Would you fly on an electric plane? And what technology is needed to make this unholy powertrain work? The challenges will lead to extraordinary designs...
This is the electric aviation thread!
This is the electric aviation thread!

In this thread we'll cover:
-Different electric & hybrid aircraft power systems.
-The challenge of full electric: Closing the energy gulf.
-Enabling tech: Batteries, motors, aerodynamics.
-Will it work?
Expect incredible concepts & links to specialist aerodynamics threads!
-Different electric & hybrid aircraft power systems.
-The challenge of full electric: Closing the energy gulf.
-Enabling tech: Batteries, motors, aerodynamics.
-Will it work?
Expect incredible concepts & links to specialist aerodynamics threads!

Cycle 1: Turbo-electric power.
A gas turbine engine with generator, DC buses & convertor drives electric motors, no battery storage: This could eat 10% efficiency, but buys the ability for integrated airframe concepts such as boundary layer ingestion & distributed propulsion.
A gas turbine engine with generator, DC buses & convertor drives electric motors, no battery storage: This could eat 10% efficiency, but buys the ability for integrated airframe concepts such as boundary layer ingestion & distributed propulsion.

Hybrid-electric.
Like a car engine, an aircraft engine is most efficient at it's design cruise condition. By using rechargeable batteries & electric motors, hybrid cycles try to smooth out engine demand so it spends more time at it's most efficient point.
Like a car engine, an aircraft engine is most efficient at it's design cruise condition. By using rechargeable batteries & electric motors, hybrid cycles try to smooth out engine demand so it spends more time at it's most efficient point.

Cycle 2: Series hybrid.
A turbo electric layout plus a battery bank, the propulsor is electrically driven. Heavier even than the turbo electric cycle, it does however allow the engine to stay at optimal running condition, a net benefit for short haul & regional aircraft.


A turbo electric layout plus a battery bank, the propulsor is electrically driven. Heavier even than the turbo electric cycle, it does however allow the engine to stay at optimal running condition, a net benefit for short haul & regional aircraft.


Cycle 3: Parallel hybrid.
A transmission box allows either engine or electric motor to power the prop. More complex but lighter than series hybrid with fewer conversion losses, but leads to the engine running off-design more often. Considered less efficient than series hybrid.
A transmission box allows either engine or electric motor to power the prop. More complex but lighter than series hybrid with fewer conversion losses, but leads to the engine running off-design more often. Considered less efficient than series hybrid.

The trouble with hybrids is that, just as a hybrid car is best at town & city driving, a hybrid plane is best at short haul & general aviation: Long haul aircraft spend too long at their design condition for hybrid power systems to be of much use.
What about pure electric?
What about pure electric?

Cycle 4: Battery electric.
Conceptually the simplest setup, it's simultaneously the most "green", as a zero emissions aircraft, and the most difficult, which we'll get into.
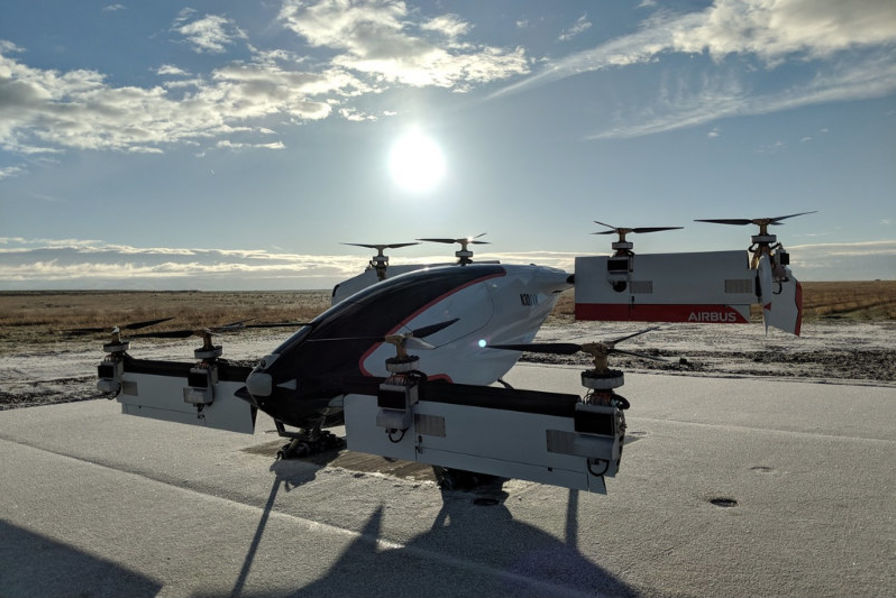
Pictured: The RR 'Spirit Of Innovation' demonstrator. At 345mph, the fastest electric plane.


Conceptually the simplest setup, it's simultaneously the most "green", as a zero emissions aircraft, and the most difficult, which we'll get into.
Pictured: The RR 'Spirit Of Innovation' demonstrator. At 345mph, the fastest electric plane.


If we do it, it won't be for convenience: The specific energy of kerosene is 48 times higher than lithium ion batteries: An unbridgeable gulf?
Electric motors are 90%+ efficient while the thermodynamic efficiency of gas turbines are ~55%, making the ratio 'only' 1:29
Electric motors are 90%+ efficient while the thermodynamic efficiency of gas turbines are ~55%, making the ratio 'only' 1:29

Enablers 1: Batteries.
Li-ion batteries, the gold standard, max at ~250Wh/kg.
Li-sulphur, on the Airbus Zephyr have shown 500Wh/kg but so far only 1350 cycles.
Solid state: Fast-charging and 500-1000Wh/kg. Under development.
Li-Air: Potentially 1700Wh/kg, but a long way off.


Li-ion batteries, the gold standard, max at ~250Wh/kg.
Li-sulphur, on the Airbus Zephyr have shown 500Wh/kg but so far only 1350 cycles.
Solid state: Fast-charging and 500-1000Wh/kg. Under development.
Li-Air: Potentially 1700Wh/kg, but a long way off.


Enablers 2: Motors.
Conventional motors have a specific power of 1-5kW/kg, less than gas turbines.
-In 2021 H3X & Wright Electric tested 250kW & 2MW motors with 13 & 10kW/kg.
The EU sponsored ASuMED project is developing high temperature superconductor motors for 20kW/kg.
Conventional motors have a specific power of 1-5kW/kg, less than gas turbines.
-In 2021 H3X & Wright Electric tested 250kW & 2MW motors with 13 & 10kW/kg.
The EU sponsored ASuMED project is developing high temperature superconductor motors for 20kW/kg.

Batteries of 800Wh/kg are probably a minimum for electric aviation: If we assume that 1000 is achievable then that brings the usable specific energy ratio with kerosene down to 1:7.
This means that aerodynamics must do some heavy lifting to get it down to low single figures...
This means that aerodynamics must do some heavy lifting to get it down to low single figures...

Enablers 3: Distributed propulsion.
Electric powertrains allow this: Extremely high bypass low pressure ratio propulsors with blown wing effects maximizing efficiency.
The hybrid electric EcoPulse aircraft shown is halfway through flight testing proving this concept.
Electric powertrains allow this: Extremely high bypass low pressure ratio propulsors with blown wing effects maximizing efficiency.
The hybrid electric EcoPulse aircraft shown is halfway through flight testing proving this concept.

A thread on distributed propulsion is linked below, featuring the ONERA Dragon concept: A medium range airliner showing a 7%-12% efficiency benefit from distributed propulsion alone. Hybrid power storage could increase this further.
https://twitter.com/Jordan_W_Taylor/status/1670112250755948544?t=EvhJ6JysWwG5CfOiDEs3RA&s=19
Enablers 4: Boundary layer ingestion.
This wake energy management technique reduces flow field energy loss and can improve the efficiency of propulsors by embedding them in the aircraft boundary layer. A structurally robust well-sited prop is needed.
This wake energy management technique reduces flow field energy loss and can improve the efficiency of propulsors by embedding them in the aircraft boundary layer. A structurally robust well-sited prop is needed.
https://twitter.com/Jordan_W_Taylor/status/1717989719739433047?t=Q90Ef21MO7yxSOfiPz96rg&s=19
Enablers 5: Blended wing/ body design.
Definitely the biggest ask of airframers & airports, and not strictly necessary, it remains a potentially optimal platform from an efficiency standpoint, and works well with distributed propulsion & BLI.
Definitely the biggest ask of airframers & airports, and not strictly necessary, it remains a potentially optimal platform from an efficiency standpoint, and works well with distributed propulsion & BLI.
https://twitter.com/Jordan_W_Taylor/status/1669954817316233217?t=L_-OHNTGXydllyU4exnmsw&s=19
The NASA N3-X concept uses all three aero enablers in a long range turbo-electric flying wing with cryocoolers enabling superconducting motors and higher turbine inlet temperature.
60% more fuel efficient than current state of the art, it's an idealised design but instructive.
60% more fuel efficient than current state of the art, it's an idealised design but instructive.

Another rich opportunity for hybrid power is helicopter aviation, where it would be worth 10% in efficiency all on it's own without other improvements. Airbus recently tested this as part of an emergency back up power system for the FlightLab helicopter. 

Novel hybrid electric/ turbo-electric power architectures, with a gas turbine engine at the core, have huge potential from short to long range, and we should move that way, but the aerospace industry might not leap without a push.
What about pure electric aircraft..?
What about pure electric aircraft..?

Frankly, pure electric is a lost cause everywhere except short range and city transport niches: The specific energy gulf is just too large.
But it's still important: Electric aviation's huge energy challenge forces it to deal with unconventional design, and this is it's value.
But it's still important: Electric aviation's huge energy challenge forces it to deal with unconventional design, and this is it's value.

The city eVTOL niche is tiny, almost a joke, but it's the only electric aviation sector plausible right now, making it a technology incubator.
Inconsistent regulation could kill it dead, and it's important we don't do that: Technology grows from seeds, which we should water.


Inconsistent regulation could kill it dead, and it's important we don't do that: Technology grows from seeds, which we should water.


So let's hear it for the challenge of electric aviation, because it might, just maybe, be a catalyst that will move us beyond the tube, wing & twin configuration.
So the future might actually look like the future.
Papers used are shown, I hope you enjoyed this!




So the future might actually look like the future.
Papers used are shown, I hope you enjoyed this!




• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh