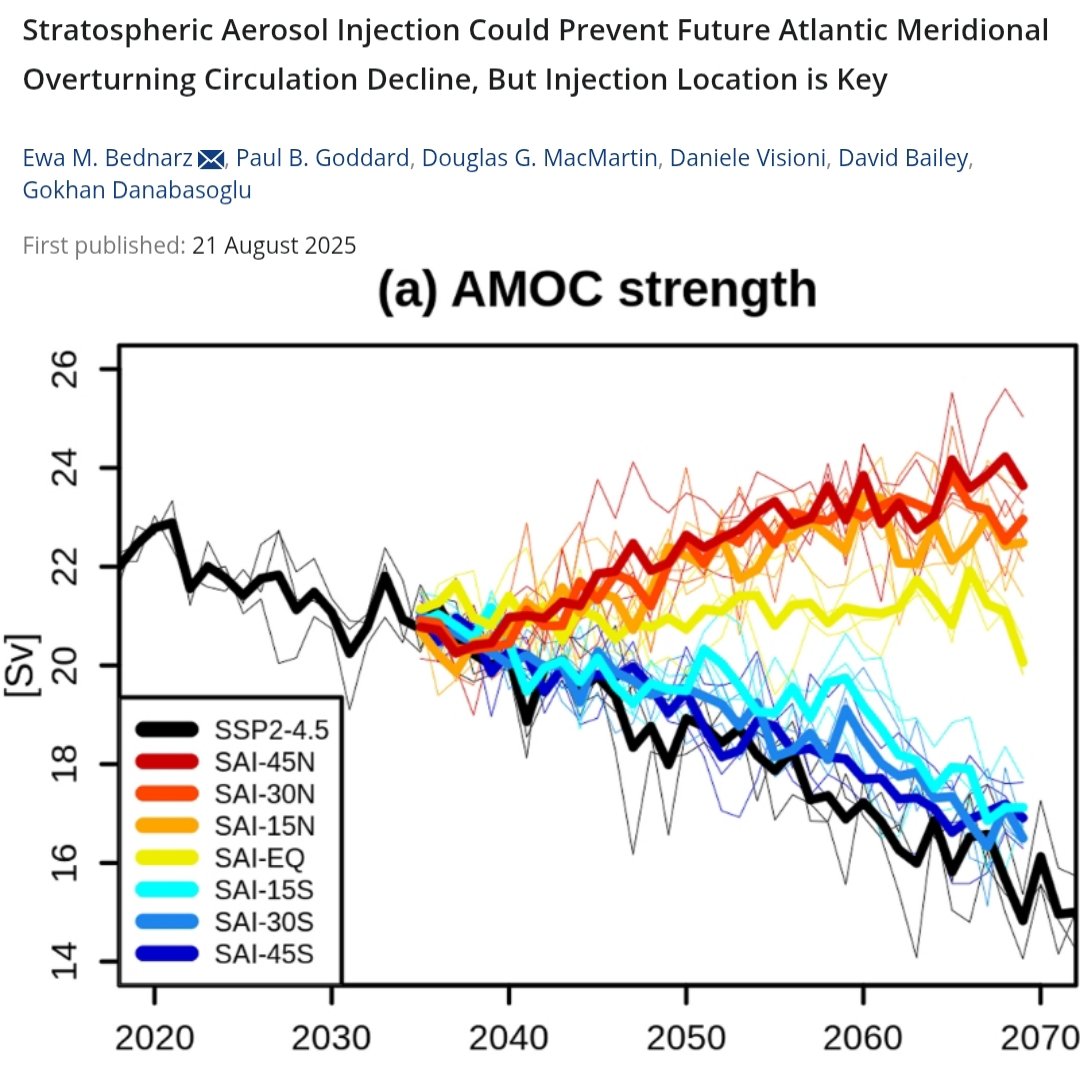
🚨New Nature Geoscience study shows that blooms of Phaeocystis antarctica (microalgae) in the Southern Ocean ~14,000 yrs ago massively drew down CO₂, stabilizing climate. Their decline today could have global consequences.
#CarbonSink #CarbonDrawdown
Details🧵1/9
#CarbonSink #CarbonDrawdown
Details🧵1/9
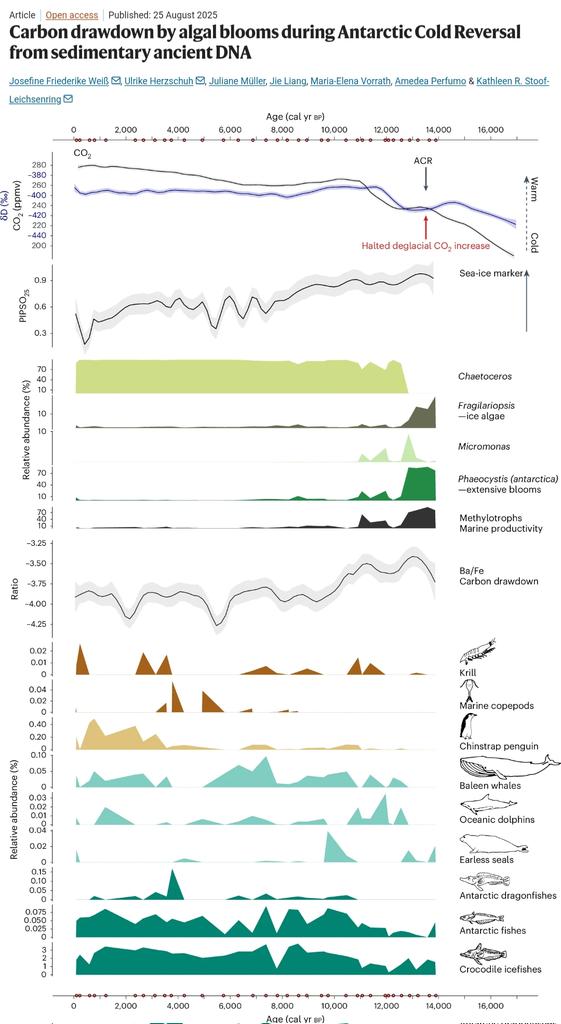
2/ Microalgae are pivotal in the Southern Ocean carbon cycle.
A new study from the Alfred Wegener Institute (AWI) reveals that during the Antarctic Cold Reversal (14.7–12.7k yrs BP), algal blooms slowed the rise of atmospheric CO₂.
A new study from the Alfred Wegener Institute (AWI) reveals that during the Antarctic Cold Reversal (14.7–12.7k yrs BP), algal blooms slowed the rise of atmospheric CO₂.
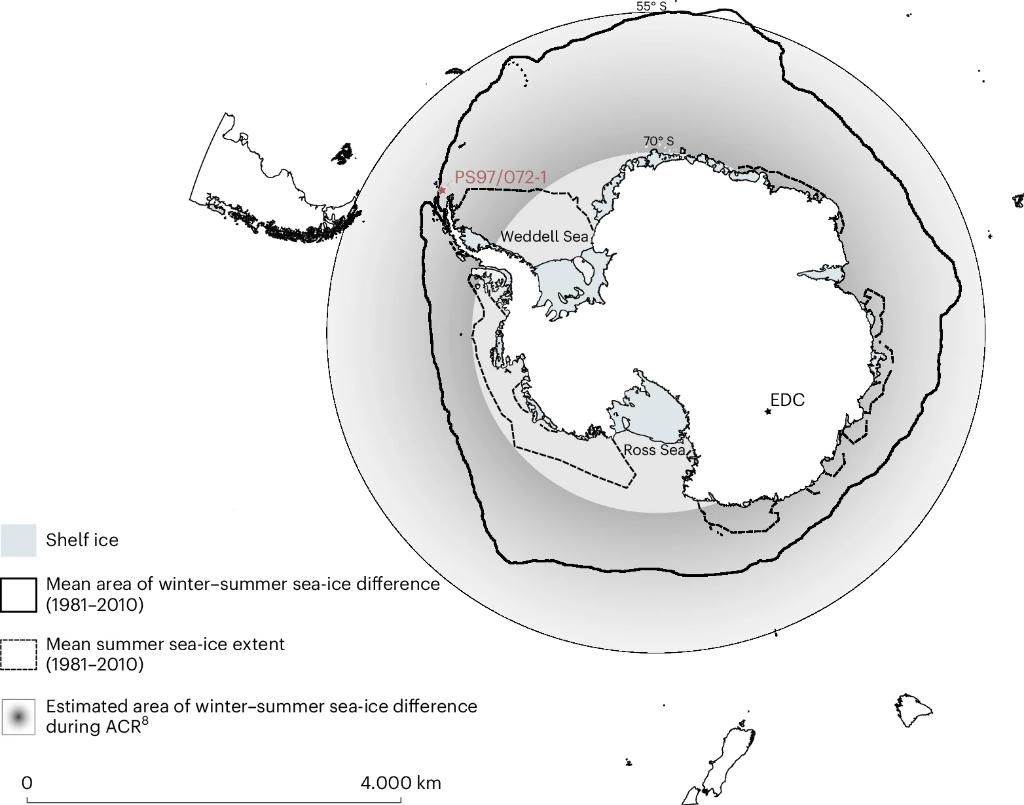
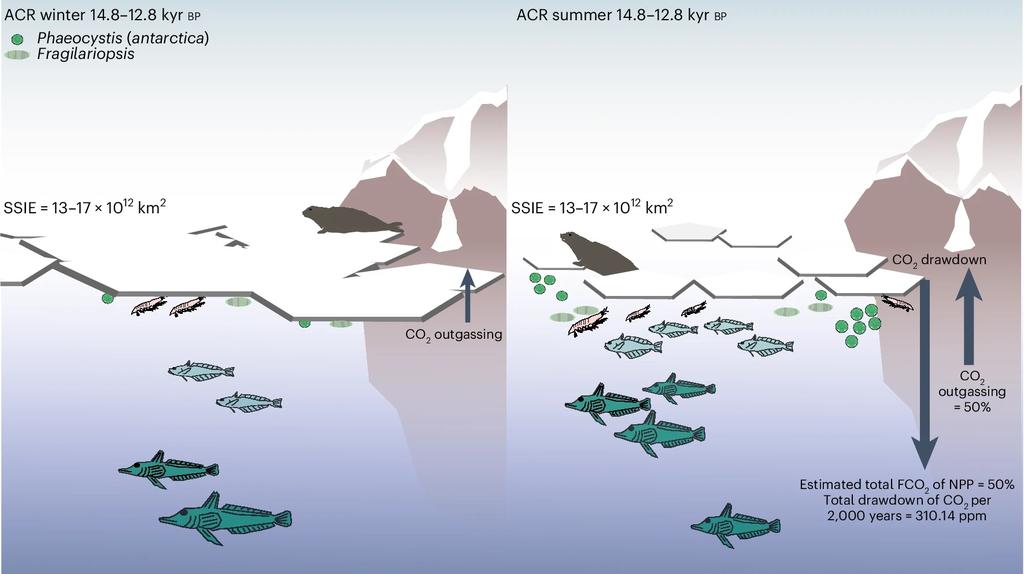
3/ At the end of the last ice age, the Antarctic Cold Reversal brought vast winter sea ice followed by strong spring melt.
These unique conditions fueled Phaeocystis antarctica blooms, exceptionally efficient at capturing and exporting carbon.
These unique conditions fueled Phaeocystis antarctica blooms, exceptionally efficient at capturing and exporting carbon.
4/ Until now, Phaeocystis remained invisible in climate archives. Unlike diatoms, it leaves no durable microfossils.
The AWI team overcame this by analyzing sedimentary ancient DNA (sedaDNA) from a 2,000 m deep Bransfield Strait core.
The AWI team overcame this by analyzing sedimentary ancient DNA (sedaDNA) from a 2,000 m deep Bransfield Strait core.
5/ The sedaDNA revealed Phaeocystis dominance during the ACR, coinciding with elevated Ba/Fe ratios, a proxy for organic carbon input.
Together, these data show that algal blooms drove a significant atmospheric CO₂ plateau.
Together, these data show that algal blooms drove a significant atmospheric CO₂ plateau.
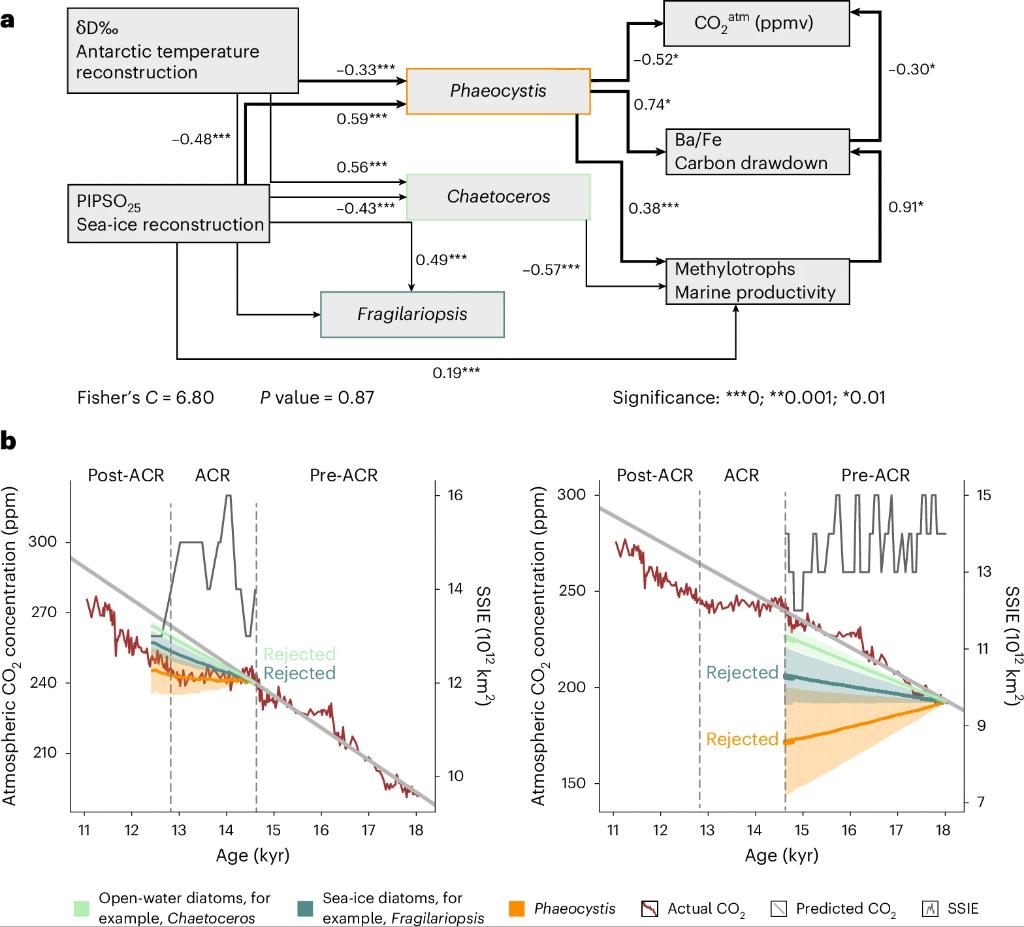
6/ Statistical modeling indicates that Phaeocystis blooms could have reduced CO₂ by up to ~20 ppm, closely matching ice-core records.
7/ But as Phaeocystis relies on pronounced sea-ice seasonality, accelerating sea-ice loss in the Southern Ocean is collapsing its niche, posing risks to carbon storage & climate regulation. 
8/ Beyond CO₂ uptake, Phaeocystis produces dimethyl sulfide (DMS), a gas that seeds clouds & enhances sunlight reflection.
Its decline could reduce cloud cover, amplifying warming through multiple feedbacks.
Its decline could reduce cloud cover, amplifying warming through multiple feedbacks.
📝For more details, read the study entitled "Carbon drawdown by algal blooms during Antarctic Cold Reversal from sedimentary ancient DNA" here:
🧵9/9 #CarbonSink #Microalgaenature.com/articles/s4156…
🧵9/9 #CarbonSink #Microalgaenature.com/articles/s4156…
"unroll" @threadreaderapp
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh