1. MSI-H/dMMR: the perfect storm for immunotherapy 🔥
▫️High TMB, tons of neoantigens, and inflamed tumors. Long-term survivors, even cures.
▫️Up to 40% still fail.
Cure or collapse, the paradox of MSI-H/dMMR 🧵⤵️
doi.org/10.1038/s41571…
▫️High TMB, tons of neoantigens, and inflamed tumors. Long-term survivors, even cures.
▫️Up to 40% still fail.
Cure or collapse, the paradox of MSI-H/dMMR 🧵⤵️
doi.org/10.1038/s41571…
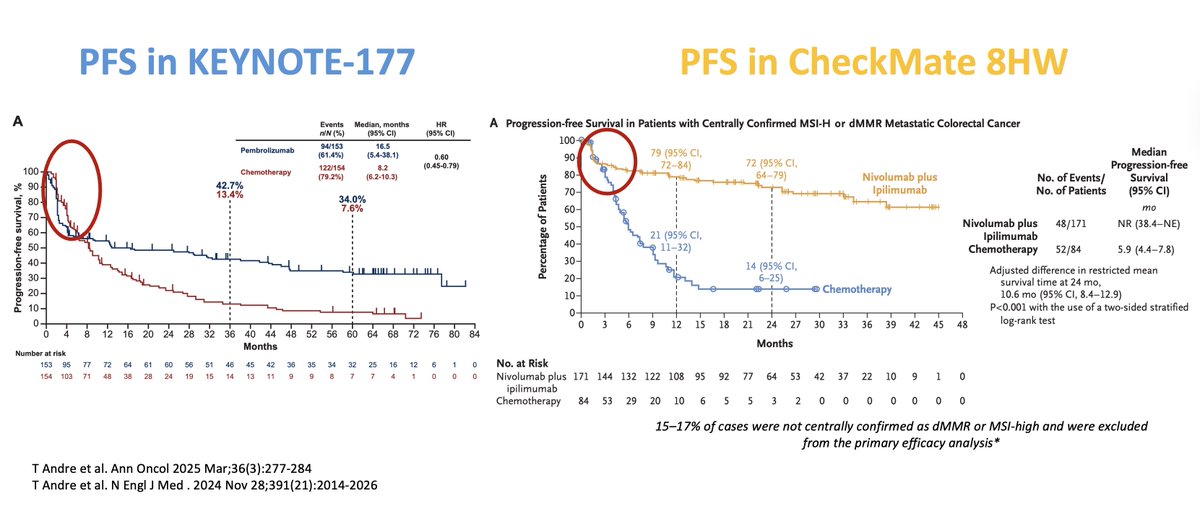
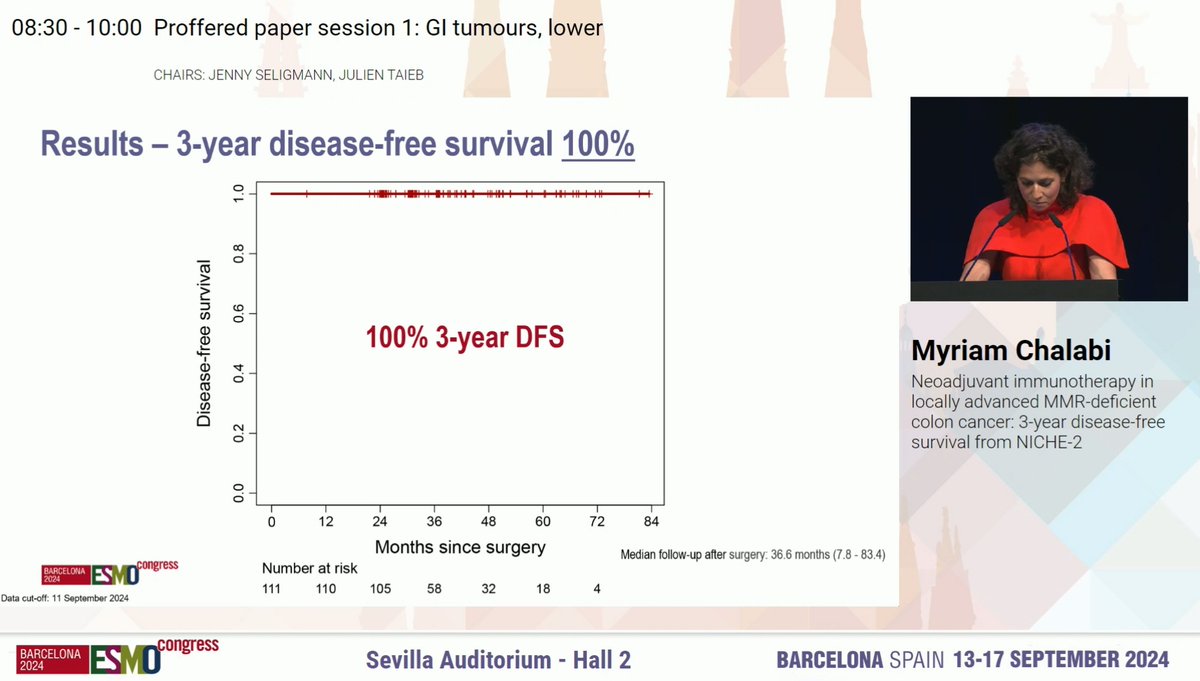
2. The success story 📈
Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Immunotherapy vs chemo
KEYNOTE-177 →↑ PFS, ORR ~45%, CR ~30%.
CheckMate-8HW → ORR ~70%, 2-yr PFS ~72%.
Localized CRC: NICHE-2 → 95% MPR, 67% pCR, 3-yr DFS 100% 😱
ICI achieves durable survival and, in some cases, cure.

Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Immunotherapy vs chemo
KEYNOTE-177 →↑ PFS, ORR ~45%, CR ~30%.
CheckMate-8HW → ORR ~70%, 2-yr PFS ~72%.
Localized CRC: NICHE-2 → 95% MPR, 67% pCR, 3-yr DFS 100% 😱
ICI achieves durable survival and, in some cases, cure.
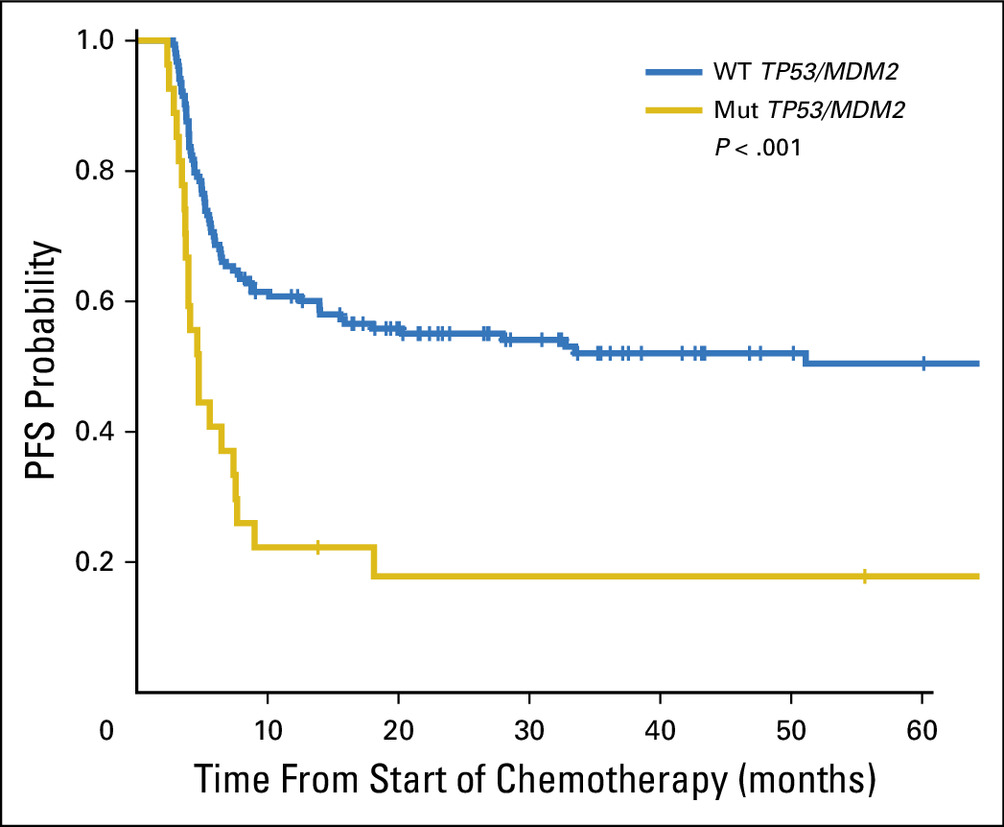
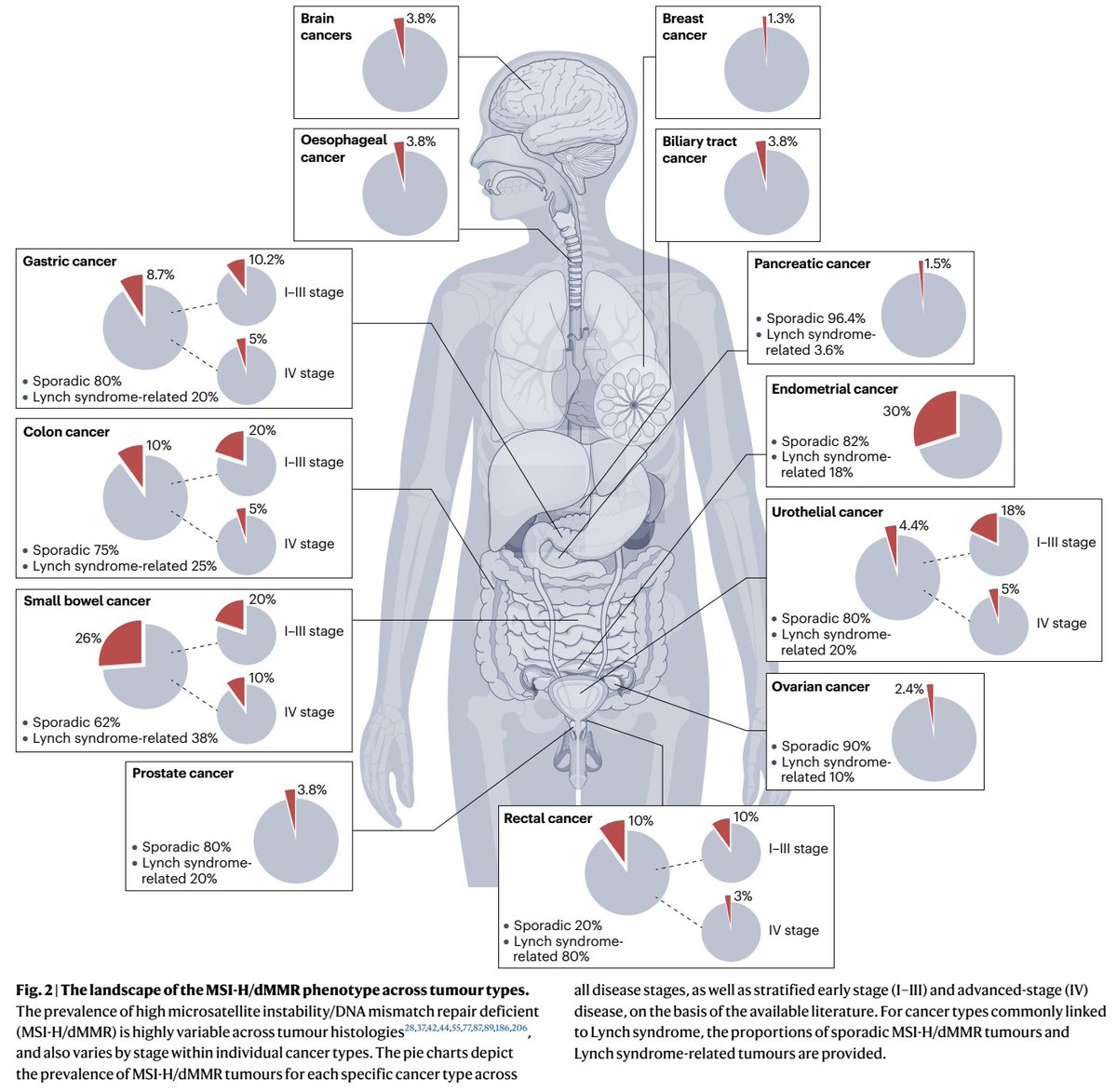
3. Why it fails I: Antigen invisibility
Even in MSI-H/dMMR, up to 40% resist IO.
Key mechanism: loss of antigen presentation.
▫️B2M mutations → no MHC-I
▫️JAK1/2 mutations → impaired IFN-γ signaling
If T cells can’t see the tumor, they can’t kill it.
tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.10…
Even in MSI-H/dMMR, up to 40% resist IO.
Key mechanism: loss of antigen presentation.
▫️B2M mutations → no MHC-I
▫️JAK1/2 mutations → impaired IFN-γ signaling
If T cells can’t see the tumor, they can’t kill it.
tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.10…
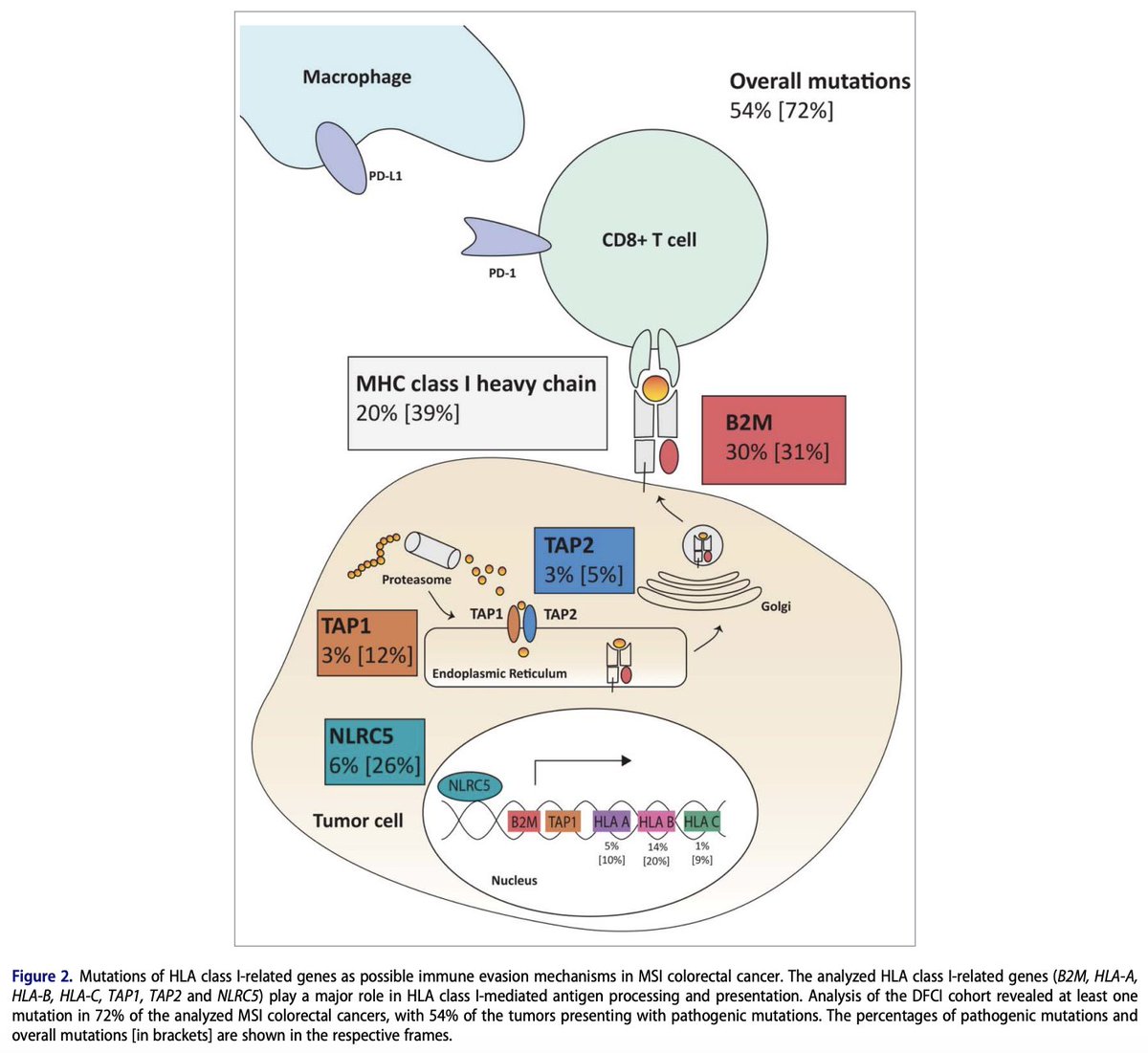
4. Why it fails II: Immune desert & suppression
Some MSI-H/dMMR tumors lack T-cell infiltration or build suppressive niches:
▫️WNT/β-catenin activation → T-cell exclusion
▫️TGF-β & VEGF → stromal barrier
▫️Myeloid & Tregs → suppress effector T cells
mdpi.com/2528868
Some MSI-H/dMMR tumors lack T-cell infiltration or build suppressive niches:
▫️WNT/β-catenin activation → T-cell exclusion
▫️TGF-β & VEGF → stromal barrier
▫️Myeloid & Tregs → suppress effector T cells
mdpi.com/2528868
5. Why it fails III. Adaptive mutability
MSI-H/dMMR tumors are unstable by nature
▫️Homopolymer shifts→ frameshifts
▫️Neoantigen “switching”→ immune escape
The hypermutation that drives immunogenicity also fuels resistance.
rdcu.be/eGLfw
MSI-H/dMMR tumors are unstable by nature
▫️Homopolymer shifts→ frameshifts
▫️Neoantigen “switching”→ immune escape
The hypermutation that drives immunogenicity also fuels resistance.
rdcu.be/eGLfw
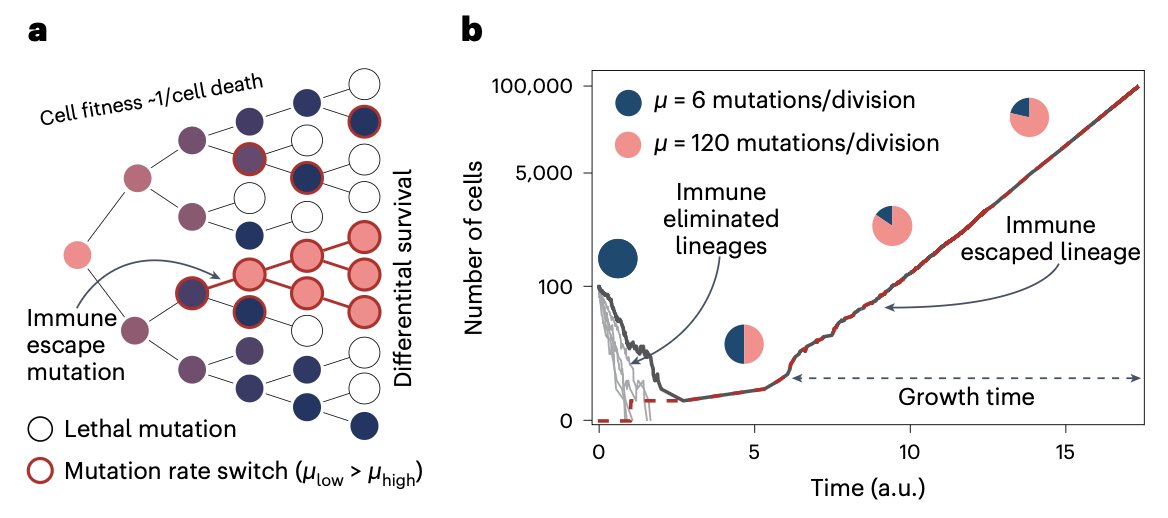
6. Why it fails IV: Epigenetics
Not all MSI-H are equal:
▫️Lynch (germline): highly immunogenic
▫️MLH1-hypermethylated (sporadic): weaker ORR (~30–35% vs ~50–60% in Lynch)
▫️CIMP-high: silences immune genes
Epigenetic heterogeneity shapes outcomes.
…-sciencedirect-com.pbidi.unam.mx:2443/science/articl…
Not all MSI-H are equal:
▫️Lynch (germline): highly immunogenic
▫️MLH1-hypermethylated (sporadic): weaker ORR (~30–35% vs ~50–60% in Lynch)
▫️CIMP-high: silences immune genes
Epigenetic heterogeneity shapes outcomes.
…-sciencedirect-com.pbidi.unam.mx:2443/science/articl…
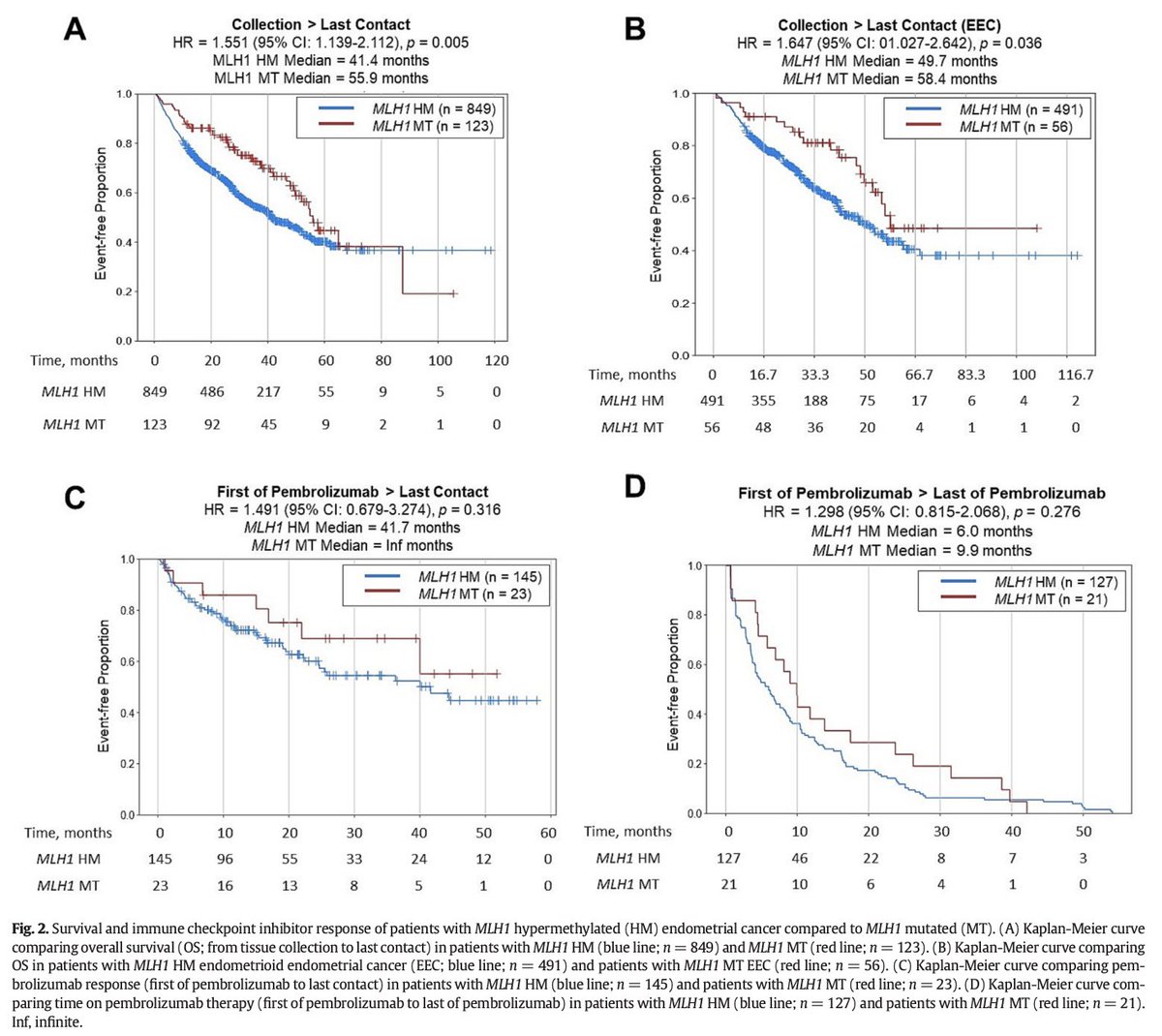
7. Clinical subgroups
▫️Lynch syndrome: earlier onset, higher TILs, better IO durability.
▫️Sporadic MLH1-hypermethylated CRC: older pts, more immune exclusion, less durable.
Same MSI-H label, different biology & different outcomes.
▫️Lynch syndrome: earlier onset, higher TILs, better IO durability.
▫️Sporadic MLH1-hypermethylated CRC: older pts, more immune exclusion, less durable.
Same MSI-H label, different biology & different outcomes.
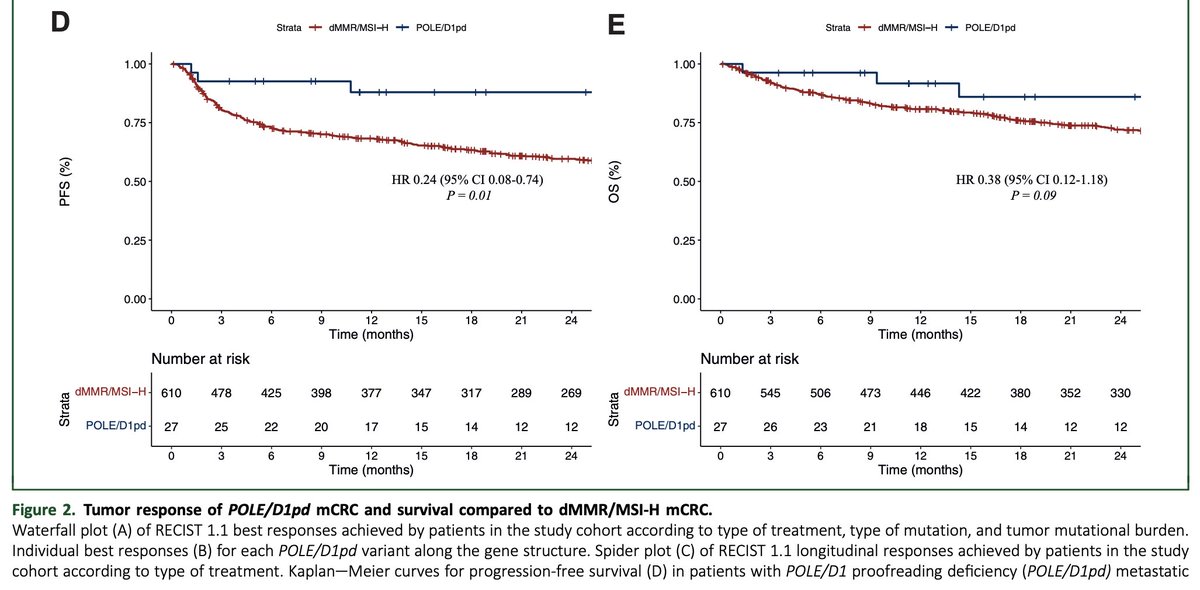
8. The ultramutator subset
Not all hypermutated CRCs are MSI-H.
A rare group, POLE/POLD1 proofreading-deficient (~1% of mCRC) achieves:
ORR ~89%
2-yr PFS ~88%
2-yr OS ~86%
This “ultramutator” phenotype demonstrates remarkable IO sensitivity.
annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923-…
Not all hypermutated CRCs are MSI-H.
A rare group, POLE/POLD1 proofreading-deficient (~1% of mCRC) achieves:
ORR ~89%
2-yr PFS ~88%
2-yr OS ~86%
This “ultramutator” phenotype demonstrates remarkable IO sensitivity.
annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923-…
9. DNA repair crosstalk
In MSI-H CRC, MMRd may overlap with HRR defects.
This alters neoantigen repertoire and modulates IO sensitivity.
Ongoing trials are evaluating PARP inhibitors + IO in this setting.
rdcu.be/eGLkK
In MSI-H CRC, MMRd may overlap with HRR defects.
This alters neoantigen repertoire and modulates IO sensitivity.
Ongoing trials are evaluating PARP inhibitors + IO in this setting.
rdcu.be/eGLkK

10. Diagnostic discordance
MSI-H/dMMR can be defined differently:
▫️IHC → protein loss, but may miss subclonal/atypical
▫️PCR → locus-limited, false negatives
▫️NGS → captures mutational signatures
Testing method matters.
acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.10…
MSI-H/dMMR can be defined differently:
▫️IHC → protein loss, but may miss subclonal/atypical
▫️PCR → locus-limited, false negatives
▫️NGS → captures mutational signatures
Testing method matters.
acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.10…
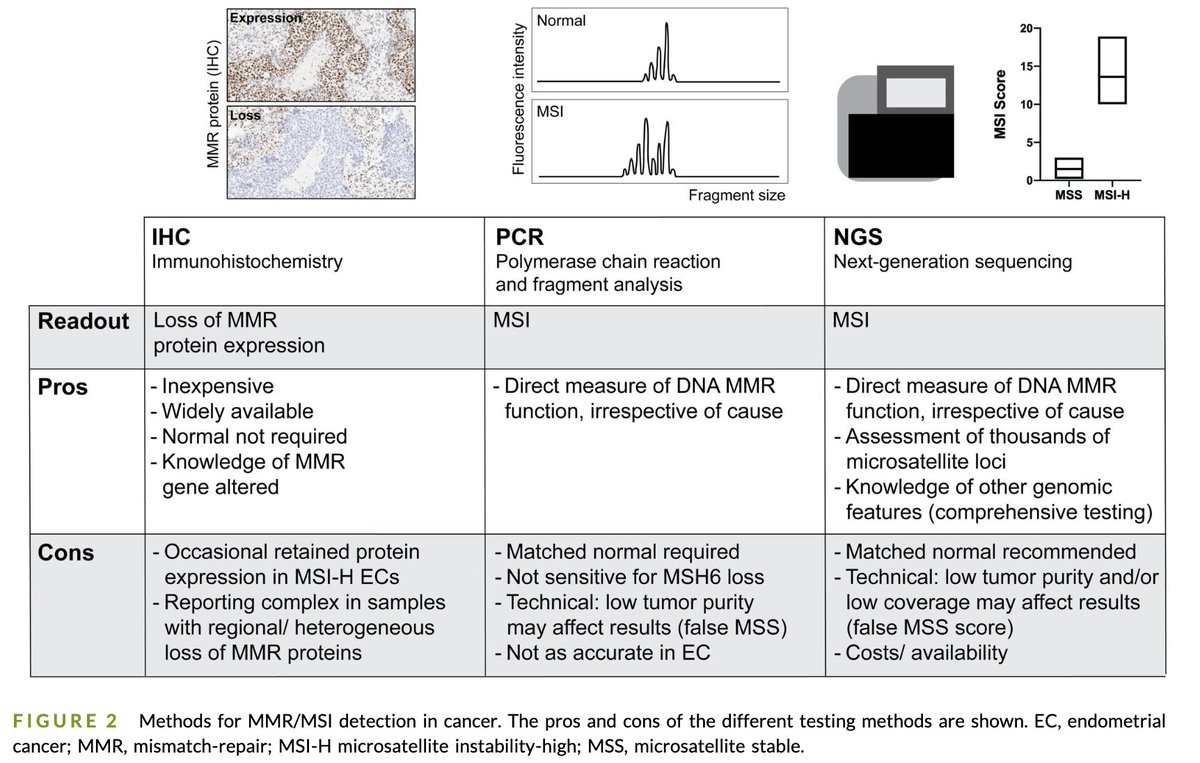
11. Clinical consequence
▫️Some patients are MSI-H by PCR but not by IHC (or vice versa).
▫️NGS refines biology, distinguishing clonal vs subclonal neoantigens.
📣 Misclassification helps explain the “fail” rate📣
▫️Some patients are MSI-H by PCR but not by IHC (or vice versa).
▫️NGS refines biology, distinguishing clonal vs subclonal neoantigens.
📣 Misclassification helps explain the “fail” rate📣
12. Emerging biomarkers
▫️NOTCH1 mutations: ↑CD8⁺ infiltration, better OS
▫️IFNγ/T-cell inflamed GEP: stratifies IO benefit
▫️ctDNA clearance (MRD): early marker of durable CR
Host factors
▫️Microbiome, antibiotics/steroids modulate efficacy
▫️NOTCH1 mutations: ↑CD8⁺ infiltration, better OS
▫️IFNγ/T-cell inflamed GEP: stratifies IO benefit
▫️ctDNA clearance (MRD): early marker of durable CR
Host factors
▫️Microbiome, antibiotics/steroids modulate efficacy
13. The combination era
MSI-H/dMMR has moved beyond PD-1 monotherapy:
→ PD-1 + CTLA-4
→ PD-1 + LAG-3
→ IO + PARPi or VEGF blockade, others
MSI-H/dMMR has moved beyond PD-1 monotherapy:
→ PD-1 + CTLA-4
→ PD-1 + LAG-3
→ IO + PARPi or VEGF blockade, others
14. The story continues
The next frontier: Refine biomarkers, embrace combinations & transform paradox into progress, overcoming resistance.
Still to be conquered: MMR-proficient (MSS) tumors🔮.
The next frontier: Refine biomarkers, embrace combinations & transform paradox into progress, overcoming resistance.
Still to be conquered: MMR-proficient (MSS) tumors🔮.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh