Vaccines likely lower transmission, in addition to reducing infection and severe illness. New study shows Novavax and Moderna significantly reduce viral load (amount of virus) in the upper respiratory tract.
academic.oup.com/jid/advance-ar…

academic.oup.com/jid/advance-ar…
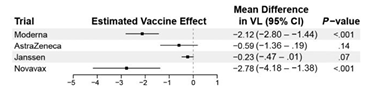
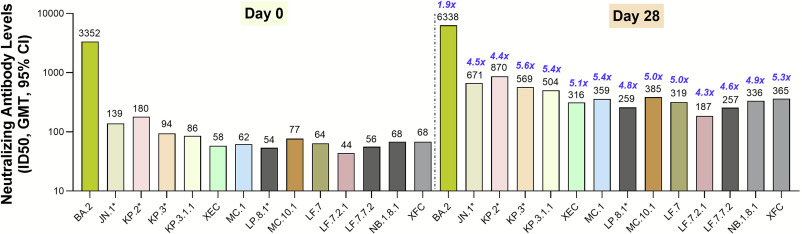
Novavax reduces viral load by 2.78 log10, while the Moderna vaccine was 2.12. The log10 scale is 10x for each step, indicating Moderna reduces viral load by just over 100x, and Novavax reduces viral load by over 600x. No significant reductions seen for others. 
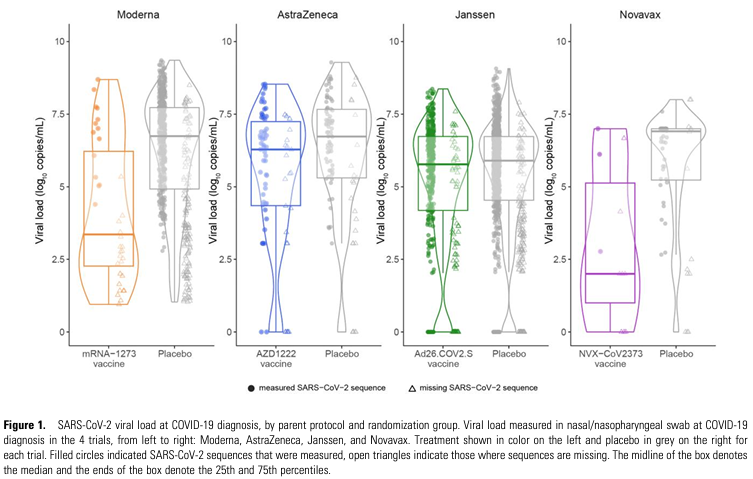

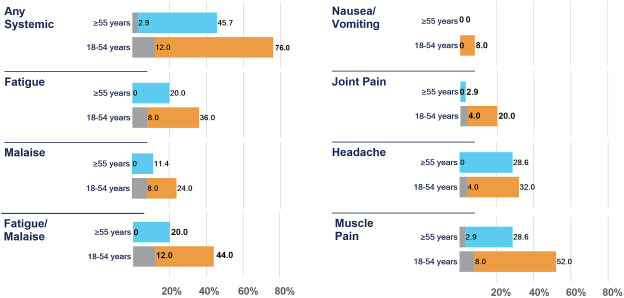
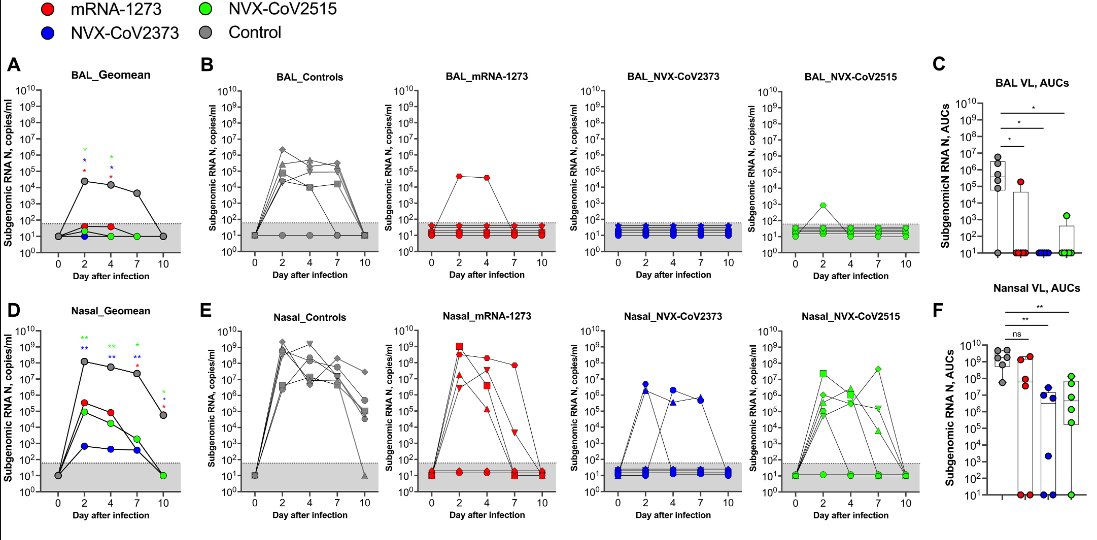
These results are in line with earlier animal models where the Novavax platform was associated with the largest decrease in viral replication in the upper respiratory tract.
science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…

science.org/doi/10.1126/sc…
Vaccines likely reduce chances of 1) being infected, 2) developing severe illness if infected, 3) transmitting the virus to others.
Increasing vaccine uptake reduces community circulation. Lower circulation overall helps everyone, from kids to the elderly. Fewer sick days. Improves economic activity. Reduces long COVID. Fewer empty seats at the family dining table.
I should note that Pfizer was not evaluated in the study being discussed, but it could have a similar reduction to moderna based on prior studies.
nature.com/articles/s4159…
nature.com/articles/s4159…
Clarification - *just over 100x" is used to indicate how close it is to 100, not a comparative indicator to novavax. The estimates are not statistically significantly different - both NVX and Moderna (& likely Pfizer as well) reduce viral load.
One more follow-up. Yes, this study is not with the current strains and w/o widespread preexisting immunity. However, many of the same immunologic principles should still be in effect today.
One potential avenue: the majority of the NVX response is not via IgG, but by mechanisms including FC effector functions. These are uniquely good at targeting viral particles for phagocytosis (clearing virus).
nature.com/articles/s4146…
nature.com/articles/s4146…
https://x.com/michaelzlin/status/1835228632412811624?t=MK_clsNhBOZjGXcuTbMhmQ&s=19
There's inadequate data to quantify exact reductions expected today (likely a moving number & different per person), but it would be hard to discount the human & animal (BA.5) data entirely. Certain COVID-19 vaccines have, and likely still reduce viral load and transmission
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh