OK, science geeks. Sex testing and sport.
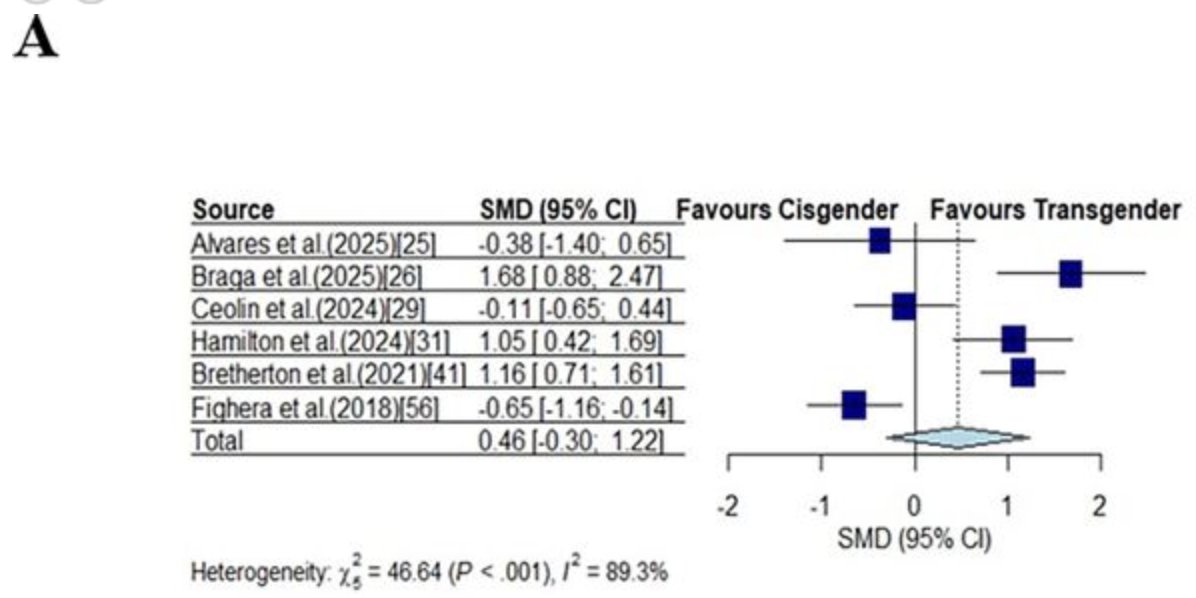
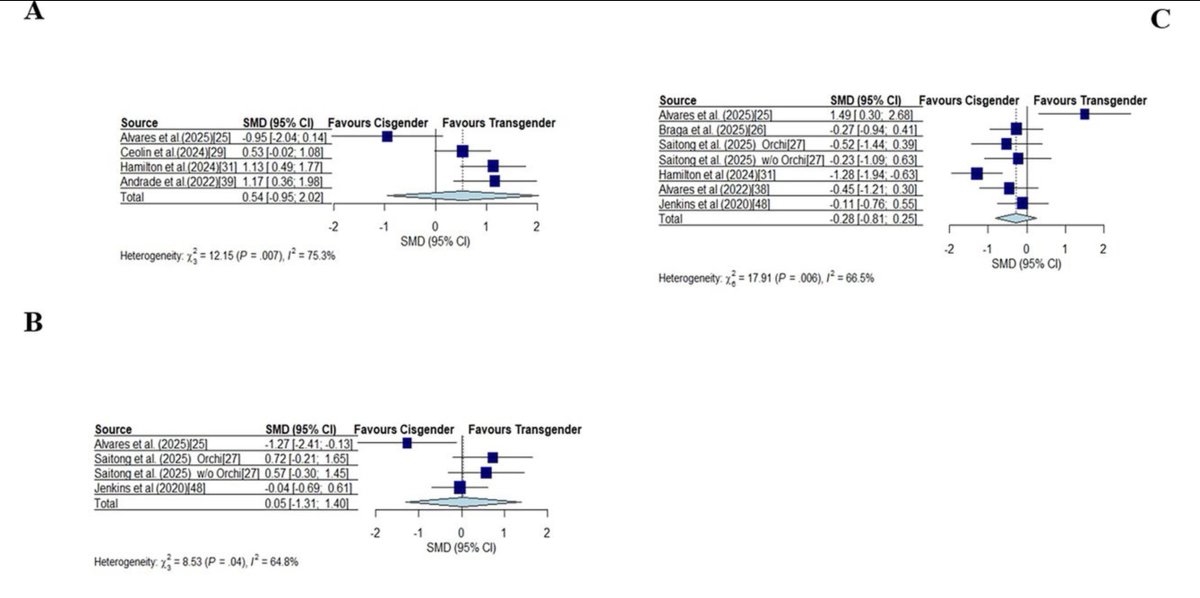
There are many people spreading misinformation about the reliability of sex testing, repeating arguments made for its abolition some 25 years ago.
I don’t know if they have noticed that we’ve undergone something of a genetics revolution over the past few decades 😀
There are many people spreading misinformation about the reliability of sex testing, repeating arguments made for its abolition some 25 years ago.
I don’t know if they have noticed that we’ve undergone something of a genetics revolution over the past few decades 😀

So let’s look at some chromosomes.
Historically, chromosomes were analysed by adding a chemical dye to cells and looking at their shape and size. Given that most animals have two copies of each chromosome, the pairs could be lined up by matching their shape and size.
These are chromosomes stained with a dye called hemotoxylin. I still use this dye in the lab today.
Historically, chromosomes were analysed by adding a chemical dye to cells and looking at their shape and size. Given that most animals have two copies of each chromosome, the pairs could be lined up by matching their shape and size.
These are chromosomes stained with a dye called hemotoxylin. I still use this dye in the lab today.

Nettie Stevens discovered sex chromosomes in the early 1900s, after noting that female worms had twenty big chromosomes while male worms had nineteen big chromosomes and plus a small one.
Further, she noted that Worm Sperm either had ten big chromosomes or nine big chromosomes plus a small chromosome.
She reasoned that the small chromosome carried by some sperm makes male babies, while the sperm carrying the tenth big chromosome made female babies.
Brilliant woman, but her discoveries were overshadowed by the male scientists of the era, of course.

Further, she noted that Worm Sperm either had ten big chromosomes or nine big chromosomes plus a small chromosome.
She reasoned that the small chromosome carried by some sperm makes male babies, while the sperm carrying the tenth big chromosome made female babies.
Brilliant woman, but her discoveries were overshadowed by the male scientists of the era, of course.


In the ensuing decades, improvements in sample preparation, the types of dyes used, and the optics of looking at tiny samples, meant scientists could start to score chromosomes not just by size and shape, but by the pattern the dyes made on each pair of chromosomes. This made the tedious work of matching up pairs much easier.



In the 1940s, Murray Barr discovered a tightly-packed ball of chromosome material hanging around the edges of the female cell nucleus. He named this the Barr Body.
He also developed, in the 1950s, the cheek swab as a way of sampling human chromosomes.


He also developed, in the 1950s, the cheek swab as a way of sampling human chromosomes.


In the 1960s, Mary Lyon discovered that in female mammals, who have two copies of the X chromosome, one of those Xs is shut down. We now know that this process is needed to regulate the amount of active X chromosome genes a cell can handle. Males, with only one X, don’t need to do this.
The tightly-packed ball of chromosome material discovered in the 1940s - the Barr body - is this inactivated X chromosome. The process of packing the X ball is called Lyonization. It is this process of shutting down one X chromosome that gives us beautiful (female) lion-like creatures.
The process is also important in understanding how sex-linked genetic diseases affect females differently. Including in my own research.
The tightly-packed ball of chromosome material discovered in the 1940s - the Barr body - is this inactivated X chromosome. The process of packing the X ball is called Lyonization. It is this process of shutting down one X chromosome that gives us beautiful (female) lion-like creatures.
The process is also important in understanding how sex-linked genetic diseases affect females differently. Including in my own research.

It was soon realised that looking for Barr bodies - which give a very intense and obvious dye signal – was a quick way of checking what sex an animal was.
Including, in 1968, human animals playing female sport.
Females with two Xs have this bright dye spot, males with only one X don’t. Simple, right?
But some males have an extra X (XXY, Klinefelter Syndrome) and they pack their second X down, just like females, giving a positive signal on the Barr body test. And some females only have one X (X0, Turner Syndrome) and no Barr body.
The Barr body test could tell you about second or extra X chromosomes, but this wasn’t the best way to understand the sex of the person.
Including, in 1968, human animals playing female sport.
Females with two Xs have this bright dye spot, males with only one X don’t. Simple, right?
But some males have an extra X (XXY, Klinefelter Syndrome) and they pack their second X down, just like females, giving a positive signal on the Barr body test. And some females only have one X (X0, Turner Syndrome) and no Barr body.
The Barr body test could tell you about second or extra X chromosomes, but this wasn’t the best way to understand the sex of the person.

In 1992, sex testing sport switched to the more accurate method of trying to find a gene on the Y chromosome called SRY. This gene is considered a master switch in male development.
The test was done in a chemical reaction (the polymerase chain reaction, for the geeks) to rapidly replicate large amounts of the SRY gene from a DNA sample, which could then be detected by routine DNA gel analysis. If SRY isn’t in the sample, you don’t get any replication.
Can anyone take a guess at the sex of the fetus in the image below?
The test was done in a chemical reaction (the polymerase chain reaction, for the geeks) to rapidly replicate large amounts of the SRY gene from a DNA sample, which could then be detected by routine DNA gel analysis. If SRY isn’t in the sample, you don’t get any replication.
Can anyone take a guess at the sex of the fetus in the image below?

But, of course, some males may have the SRY gene but they do not develop as a healthy male. That is, they have a disorder of sex development.
In 1999, sex testing was abolished, given the unusual results popping in the female athletes, the potential for trauma in those athletes, and the prevailing opinion that having a male XY DSD probably didn’t matter in female sport.
In 1999, sex testing was abolished, given the unusual results popping in the female athletes, the potential for trauma in those athletes, and the prevailing opinion that having a male XY DSD probably didn’t matter in female sport.
Of course, today, that prevailing opinion from over two decades ago has been overturned. We understand more about sports performance, male advantage, and what anatomical features contribute to it.
We have far easier and cheaper ways of looking at chromosomes and DNA, and we have stronger ethical frameworks regarding genetic testing. The “bad old days” that the International Olympic Committee evoke to obstruct sex testing that would protect the female category is a red herring.
We have far easier and cheaper ways of looking at chromosomes and DNA, and we have stronger ethical frameworks regarding genetic testing. The “bad old days” that the International Olympic Committee evoke to obstruct sex testing that would protect the female category is a red herring.
Today, testing for sex is routine. Our sampling is better, and we can find sex chromosomes from really small amounts of suboptimal material. As many mother’s will know, we can find fetal sex chromosomes from Mum’s blood sample. Our dyes are better. Our imaging is better.
Forget dyes that showed us size and shape, forget dyes that give us patterns of bands, and start looking at light-emitting molecular dyes that bond to specific genes on specific chromosomes instead (and light up two green Xs and one red SRY). Look at how a computer can read those signals.

Forget dyes that showed us size and shape, forget dyes that give us patterns of bands, and start looking at light-emitting molecular dyes that bond to specific genes on specific chromosomes instead (and light up two green Xs and one red SRY). Look at how a computer can read those signals.


I mean, even this Beetle Lady can do it ;)
The flashes of red light you see? That’s from my published research, flagging an X chromosome gene that underpins a sex-linked genetic disease that is lethal in male fetuses.
The flashes of red light you see? That’s from my published research, flagging an X chromosome gene that underpins a sex-linked genetic disease that is lethal in male fetuses.

Forget those gels of a single rapidly replicated gene and start thinking about putting those light-emitting flags into the chemical reaction instead. The more replication, the brighter the light signal. And why not add multiple genes to the same process. And trust me, a light detector can see things your eye cannot.
See those differently coloured lines? They are different pieces of DNA being rapidly replicated in the same sample.
See those differently coloured lines? They are different pieces of DNA being rapidly replicated in the same sample.

And why stop at whether a gene is there or not? Why not look at the sequence of a gene? Gone are the painstaking days of moving down a radioactive image with a ruler. I can get a computer to read a gene sequence for me in a few days for a few pounds. And even this is by a fairly cheap and old-fashioned method.



In 2003, the Human Genome Project was completed. This was first full sequencing of all the genes (plus everything else in between) on all the chromosomes in a human being.
It took a global effort 13 years to complete, and cost $billions.
Today, not so much. We can sequence the entire gene set of a human being in a matter of weeks for $hundreds.
It took a global effort 13 years to complete, and cost $billions.
Today, not so much. We can sequence the entire gene set of a human being in a matter of weeks for $hundreds.

The IOC is fervently hoping that renewed calls for sex testing sport quietly go away.
Ironically, they probably will. Because now on the horizon of this genetic revolution is, quite simply, standard screening of whole genomes in newborn babies.
No longer will we have to trust a midwife to take a guess 😉

Ironically, they probably will. Because now on the horizon of this genetic revolution is, quite simply, standard screening of whole genomes in newborn babies.
No longer will we have to trust a midwife to take a guess 😉


• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh