1/ DeepSeek-R1 incentivizes reasoning in LLMs through reinforcement learning
This changes everything: Researchers are teaching large language models to develop independent, deep thinking - without humans dictating every single step of the thought process. A game changer for AI performance and autonomy.
Lets break it down, a 🧵
This changes everything: Researchers are teaching large language models to develop independent, deep thinking - without humans dictating every single step of the thought process. A game changer for AI performance and autonomy.
Lets break it down, a 🧵

2/ Many models are currently only able to perform well in calculations or solve standard tasks when humans guide them step by step (“chain of thought”) or provide examples. This dependency costs time and money and limits what is possible.
3/ DeepSeek-R1 uses *purely* reinforcement learning (RL): the model receives feedback based *solely* on whether the end result is correct - not on how it got there. Analogous to a child who learns through feedback, not by memorizing all the intermediate steps. 

4/ Why this is groundbreaking:
Because DeepSeek-R1 *automatically* learns advanced thinking strategies: self-checking, strategy adaptation, reflection. In tests such as math Olympiads, it outperforms RL-trained models that have worked with human thought processes.
Because DeepSeek-R1 *automatically* learns advanced thinking strategies: self-checking, strategy adaptation, reflection. In tests such as math Olympiads, it outperforms RL-trained models that have worked with human thought processes.
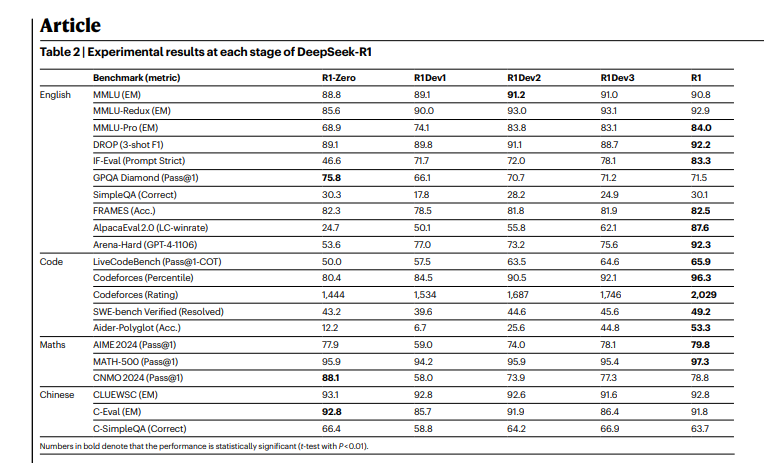
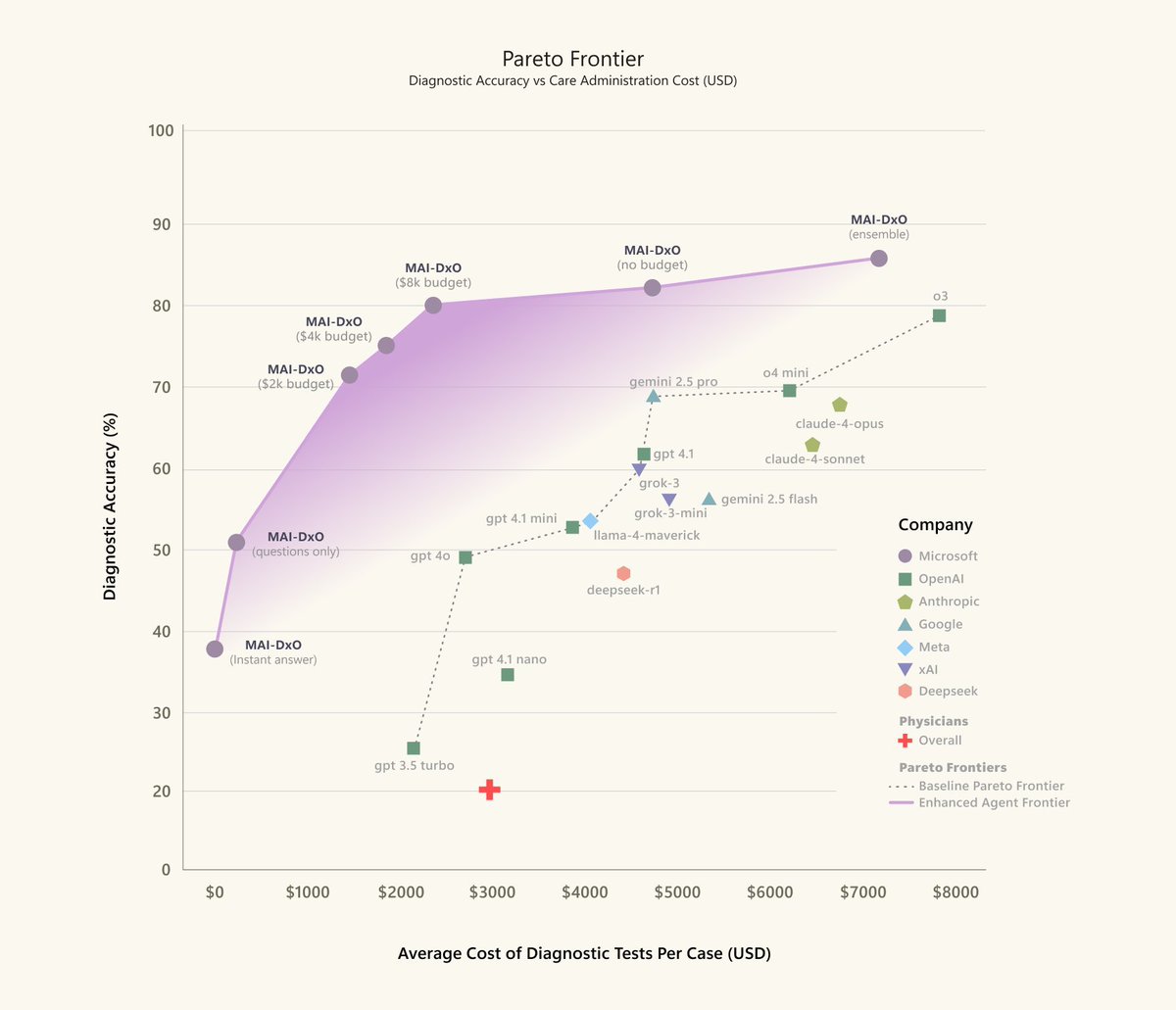
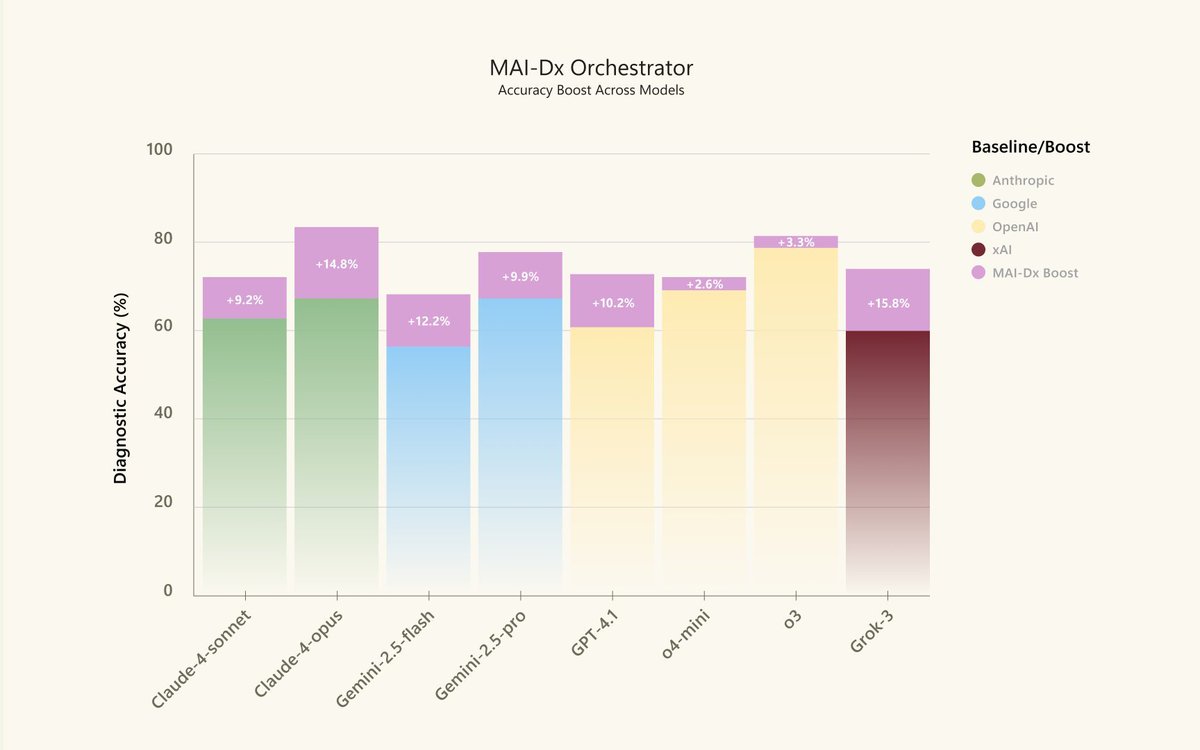
5/ In the next 1-2 years, we could see models that solve complex scientific, technical, and logical tasks almost as well as experts, but much more efficiently. More automation, better assistance - in code, in research, in teaching.
7/ This could change everything, literally
https://twitter.com/1573399256836309009/status/1968695269761106281
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh