Lost in the recent ACIP meeting: A lack of distinction between non-mRNA Novavax & mRNA. They voted on restrictions largely based on mRNA-specific concerns (many false assertions) when these issues flat-out don't apply to Novavax. A brief overview
The ACIP voted to add language about six additional risks with COVID vaccines. Let's see how those apply to Novavax 

1. Poor effectiveness & duration?
Effectiveness of COVID vaccines remains strong (around 50%). Importantly, these are population level estimates comparing against a background of infection-acquired immunity (see CDC slide).

Effectiveness of COVID vaccines remains strong (around 50%). Importantly, these are population level estimates comparing against a background of infection-acquired immunity (see CDC slide).


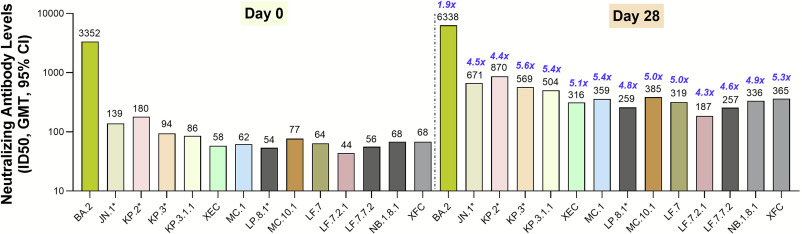
Further, duration is likely different across platforms. Although it's nearly impossible to evaluate duration with behavioral differences, variant shifts, etc., the Novavax platform has shown excellent durability up to 1 year in multiple studies
https://x.com/Daniel_E_Park/status/1953532292812481016
2. Increased risk after vaccination?
They repeatedly cited the Cleveland Clinic study. See fact check for more on this and why the assertion is probably not true. Either way, this update clearly notes mRNA, not protein. factcheck.org/2023/06/sciche…
They repeatedly cited the Cleveland Clinic study. See fact check for more on this and why the assertion is probably not true. Either way, this update clearly notes mRNA, not protein. factcheck.org/2023/06/sciche…

3. Myocarditis risk with vaccination?
The key point is that the risk of myocarditis is greater with infection compared with vaccination.
heart.org/en/news/2022/0…
Although they only cite mRNA, here is a NVX risk benefit analysis w/ myocarditis: sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
The key point is that the risk of myocarditis is greater with infection compared with vaccination.
heart.org/en/news/2022/0…
Although they only cite mRNA, here is a NVX risk benefit analysis w/ myocarditis: sciencedirect.com/science/articl…

4. Post-vaccine syndrome?
Again their slides only note mRNA here. Although important to research this rare outcome, it's certainly not common enough to guide policy. It'd be like removing seat belts from all cars because in a few accidents a year, they contribute to the outcome

Again their slides only note mRNA here. Although important to research this rare outcome, it's certainly not common enough to guide policy. It'd be like removing seat belts from all cars because in a few accidents a year, they contribute to the outcome


5. Lipid nano-particle persistence?
Well, Novavax doesn't have LNPs. Also, preclinical and clinical studies show lipid nanoparticles are biodegradable, rapidly cleared, and have an acceptable safety profile.
nature.com/articles/s4157…
Well, Novavax doesn't have LNPs. Also, preclinical and clinical studies show lipid nanoparticles are biodegradable, rapidly cleared, and have an acceptable safety profile.
nature.com/articles/s4157…

6. Birth defects?
There was some debate about internal numbers from a Pfizer RCT in pregnant women. Aside from the fact that, again, mRNA was the focus - it seemed clear that many of the malformations were present before vaccination.
There was some debate about internal numbers from a Pfizer RCT in pregnant women. Aside from the fact that, again, mRNA was the focus - it seemed clear that many of the malformations were present before vaccination.

Importantly, COVID-19 infection in pregnancy raises risks of severe illness, ICU admission, preterm birth, and stillbirth. Vaccination reduces those risks.
Further, maternal antibodies provide newborns w/ protection in the first months of life.
acog.org/news/news-rele…
Further, maternal antibodies provide newborns w/ protection in the first months of life.
acog.org/news/news-rele…
Summary: Six tenuous or wrong claims about COVID vaccines drove new restrictions. Four are irrelevant to protein-based Novavax, two only mildly so, yet the less-reactogenic NVX gets lumped in anyway. Hopefully future discussions are more nuanced.
https://x.com/Daniel_E_Park/status/1865955858024206468
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh