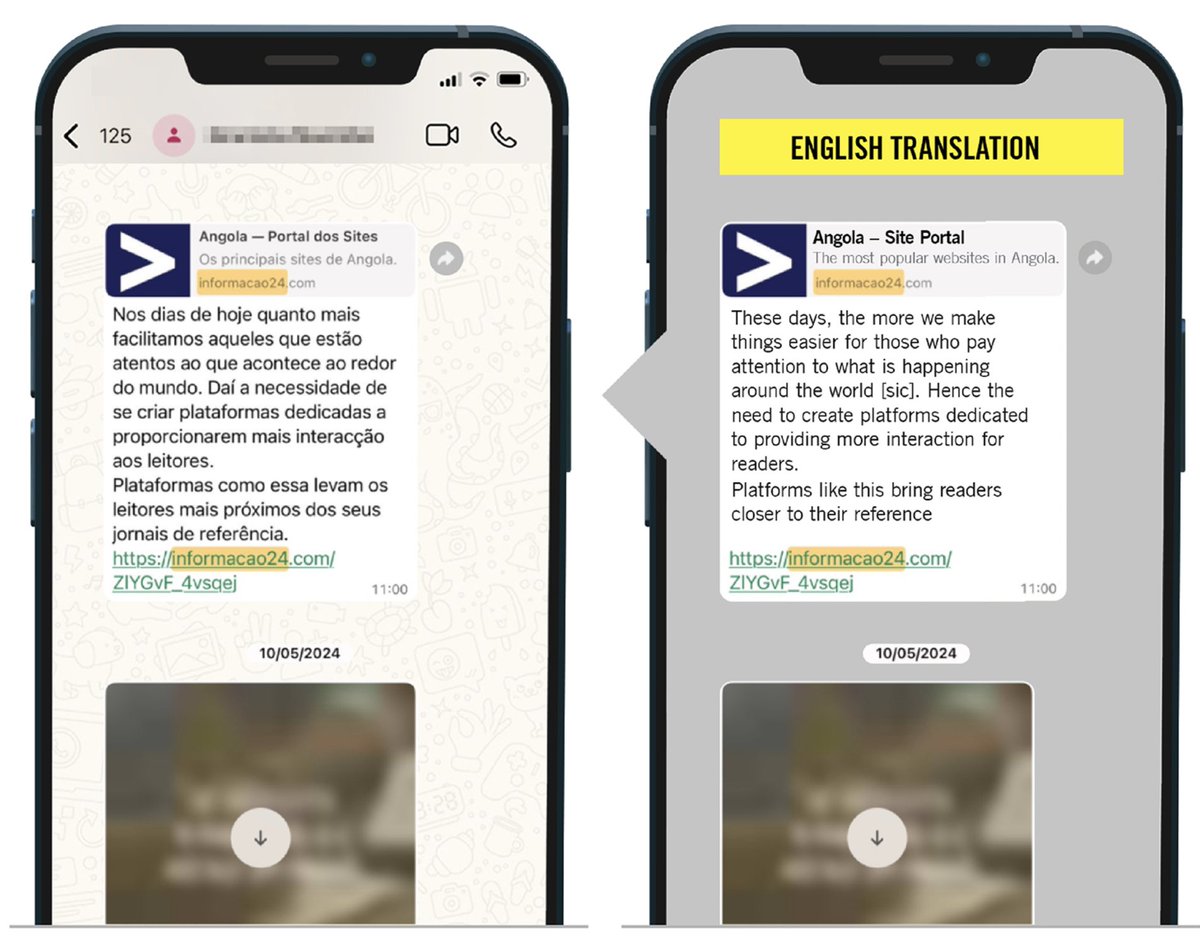
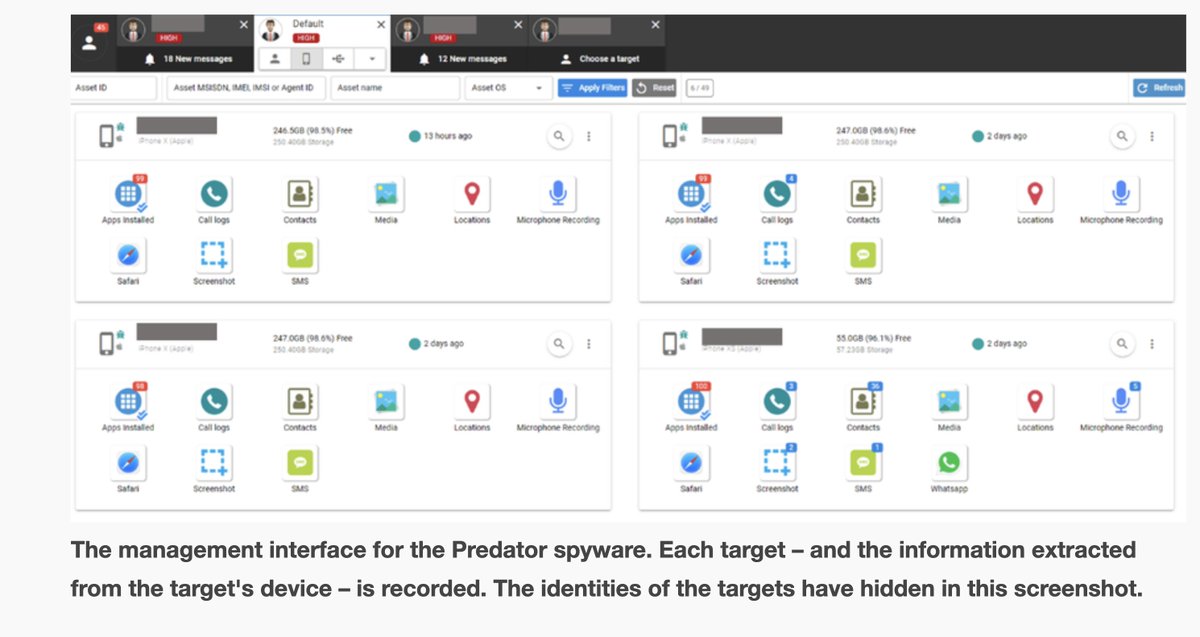
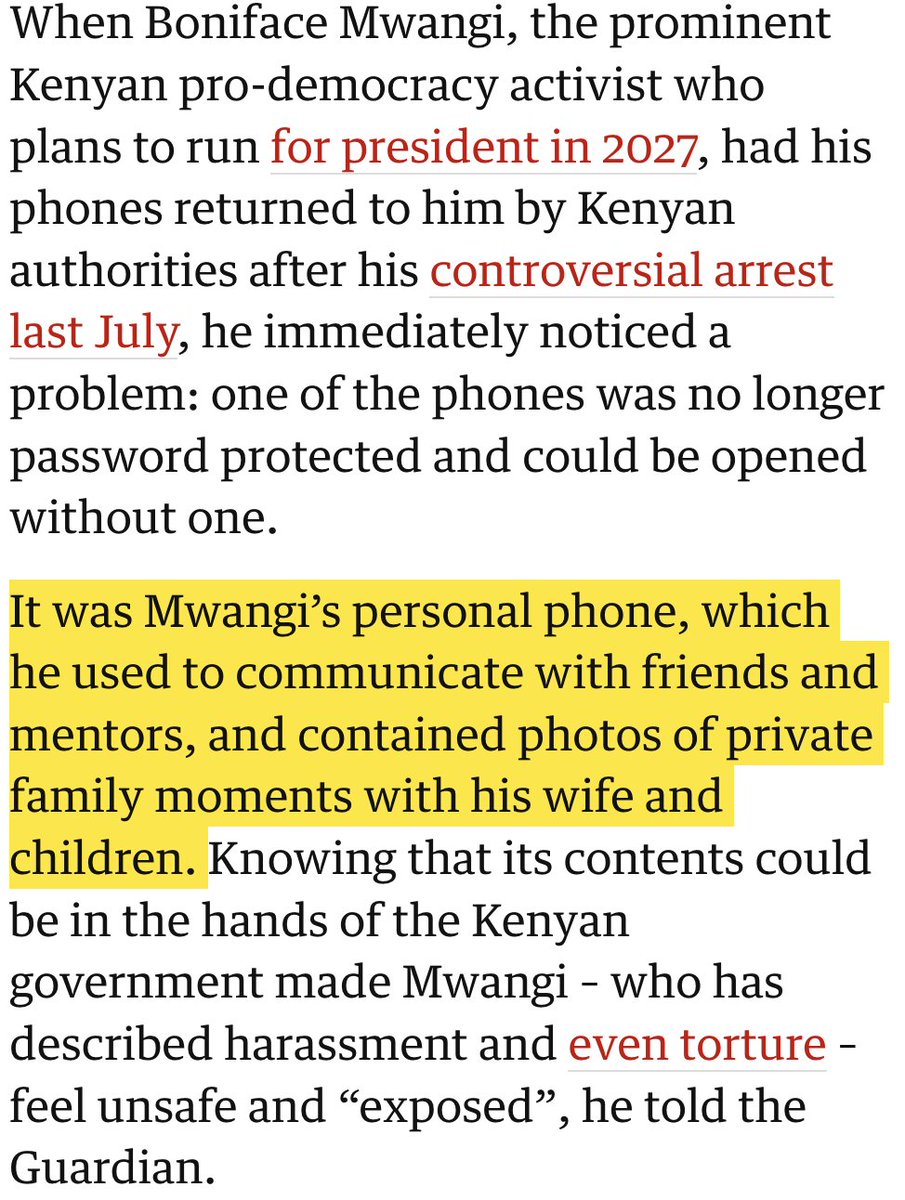
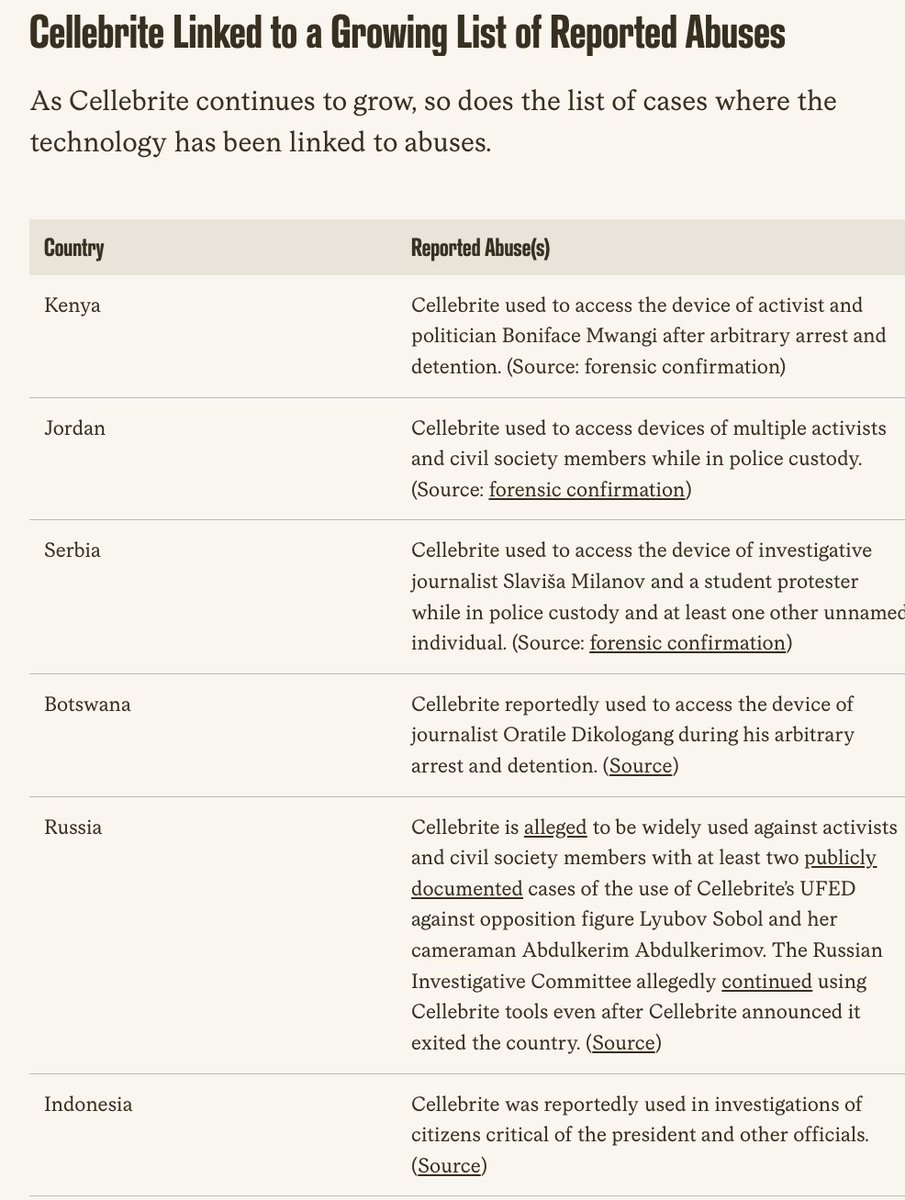
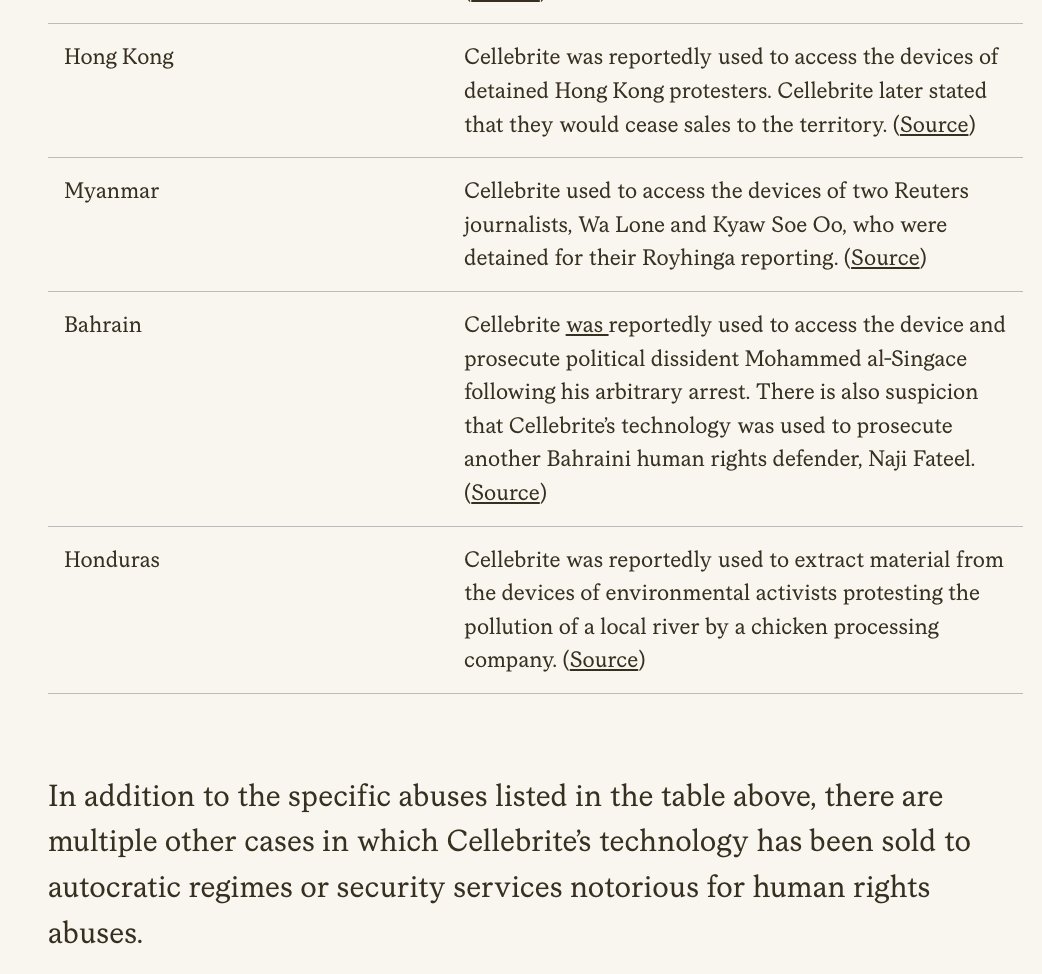
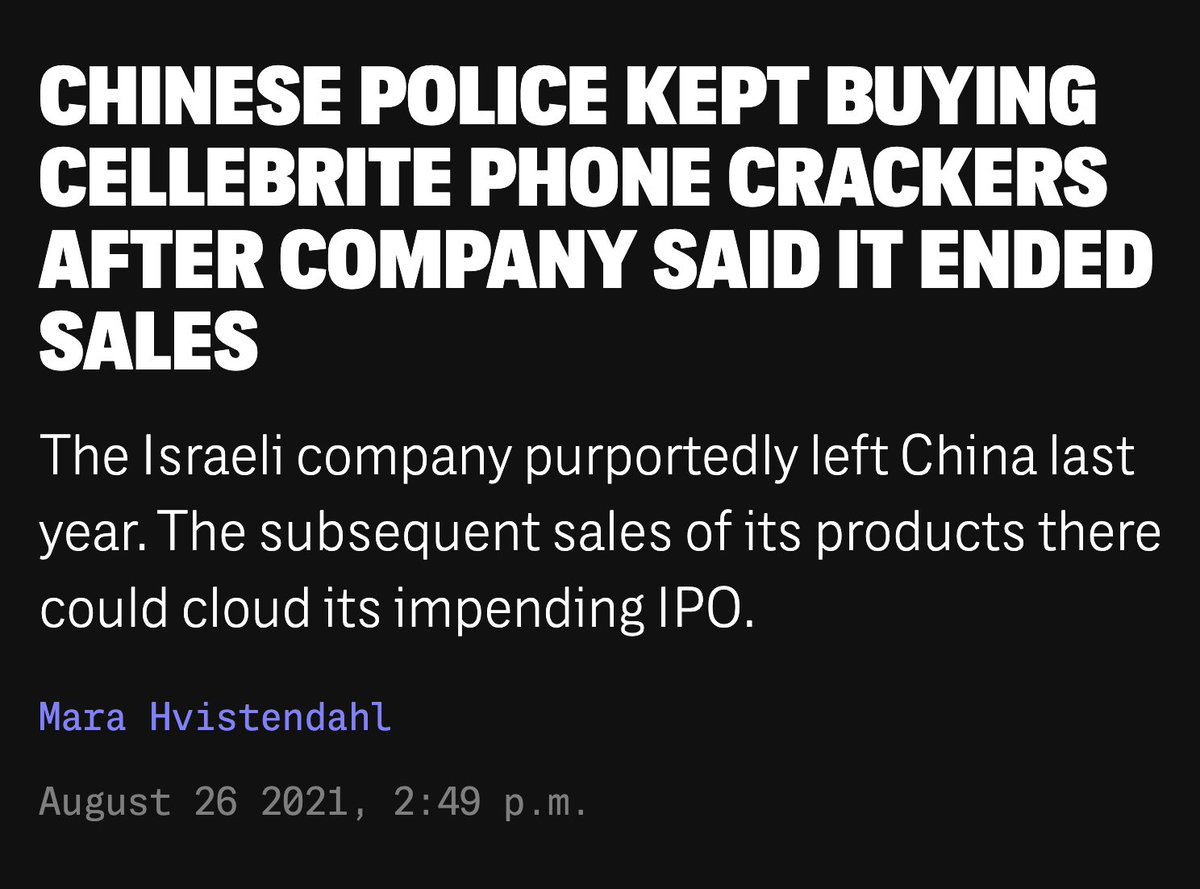
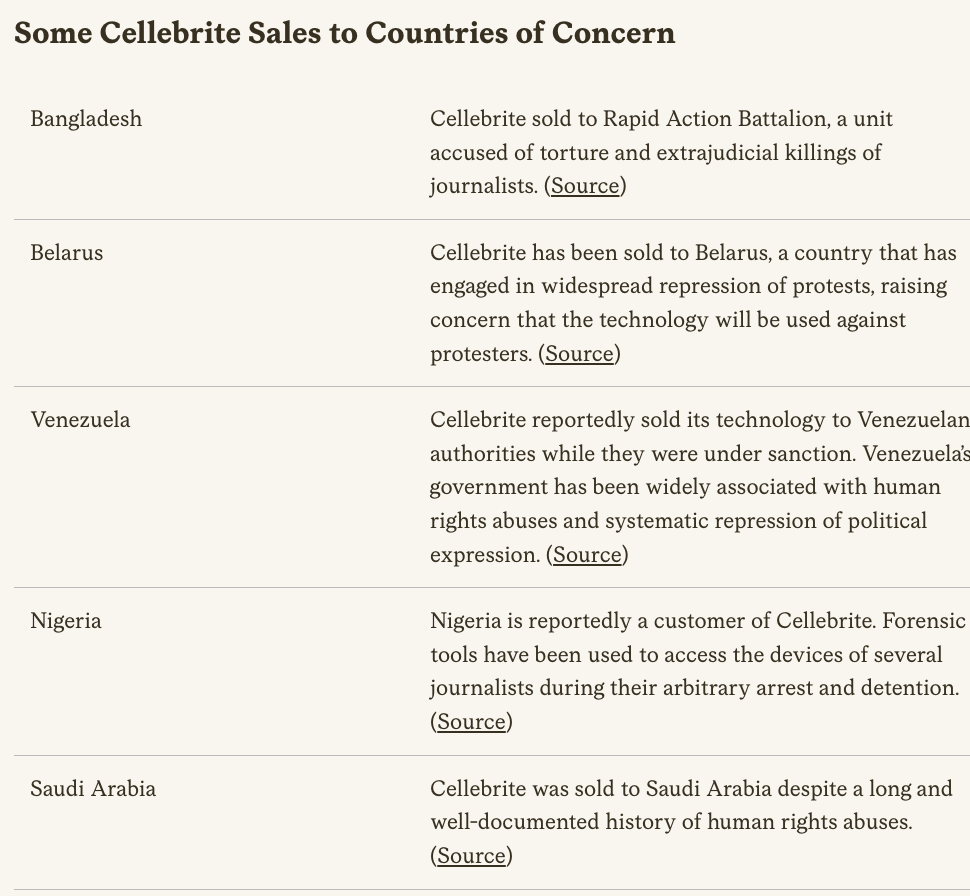
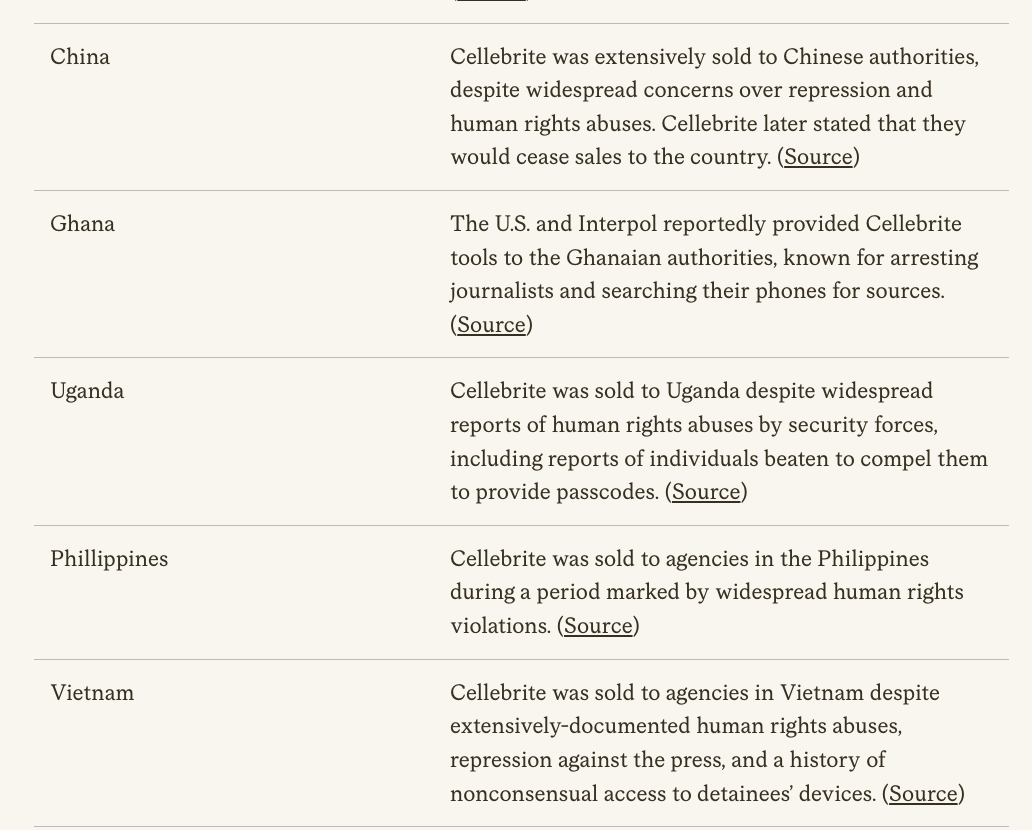
🚨NEW REPORT: exposing a new hacking tactic.
🇷🇺Russian state-backed hackers used an App-Specific Password attack against prominent Russia expert @KeirGiles & others.
It's like they know what we all expect from them...and then did the opposite 1/
By us @citizenlab & @google's GTIG


🇷🇺Russian state-backed hackers used an App-Specific Password attack against prominent Russia expert @KeirGiles & others.
It's like they know what we all expect from them...and then did the opposite 1/
By us @citizenlab & @google's GTIG



2/ Let's begin: @KeirGiles gets a message purporting to be from @StateDept asking for a consultation.
The attackers send the message from a @gmail, but CC'd a bunch of email addresses @ state.gov.
Strong credibility signal to have a bunch of gov ppl on the CC line right?
Well, what the attackers were counting on is that the State Dept mailserver just accepts all email addresses without emitting a bounce.
So they seem to have just created some fake State Dept staff names and addresses.
The attackers send the message from a @gmail, but CC'd a bunch of email addresses @ state.gov.
Strong credibility signal to have a bunch of gov ppl on the CC line right?
Well, what the attackers were counting on is that the State Dept mailserver just accepts all email addresses without emitting a bounce.
So they seem to have just created some fake State Dept staff names and addresses.

3/ The attackers wait for the 2nd interaction to introduce the pivotal deception: getting @KeirGiles to 'connect to a secure platform.'
In the next days they patiently walk him through what they want him to do, even sending a very official looking (but fake) State Dept. document

In the next days they patiently walk him through what they want him to do, even sending a very official looking (but fake) State Dept. document


4/ The attack works like this: the attackers try to deceive @keirgiles into creating and sharing an App-Specific Password (ASP) with them.
They do this by reframing ASPs as something that will let him access a secure resource (spoiler: not how this works)
What's an ASP? Well, not every app that users want to use supports Multi-Factor Authentication.
Some older email clients for example don't. So providers like @Google let users create a special password just for those apps.

They do this by reframing ASPs as something that will let him access a secure resource (spoiler: not how this works)
What's an ASP? Well, not every app that users want to use supports Multi-Factor Authentication.
Some older email clients for example don't. So providers like @Google let users create a special password just for those apps.


5/ This attack was like slow food. 10 email exchanges over several weeks! Very much not your run-of-the-mill phishing.
Ultimately, @KeirGiles realized something was wrong and got in touch with us @citizenlab, but not before the attackers got access
Ultimately, @KeirGiles realized something was wrong and got in touch with us @citizenlab, but not before the attackers got access
https://x.com/KeirGiles/status/1933930304999236026
@KeirGiles @citizenlab 6/ Takeaway for us: some sophisticated threat actors are feeling pressure & innovating.
Trying to move away from smash & grab phishing for passwords (& maybe your 2nd factor code)... and going for something more subtle, slower perhaps less detectable.
citizenlab.ca/2025/06/russia…
Trying to move away from smash & grab phishing for passwords (& maybe your 2nd factor code)... and going for something more subtle, slower perhaps less detectable.
citizenlab.ca/2025/06/russia…
7/ Who targeted @KeirGiles? Folks at @google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) have analysis & attribution! Great!
🇷🇺#UNC6293, a Russia state-sponsored threat actor w/additional low confidence association to #APT29 (that would be the Russian #SVR)
By @gabby_roncone & @wxs
cloud.google.com/blog/topics/th…
🇷🇺#UNC6293, a Russia state-sponsored threat actor w/additional low confidence association to #APT29 (that would be the Russian #SVR)
By @gabby_roncone & @wxs
cloud.google.com/blog/topics/th…

8/ There were so many clever bits to this attack, it's easy to imagine a lot of people falling for it.
Everything was clean. The doc looked real. The language was right. Email addresses at the State Dept. seemed to be CC'd.. I could go on.
They even had Keir enter "ms.state. gov" into the ASP name...
(this doesn't do anything but further the deception that he's adding an external app to his Gmail, that name field accepts any text you want to put in there)
Everything was clean. The doc looked real. The language was right. Email addresses at the State Dept. seemed to be CC'd.. I could go on.
They even had Keir enter "ms.state. gov" into the ASP name...
(this doesn't do anything but further the deception that he's adding an external app to his Gmail, that name field accepts any text you want to put in there)

@KeirGiles @citizenlab @Google @gabby_roncone @wxs 9/ Targeting App-Specific Passwords is novel.
But it's just part of a trend of state-backed attackers innovating & moving beyond simple phishing.
The folks @volexity have been doing great work on this theme.
Recommended Reads: volexity.com/blog/2025/02/1…
volexity.com/blog/2025/04/2…
But it's just part of a trend of state-backed attackers innovating & moving beyond simple phishing.
The folks @volexity have been doing great work on this theme.
Recommended Reads: volexity.com/blog/2025/02/1…
volexity.com/blog/2025/04/2…
10/ Coda: Every @citizenlab report is a team production. Especially when they come together fast.
Big props to my coauthors @PDXbek & @billmarczak and the many colleagues & coworkers that jumped in here to help out and get this report done!
Plus special thanks to @KeirGiles for so graciously working with us to understand & get his case shared.
Big props to my coauthors @PDXbek & @billmarczak and the many colleagues & coworkers that jumped in here to help out and get this report done!
Plus special thanks to @KeirGiles for so graciously working with us to understand & get his case shared.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh