How LLMs work, clearly explained:
Before diving into LLMs, we must understand conditional probability.
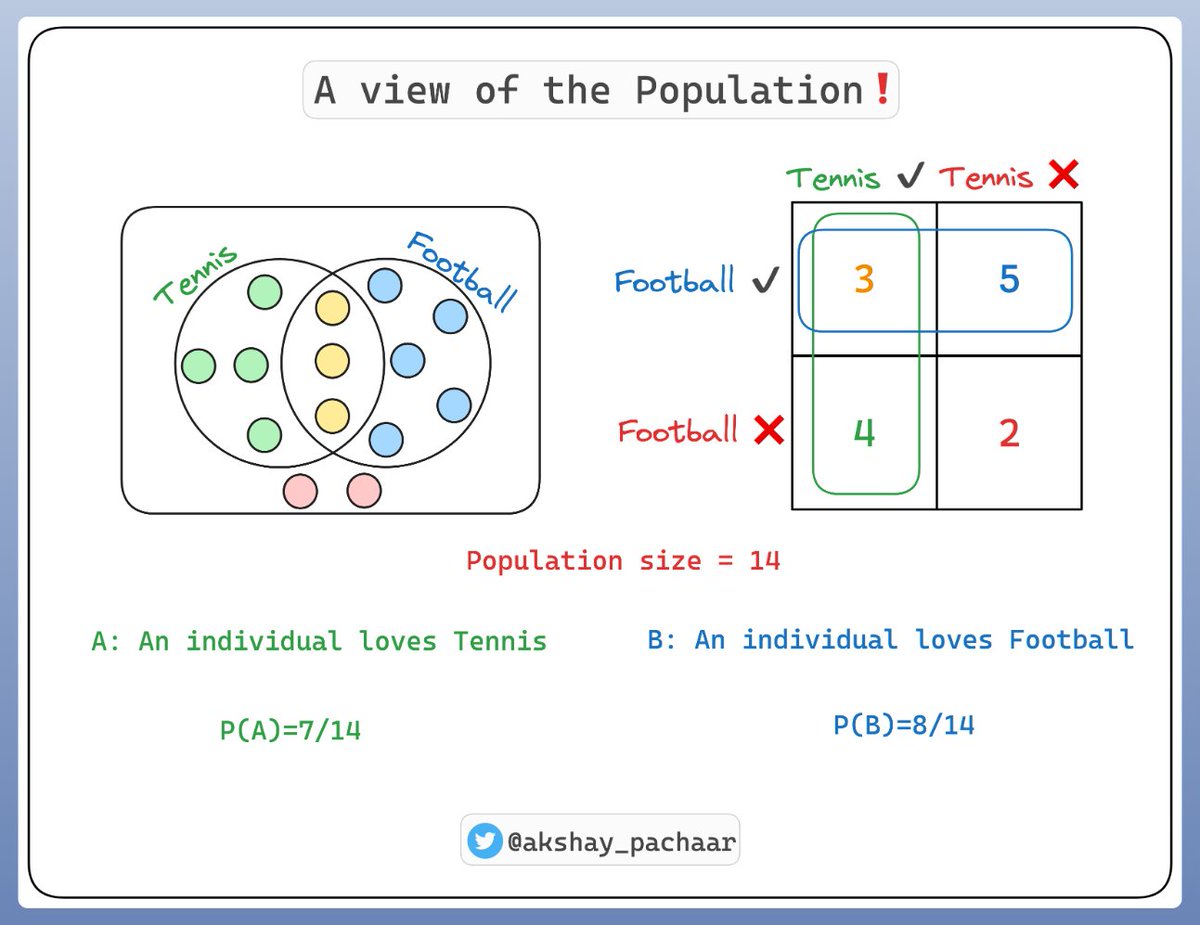
Let's consider a population of 14 individuals:
- Some of them like Tennis 🎾
- Some like Football ⚽️
- A few like both 🎾 ⚽️
- And few like none
Here's how it looks 👇
Let's consider a population of 14 individuals:
- Some of them like Tennis 🎾
- Some like Football ⚽️
- A few like both 🎾 ⚽️
- And few like none
Here's how it looks 👇
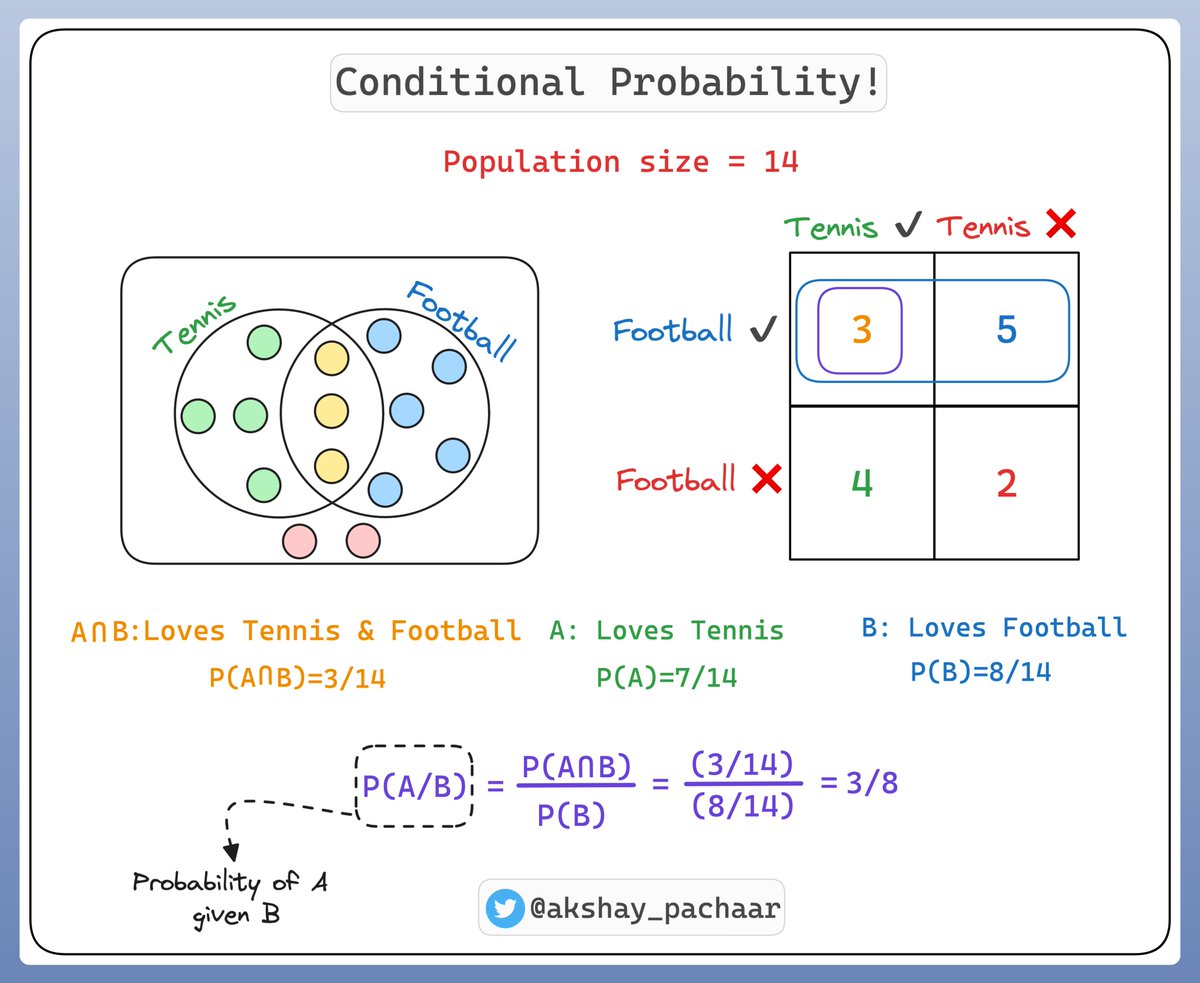
So what is Conditional probability ⁉️
It's a measure of the probability of an event given that another event has occurred.
If the events are A and B, we denote this as P(A|B).
This reads as "probability of A given B"
Check this illustration 👇
It's a measure of the probability of an event given that another event has occurred.
If the events are A and B, we denote this as P(A|B).
This reads as "probability of A given B"
Check this illustration 👇
For instance, if we're predicting whether it will rain today (event A), knowing that it's cloudy (event B) might impact our prediction.
As it's more likely to rain when it's cloudy, we'd say the conditional probability P(A|B) is high.
That's conditional probability for you! 🎉
As it's more likely to rain when it's cloudy, we'd say the conditional probability P(A|B) is high.
That's conditional probability for you! 🎉
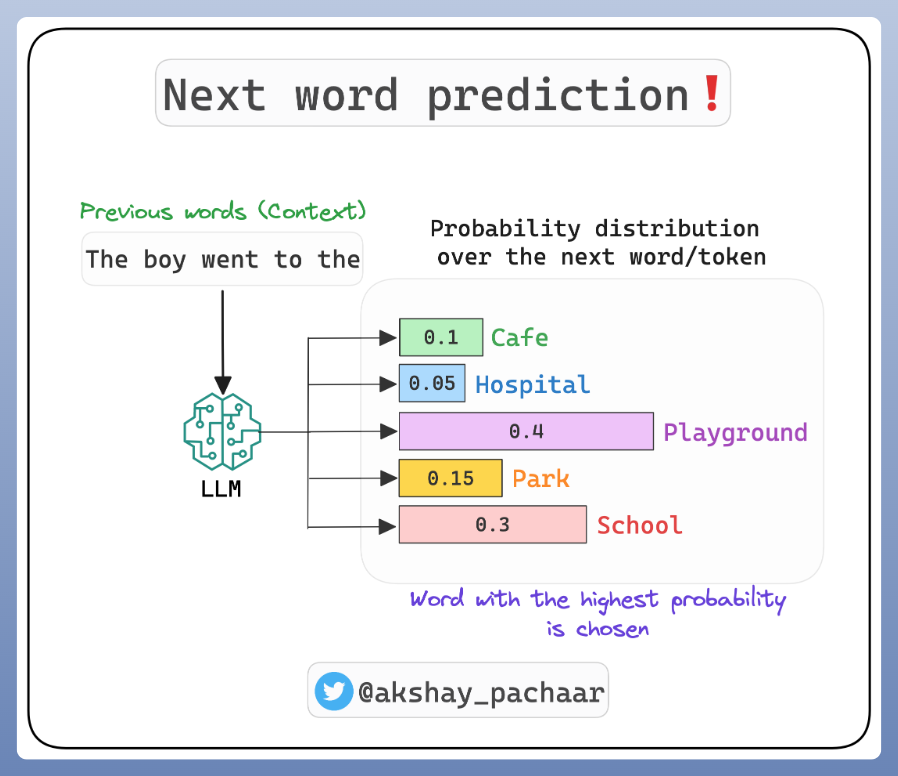
Now, how does this apply to LLMs like GPT-4❓
These models are tasked with predicting the next word in a sequence.
This is a question of conditional probability: given the words that have come before, what is the most likely next word?
These models are tasked with predicting the next word in a sequence.
This is a question of conditional probability: given the words that have come before, what is the most likely next word?

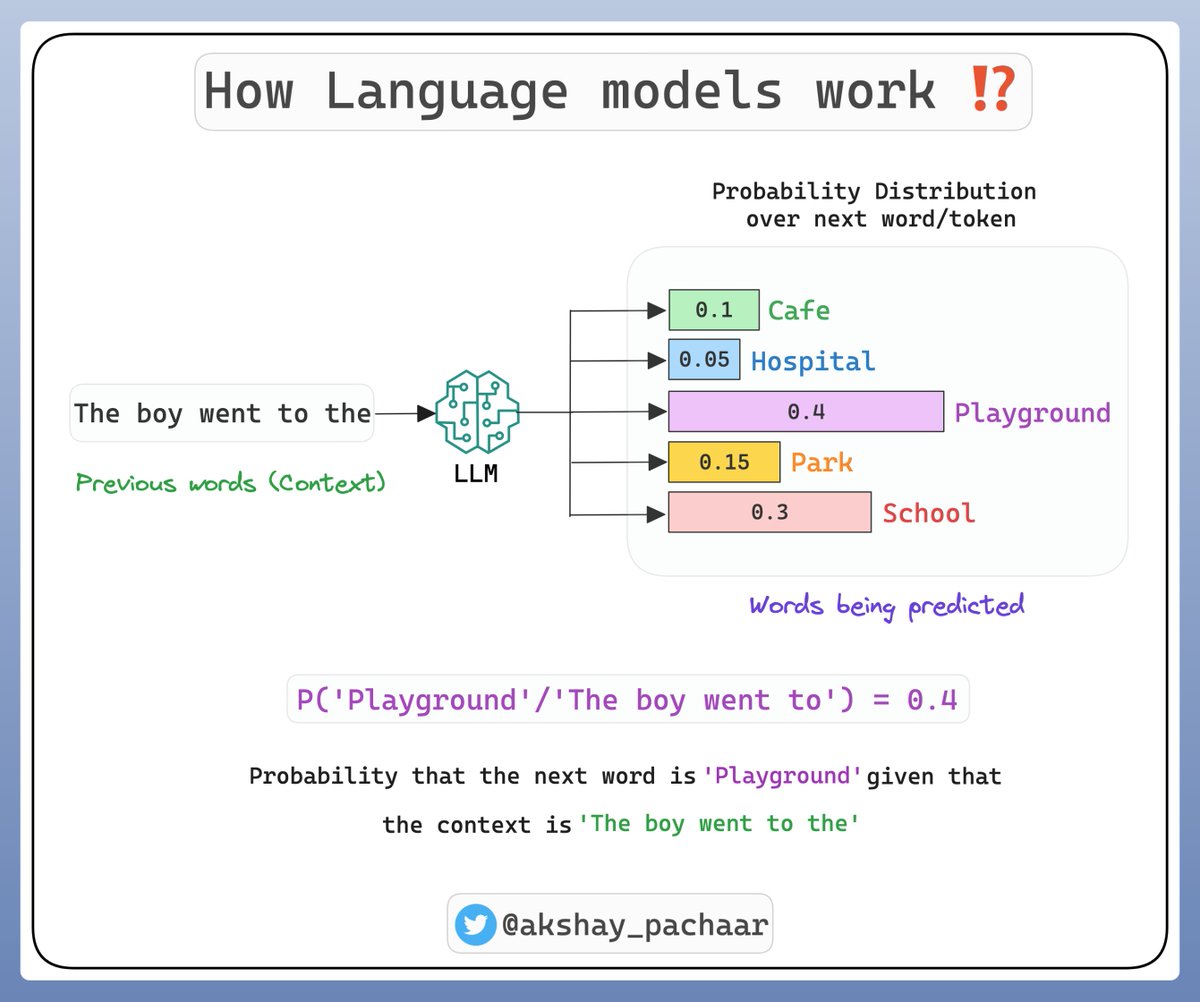
To predict the next word, the model calculates the conditional probability for each possible next word, given the previous words (context).
The word with the highest conditional probability is chosen as the prediction.
The word with the highest conditional probability is chosen as the prediction.
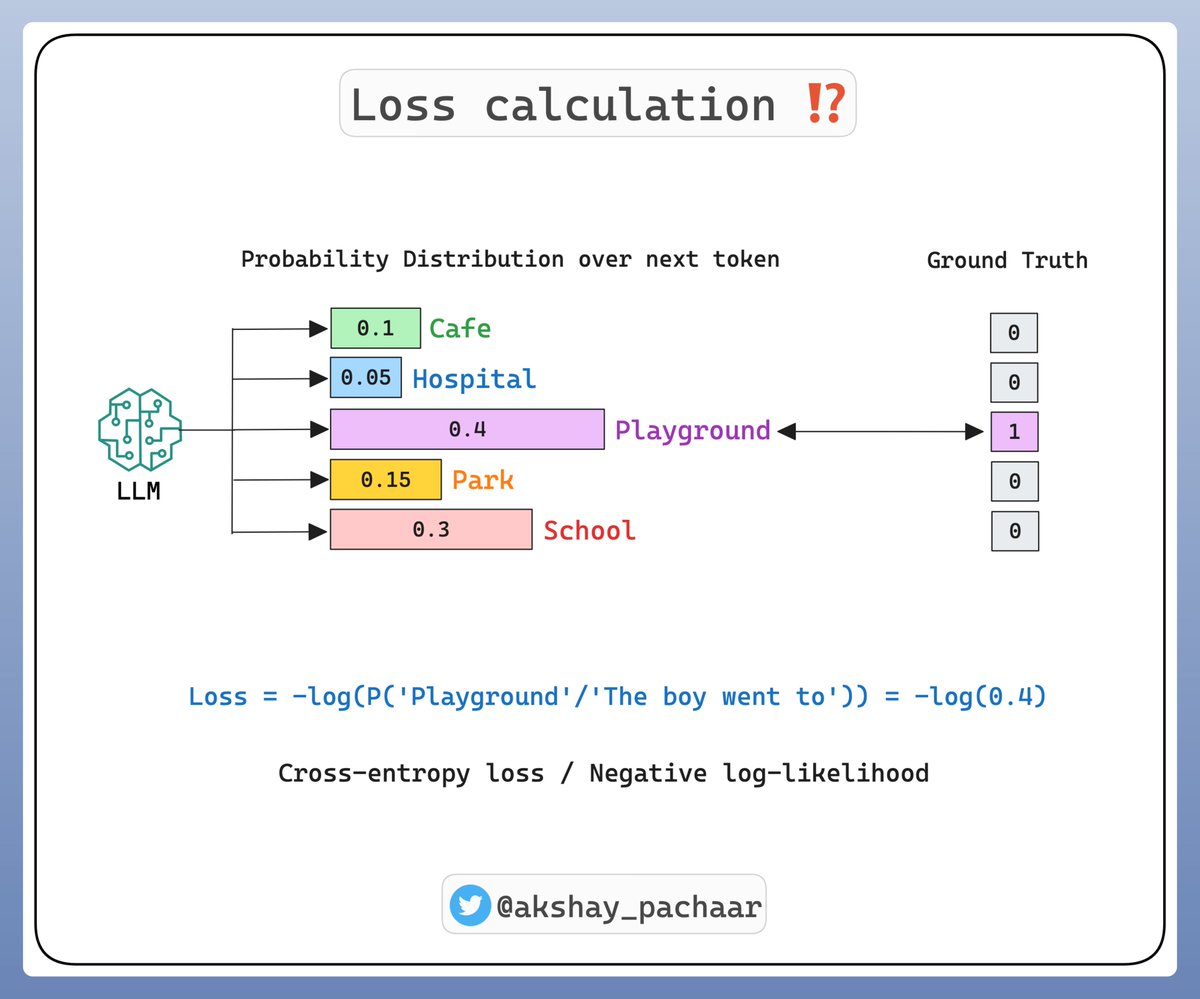
The LLM learns a high-dimensional probability distribution over sequences of words.
And the parameters of this distribution are the trained weights!
The training or rather pre-training** is supervised.
I'll talk about the different training steps next time!**
Check this 👇
And the parameters of this distribution are the trained weights!
The training or rather pre-training** is supervised.
I'll talk about the different training steps next time!**
Check this 👇
Hopefully, this thread has demystified a bit of the magic behind LLMs and the concept of conditional probability.
Here's the gist of what we learned today:
Here's the gist of what we learned today:
Working with LLMs is going to to be a high leverage skill!
@LightningAI provides state of the art tutorials on LLMs & LLMOps!
An integrated AI developer platform with access to FREE GPUs & VSCode right in your browser!
Check this: lightning.ai/lightning-ai/h…
@LightningAI provides state of the art tutorials on LLMs & LLMOps!
An integrated AI developer platform with access to FREE GPUs & VSCode right in your browser!
Check this: lightning.ai/lightning-ai/h…
If you interested in:
- Python 🐍
- Machine Learning 🤖
- AI Engineering ⚙️
Find me → @akshay_pachaar ✔️
My weekly Newsletter on AI Engineering, Join 9k+ readers: @ML_Spring
Cheers! 🥂
- Python 🐍
- Machine Learning 🤖
- AI Engineering ⚙️
Find me → @akshay_pachaar ✔️
My weekly Newsletter on AI Engineering, Join 9k+ readers: @ML_Spring
Cheers! 🥂
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh






