Did you know, a single taproot address can have many different spending conditions?
Now you can visualize all of the revealed scripts for a taproot address on !
here's how it works 🧵 mempool.space
Now you can visualize all of the revealed scripts for a taproot address on !
here's how it works 🧵 mempool.space
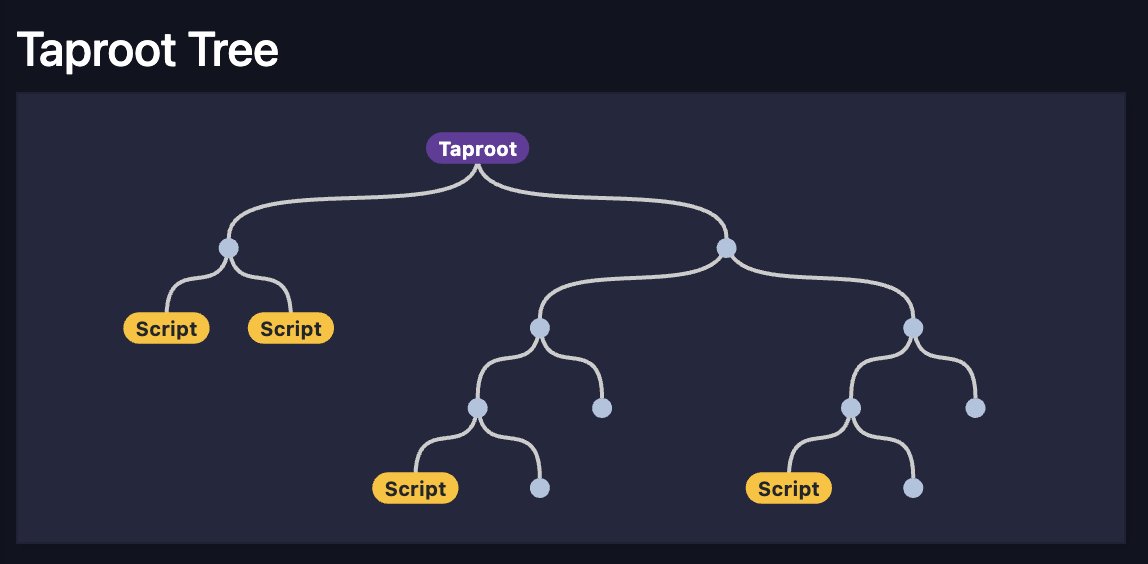
Taproot uses merkle trees to commit to spending scripts.
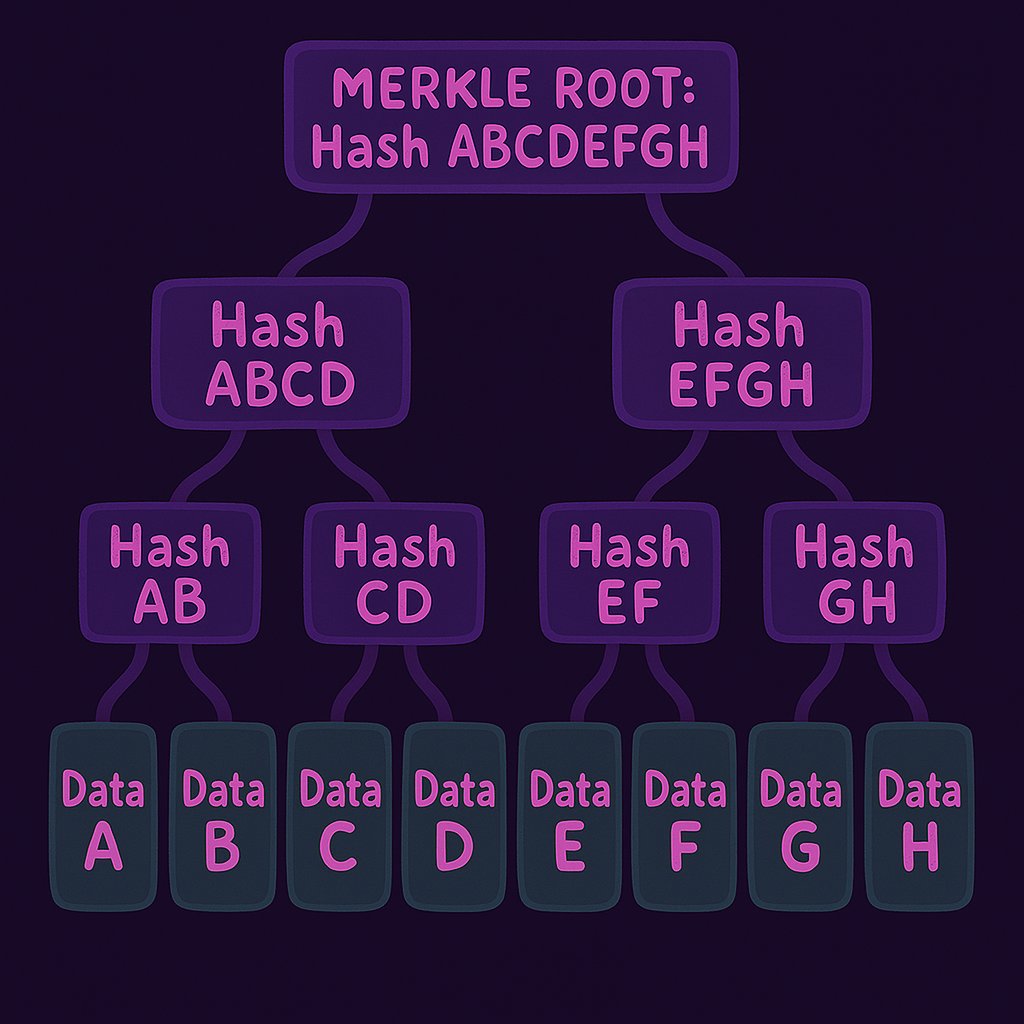
Merkle trees are binary trees where each leaf consists of data (in our case, Bitcoin scripts) and each branch is a hash of its children, culminating in a single "root" hash.
Merkle trees are binary trees where each leaf consists of data (in our case, Bitcoin scripts) and each branch is a hash of its children, culminating in a single "root" hash.
A taproot output can be spent by revealing and satisfying one of these scripts, together with a "merkle path" which proves that the script belongs to output's taproot tree.
This gives some clues about the structure of the tree, but allows any other spending scripts to remain private.
This gives some clues about the structure of the tree, but allows any other spending scripts to remain private.

If a taproot address is reused and spent from with different script paths, mempool.space's new taproot tree visualization will combine all of the revealed scripts and merkle paths to reconstruct as much of the tree as possible.
mempool.space/address/bc1p9d…
mempool.space/address/bc1p9d…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





