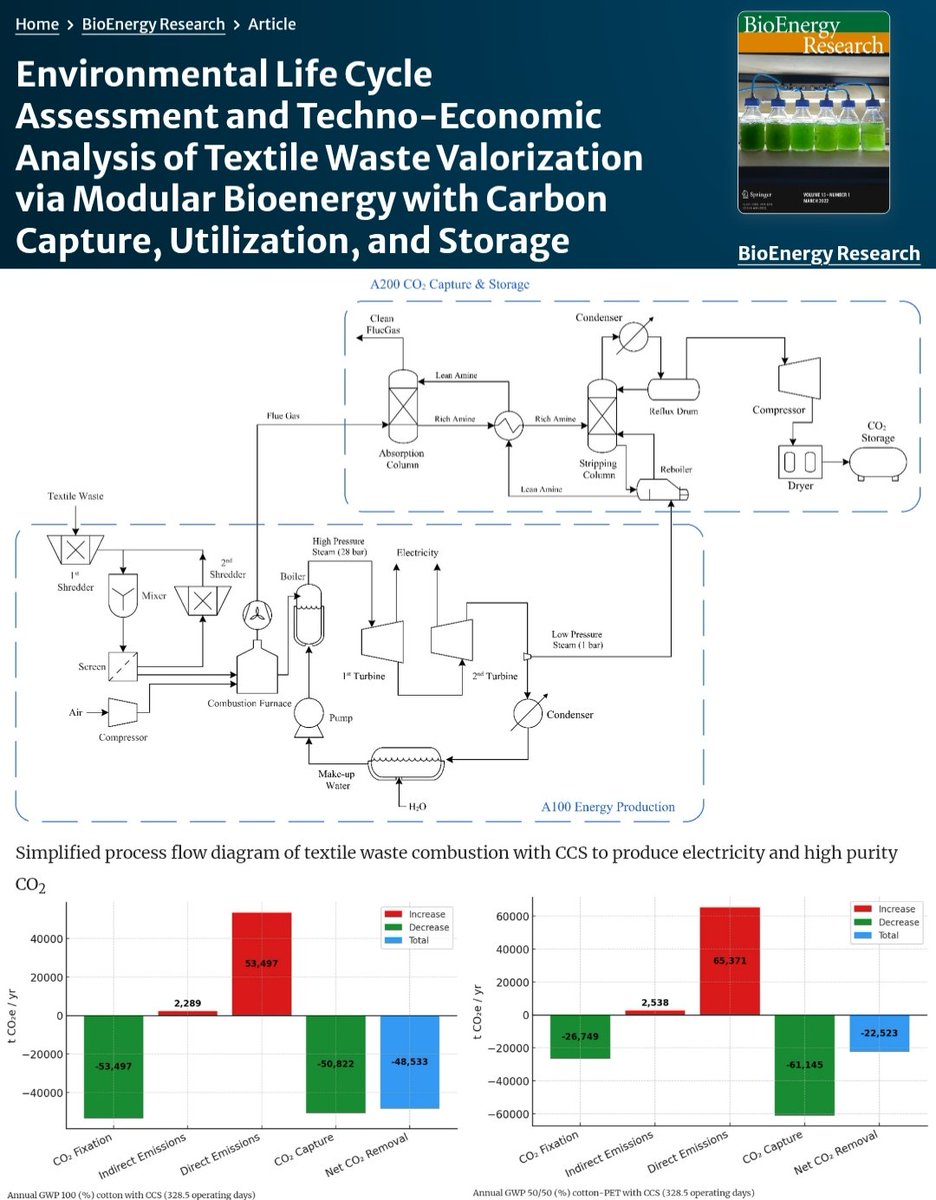
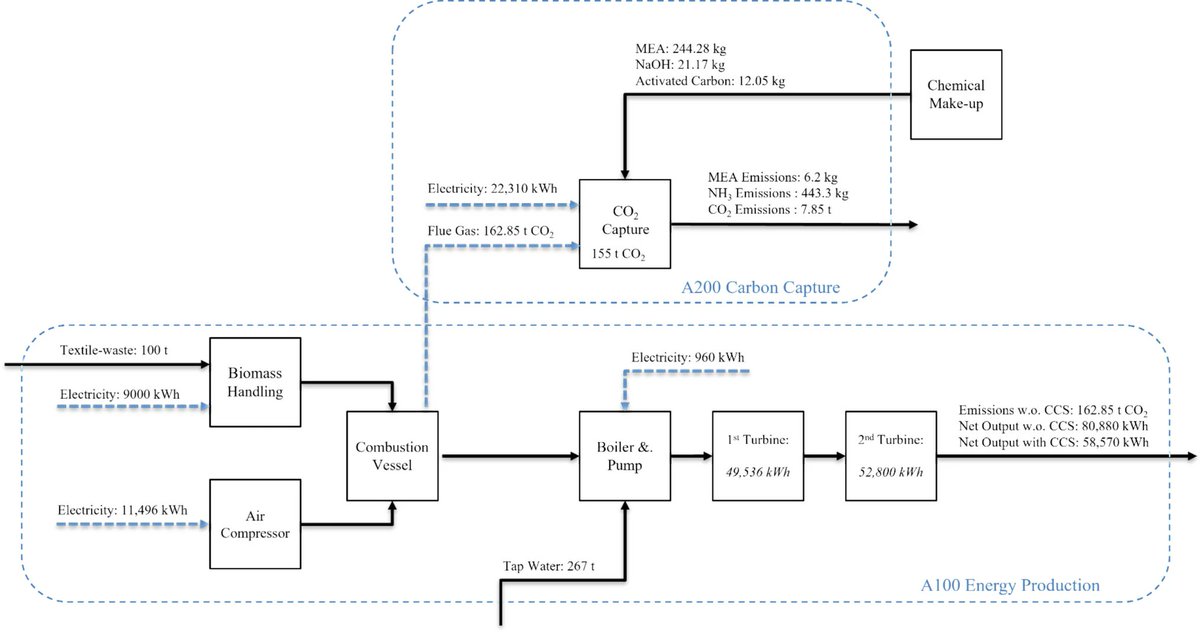
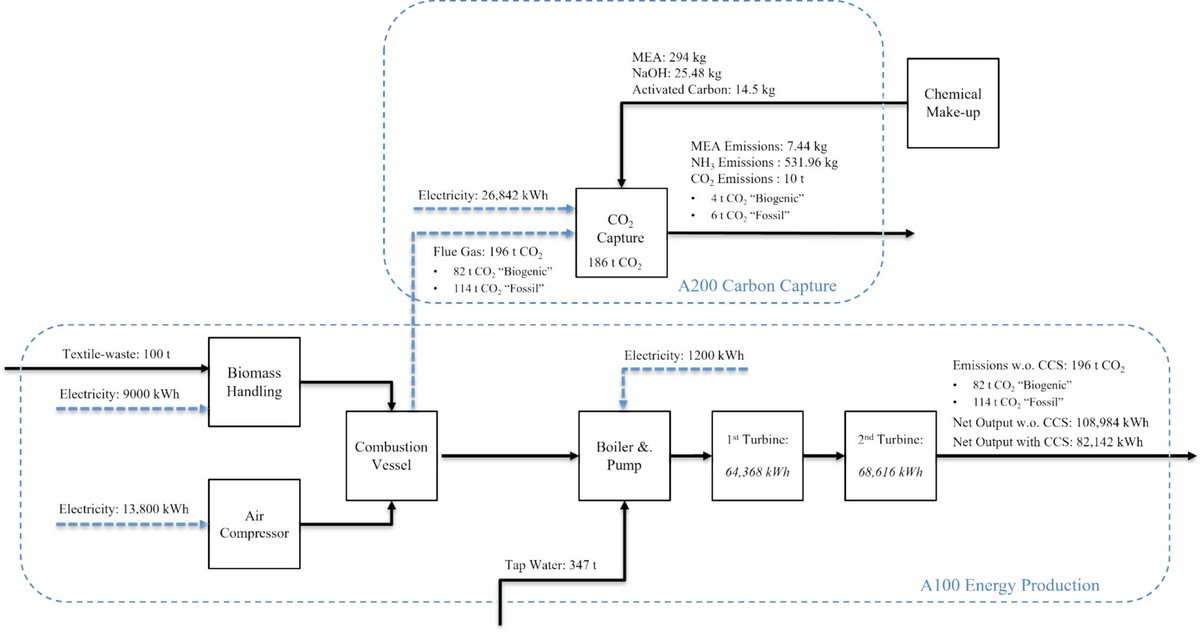
🚨Is carbon dioxide removal (#CDR) in the Arctic really feasible?
A new peer-reviewed study systematically assessed proposed Arctic CDR pathways and finds that feasibility is far more limited than often assumed.
DETAILS🧵1/14
A new peer-reviewed study systematically assessed proposed Arctic CDR pathways and finds that feasibility is far more limited than often assumed.
DETAILS🧵1/14
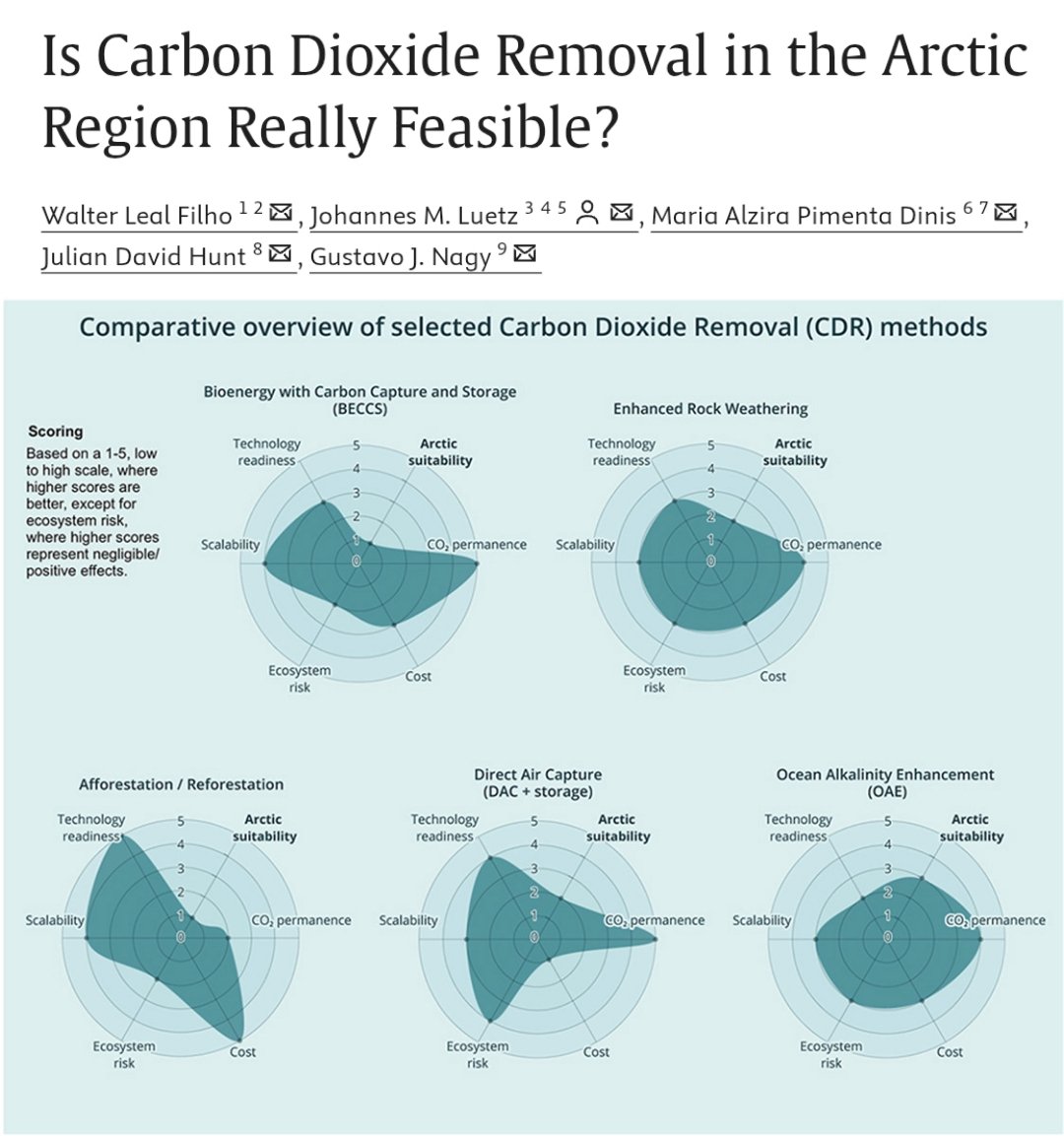
2/ As Arctic warms rapidly (4x) & attracts attention for climate interventions, can it host CDR at meaningful scale?
To answer this, authors conducted a comparative assessment of major CDR approaches proposed for Arctic regions, spanning both nature-based & engineered methods.
To answer this, authors conducted a comparative assessment of major CDR approaches proposed for Arctic regions, spanning both nature-based & engineered methods.
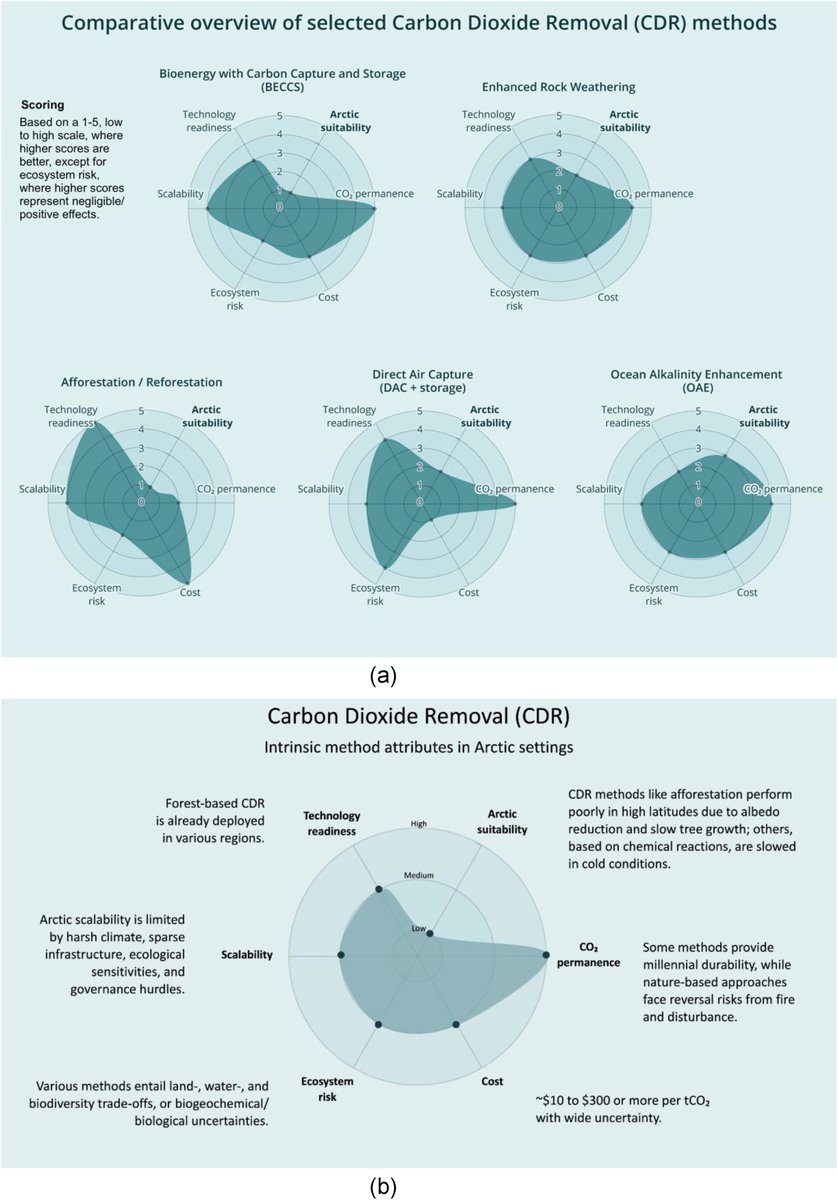
3/ The analysis draws on existing empirical studies, pilot projects, and modeling literature, evaluating each CDR pathway against biophysical constraints, technical readiness, environmental risks, and governance requirements. 
4/ The researchers examined nature-based options first, including peatland restoration, wetland conservation, and coastal blue-carbon ecosystems, which are often cited as low-risk Arctic CDR opportunities.
5/ They find that while these systems already store substantial carbon, their additional removal potential is limited and highly variable, constrained by short growing seasons, permafrost dynamics, hydrology, and methane emissions. 

6/ Importantly, the study notes that many benefits of nature-based approaches come from avoided emissions and protection of existing stocks, rather than large increases in net CO₂ uptake.
7/ The authors then assessed engineered CDR approaches, including direct air carbon capture and storage (DACCS), enhanced rock weathering, and ocean-based methods proposed for cold regions.
8/ Here, the findings are more restrictive.
Arctic conditions pose major challenges related to energy availability, infrastructure, transport, and long-term monitoring, all of which are essential for engineered CDR.
Arctic conditions pose major challenges related to energy availability, infrastructure, transport, and long-term monitoring, all of which are essential for engineered CDR.

9/ While low temperatures may marginally improve capture efficiency for some technologies, the study finds that these gains are outweighed by logistical complexity, high costs, and operational risks.
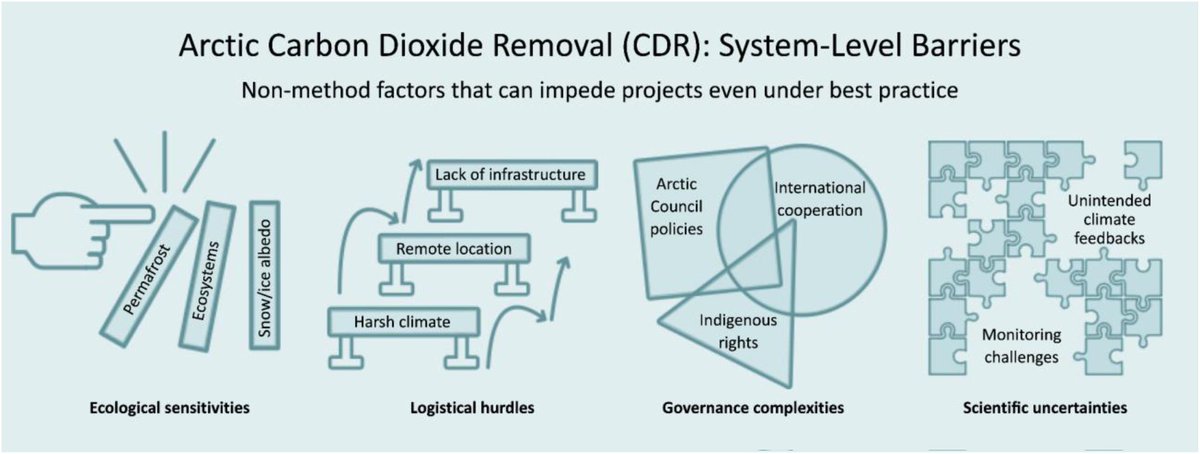
10/ Across all pathways, the authors identify measurement, reporting, and verification as a central unresolved issue, given the remoteness, seasonality, and environmental sensitivity of Arctic systems.
11/ Governance is another key finding.
The study highlights the absence of clear regulatory frameworks for Arctic CDR, particularly where projects intersect with Indigenous lands, shared ecosystems, and international jurisdictions.
The study highlights the absence of clear regulatory frameworks for Arctic CDR, particularly where projects intersect with Indigenous lands, shared ecosystems, and international jurisdictions.

12/ Taken together, the evidence leads to a consistent conclusion: no assessed CDR method currently demonstrates high feasibility for large-scale deployment in the Arctic under present conditions.
13/ The authors caution that Arctic CDR cannot substitute for emissions cuts, given its limited, uncertain & slow potential.
They argue near-term priorities should be protecting existing carbon stores, minimizing ecosystem disturbance, and strengthening governance & monitoring.
They argue near-term priorities should be protecting existing carbon stores, minimizing ecosystem disturbance, and strengthening governance & monitoring.
📝For more details, read the study entitled "Is Carbon Dioxide Removal in the Arctic Region Really Feasible?" here:
🧵14/14 #CDR #CarbonSequestrationsciencedirect.com/science/articl…
🧵14/14 #CDR #CarbonSequestrationsciencedirect.com/science/articl…
"unroll" @threadreaderapp
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh