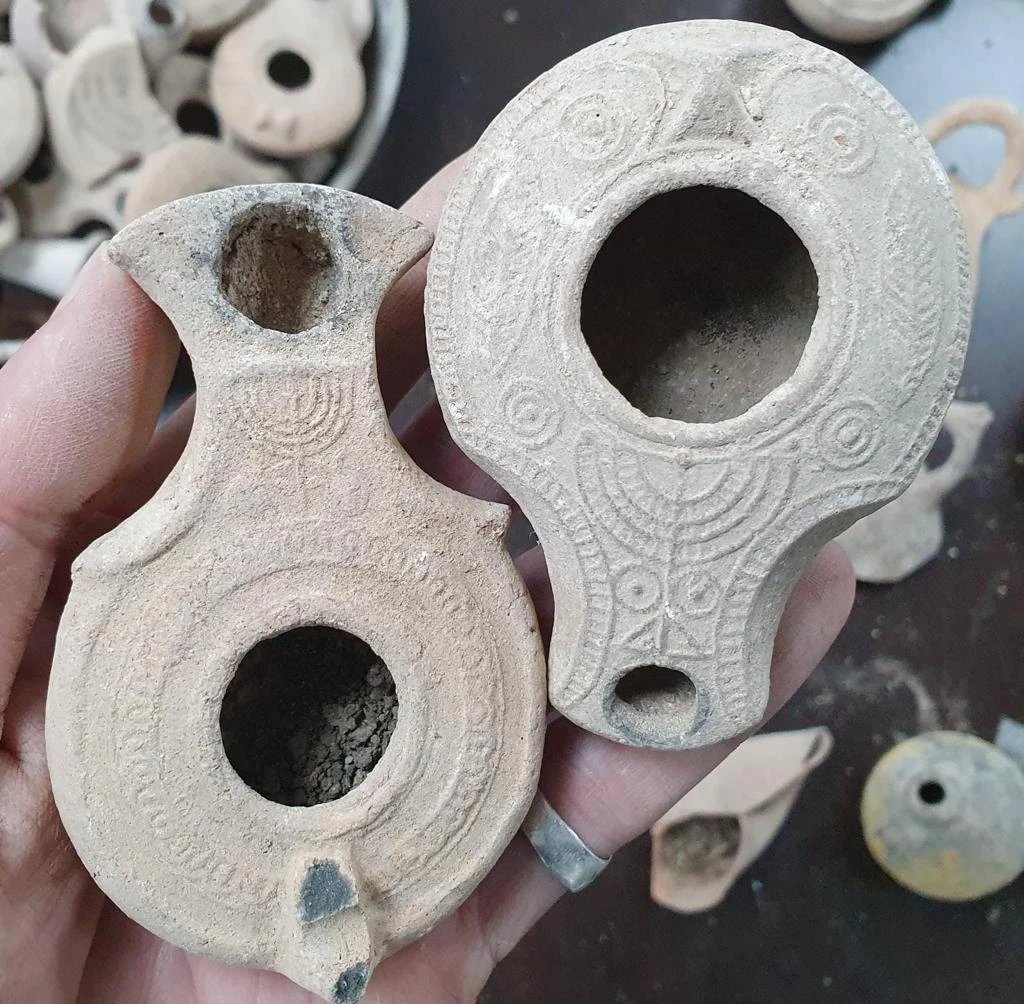
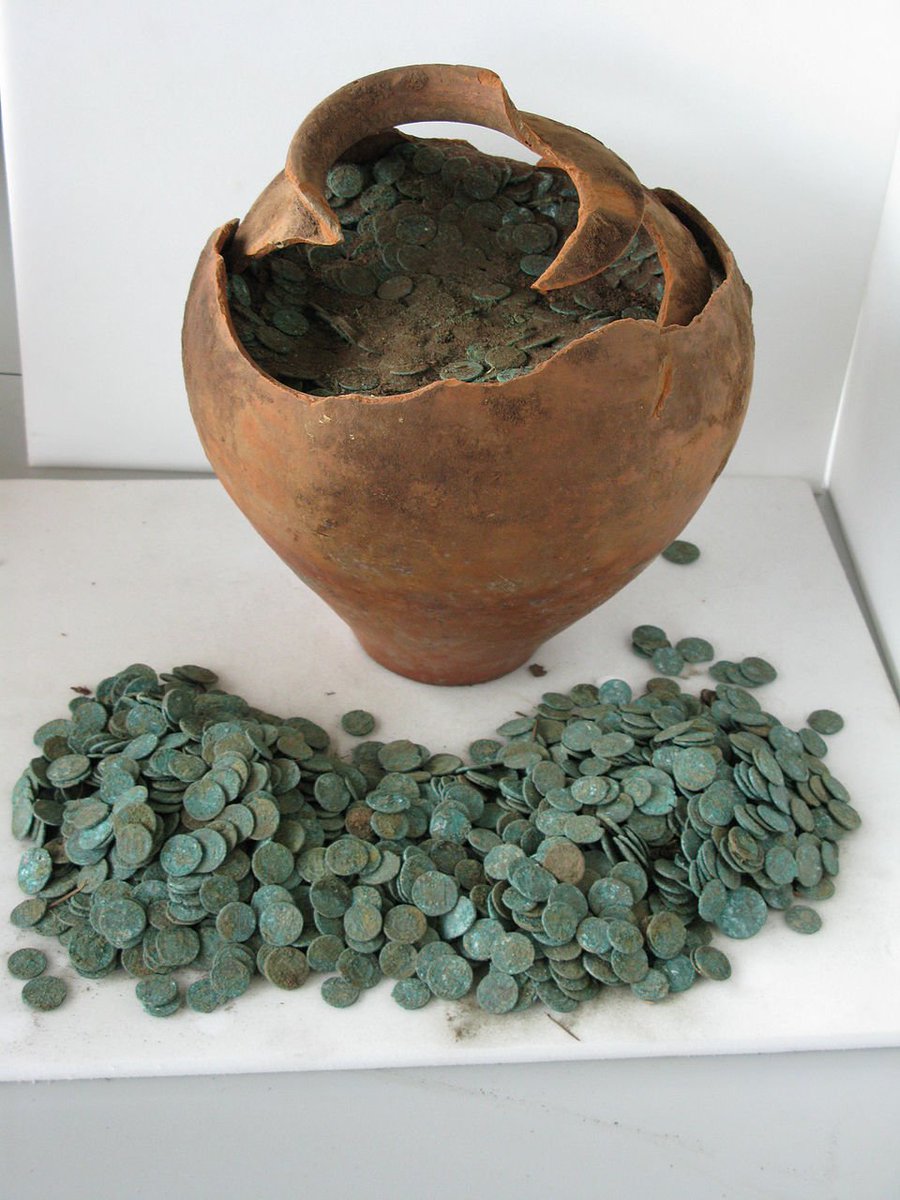
Yes, as is evident by the Bar Kochba Revolt between 132 and 136 CE which ultimately failed. Many ancient coins were found in Israel & date to the revolt. This one has a picture of the Temple & reads 'To the freedom of Jerusalem'.
After the destruction of the temple (70 CE) by the Titus and the Romans, many Jews were taken to exile.
In 131 CE Emperor Hadrian renamed Jerusalem "Aelia Capitolina" and constructed the Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus on the site of the former Jewish temple. Jews were banned from Jerusalem and Roman Judaea was renamed "Syria Palaestina", from which is derived "Palestine" in English and "Filistin" in Arabic.
But did any Jews stay?
Yes, as is evident by the Bar Kochba Revolt between 132 and 136 CE which ultimately failed. Many ancient coins were found in Israel & date to the revolt. This one has a picture of the Temple & reads 'To the freedom of Jerusalem'.

3rd - 5th century:
After suppressing the Bar Kochba revolt, the Romans permitted a hereditary rabbinical patriarch from the House of Hillel to represent the Jews in dealings with the Romans.
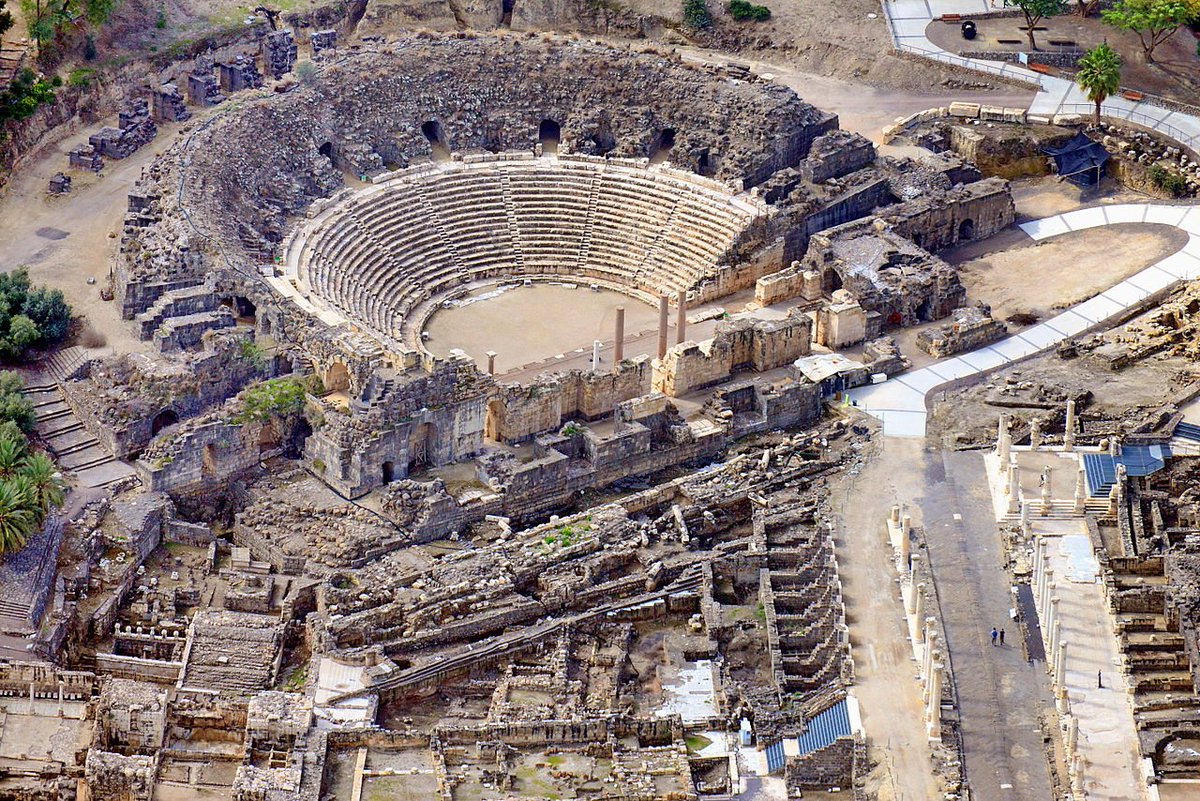
The main Jewish population center was now the Galilee, and there were also significant Jewish communities in Beit She'an, Caesarea, the Golan Heights, and along the edges of Judea.
It was also the time when the Tannaim and Amoraim were active in debating and recording the Jewish Oral Law. Their discussions and religious instructions were compiled in the form of the Mishnah by Judah the Prince around 200 CE.
These texts were the foundation of the Jerusalem Talmud, which was redacted in around 400 CE, probably in Tiberias.

After suppressing the Bar Kochba revolt, the Romans permitted a hereditary rabbinical patriarch from the House of Hillel to represent the Jews in dealings with the Romans.
The main Jewish population center was now the Galilee, and there were also significant Jewish communities in Beit She'an, Caesarea, the Golan Heights, and along the edges of Judea.
It was also the time when the Tannaim and Amoraim were active in debating and recording the Jewish Oral Law. Their discussions and religious instructions were compiled in the form of the Mishnah by Judah the Prince around 200 CE.
These texts were the foundation of the Jerusalem Talmud, which was redacted in around 400 CE, probably in Tiberias.


6th - 7th century:
In 613, a Jewish revolt against the Byzantine Empire led by Nehemiah ben Hushiel and Benjamin of Tiberias broke out. Jewish soldiers from Tiberias, Nazareth, and other Galilee settlements joined forces with Persian invaders to capture Jerusalem in 614. The great majority of Christians in Jerusalem were subsequently deported to Persia. The Jews gained autonomy in Jerusalem, with Hushiel appointed ruler of the city. Hushiel began making arrangements for the construction of the Third Temple and sorting out genealogies to establish a new High Priesthood.
Jewish dominance in Jerusalem lasted until 617, when the Persians reneged on their alliance with the Jews. Further Jewish settlement in and around Jerusalem was prohibited, a synagogue on the Temple Mount was demolished, and heavy taxes were imposed on the Jews.
With the return of the Byzantines in 628, the Byzantine Emperor promised to restore Jewish rights and received Jewish help in ousting the Persians with the aid of Benjamin of Tiberias. Heraclius later reneged on the agreement after reconquering Palestine. A general massacre of the Jewish population ensued, devastating the Jewish communities of Jerusalem and the Galilee.
In 613, a Jewish revolt against the Byzantine Empire led by Nehemiah ben Hushiel and Benjamin of Tiberias broke out. Jewish soldiers from Tiberias, Nazareth, and other Galilee settlements joined forces with Persian invaders to capture Jerusalem in 614. The great majority of Christians in Jerusalem were subsequently deported to Persia. The Jews gained autonomy in Jerusalem, with Hushiel appointed ruler of the city. Hushiel began making arrangements for the construction of the Third Temple and sorting out genealogies to establish a new High Priesthood.
Jewish dominance in Jerusalem lasted until 617, when the Persians reneged on their alliance with the Jews. Further Jewish settlement in and around Jerusalem was prohibited, a synagogue on the Temple Mount was demolished, and heavy taxes were imposed on the Jews.
With the return of the Byzantines in 628, the Byzantine Emperor promised to restore Jewish rights and received Jewish help in ousting the Persians with the aid of Benjamin of Tiberias. Heraclius later reneged on the agreement after reconquering Palestine. A general massacre of the Jewish population ensued, devastating the Jewish communities of Jerusalem and the Galilee.

7th - 10th century:
In 638 CE, the Byzantine Empire lost the Levant to the Arab Islamic Empire. At the time of the Arab conquest in the 7th century, the majority of the population was Jewish or Samaritan. Estimates of the Jews of Palestine numbered between 150,000 and 400,000 at the time.
After the conquest, Jewish communities began to grow and flourish. Jews were allowed to settle in Jerusalem, it was the first time, after almost 500 years of oppressive Christian rule, that Jews were allowed to enter and worship freely in their holy city.
However, that quickly changed with the building of the Dome of the Rock (691) on the Temple Mount and forcing Jews and Christians to pay a special tax (Jiziyah).
From the middle of the ninth century to the 11th century, the Israeli Gaonate served as the chief Talmudic academy and central legalistic body of the Jewish community in Israel. The Gaonate moved from Tiberias to Jerusalem in the mid-ninth century (it competed with the Babylonian Gaonate for the support of diaspora communities).
In 1071, after Jerusalem was conquered by the Seljuq Turks, the Gaonate was expelled from Jerusalem and relocated to Tyre.
In 638 CE, the Byzantine Empire lost the Levant to the Arab Islamic Empire. At the time of the Arab conquest in the 7th century, the majority of the population was Jewish or Samaritan. Estimates of the Jews of Palestine numbered between 150,000 and 400,000 at the time.
After the conquest, Jewish communities began to grow and flourish. Jews were allowed to settle in Jerusalem, it was the first time, after almost 500 years of oppressive Christian rule, that Jews were allowed to enter and worship freely in their holy city.
However, that quickly changed with the building of the Dome of the Rock (691) on the Temple Mount and forcing Jews and Christians to pay a special tax (Jiziyah).
From the middle of the ninth century to the 11th century, the Israeli Gaonate served as the chief Talmudic academy and central legalistic body of the Jewish community in Israel. The Gaonate moved from Tiberias to Jerusalem in the mid-ninth century (it competed with the Babylonian Gaonate for the support of diaspora communities).
In 1071, after Jerusalem was conquered by the Seljuq Turks, the Gaonate was expelled from Jerusalem and relocated to Tyre.

11th - 13th century:
From 1099 to 1291 the Christian Crusaders "mercilessly persecuted and slaughtered the Jews of Israel".
During the First Crusade, Jews were among the population who tried in vain to defend against the Crusaders during the Siege of Jerusalem. When Jerusalem fell, a massacre of Jews occurred when the synagogue they were seeking refuge in was set alight. Almost all perished.
Jewish communities in Israel were apparently left undisturbed during the Second Crusade.
Benjamin of Tudela and Pethahiah of Regensburg, who visited around 1160 and 1180 respectively, found well-established Jewish communities in Ashkelon, Ramleh, Caesarea, Tiberias, and Acre. However, they found only a handful of Jews in Jerusalem.

From 1099 to 1291 the Christian Crusaders "mercilessly persecuted and slaughtered the Jews of Israel".
During the First Crusade, Jews were among the population who tried in vain to defend against the Crusaders during the Siege of Jerusalem. When Jerusalem fell, a massacre of Jews occurred when the synagogue they were seeking refuge in was set alight. Almost all perished.
Jewish communities in Israel were apparently left undisturbed during the Second Crusade.
Benjamin of Tudela and Pethahiah of Regensburg, who visited around 1160 and 1180 respectively, found well-established Jewish communities in Ashkelon, Ramleh, Caesarea, Tiberias, and Acre. However, they found only a handful of Jews in Jerusalem.


13th-16th century:
In 1211, the Jewish community in the country was strengthened by the arrival of a group headed by over 300 rabbis from France and England, among them Rabbi Samson ben Abraham of Sens.
The era of Mamluk rule (1260 - 1517) saw the Jewish population shrink substantially due to oppression and economic stagnation.
There are many accounts of Jews wishing to return to Israel (Nachmanidies, Meir of Rothenburg, Ishtori Haparchi) but many were unsuccessful.
In 1438, Italian rabbi Elijah of Ferrara settled in Jerusalem and became a lecturer and dayyan.
In 1488, Italian commentator and spiritual leader Obadiah ben Abraham arrived in Jerusalem. He found the city forsaken holding about seventy poor Jewish families, but soon they would grow to 200.
In Safed, the situation fared better. Thanks to Joseph Saragossi who had arrived in the closing years of the 15th century, Safed had developed into the largest concentration of Jews in Israel. With the help of the Sephardic immigration from Spain, the Jewish population had increased to 10,000 by the early 16th century.

In 1211, the Jewish community in the country was strengthened by the arrival of a group headed by over 300 rabbis from France and England, among them Rabbi Samson ben Abraham of Sens.
The era of Mamluk rule (1260 - 1517) saw the Jewish population shrink substantially due to oppression and economic stagnation.
There are many accounts of Jews wishing to return to Israel (Nachmanidies, Meir of Rothenburg, Ishtori Haparchi) but many were unsuccessful.
In 1438, Italian rabbi Elijah of Ferrara settled in Jerusalem and became a lecturer and dayyan.
In 1488, Italian commentator and spiritual leader Obadiah ben Abraham arrived in Jerusalem. He found the city forsaken holding about seventy poor Jewish families, but soon they would grow to 200.
In Safed, the situation fared better. Thanks to Joseph Saragossi who had arrived in the closing years of the 15th century, Safed had developed into the largest concentration of Jews in Israel. With the help of the Sephardic immigration from Spain, the Jewish population had increased to 10,000 by the early 16th century.


16th - 21st century:
Israel was conquered by Turkish Sultan Selim II in 1517. At the onset of Ottoman rule, there were an estimated 5,000 Jews, comprising about 1,000 Jewish families. Jews mainly lived in Jerusalem, Nablus, Hebron, Gaza, Safed, and villages in the Galilee. The Jewish community was composed of both descendants of Jews who had never left the land and Jewish migrants from the diaspora.
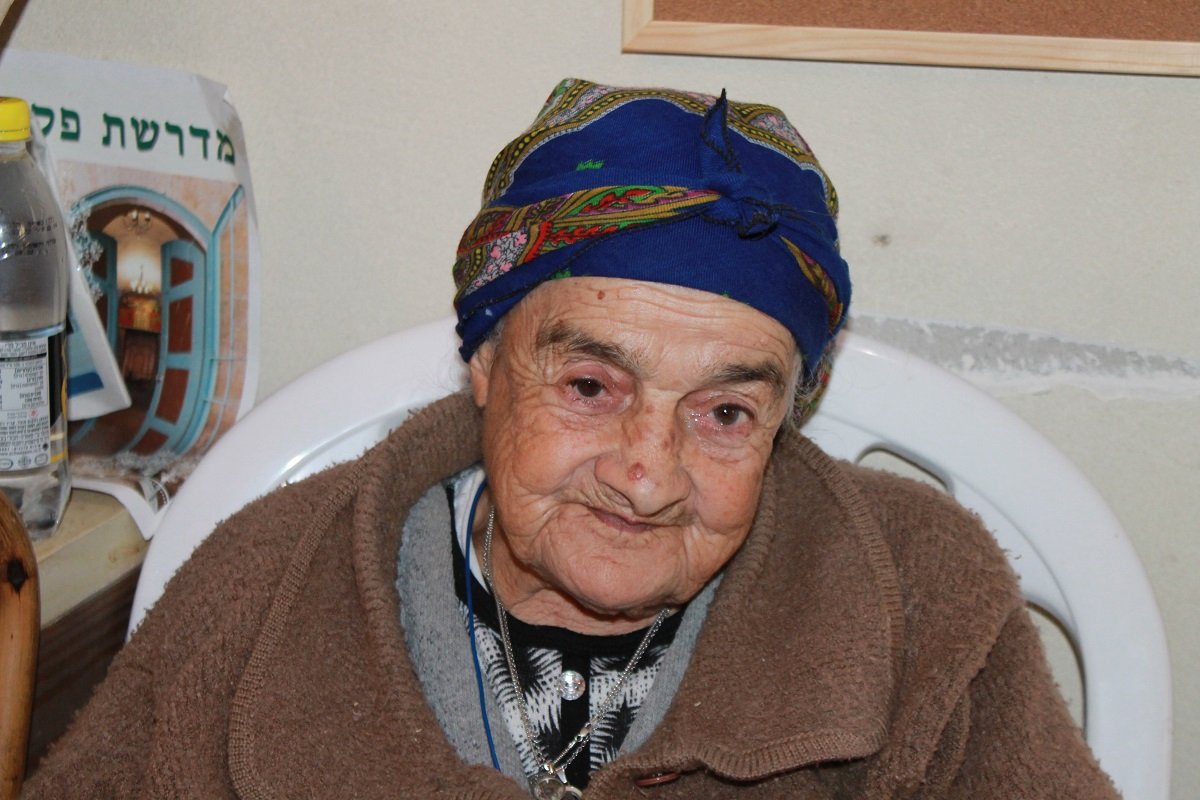
One of the amazing stories of a family that never left is the Zinati family of Peki'in who have stayed in Israel since the destruction of the 2nd Temple.
Margalit Zinati (93) is the last descendant of the family and lives in the village to this day.
According to local tradition, the ancient synagogue of Peki'in was built on the site where Rabbi Joshua ben Hananiah taught before the Bar Kokhba revolt, and Rabbi Shimon bar Yochai after it.
The fact that 3 ancient stone tablets were found in the synagogue and date to the 2nd century - strengthens this tradition.

Israel was conquered by Turkish Sultan Selim II in 1517. At the onset of Ottoman rule, there were an estimated 5,000 Jews, comprising about 1,000 Jewish families. Jews mainly lived in Jerusalem, Nablus, Hebron, Gaza, Safed, and villages in the Galilee. The Jewish community was composed of both descendants of Jews who had never left the land and Jewish migrants from the diaspora.
One of the amazing stories of a family that never left is the Zinati family of Peki'in who have stayed in Israel since the destruction of the 2nd Temple.
Margalit Zinati (93) is the last descendant of the family and lives in the village to this day.
According to local tradition, the ancient synagogue of Peki'in was built on the site where Rabbi Joshua ben Hananiah taught before the Bar Kokhba revolt, and Rabbi Shimon bar Yochai after it.
The fact that 3 ancient stone tablets were found in the synagogue and date to the 2nd century - strengthens this tradition.

This is only the tip of the iceberg, our history is much richer and I had to skip a lot of fascinating stories.
Let me know if you want more historical/archeological threads.
Shabbat Shalom. 🕯️🕯️🇮🇱
Let me know if you want more historical/archeological threads.
Shabbat Shalom. 🕯️🕯️🇮🇱
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




![Reverse of a Yehud coin from the Persian era, with lily (symbol of Jerusalem)[1] By Fiddler7 - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=4513133](https://pbs.twimg.com/media/G-8CdefWAAAsrfU.png)