👑 Charlemagne: the warrior-king who forged Europe with sword and faith ⚔️✝️
In the chaos of early medieval Europe — divided by tribes, warlords, and collapsing empires — one man rose with an unshakable dream: to unite the continent under one rule, one law, and one faith. His name? Charlemagne, or Karol Wielki — the Father of Europe 🌍🏛️.
Let’s explore the epic life of the man who brought a broken continent to its knees and built the foundations of a united Europe 🧵👇
In the chaos of early medieval Europe — divided by tribes, warlords, and collapsing empires — one man rose with an unshakable dream: to unite the continent under one rule, one law, and one faith. His name? Charlemagne, or Karol Wielki — the Father of Europe 🌍🏛️.
Let’s explore the epic life of the man who brought a broken continent to its knees and built the foundations of a united Europe 🧵👇
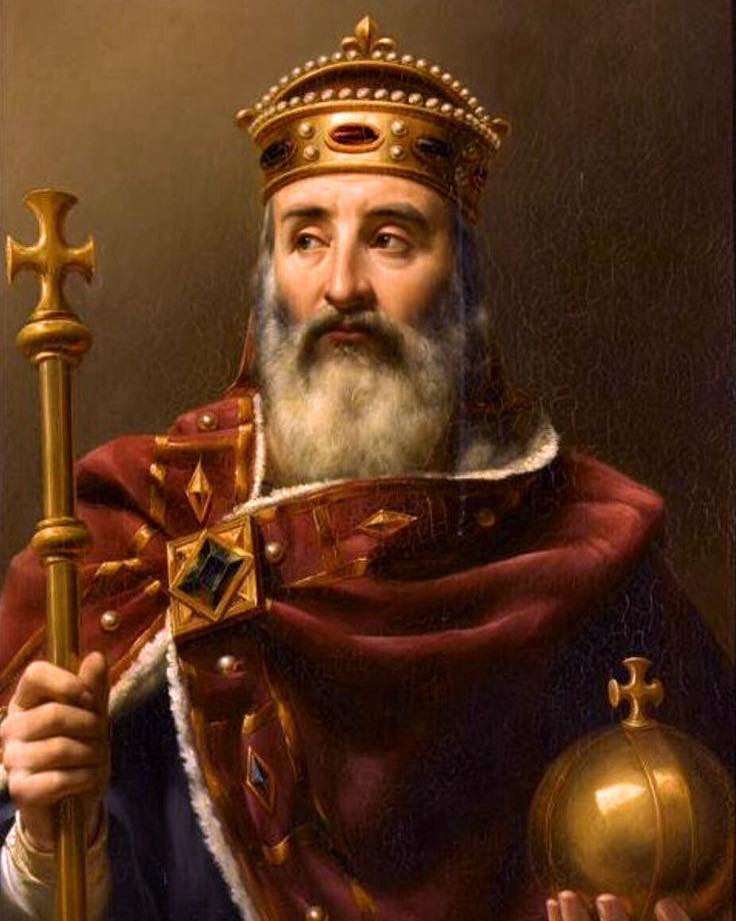

1️⃣ Rise of a king: from Frankish warlord to emperor of the West 🏰🗺️
Born in 742, Charlemagne inherited the Frankish kingdom after the death of his father, Pippin the Short. But ruling wasn't enough — he envisioned dominion, not just survival. Through relentless campaigns, he expanded Frankish rule across modern-day France, Germany, Italy, the Low Countries, and beyond ⚔️🏇.
He fought over 50 military campaigns, subduing the Lombards, Saxons, and Avars. His wars were brutal, but always tied to a higher purpose: spreading Christianity and creating a divine empire aligned with Rome ✝️🔥.
By Christmas Day, 800, Charlemagne was crowned "Emperor of the Romans" by Pope Leo III in St. Peter’s Basilica — reviving the idea of a Christian Roman Empire in the West, three centuries after its fall 🕍👑.
Born in 742, Charlemagne inherited the Frankish kingdom after the death of his father, Pippin the Short. But ruling wasn't enough — he envisioned dominion, not just survival. Through relentless campaigns, he expanded Frankish rule across modern-day France, Germany, Italy, the Low Countries, and beyond ⚔️🏇.
He fought over 50 military campaigns, subduing the Lombards, Saxons, and Avars. His wars were brutal, but always tied to a higher purpose: spreading Christianity and creating a divine empire aligned with Rome ✝️🔥.
By Christmas Day, 800, Charlemagne was crowned "Emperor of the Romans" by Pope Leo III in St. Peter’s Basilica — reviving the idea of a Christian Roman Empire in the West, three centuries after its fall 🕍👑.

2️⃣ More than a conqueror: the Carolingian Renaissance 📚⚖️
Charlemagne wasn’t just a sword-wielding monarch — he was a reformer, educator, and visionary. Believing that power must rest on knowledge and law, he launched what became known as the Carolingian Renaissance 🌟.
He established schools in monasteries and cathedrals, preserved ancient Roman texts, and promoted Latin literacy. Under his rule, even his court became a center of learning — attracting scholars like Alcuin of York 🧠📜.
His Capitularies — royal decrees — brought a semblance of legal order to his vast empire, setting standards for justice, trade, and religion. Roads were rebuilt, taxes organized, and Christian missionaries sent across Europe 🚧📖✝️.
He created a model for Christian kingship: not only mighty in battle, but also wise in law and pious in spirit — a legacy that shaped medieval kings for centuries 💼🛡️.
Charlemagne wasn’t just a sword-wielding monarch — he was a reformer, educator, and visionary. Believing that power must rest on knowledge and law, he launched what became known as the Carolingian Renaissance 🌟.
He established schools in monasteries and cathedrals, preserved ancient Roman texts, and promoted Latin literacy. Under his rule, even his court became a center of learning — attracting scholars like Alcuin of York 🧠📜.
His Capitularies — royal decrees — brought a semblance of legal order to his vast empire, setting standards for justice, trade, and religion. Roads were rebuilt, taxes organized, and Christian missionaries sent across Europe 🚧📖✝️.
He created a model for Christian kingship: not only mighty in battle, but also wise in law and pious in spirit — a legacy that shaped medieval kings for centuries 💼🛡️.

3️⃣ Legacy of a titan: death and the birth of Europe 🇪🇺🕊️
Charlemagne died in 814, leaving behind a colossal empire. Though his empire was soon divided among his heirs, its ideaendured. He had created the first vision of a unified Christian Europe, centuries before the EU ever existed 🔄🌍.
He is still revered as the "Father of Europe" — a figure claimed by both France and Germany, and commemorated in European politics, art, and memory 🇫🇷🇩🇪.
Modern Europe still echoes his dream: unity through shared law, identity, and purpose. And though his methods were often harsh, his ambition was civilization itself.
Charlemagne died in 814, leaving behind a colossal empire. Though his empire was soon divided among his heirs, its ideaendured. He had created the first vision of a unified Christian Europe, centuries before the EU ever existed 🔄🌍.
He is still revered as the "Father of Europe" — a figure claimed by both France and Germany, and commemorated in European politics, art, and memory 🇫🇷🇩🇪.
Modern Europe still echoes his dream: unity through shared law, identity, and purpose. And though his methods were often harsh, his ambition was civilization itself.

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh