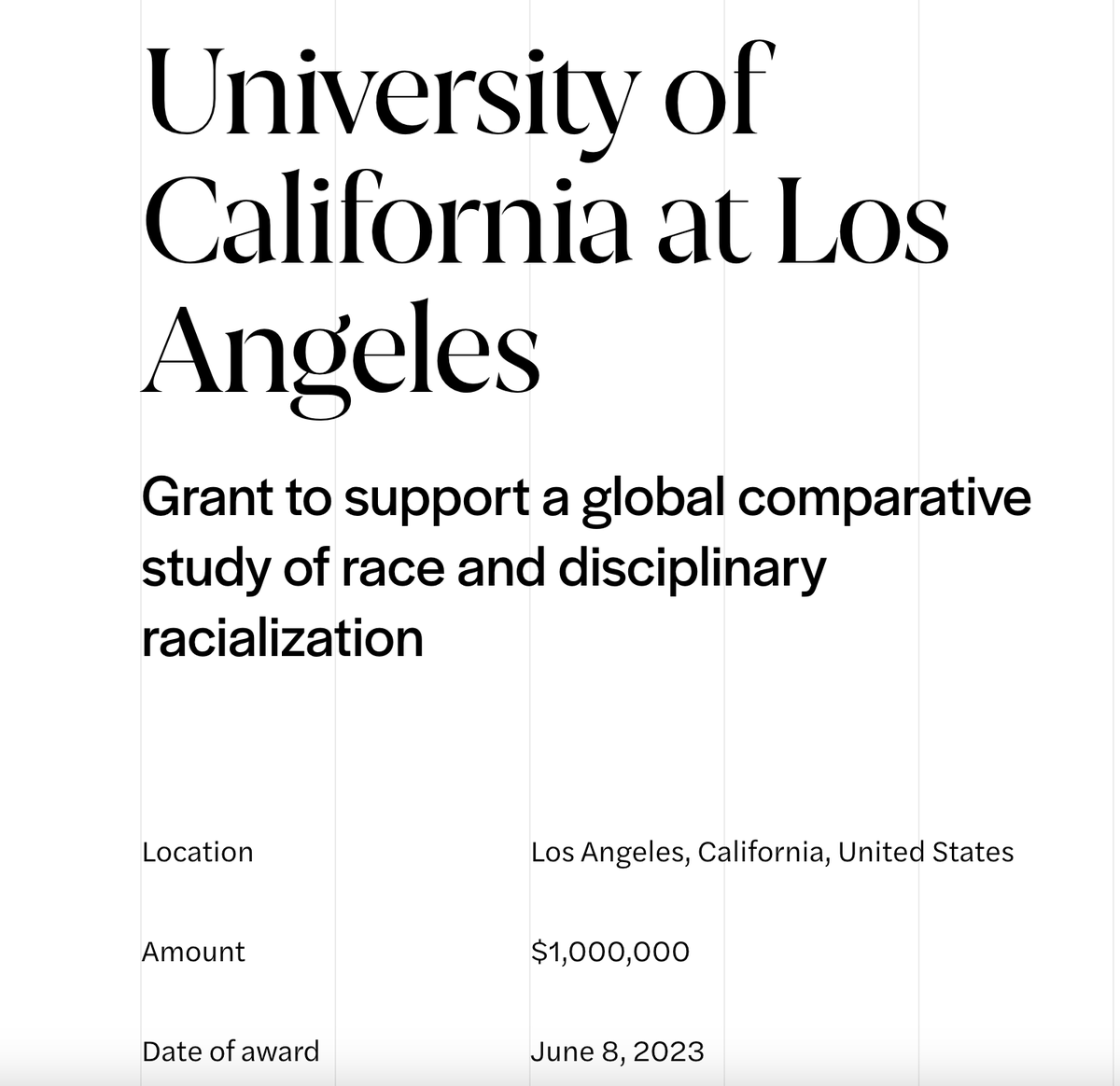
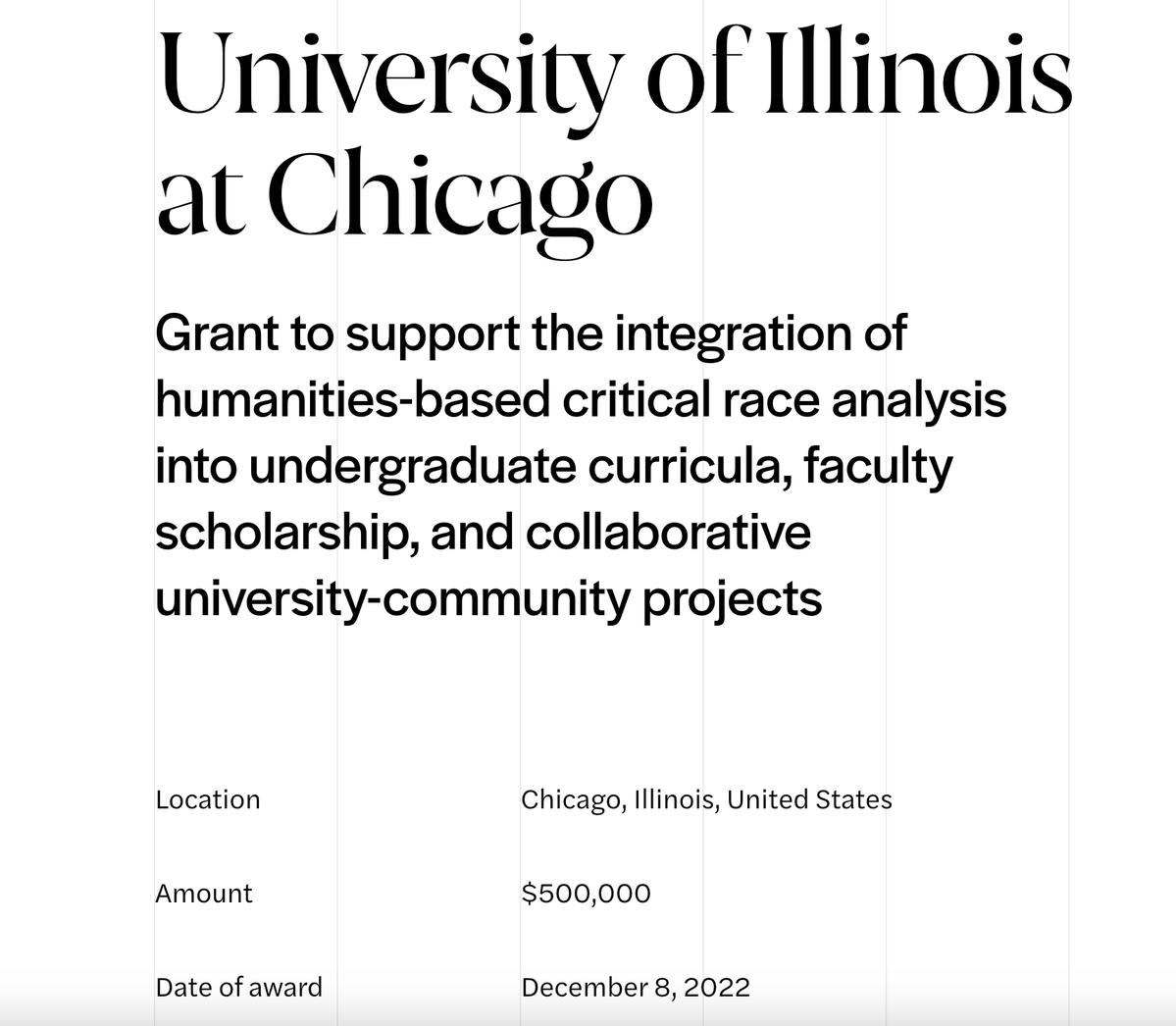
Do universities discriminate against white candidates? Yes. Especially when hiring professors focused on identity/social justice.
These positions give universities plausible deniability for race-based hiring, which is common in academia.
I have receipts. 🧵
These positions give universities plausible deniability for race-based hiring, which is common in academia.
I have receipts. 🧵

It’s worth remembering the academic job market’s total saturation in positions focused on race, identity, and social justice.
Things like "indigenous Siberian studies" and classics with a focus on "race, racism, and Greek & Roman studies."



Things like "indigenous Siberian studies" and classics with a focus on "race, racism, and Greek & Roman studies."



This has entirely skewed certain disciplines. A grad student looking at a field like, say, German studies will be able to put two and two together.
There are hardly any jobs out there, and the jobs that are out there tend to fit a specific theme.
There are hardly any jobs out there, and the jobs that are out there tend to fit a specific theme.
https://x.com/JohnDSailer/status/1717236367523029437
A grad student in the shoes of David Austin Walsh might think they have the right formula: even if you’re a white guy, just specialize in the right things, then you'll have at least a shot.
That is verifiably incorrect.
Universities very explicitly say these race/identity/social justice jobs exist to target specific groups. They get very close to openly declaring their intention to discriminate in the hiring process.
That is verifiably incorrect.
Universities very explicitly say these race/identity/social justice jobs exist to target specific groups. They get very close to openly declaring their intention to discriminate in the hiring process.
I've repeatedly found search committees openly admit to using racial preferences.
Ohio State sought a professor of French studies with a "specialization in Black France."
The search committee stated that hiring a “visible minority” was a key priority—so they only invited black candidates for on campus interviews.
Ohio State sought a professor of French studies with a "specialization in Black France."
The search committee stated that hiring a “visible minority” was a key priority—so they only invited black candidates for on campus interviews.

The University of Washington conducted a search for a professor focused on diversity.
A white woman was the search committee's first choice.
A diversity committee member objected on the grounds of race.
They then re-ranked the candidates.


A white woman was the search committee's first choice.
A diversity committee member objected on the grounds of race.
They then re-ranked the candidates.


Here's the University of Washington diversity advisory committee member noting that it's "optically-speaking" a bad look that the offer to go to a white woman. 

This is the goal of "cluster hiring," hiring multiple candidates at once w/ a focus on DEI, increasingly popular in academia.
In the sciences, that means heavily weighing DEI statements. But in the humanities, it commonly involves hiring w/ a race/identity/social justice focus.
In the sciences, that means heavily weighing DEI statements. But in the humanities, it commonly involves hiring w/ a race/identity/social justice focus.

A professor friend recently told me that everyone in his university system acts like cluster hiring is just a legal form of racial quotas.
But again, we don't have to rely on rumors. Administrators have literally said that's exactly what they're doing.

But again, we don't have to rely on rumors. Administrators have literally said that's exactly what they're doing.
https://x.com/JohnDSailer/status/1702374668030578724

We have the worst of both worlds.
Our universities contort entire academic disciplines, narrowly focusing on social justice, applying de facto ideological weed-out tools like diversity statements—all for the sake of achieving (or masking) racial preferences.
Our universities contort entire academic disciplines, narrowly focusing on social justice, applying de facto ideological weed-out tools like diversity statements—all for the sake of achieving (or masking) racial preferences.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh