NEW: Louis Galarowicz (@nasorg) and I have acquired a trove of records from University of Colorado, Boulder, that show how the entire university coordinated to advance a system of brazen race-based hiring.
The receipts are pretty astonishing... 🧵
The receipts are pretty astonishing... 🧵

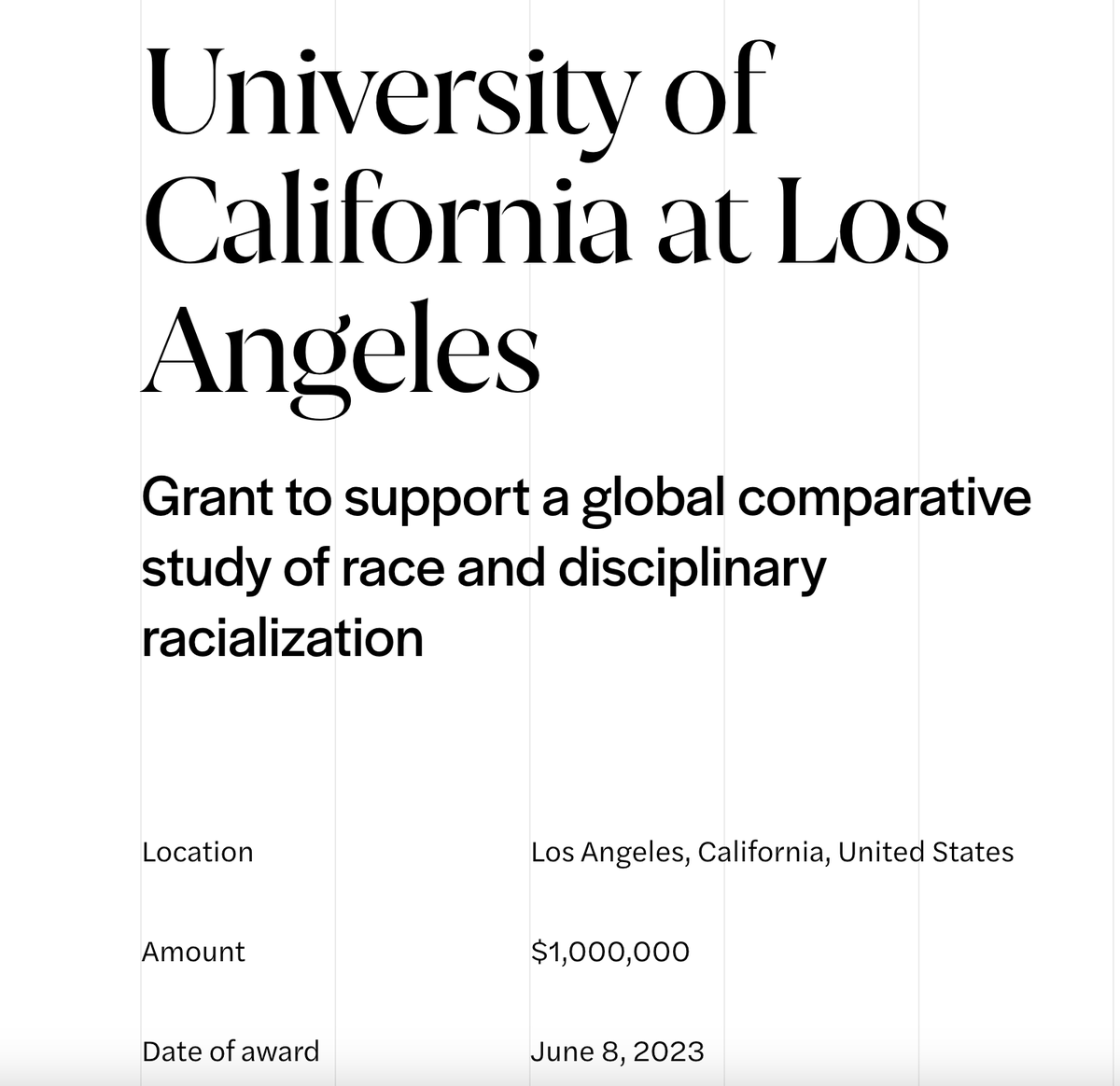
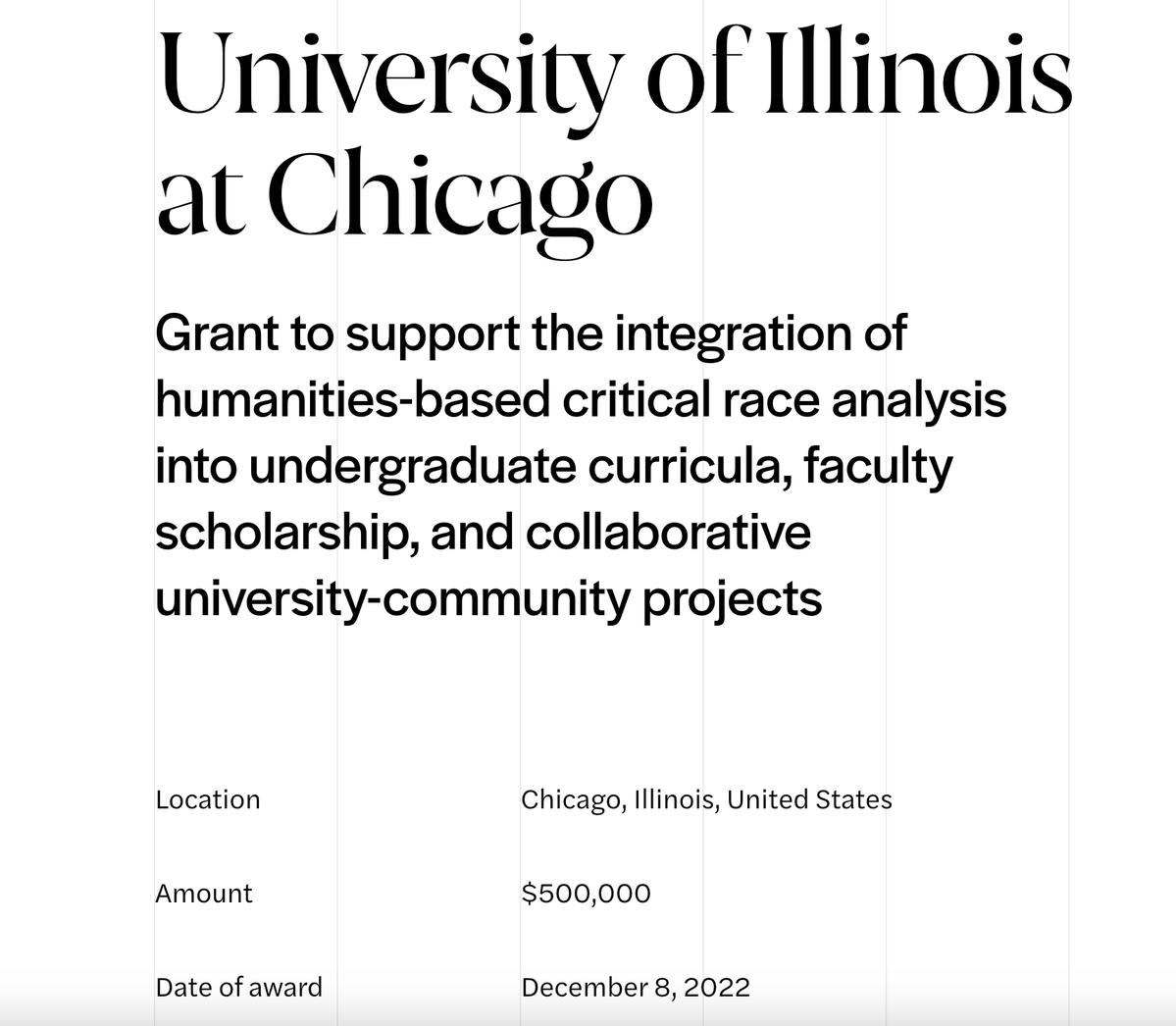
@NASorg We acquired the approved/successful proposals for the university's large-scale diversity hiring program. Here are a few examples:
The College of Engineering & Applied Sciences said its cluster hire had “the goal of doubling our underrepresented faculty in the college.”
The College of Engineering & Applied Sciences said its cluster hire had “the goal of doubling our underrepresented faculty in the college.”

@NASorg Another example:
The Renewable And Sustainable Energy Institute proposed a specific candidate—who it noted was “an outstanding BIPOC scholar” who would increase the program’s “domestic Faculty of Color...”
The Renewable And Sustainable Energy Institute proposed a specific candidate—who it noted was “an outstanding BIPOC scholar” who would increase the program’s “domestic Faculty of Color...”

@NASorg Another example:
The Department of Journalism told the admin in its proposal that “Our commitment, should we be successful with this application, is to hire someone from the BIPOC community…”
The Department of Journalism told the admin in its proposal that “Our commitment, should we be successful with this application, is to hire someone from the BIPOC community…”

@NASorg Another example:
“We have an urgent and qualified need for BIPOC femme/women of color faculty,” the Department of Ethnic Studies stated, adding that the scholar should contribute to a “thematic cluster hire in racism and racial inequality.”
“We have an urgent and qualified need for BIPOC femme/women of color faculty,” the Department of Ethnic Studies stated, adding that the scholar should contribute to a “thematic cluster hire in racism and racial inequality.”

@NASorg These are just a few examples, the list goes on and on.
The College of Media, Communications, and Information’s cluster hire, meanwhile, emphasized "hiring Black, Indigenous, Asian American, Latinx, and Pacific Islander faculty…”
But also note the disciplinary focus...
The College of Media, Communications, and Information’s cluster hire, meanwhile, emphasized "hiring Black, Indigenous, Asian American, Latinx, and Pacific Islander faculty…”
But also note the disciplinary focus...

@NASorg As we argue in the @WSJopinion, racial preferences went hand-in-hand with ideological preferences.
Notice that this proposal to hire a German studies scholar touts how she's both a woman of color and has an expertise in “anti-racist pedagogy” and “decolonizing German Studies.”
Notice that this proposal to hire a German studies scholar touts how she's both a woman of color and has an expertise in “anti-racist pedagogy” and “decolonizing German Studies.”

@NASorg @WSJopinion One of the most remarkable troves of public records I've ever received, the implications here are far-reaching, both for the university and for federal policy.
Read our full analysis, with full context, in the Wall Street Journal.
Read our full analysis, with full context, in the Wall Street Journal.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh