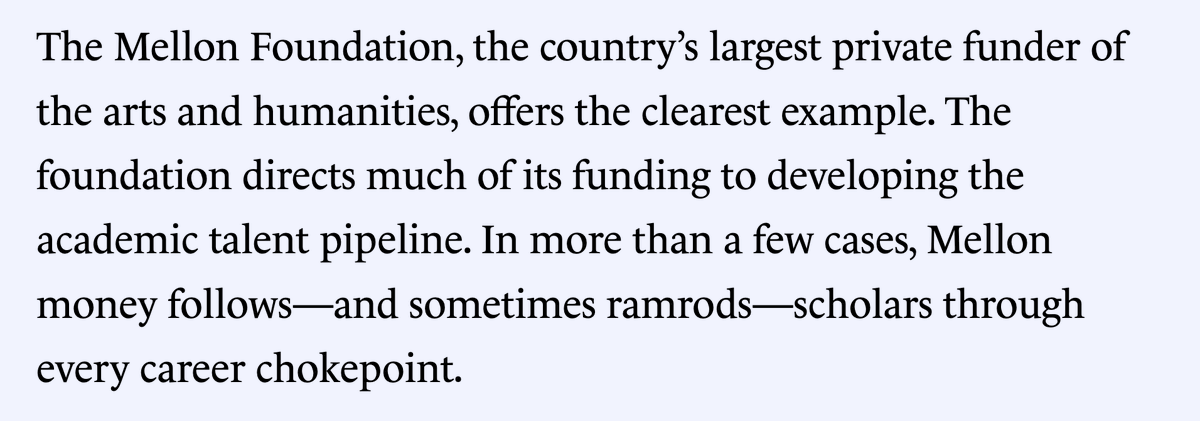
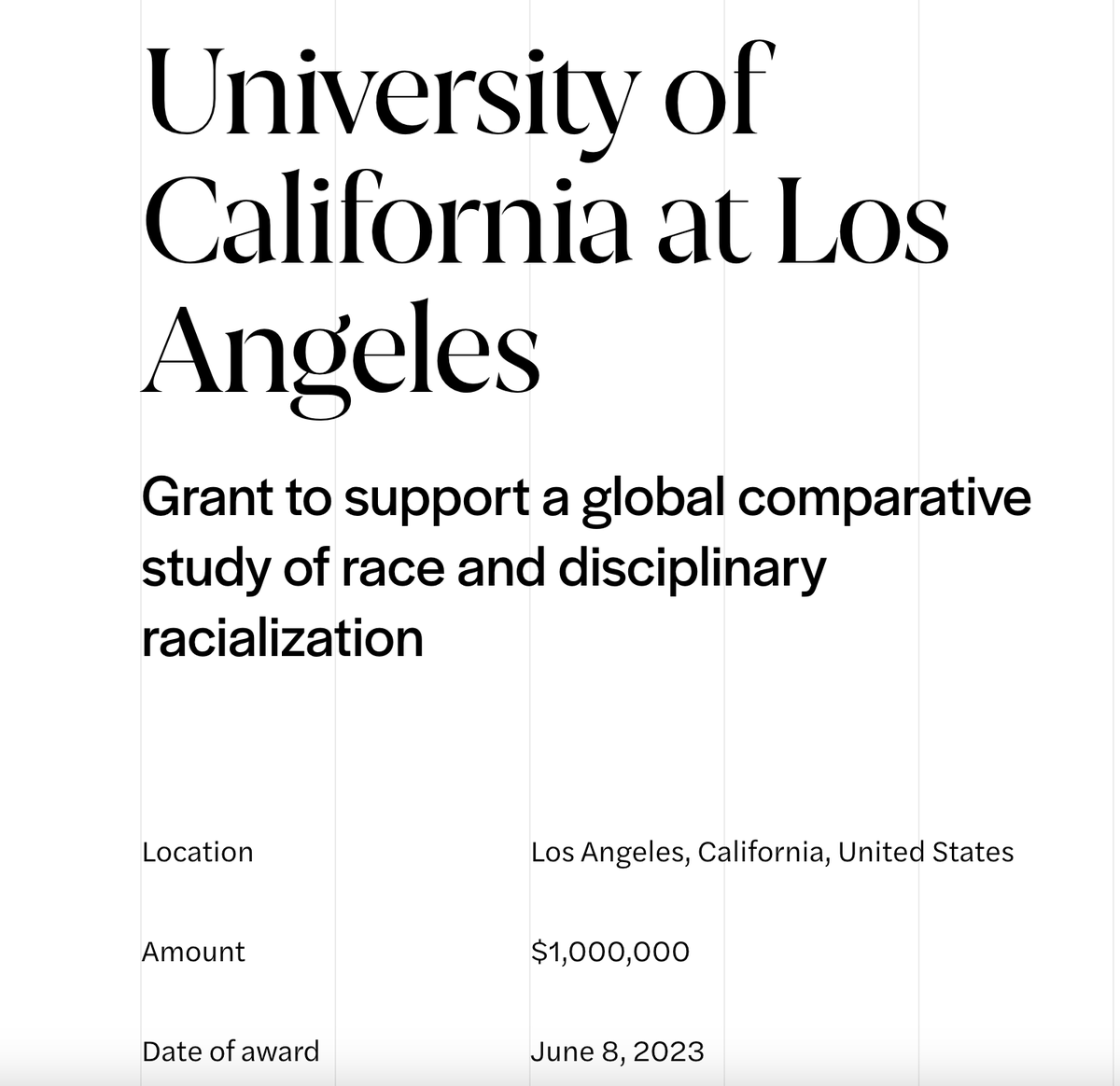
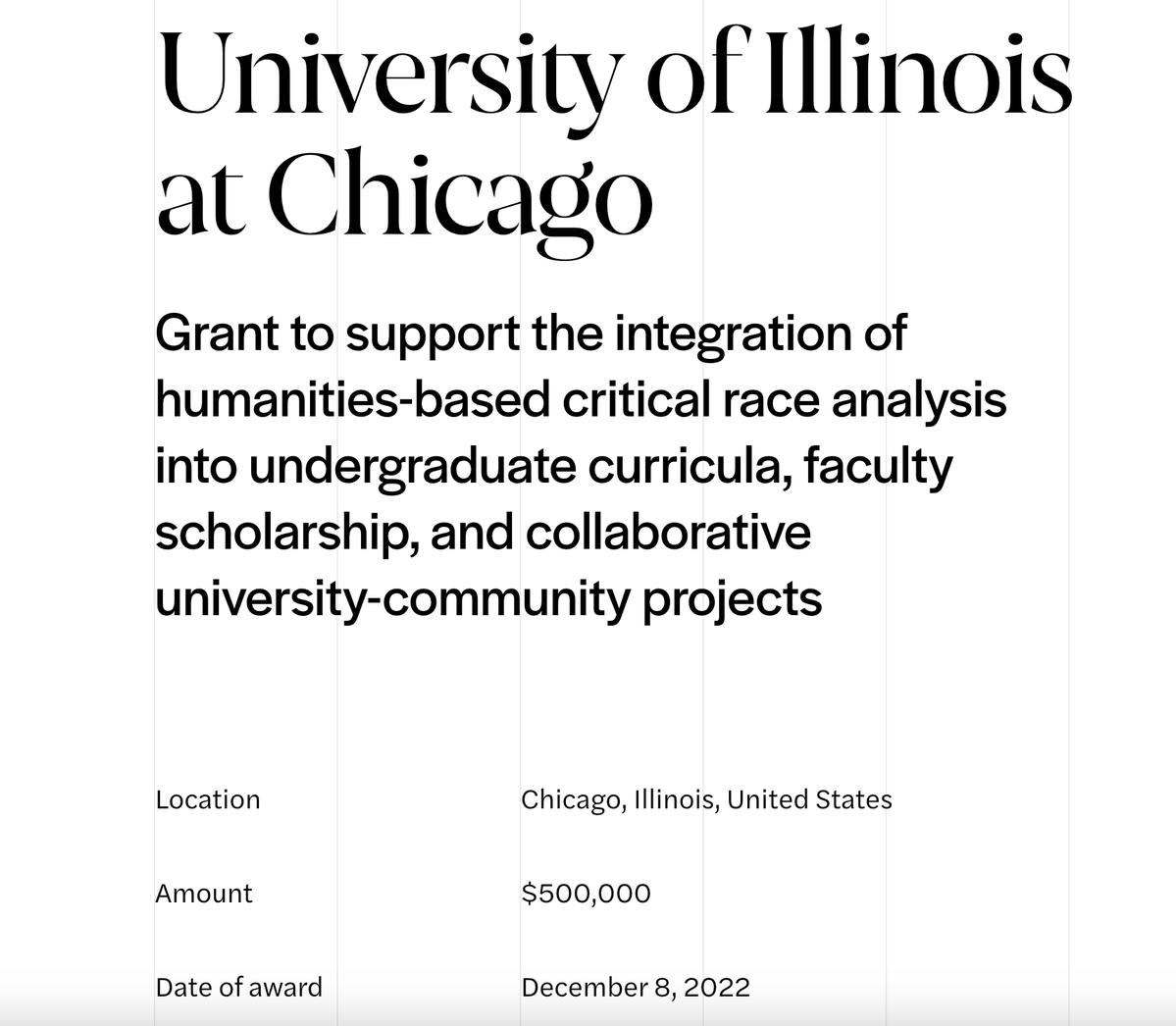
In 2022, a paper drawing from “critical whiteness studies" analyzed how "whiteness" shows up in Physics 101—concluding that, among other things, the use of whiteboards perpetuate whiteness in physics.
Here's what's crazy: this "research" was funded by the federal government.
🧵
Here's what's crazy: this "research" was funded by the federal government.
🧵

2/ But first: what's Critical Whiteness Studies?
Per the article, it's a research framework that starts with the assumption that omnipresent, invisible whiteness pervades our ordinary interactions and institutions to ensure "white dominance."
Per the article, it's a research framework that starts with the assumption that omnipresent, invisible whiteness pervades our ordinary interactions and institutions to ensure "white dominance."

3/ It's a bold starting point—with more than a hint of racial animosity. Applied to physics, it gets weird.
The article finds that the values of "abstractness" and "disembodiment" in physics ("physics values") reify whiteness and reflect human domination and entitlement.
The article finds that the values of "abstractness" and "disembodiment" in physics ("physics values") reify whiteness and reflect human domination and entitlement.

4/ It goes on to declare that, yes, even whiteboards "play a role in reconstituting whiteness as social organization."
They do this by "collaborat[ing] with white organizational culture" where ideas gain value "when written down."
Again, this is funded by, well, you...
They do this by "collaborat[ing] with white organizational culture" where ideas gain value "when written down."
Again, this is funded by, well, you...

5/ Look at the National Science Foundation's recent budget requests: The federal agency has spent a quarter-billion-dollars annually on it's "Division of Equity for Excellence in STEM."
That doesn't account for projects on race and equity funded by other division.
That doesn't account for projects on race and equity funded by other division.

6/ Thus, "Observing whiteness in introductory physics" was funded by the National Science Foundation.
It was a part of a half million dollar project unpacking which "strategies, tools, and materials" contribute to marginalization.


It was a part of a half million dollar project unpacking which "strategies, tools, and materials" contribute to marginalization.



7/ This sort of research is the most noticeable consequence of the NSF's now-well-documented push to fund social justice projects.
But, in my latest, I argue that it's not by any means the most consequential, and it's why I'm not at all convinced that "wokeness" has peaked.
But, in my latest, I argue that it's not by any means the most consequential, and it's why I'm not at all convinced that "wokeness" has peaked.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh