Have you heard the “Land Of Chem” Egyptian Pyramids Hypothesis?
A🧵
It asserts that the Egyptian pyramids were not built as tombs but as industrial-scale chemical production facilities. Engineered to produce chemicals like methane, ammonia, & acids.
A🧵
It asserts that the Egyptian pyramids were not built as tombs but as industrial-scale chemical production facilities. Engineered to produce chemicals like methane, ammonia, & acids.

Step Pyramid: This pyramid produced methane gas, from organic sources like manure or natural gas deposits. Stating its design is suited for collecting and processing methane as a base material. 
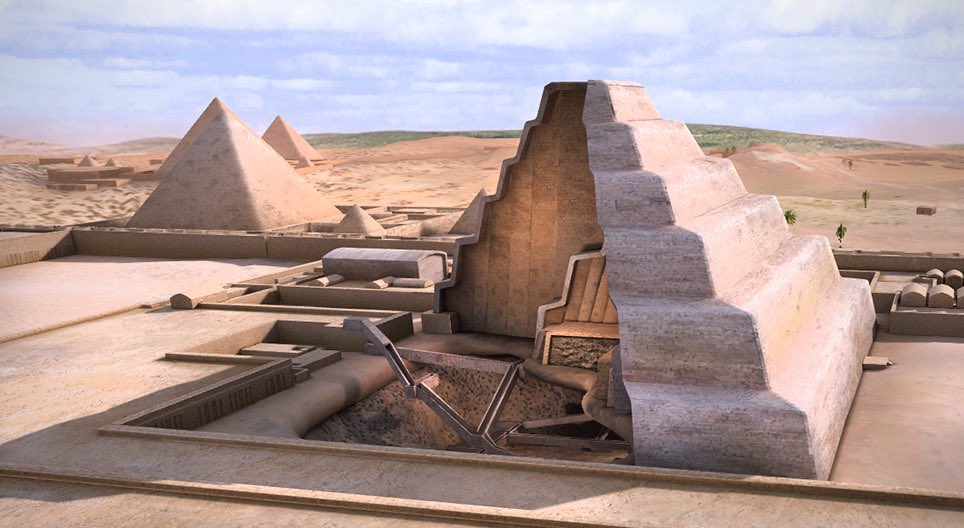

Red Pyramid: This pyramid converted methane into ammonia, as in the Haber-Bosch process. A method for synthesizing ammonia by combining nitrogen with hydrogen, derived from natural gas, under high pressure & temperature using an iron catalyst. 
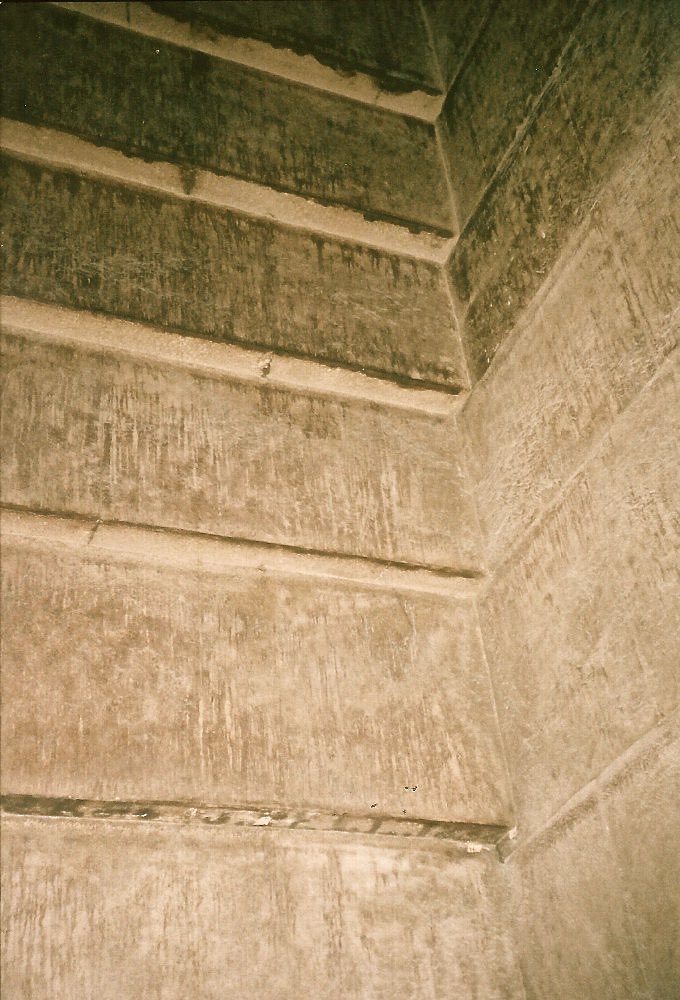



Bent Pyramid: This pyramid, took ammonia further, producing ammonium bicarbonate or nitric acid, with its unique shape & internal erosion suggesting a specialized reaction environment. 

Giza Pyramids: These produced sulfuric & hydrochloric acids, tying them to mining operations of gold & silver extraction from iron oxide deposits on the Giza Plateau. 
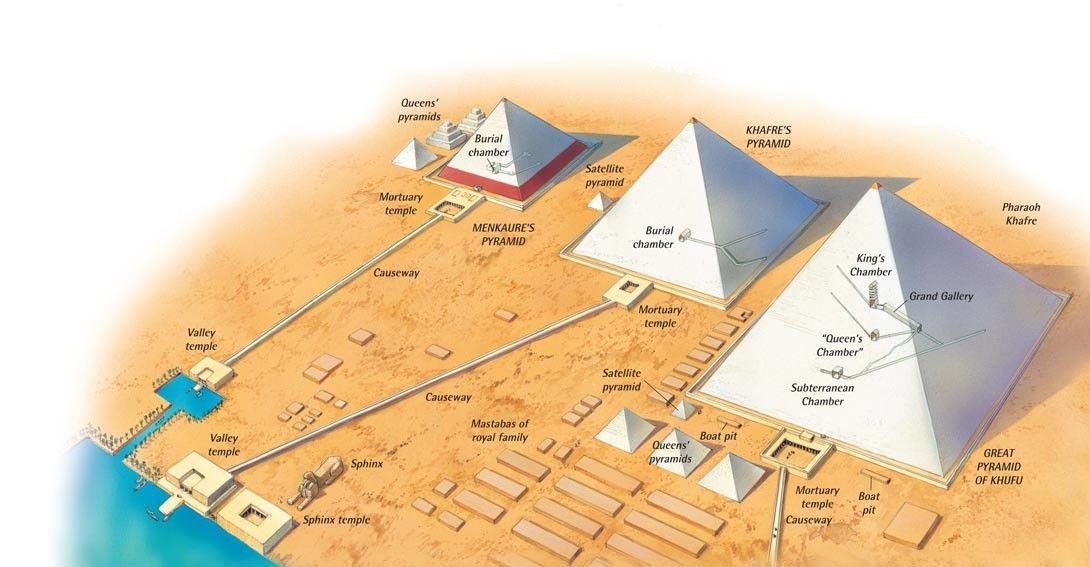
According to the hypothesis the pyramids used natural resources & forces like methane from the Nile region & water pressure in tunnels, & even lightning or telluric currents to drive chemical reactions. 

The hypothesis places the pyramid chemical operations during the Sahara Wet Period (8500–5300 BCE), before dynastic Egypt, arguing they were later repurposed as tombs or monuments when their original chemical function declined. 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh