For decades, Palestinian radicals have wrecked havoc across the Middle East.
They have no allies. Their accomplices and benefactors always pay a high price for tolerating and appeasing them.
🧵 1/20
They have no allies. Their accomplices and benefactors always pay a high price for tolerating and appeasing them.
🧵 1/20
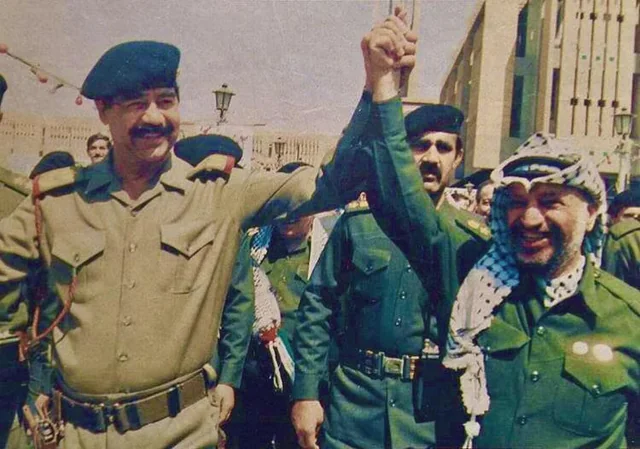

In Jordan: The PLO's growing presence in the late 1960s led to tensions with King Hussein.
By 1970, PLO fedayeen controlled parts of Amman, acting as a "state within a state," challenging Jordanian sovereignty. This culminated in the Dawson's Field hijackings.
🧵 2/20
By 1970, PLO fedayeen controlled parts of Amman, acting as a "state within a state," challenging Jordanian sovereignty. This culminated in the Dawson's Field hijackings.
🧵 2/20

The conflict escalated into Black September 1970, when PLO forces attempted to overthrow the monarchy.
Fighting resulted in thousands dead, and the PLO was expelled by July 1971.
🧵 3/20
Fighting resulted in thousands dead, and the PLO was expelled by July 1971.
🧵 3/20

In Lebanon: After expulsion from Jordan, the PLO relocated to Lebanon, establishing bases in refugee camps.
By 1975, their armed presence contributed to the outbreak of the Lebanese Civil War, arming militias and clashing with Christian factions.
🧵 4/20
By 1975, their armed presence contributed to the outbreak of the Lebanese Civil War, arming militias and clashing with Christian factions.
🧵 4/20
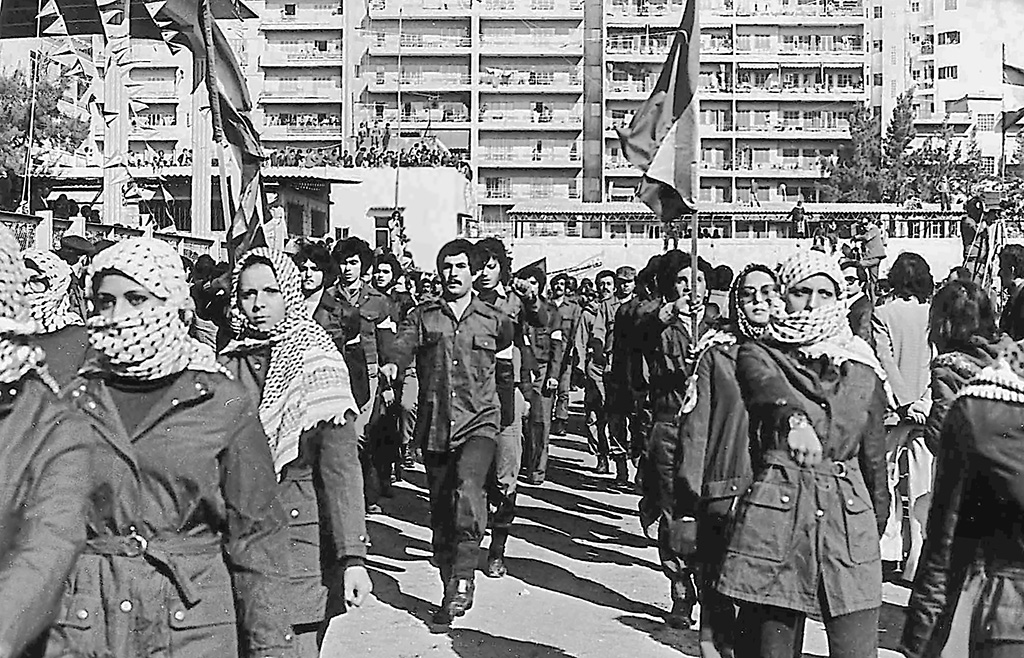

The PLO's "state within a state" in southern Lebanon led to Israeli invasions in 1978 and 1982.
The 1982 invasion forced the PLO out of Beirut, with thousands of fighters evacuated to Tunisia and other countries.
🧵 5/20
The 1982 invasion forced the PLO out of Beirut, with thousands of fighters evacuated to Tunisia and other countries.
🧵 5/20
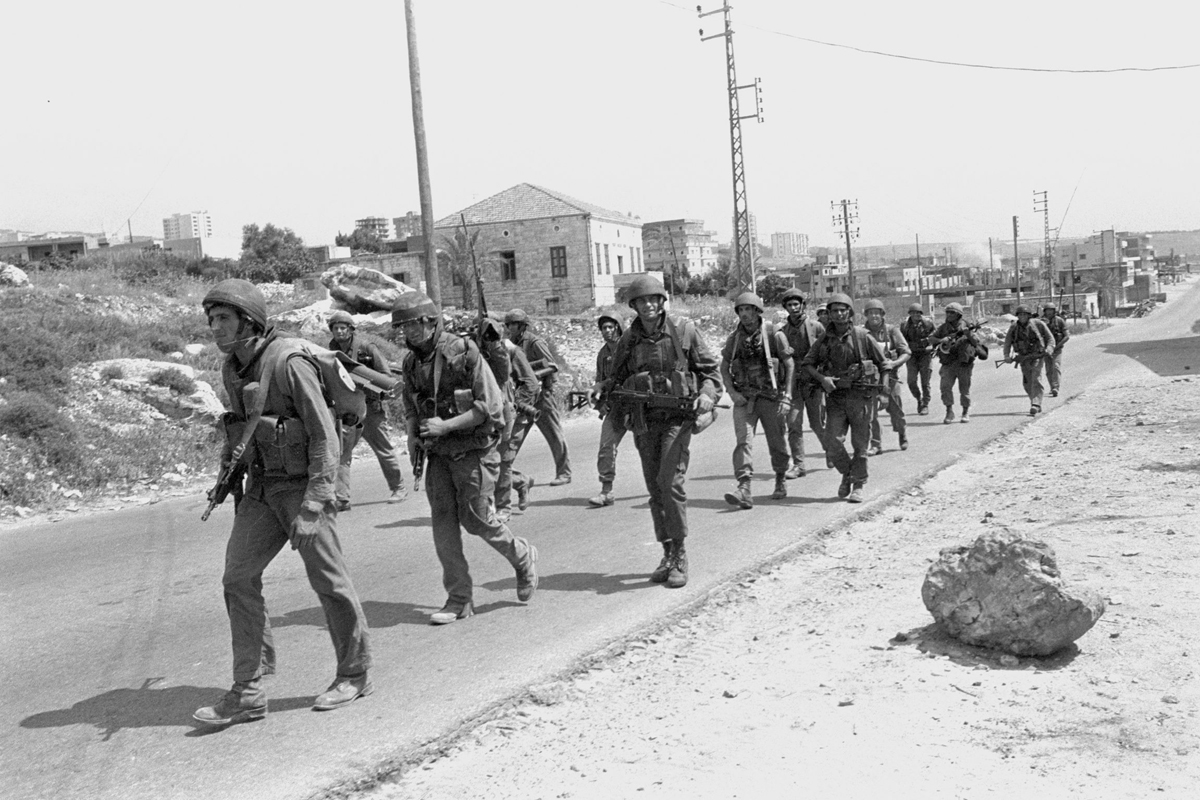

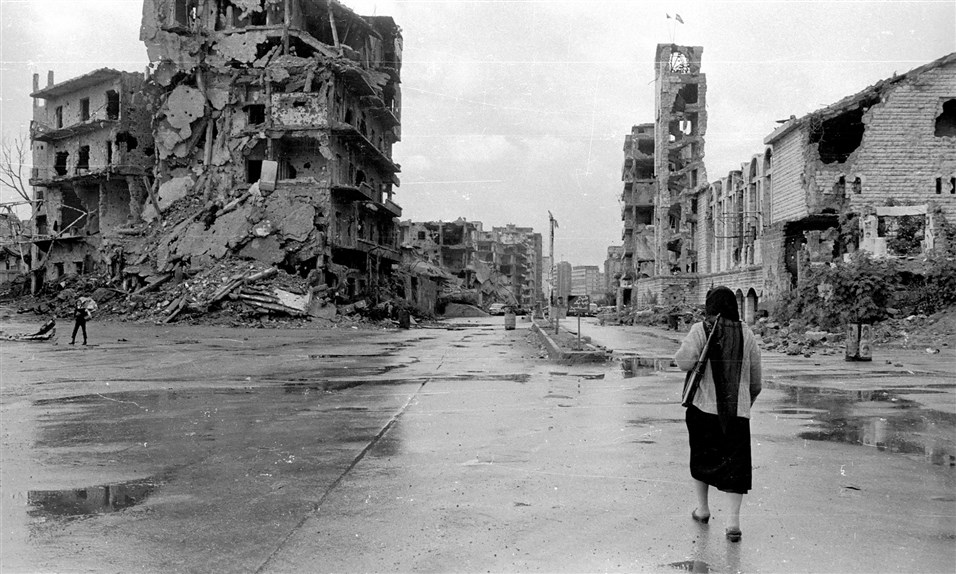
The PLO's involvement prolonged the Lebanese Civil War until 1990, with Syrian forces using PLO proxies against rivals.
The war killed over 100,000, and PLO actions drew Lebanon into broader Arab-Israeli conflicts.
🧵 6/20
The war killed over 100,000, and PLO actions drew Lebanon into broader Arab-Israeli conflicts.
🧵 6/20

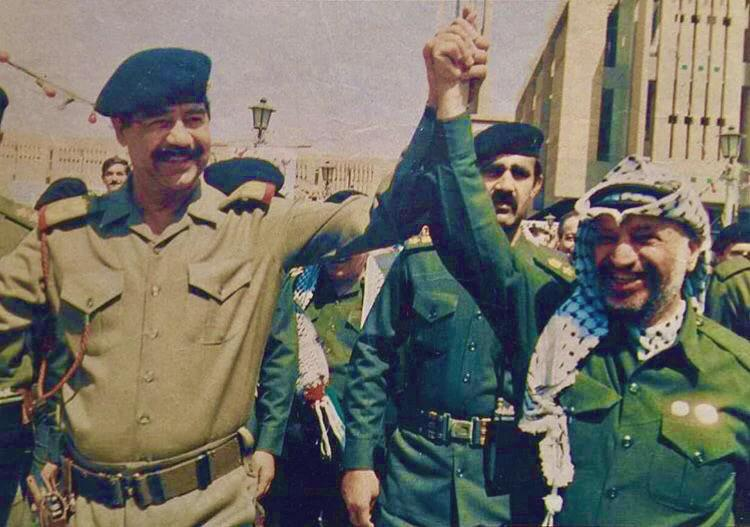
In Kuwait: During the 1990 Iraqi invasion, PLO leader Yasser Arafat supported Saddam Hussein, alienating Kuwait.
Post-liberation in 1991, Kuwait expelled over 287,000 Palestinians, citing collaboration and security threats.
🧵 7/20
Post-liberation in 1991, Kuwait expelled over 287,000 Palestinians, citing collaboration and security threats.
🧵 7/20

In Egypt: Palestinian groups like Hamas have been linked to terrorism in Sinai, aiding insurgents against Egyptian forces.
Egypt designated Hamas a terrorist organization in 2015 for supporting attacks. Gaza tunnels have facilitated smuggling and militancy.
🧵 8/20
Egypt designated Hamas a terrorist organization in 2015 for supporting attacks. Gaza tunnels have facilitated smuggling and militancy.
🧵 8/20

In Algeria: Algeria hosted PLO leaders and provided support, including declaring Palestinian independence in 1988.
Soon, the Palestinians started interfering with locals politics, contributing to the Algerian Civil War in the 1990s.
🧵 9/20
Soon, the Palestinians started interfering with locals politics, contributing to the Algerian Civil War in the 1990s.
🧵 9/20

In Syria: The PLO established bases after 1967.
During the Lebanese Civil War, Syria used the Palestine Liberation Army as proxies against Arafat's PLO factions.
🧵 10/20
During the Lebanese Civil War, Syria used the Palestine Liberation Army as proxies against Arafat's PLO factions.
🧵 10/20

A key figure: the Palestinian cleric Abdullah Azzam mentored Osama bin Laden in the 1980s during the Afghan jihad.
Azzam co-founded al-Qaeda's precursor and influenced global jihadism before his 1989 assassination.
🧵 11/20
Azzam co-founded al-Qaeda's precursor and influenced global jihadism before his 1989 assassination.
🧵 11/20

Crime in Western Europe: In Denmark, of 321 Palestinian refugees admitted in 1992, 64% had criminal convictions by 2019, including serious fines or imprisonment - far above national averages.
🧵 12/20
🧵 12/20
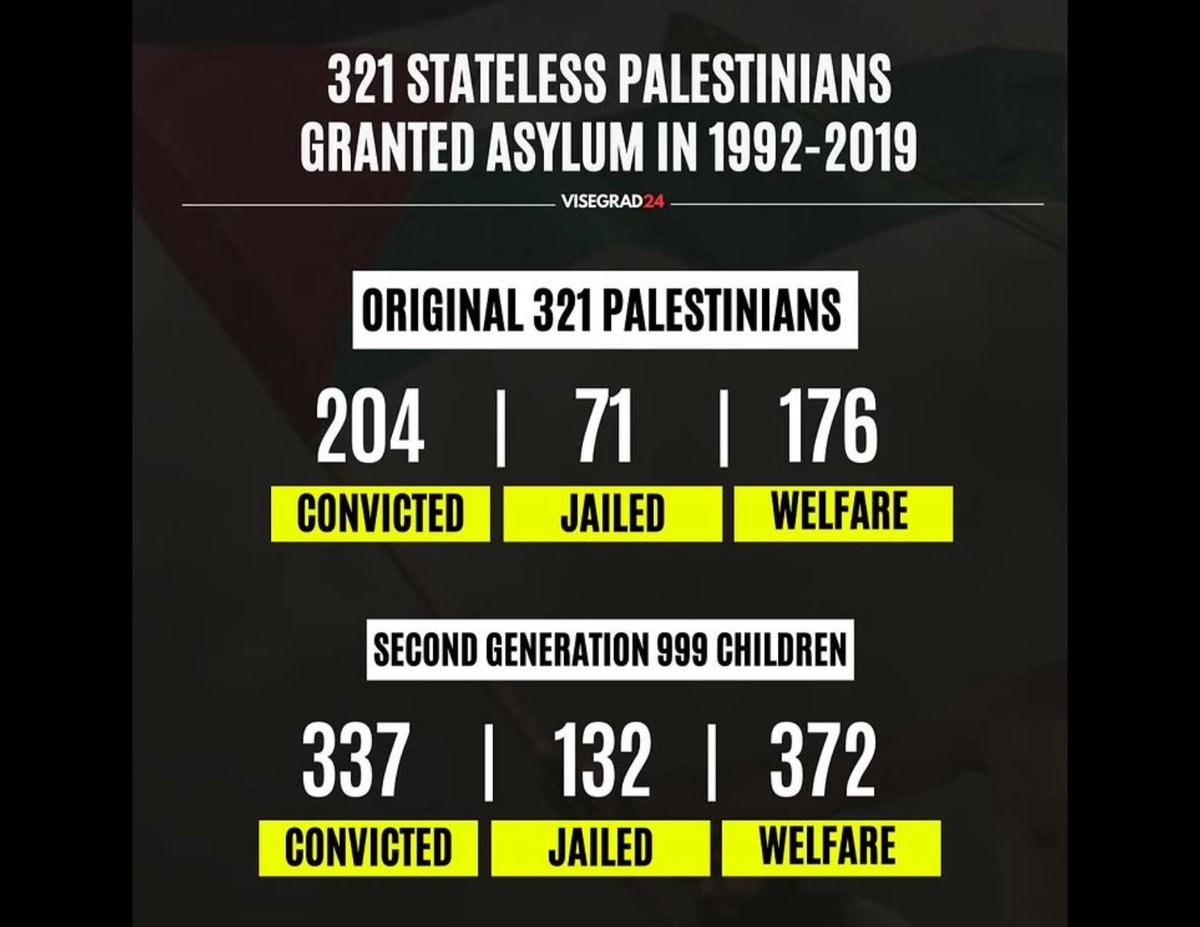
Among their children, 34% also had convictions. This overrepresentation includes violence and theft.
🧵 13/20
🧵 13/20

In Yemen: The PLO established a presence in the 1970s, aligning with South Yemen's Marxist government.
They trained fighters and supported local militias, contributing to regional instability during the Cold War proxy conflicts.
🧵 14/20
They trained fighters and supported local militias, contributing to regional instability during the Cold War proxy conflicts.
🧵 14/20

In other countries: Tunisia hosted PLO headquarters after Lebanon.
In 1985, Israel bombed the PLO base in Tunis, killing dozens, in response to terrorist attacks. This drew Tunisia into the conflict.
🧵 15/20
In 1985, Israel bombed the PLO base in Tunis, killing dozens, in response to terrorist attacks. This drew Tunisia into the conflict.
🧵 15/20
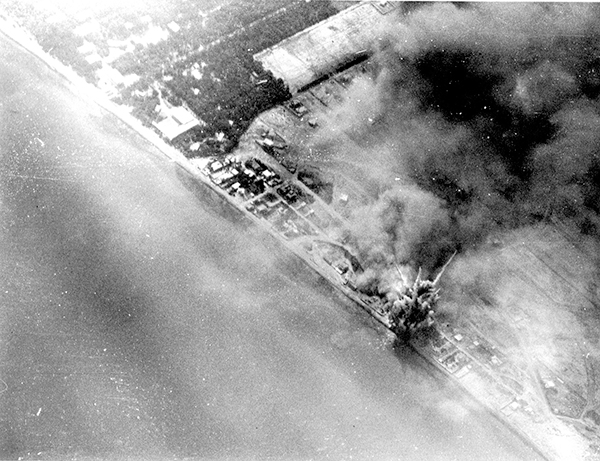

In Uganda: The 1976 Entebbe hijacking by PFLP and German revolutionaries involved diverting an Air France plane to Uganda, holding hostages.
Israeli commandos rescued them, highlighting Palestinian terrorism abroad.
🧵 16/20
Israeli commandos rescued them, highlighting Palestinian terrorism abroad.
🧵 16/20

In Sudan: PLO had ties in the 1990s; Sudan hosted bin Laden (influenced by Azzam).
Palestinian groups used Sudan for training, contributing to its designation as a state sponsor of terrorism.
🧵 17/20
Palestinian groups used Sudan for training, contributing to its designation as a state sponsor of terrorism.
🧵 17/20

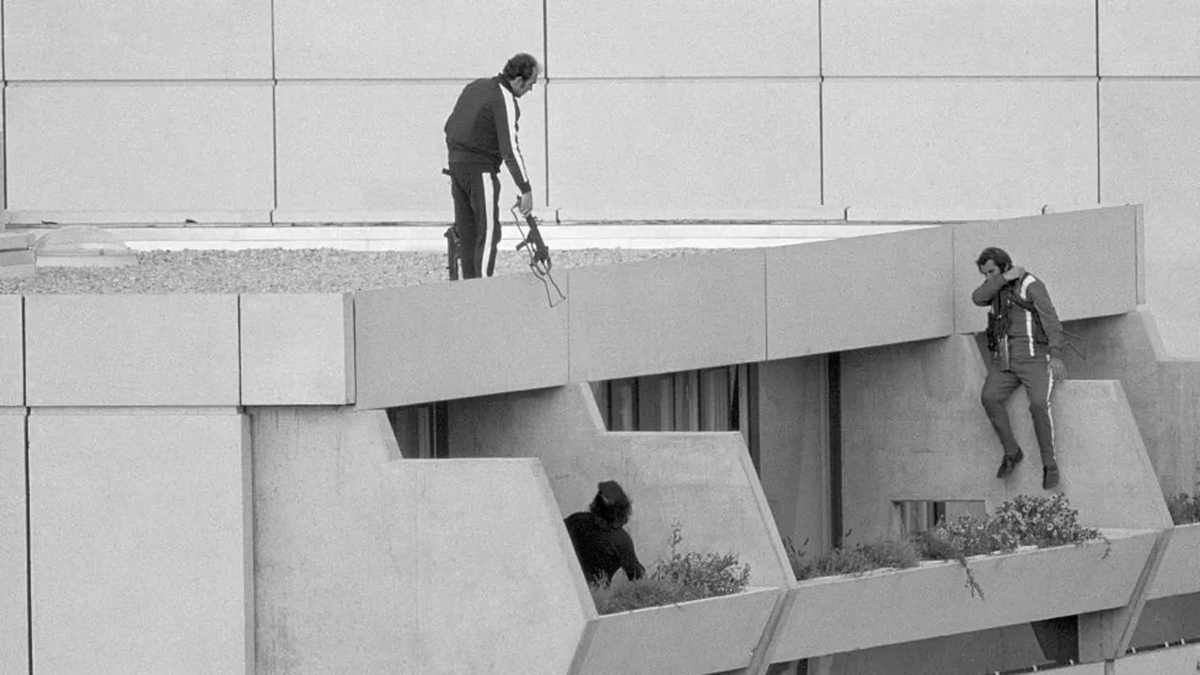
Additional interference: In Germany, the 1972 Munich Olympics massacre by Black September killed 11 Israeli athletes, disrupting the games and international security.
🧵 18/20
🧵 18/20

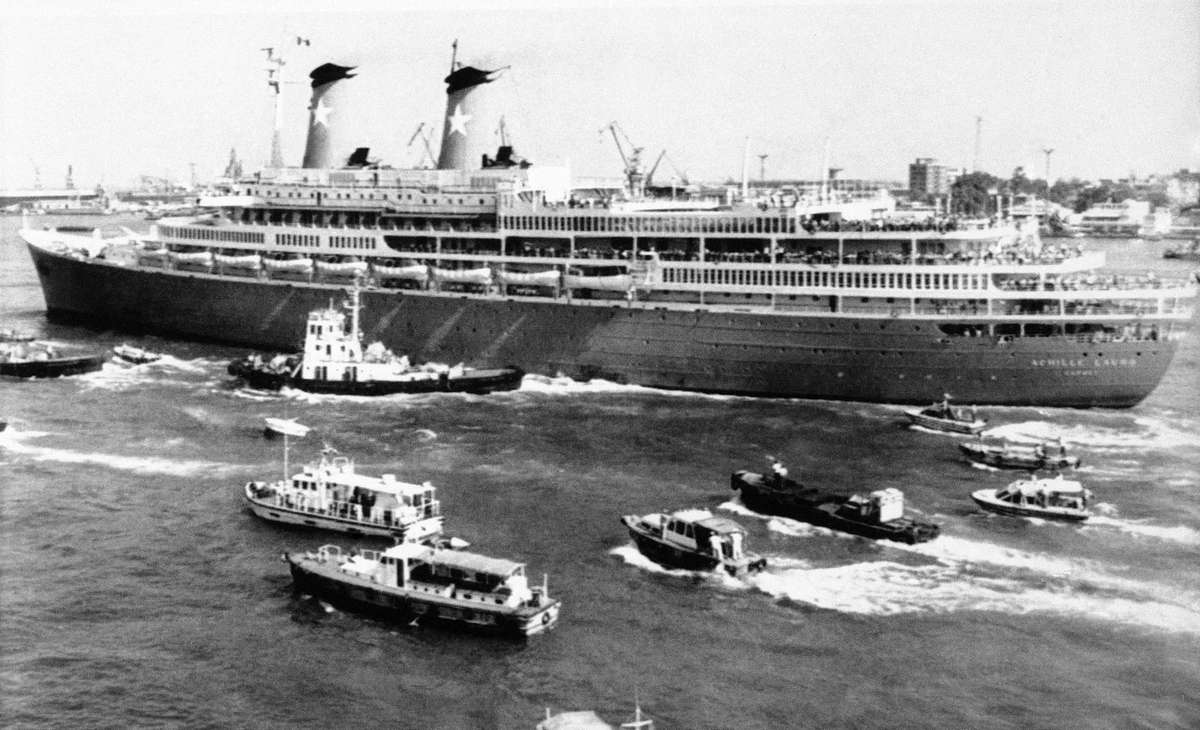
In Italy and elsewhere in Europe, Palestinian groups conducted hijackings and bombings in the 1970s-80s, like the Achille Lauro ship hijacking in 1985, affecting multiple nations.
🧵 19/20
🧵 19/20

Conclusion: These activities show how PLO and affiliated groups often destabilized host countries through militancy and alliances.
The arrival of large numbers of Palestinians resulted in serious conflicts.
🧵 20/20
The arrival of large numbers of Palestinians resulted in serious conflicts.
🧵 20/20

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





















