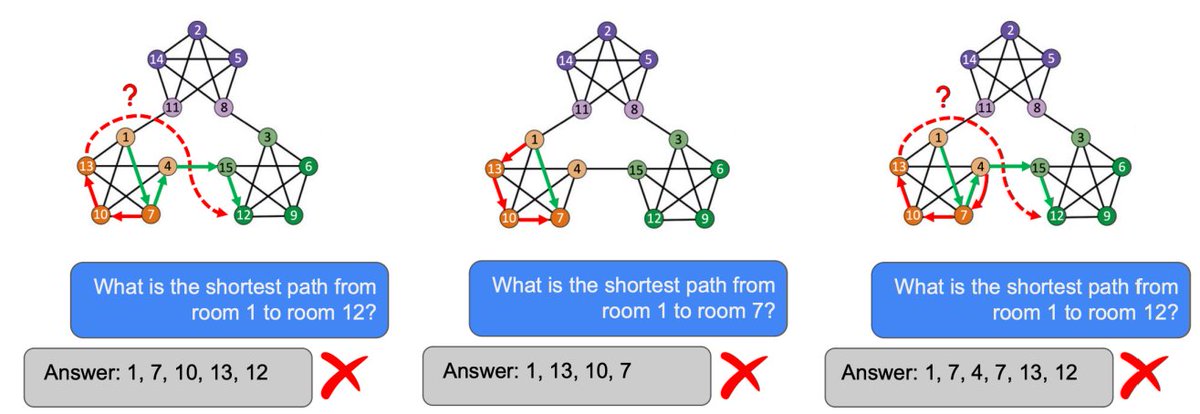
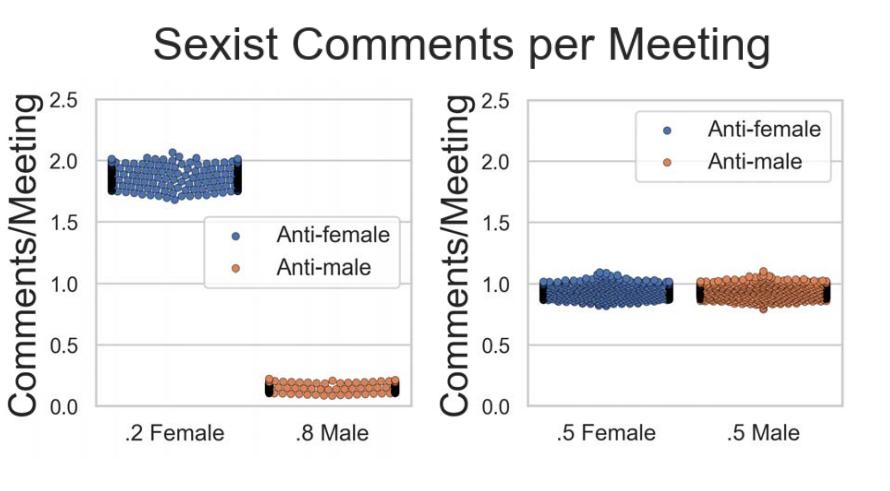
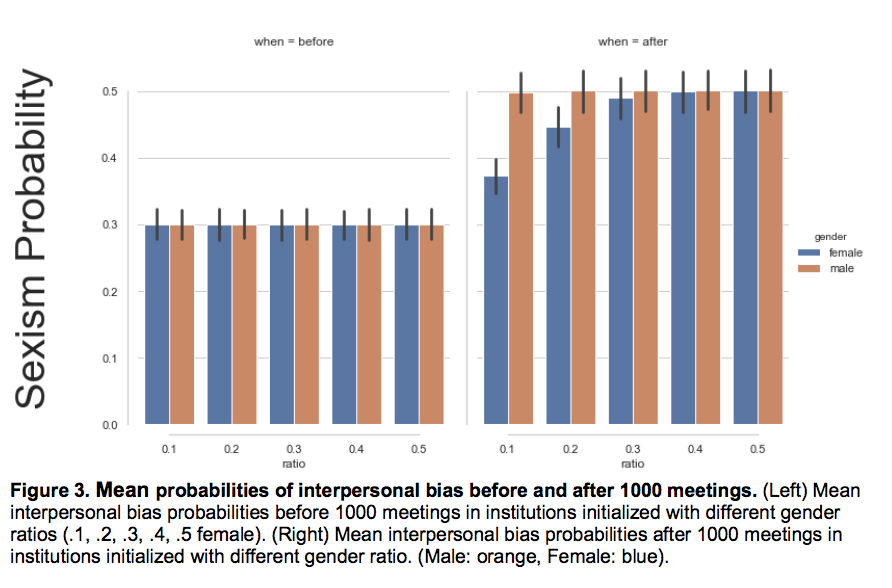
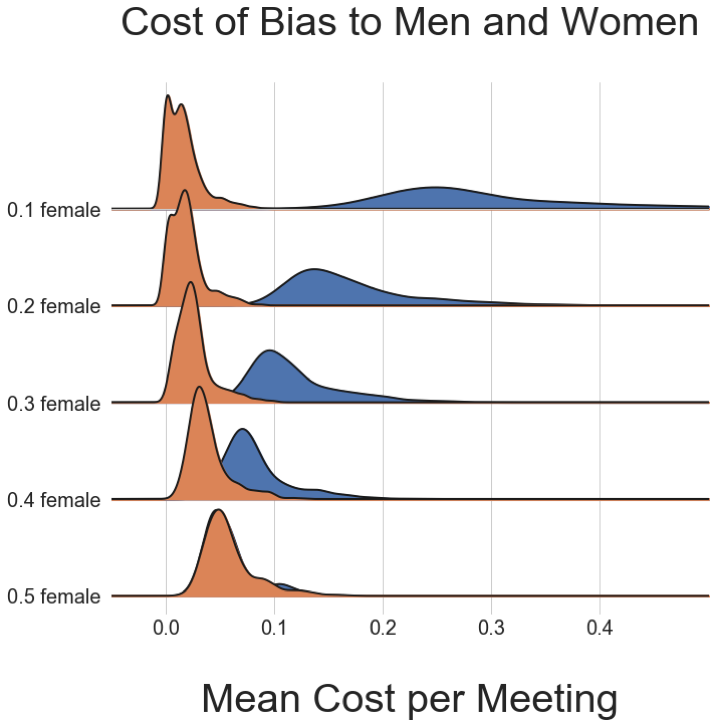
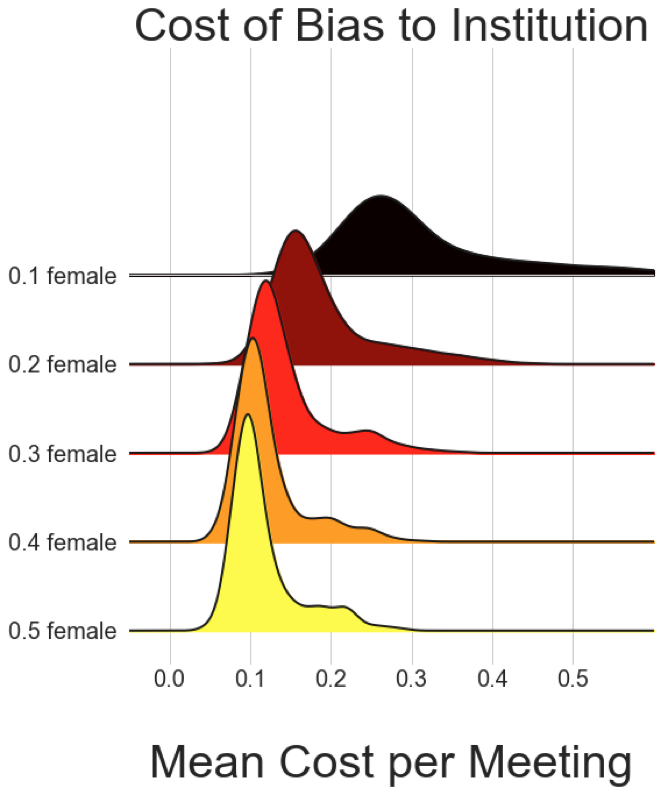
A thread on the history of RL/ML based on Andy Barto's talk #RLC2024: the Reinforcement Learning Conference.
Beyond seeing friends & giving talks/panel, talking to @RichardSSutton & hearing Andy Barto revived a need for attention to historical psych/neuro influences on AI.
1/n🧵
Beyond seeing friends & giving talks/panel, talking to @RichardSSutton & hearing Andy Barto revived a need for attention to historical psych/neuro influences on AI.
1/n🧵

Andy Barto started off the talk defining RL in terms of Search (trial & error, generate & test, variation & selection) + Memory (caching past solutions),
leading to RL as "General contextual search".
He then took us through a tour of historical intellectual influences on RL
2/n


leading to RL as "General contextual search".
He then took us through a tour of historical intellectual influences on RL
2/n


First, RL work with @RichardSSutton & contemporary intellectual influences:
The logic of computers group @ Michigan (Burks, Holland, Zeigler: cellular automata, modeling, simulation)
The systems neuroscience center @ Amherst (Arbib, Kilmer, Spinelli: Adaptive Intelligence).
3/n


The logic of computers group @ Michigan (Burks, Holland, Zeigler: cellular automata, modeling, simulation)
The systems neuroscience center @ Amherst (Arbib, Kilmer, Spinelli: Adaptive Intelligence).
3/n


Learning by Trial & Error in RL is a la Klopf's law of effect for synaptic plasticity: Hedonistic Neurons maximize local analog of pleasure & minimize local pain. Synapses active in action potential become eligible for change-increase weight if rewarded, decrease if punished
4/n



4/n


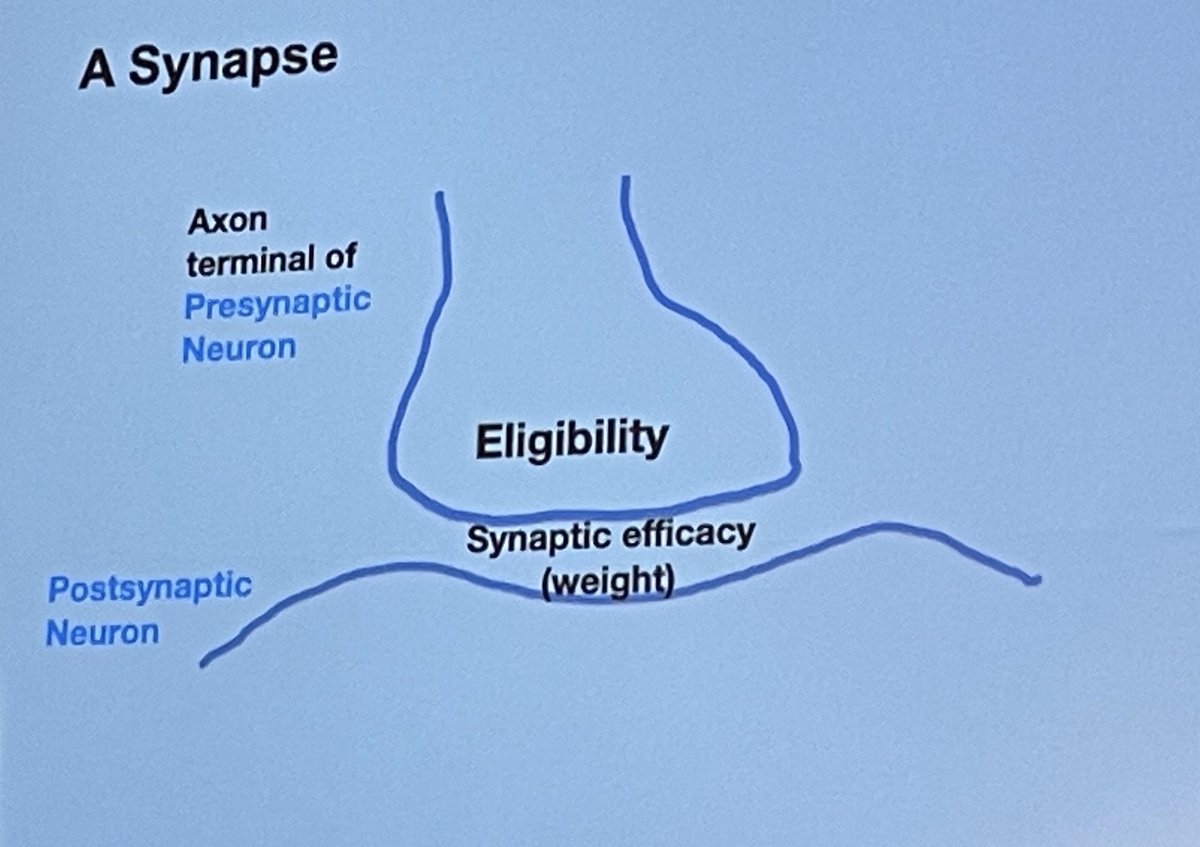
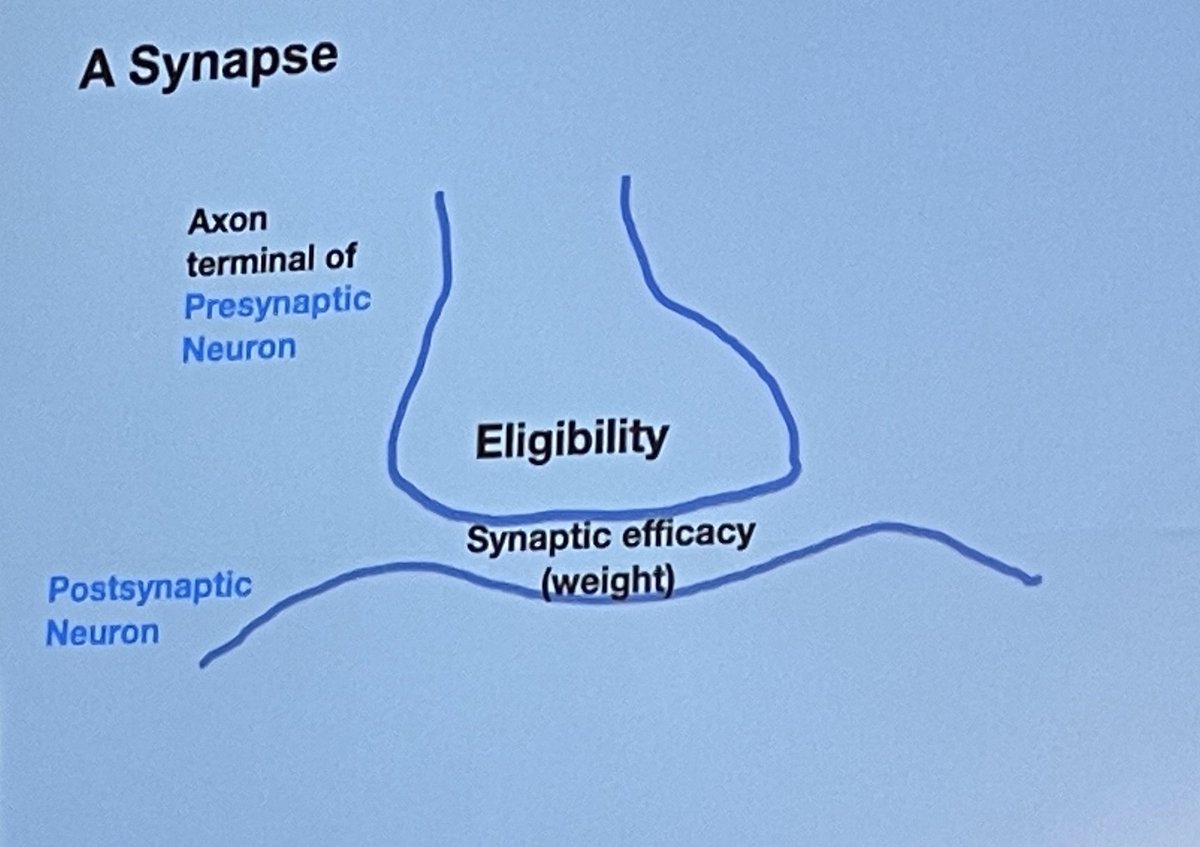
Andy Barto distinguished 2 kinds of Eligibility for weight change.
Contingent Eligibility depends on pre- and post-synaptic activity, leading to 3-factor learning rule.
Non-contingent Eligibility is triggered by only pre-synaptic activity, leading to a 2-factor learning rule.
5/n


Contingent Eligibility depends on pre- and post-synaptic activity, leading to 3-factor learning rule.
Non-contingent Eligibility is triggered by only pre-synaptic activity, leading to a 2-factor learning rule.
5/n

Bartio & @RichardSSutton's seminal first paper (1981): A modern theory of adaptive networks with expectation & prediction.
Influences include
-Klopf: learning by trial & error-idea dates back to 1800s
-adaptive intelligence
-synaptic plasticity inspired
-Sutton BA in psych!
6/n


Influences include
-Klopf: learning by trial & error-idea dates back to 1800s
-adaptive intelligence
-synaptic plasticity inspired
-Sutton BA in psych!
6/n


@RichardSSutton Barto Acknowledging the many disciplines, interactions, & lineages of ideas that shaped RL was refreshing.
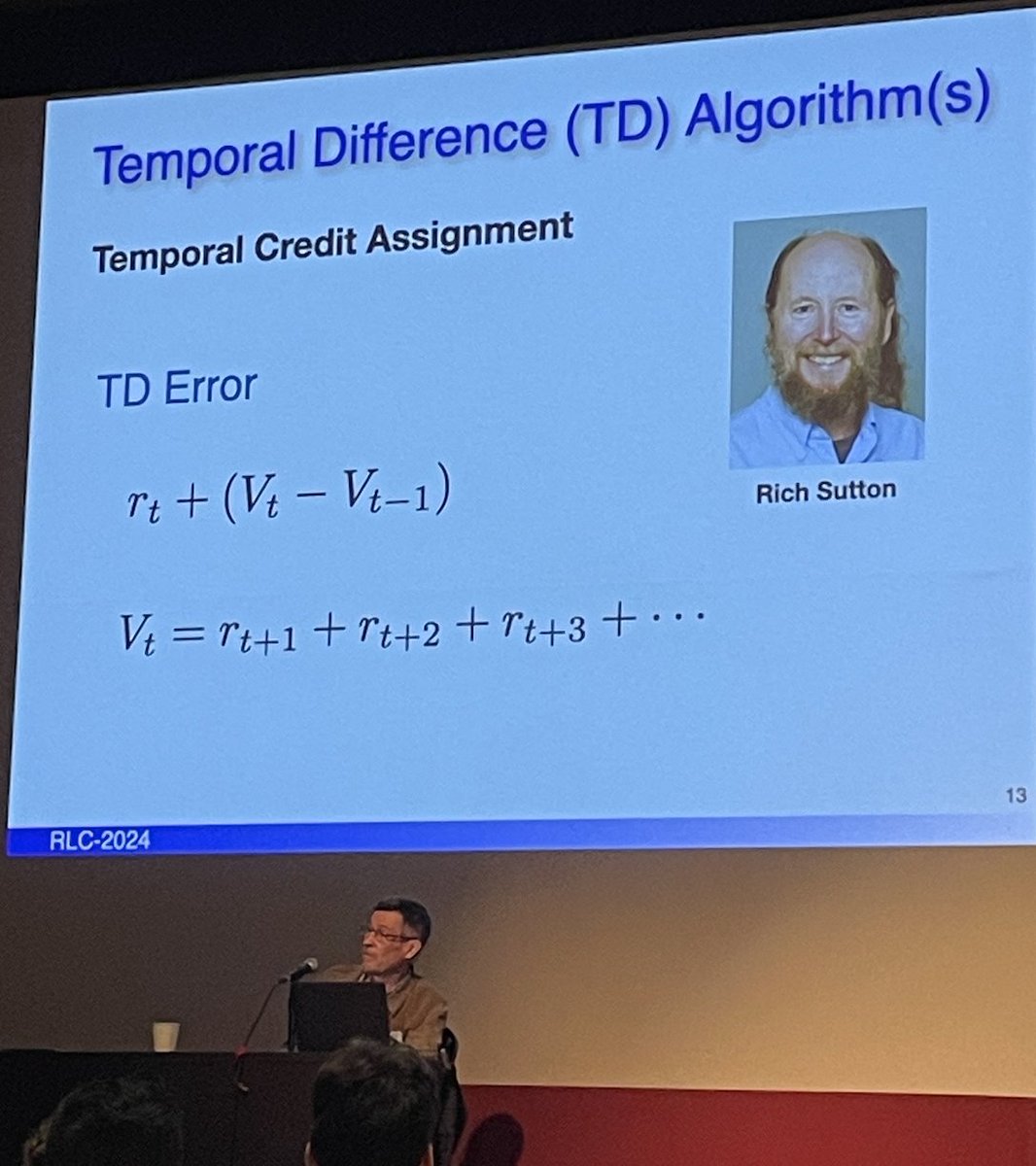
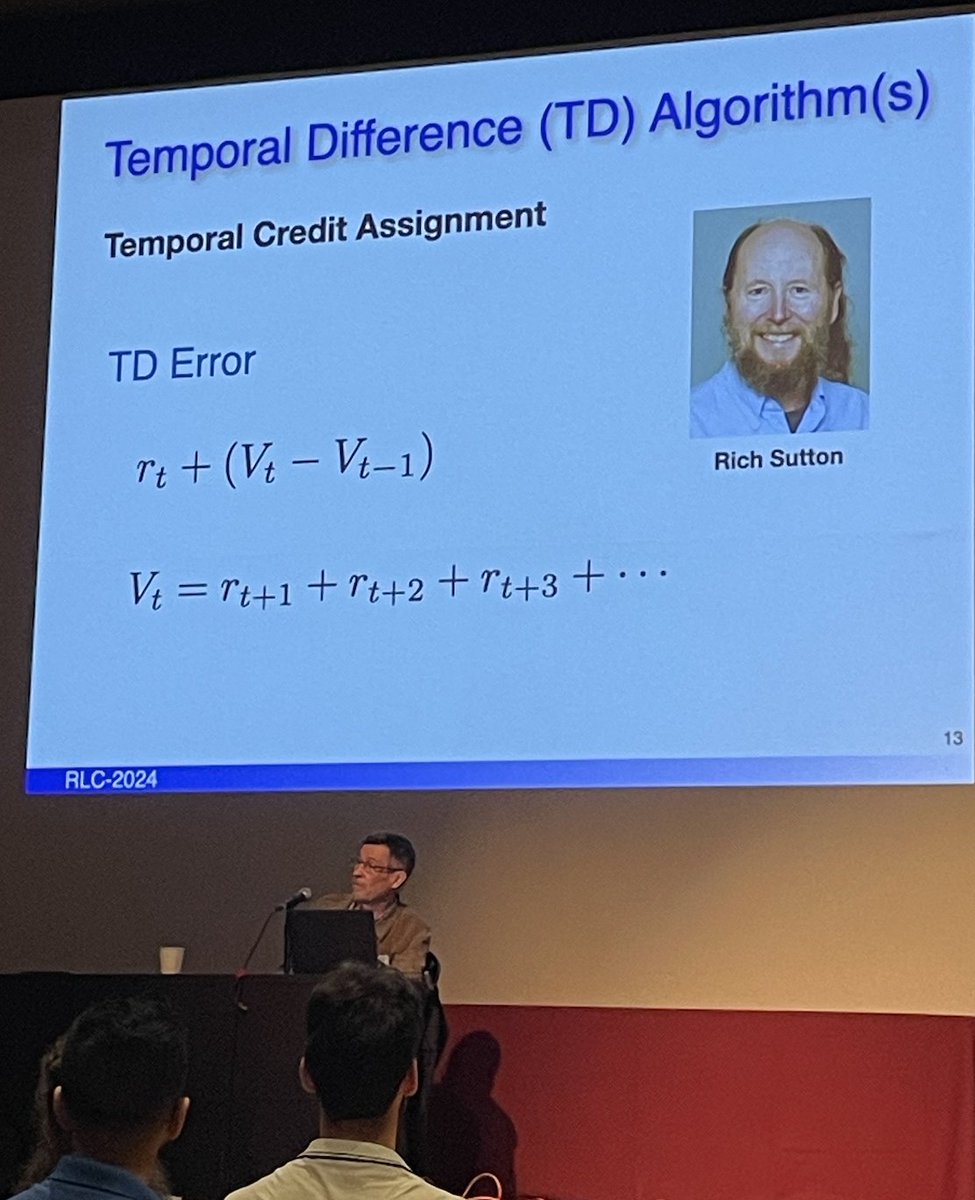
-TD error & alg for temporal credit assignment were inspired by interactions with psychology
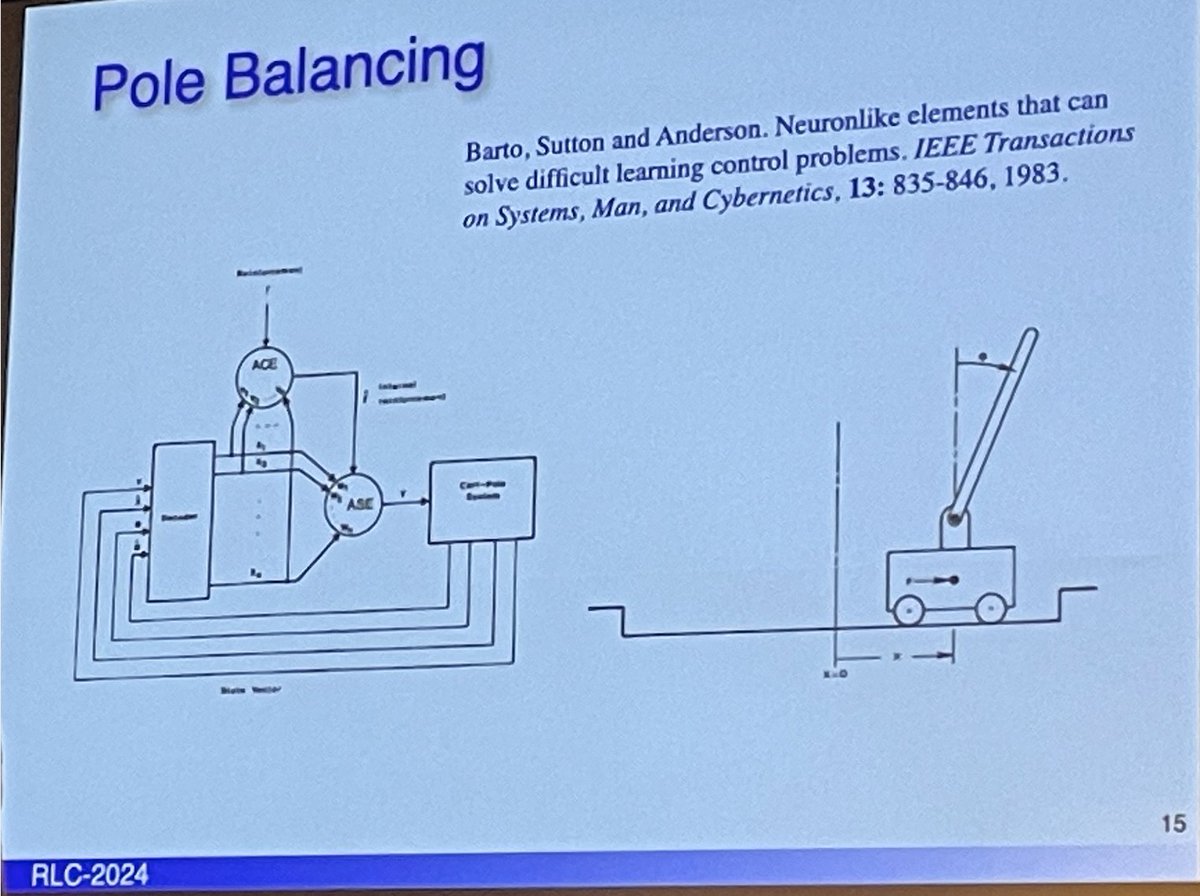
-Pole balancing paper in collaboration with Chuck Anderson
Next:actor-critic
7/n




-TD error & alg for temporal credit assignment were inspired by interactions with psychology
-Pole balancing paper in collaboration with Chuck Anderson
Next:actor-critic
7/n


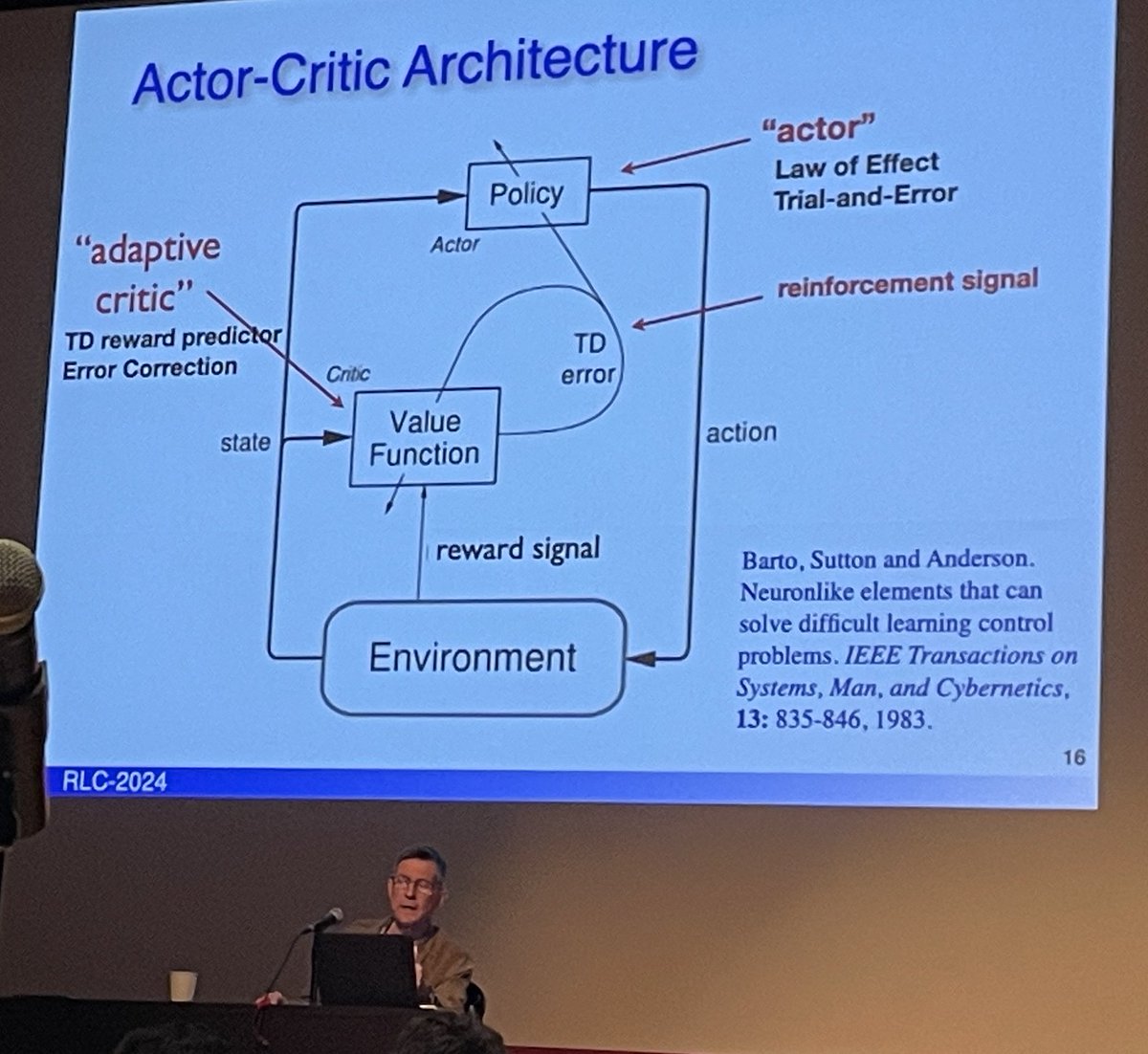
@RichardSSutton The Actor Critic architecture:
The actor is responsible for learning the policy, a mapping from states to actions, to decide which action to take in a given state.
An adaptive critic uses a value function to evaluate actor's policy & translate reward to TD error for learning.
8/n


The actor is responsible for learning the policy, a mapping from states to actions, to decide which action to take in a given state.
An adaptive critic uses a value function to evaluate actor's policy & translate reward to TD error for learning.
8/n
@RichardSSutton Second part: Barto dove into the early history of machine learning
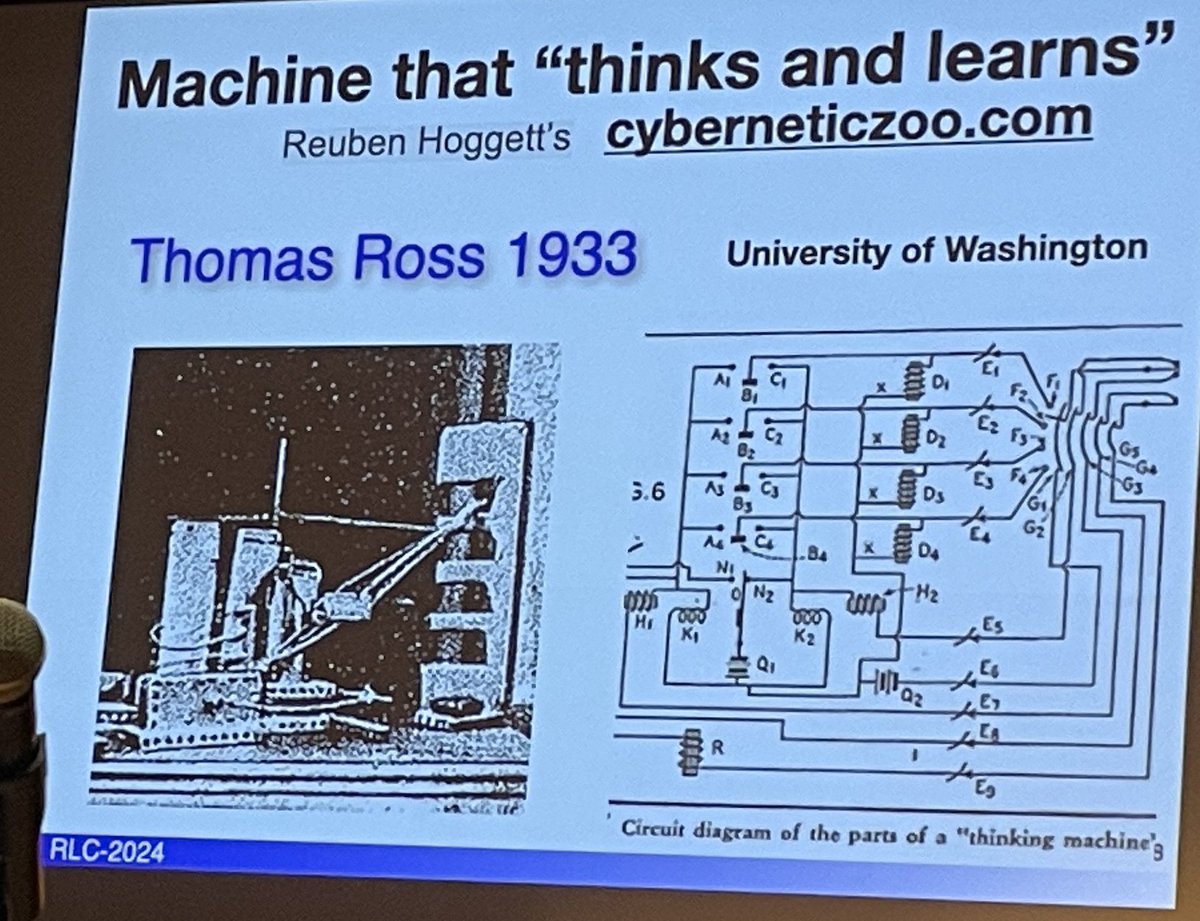
- Thomas Ross 1933 Thinking machine
- Steven Smith 1935 (psychology) Robot rats
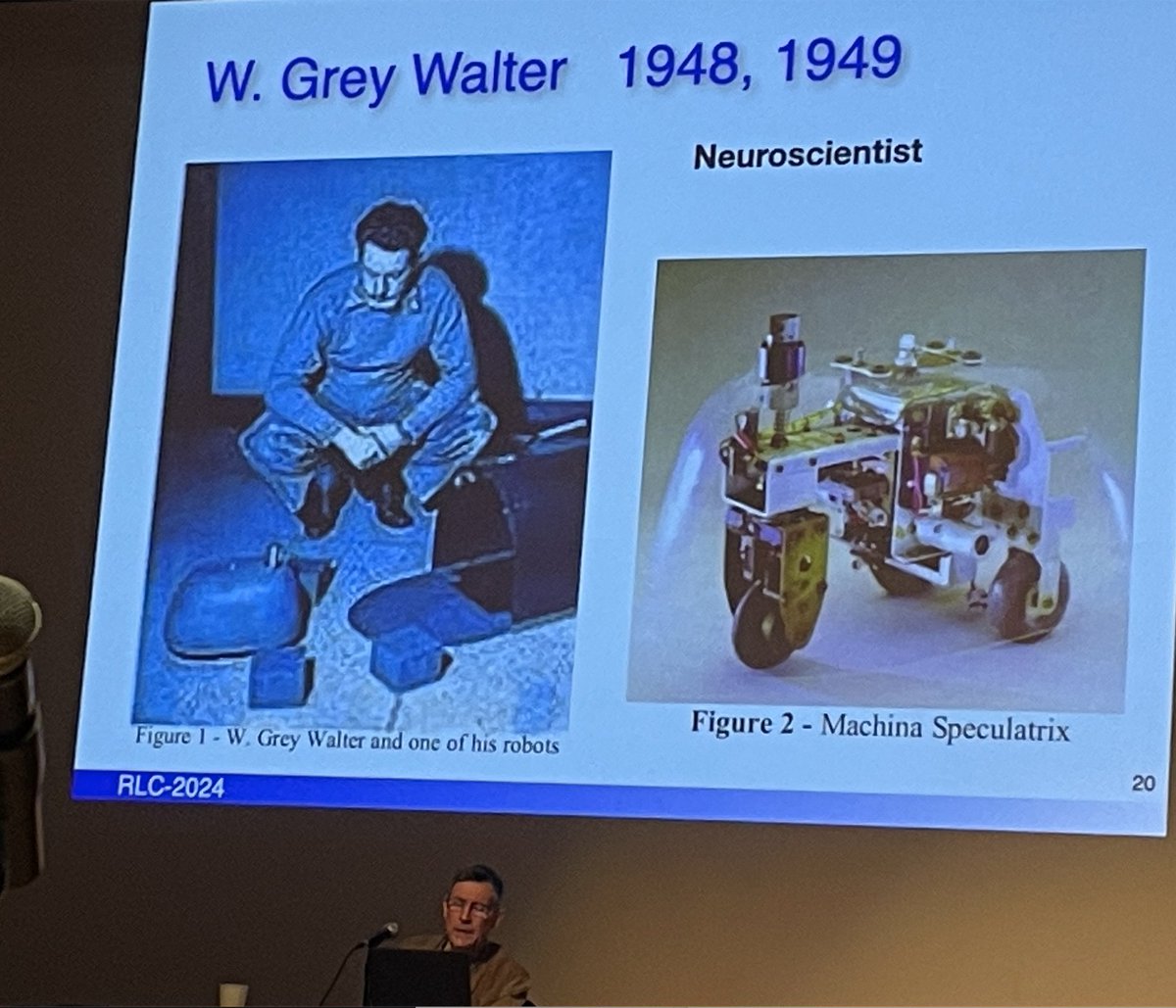
- Grey Walter 1948 (neuroscience) Machina Speculatrix
- Alan Turing 1948: Pleasure-Pain system, earliest call to implementing RL?
9/n




- Thomas Ross 1933 Thinking machine
- Steven Smith 1935 (psychology) Robot rats
- Grey Walter 1948 (neuroscience) Machina Speculatrix
- Alan Turing 1948: Pleasure-Pain system, earliest call to implementing RL?
9/n


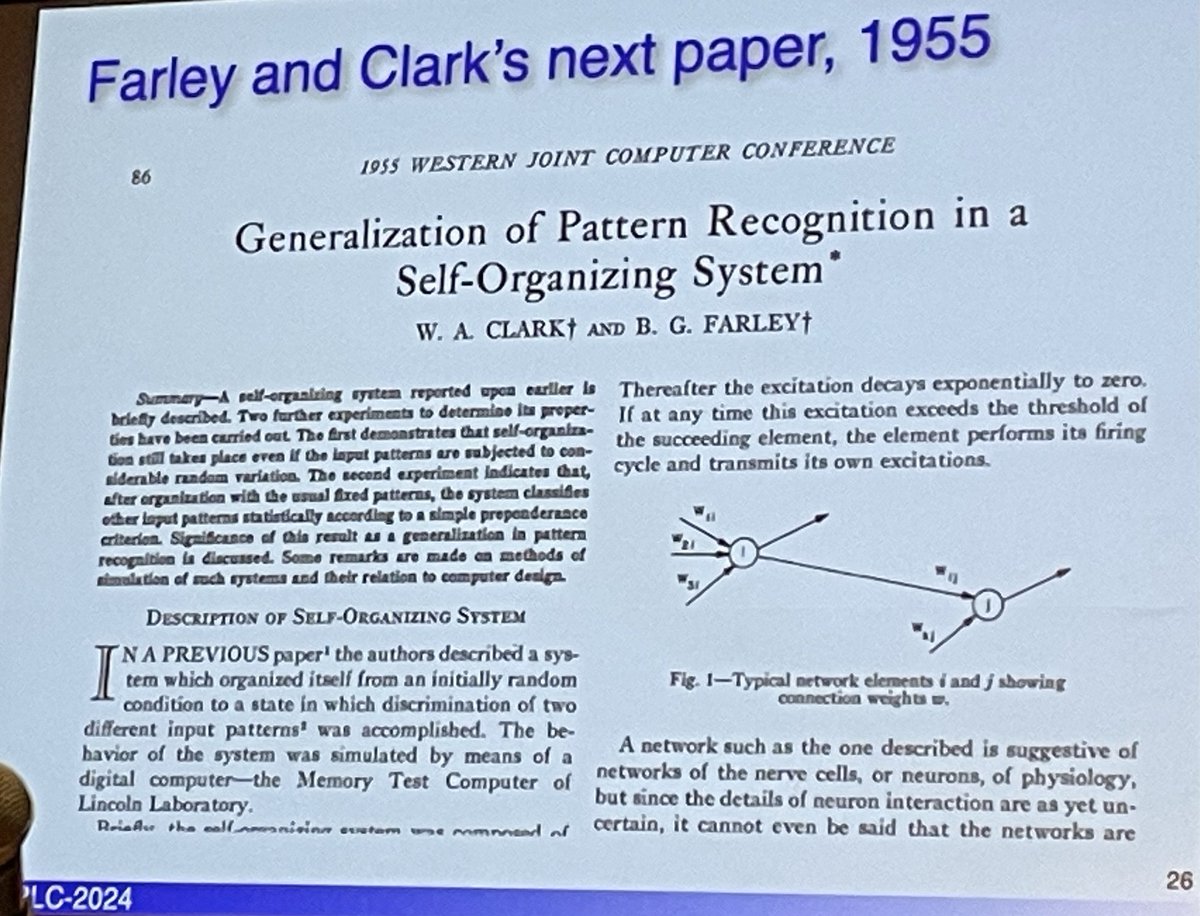
@RichardSSutton - Farley & Clark 1954 first simulation of ANN learning on a digital computer
- Minsky 1954 "Neural Nets and the brain-model problem", SNARCs (stoachstic neural-analog reinforcement calculators), "Steps towards AI" (1961).
Challenge: Structural & Temporal credit assignment
10/n




- Minsky 1954 "Neural Nets and the brain-model problem", SNARCs (stoachstic neural-analog reinforcement calculators), "Steps towards AI" (1961).
Challenge: Structural & Temporal credit assignment
10/n

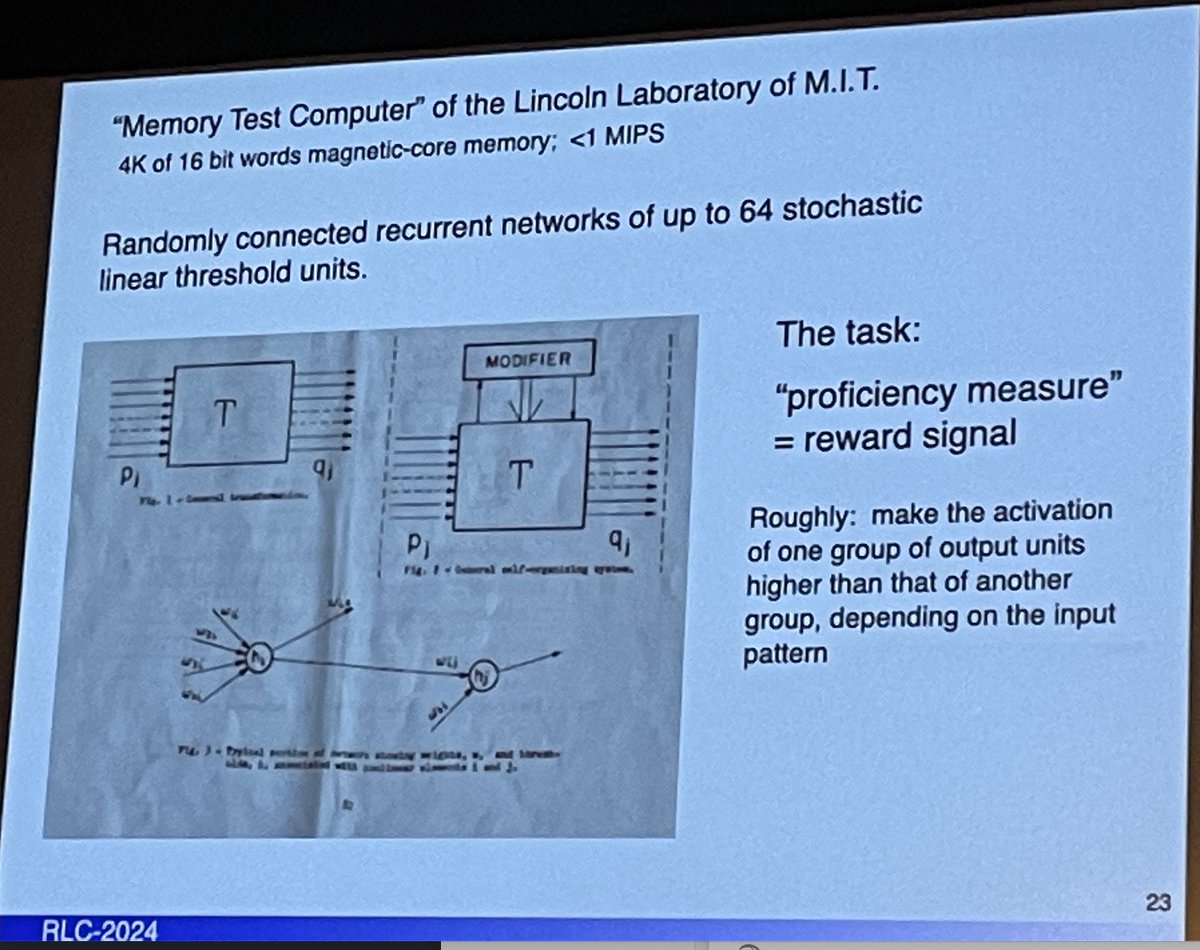


@RichardSSutton - Farley & Clark 1955 generalization of pattern recognition in self-organizing system
- Frank Rosenblatt 1958 Perceptron "Foundation of AI"
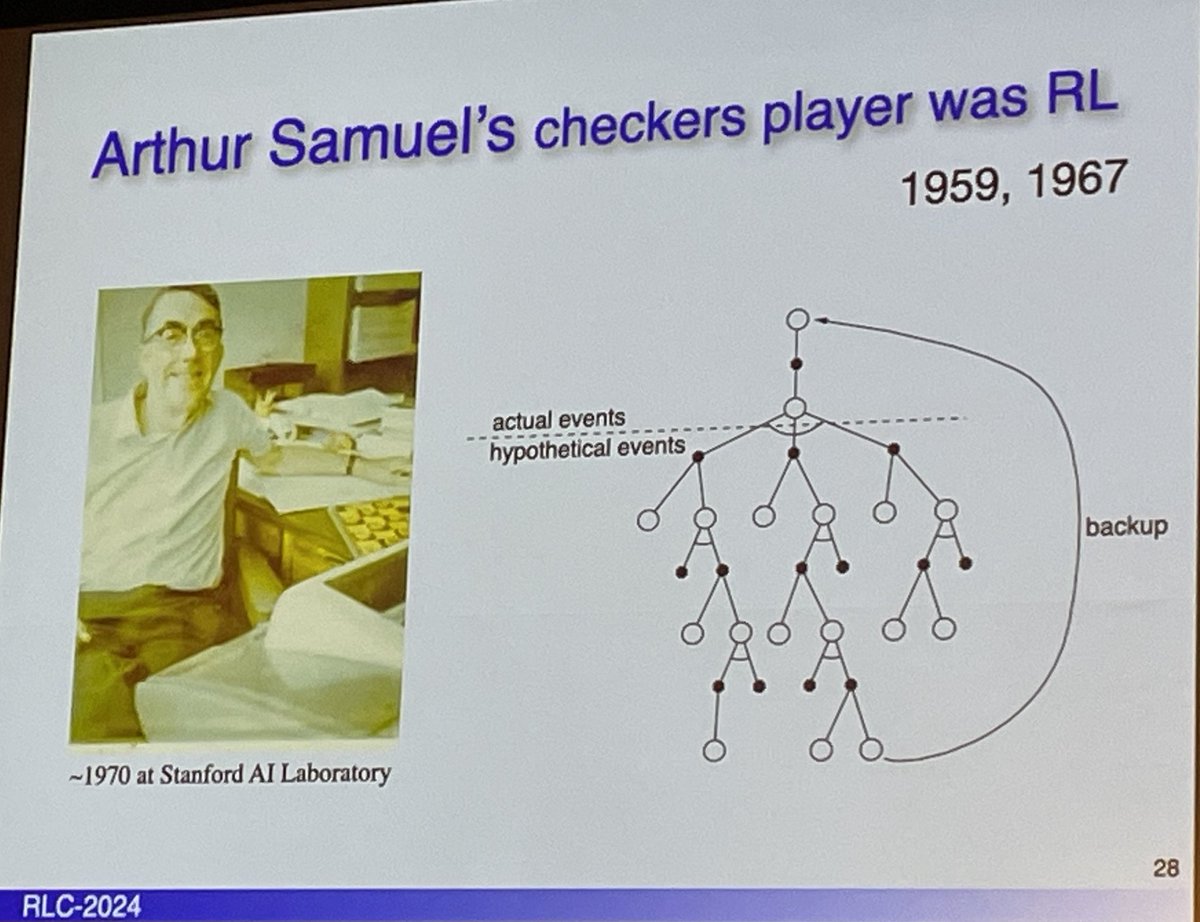
- Arthur Samuel 1959-67 Checkers player (was RL)
- Widrow & Hoff 1960 Adaptive Linear Neuron, Widrow -Hoff algorithm, LMS
11/n




- Frank Rosenblatt 1958 Perceptron "Foundation of AI"
- Arthur Samuel 1959-67 Checkers player (was RL)
- Widrow & Hoff 1960 Adaptive Linear Neuron, Widrow -Hoff algorithm, LMS
11/n


@RichardSSutton - Widrow et al 1973 Selective Bootstrap Adaptation. Rewarded? Treat committed action as target, do LMS. Punished: treat alternative action as target then LMS.
- Michael Tsetlin 1960s Learning Automata (& modeling biological systems 1973), teams & games
12/n


- Michael Tsetlin 1960s Learning Automata (& modeling biological systems 1973), teams & games
12/n


- Schultz Dayan Montague 1997 Reward-Prediction-Error in brains: Phasic activity of dopamine neurons signals the error between an old & a new estimate of future reward
Barto noted the critic in RL can take virtually any unmodeled influence & turn that into a learning signal
13/n


Barto noted the critic in RL can take virtually any unmodeled influence & turn that into a learning signal
13/n

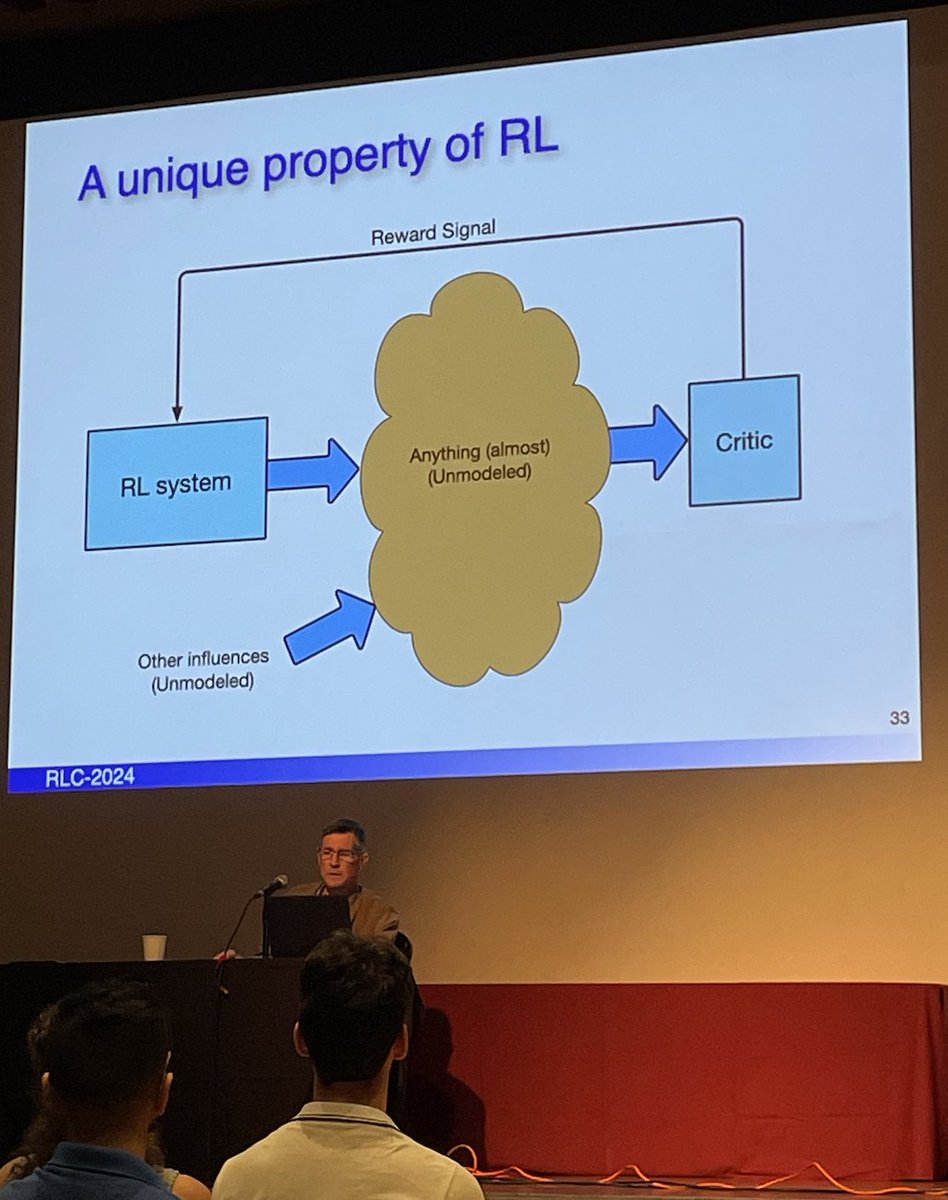
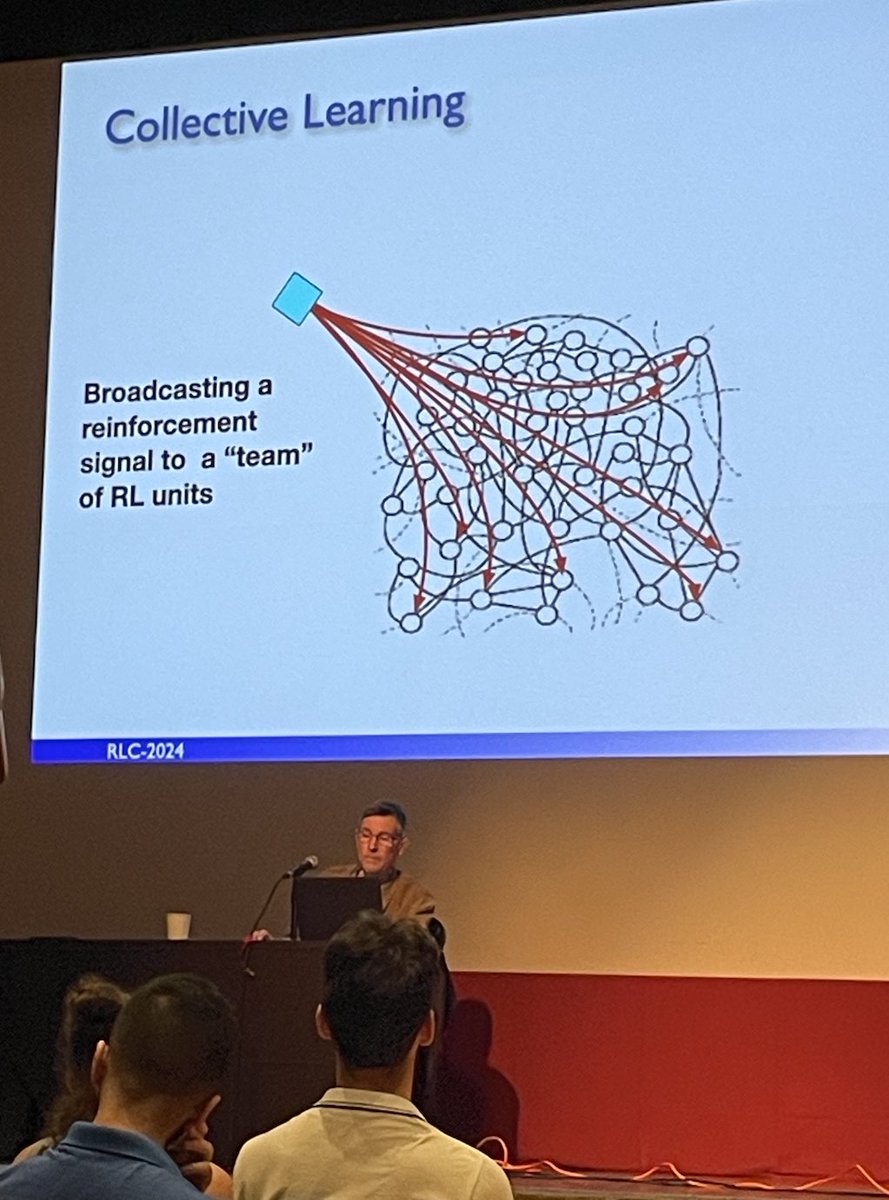
Dopamine inspired Collective Learning, reinforcement is broadcasted to a team of RL units. Potential alt to back prop, but RL broadcast didn't scale: structural credit assignment problem (getting signal to the right place).
cf Barto 1985 Learning by statistical cooperation
14/n



cf Barto 1985 Learning by statistical cooperation
14/n


In the end, a call for critical thinking. Andy Barto shared stories to caution against the challenges of designing reward signals.
Quoting Norbert Wiener's example of The Monkey's paw:
"... it grants what you asked for, not what you should have asked for or what you intend"
15/n
Quoting Norbert Wiener's example of The Monkey's paw:
"... it grants what you asked for, not what you should have asked for or what you intend"
15/n

Andy Barto then thanked his former students, said RL is not a cult, & found himself facing a standing ovation by the audience.
I appreciated the history of ML from the POV of developing a learning framework, & how interdisciplinary interactions of ideas shaped it.
TY #RLC2024
n/n
I appreciated the history of ML from the POV of developing a learning framework, & how interdisciplinary interactions of ideas shaped it.
TY #RLC2024
n/n

Many thanks to all organizers, esp @MarlosCMachado & @robertarail for heroic paper awards & for making RLC a warm & friendly experience.
Special thanks to @RichardSSutton for continual support & generous discussions on both specific & big picture ideas on learning & intelligence.
Special thanks to @RichardSSutton for continual support & generous discussions on both specific & big picture ideas on learning & intelligence.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh