In 1983, one man had 10 minutes to decide the fate of the world.
Stanislav Petrov sat at his console as alarms blared: 5 U.S. nuclear missiles were "en route" to Russia.
He had two choices: launch a counterstrike or trust his gut.
What he did next saved humanity. Here's how...

Stanislav Petrov sat at his console as alarms blared: 5 U.S. nuclear missiles were "en route" to Russia.
He had two choices: launch a counterstrike or trust his gut.
What he did next saved humanity. Here's how...


The Cold War was a period of heightened tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union.
It was marked by an arms race, espionage, and proxy wars, but no direct conflict between the two superpowers.

It was marked by an arms race, espionage, and proxy wars, but no direct conflict between the two superpowers.


In the 1980s, The Soviets introduced a satellite-based early-warning system designed to detect U.S. missile launches.
While this technology represented a significant leap forward, it was far from perfect—a fact that would become painfully clear.
While this technology represented a significant leap forward, it was far from perfect—a fact that would become painfully clear.
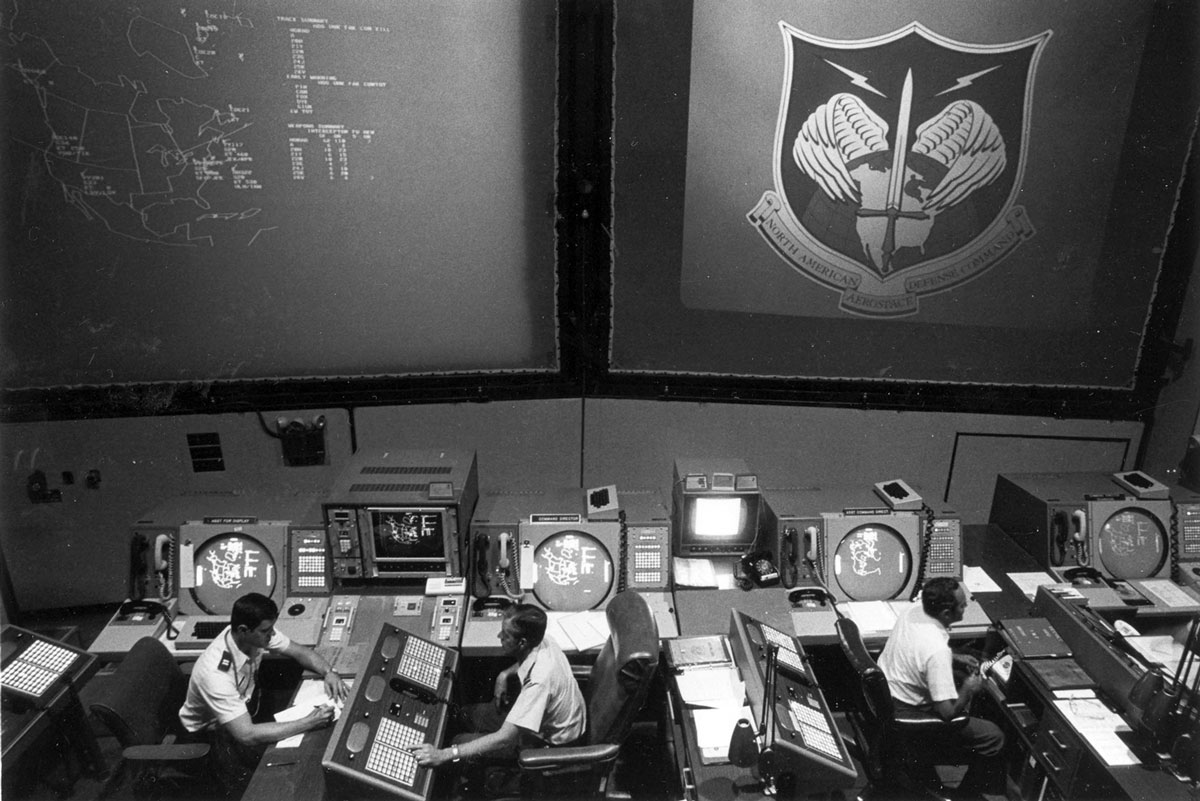
Petrov was stationed at Serpukhov-15, a Soviet early-warning command center outside Moscow.
His role was to monitor satellite data and alert his superiors of any imminent U.S. missile launches.
At 12:15 a.m., alarms blared.
His role was to monitor satellite data and alert his superiors of any imminent U.S. missile launches.
At 12:15 a.m., alarms blared.
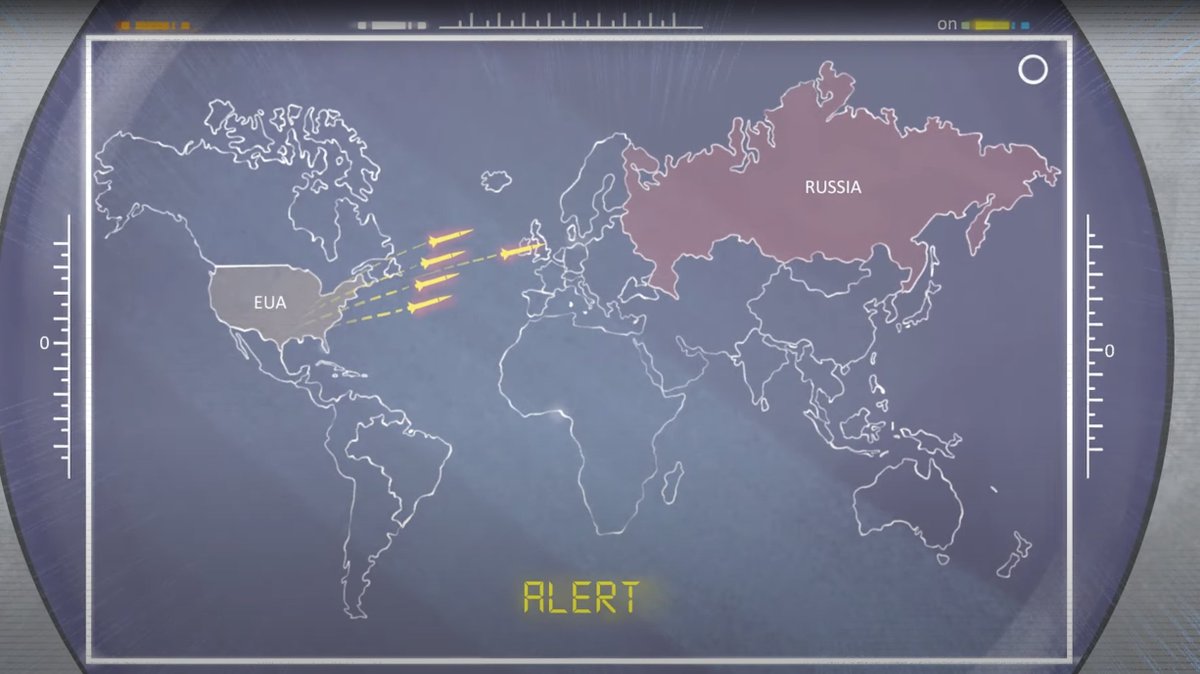
The system reported that an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) had been launched from the United States, heading straight for the Soviet Union.
Moments later, the system detected four additional missiles.
The computer classified the threat level as high.
Moments later, the system detected four additional missiles.
The computer classified the threat level as high.
Protocol dictated that Petrov immediately report the attack, which would have triggered a retaliatory strike.
In the event of mutual assured destruction, millions—if not billions—of lives were at stake.
In the event of mutual assured destruction, millions—if not billions—of lives were at stake.
Faced with a high-pressure situation, Petrov made a choice that would alter the course of history: he decided to trust his gut over the machine.
Petrov reasoned that if the U.S. were to launch a nuclear strike, it would involve hundreds of missiles, not just five.
Petrov reasoned that if the U.S. were to launch a nuclear strike, it would involve hundreds of missiles, not just five.
Additionally, the new early-warning system was untested and prone to errors.
He deemed it a false alarm and chose not to report the "attack."
Petrov’s decision didn’t end the crisis.
He deemed it a false alarm and chose not to report the "attack."
Petrov’s decision didn’t end the crisis.
For 25 agonizing minutes, he and his team awaited confirmation that no missiles had landed.
Every passing second without an explosion strengthened Petrov’s belief that he had made the right call.
Every passing second without an explosion strengthened Petrov’s belief that he had made the right call.
Eventually, it became clear that the alerts were indeed false.
The alerts were a result of sunlight reflecting off high-altitude clouds, which the satellite had misinterpreted as missile launches.
Petrov’s decision was never officially celebrated by the Soviet government.
The alerts were a result of sunlight reflecting off high-altitude clouds, which the satellite had misinterpreted as missile launches.
Petrov’s decision was never officially celebrated by the Soviet government.

In fact, he was reprimanded for failing to document the incident in his logbook.
The Soviet military quietly swept the event under the rug to avoid exposing flaws in their early-warning system.
For years, the world remained unaware of how close it had come to disaster.
The Soviet military quietly swept the event under the rug to avoid exposing flaws in their early-warning system.
For years, the world remained unaware of how close it had come to disaster.
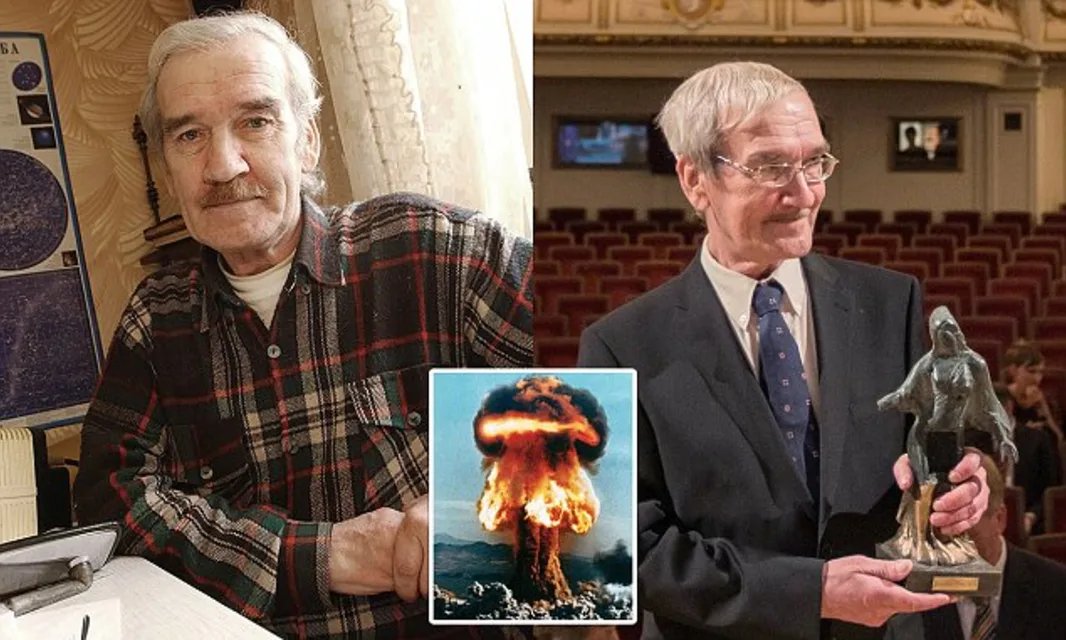
It wasn’t until 1998, when a retired Soviet commander published his memoirs, that Petrov’s actions came to light.
His story eventually gained international recognition, and he was honored with awards such as the Dresden Peace Prize and the Association of World Citizens Award.
His story eventually gained international recognition, and he was honored with awards such as the Dresden Peace Prize and the Association of World Citizens Award.

If Petrov had reported the attack as real, the Soviet Union would have launched a counterstrike.
The U.S. would have responded, leading to a full-scale nuclear war.
Studies estimated that such a conflict could result in hundreds of millions of deaths within hours.
The U.S. would have responded, leading to a full-scale nuclear war.
Studies estimated that such a conflict could result in hundreds of millions of deaths within hours.

If you find this thread, help me on my mission:
"The school and the media failed to teach you history.
My mission is to help you learn more about history and the key moments that defined our existence."
Follow me @_HistoryNerd for more...
"The school and the media failed to teach you history.
My mission is to help you learn more about history and the key moments that defined our existence."
Follow me @_HistoryNerd for more...
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh











